Содержание
- 2. Mastitis 1) Acute Mastitis : Occurs during the first month of breastfeeding. Caused by a local
- 3. Infection may spread to entire breast. Staphylococcal abscesses- single or multiple, Streptococci- spread infection in the
- 4. 2) Duct Ectasia Presents as a palpable periareolar mass with thick, white nipple secretions and occasionally
- 5. Morphology Ectatic dilated ducts are filled with inspissated secretions and numerous lipid-laden macrophages. When ruptured?marked periductal
- 6. deposits Granulomas may form around and cholesterol secretions. Subsequent mass with retraction. fibrosis? skin and irregular
- 7. 3) Granulomatous Mastitis: Can be a manifestation of systemic granulomatous diseases (e.g. polyangiitis, sarcoidosis, TB) or
- 8. Granulomatous lobular mastitis: Uncommon disease, occurs in parous women. Granulomas are closely associated with lobules, suggesting
- 9. Localized infections are most common in immunocompromised patients or adjacent to foreign objects such as breast
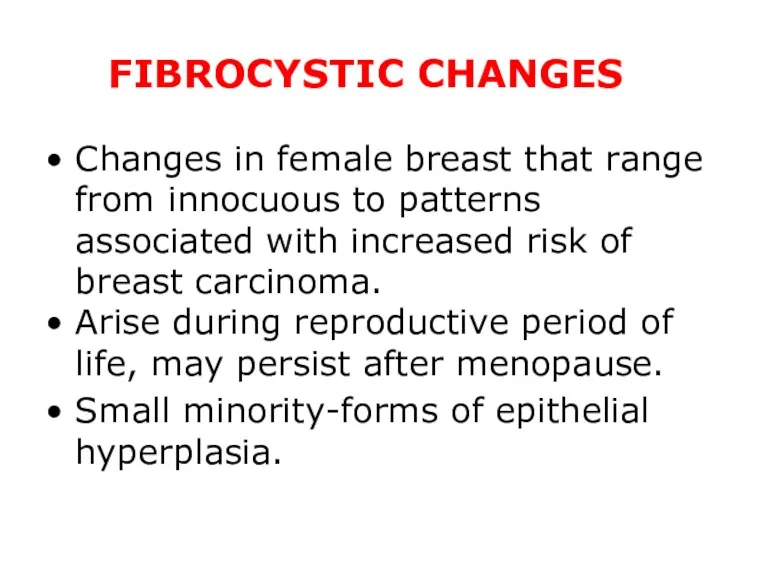
- 10. FIBROCYSTIC CHANGES Changes in female breast that range from innocuous to patterns associated with increased risk
- 11. Alterations subdivided into nonproliferative and proliferative patterns. Nonproliferative lesions- cysts and/or fibrosis and adenosis focally. Proliferative
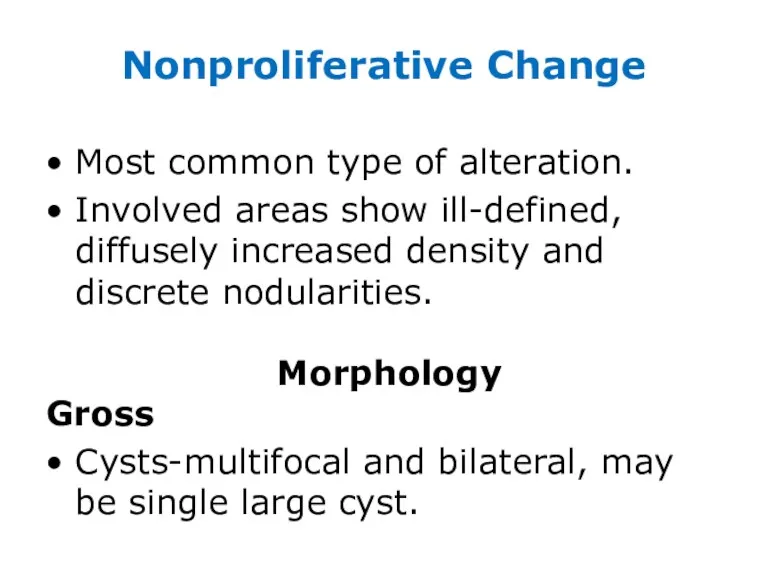
- 12. Nonproliferative Change Most common type of alteration. Involved areas show ill-defined, diffusely increased density and discrete
- 13. Cysts: Brown to blue cysts filled with serous, turbid fluid. Secretory products may calcify, appear as
- 14. Microscopy: Three principal morphologic changes: cystic change often with apocrine metaplasia, fibrosis, and focally adenosis. Cysts-
- 15. Mild epithelial proliferation- small papillary projections. Frequently, cysts are lined by large polygonal cells that have
- 16. Stroma- Compressed fibrous tissue with loss of its normal delicate, myxomatous appearance and lymphocytic infiltrate. Adenosis-
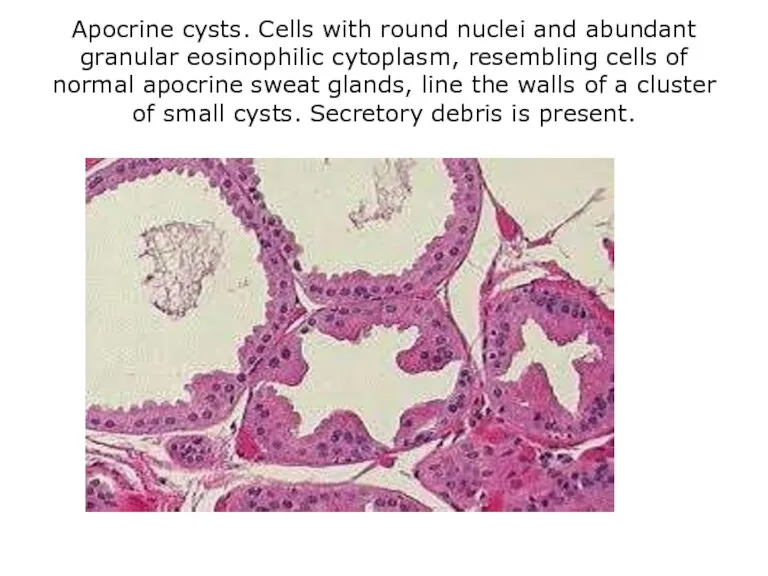
- 17. Apocrine cysts. Cells with round nuclei and abundant granular eosinophilic cytoplasm, resembling cells of normal apocrine
- 18. Proliferative Change Disease Without Atypia Lesions characterized by proliferation of epithelial cells without atypia. Small increase
- 19. Microscopy- Wide spectrum Ducts, ductules, or lobules may be filled with orderly cuboidal cells, within which
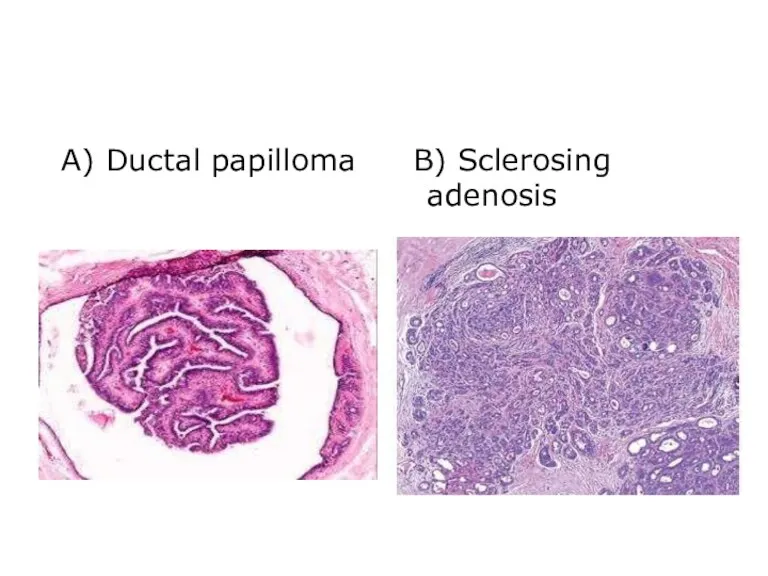
- 20. Papilloma within a dilated duct, composed of multiple branching fibrovascular cores into ductal lumen. Sclerosing Adenosis-Increased
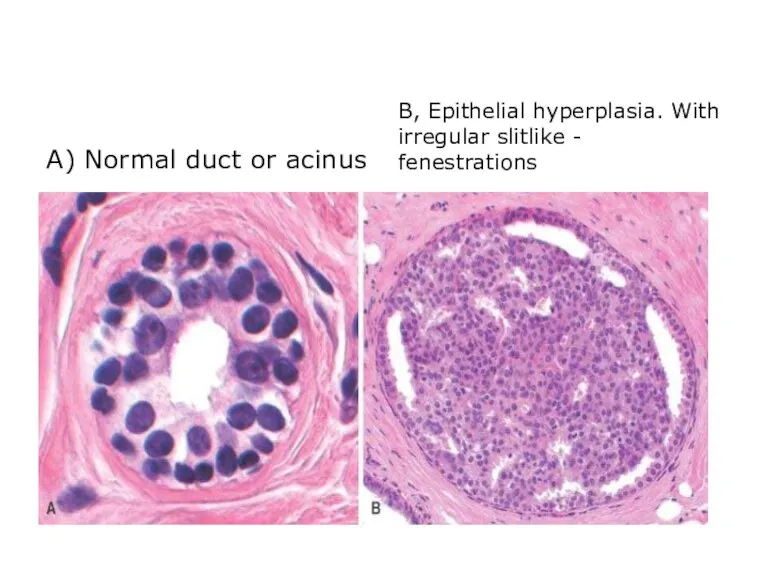
- 21. A) Normal duct or acinus B, Epithelial hyperplasia. With irregular slitlike - fenestrations
- 22. A) Ductal papilloma B) Sclerosing adenosis
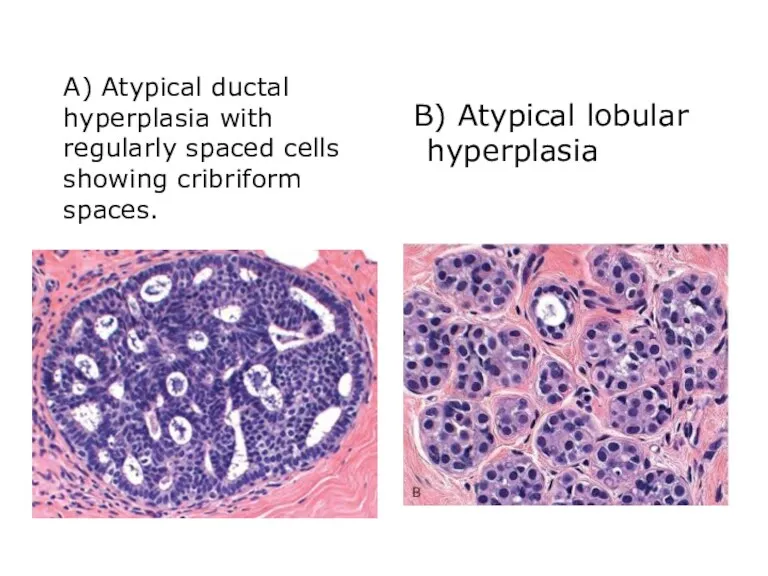
- 23. Proliferative Breast Disease with Atypia Hyperplasia with atypia is present in ducts or lobules. Moderately increased
- 24. A) Atypical ductal hyperplasia with regularly spaced cells showing cribriform spaces. B) Atypical lobular hyperplasia
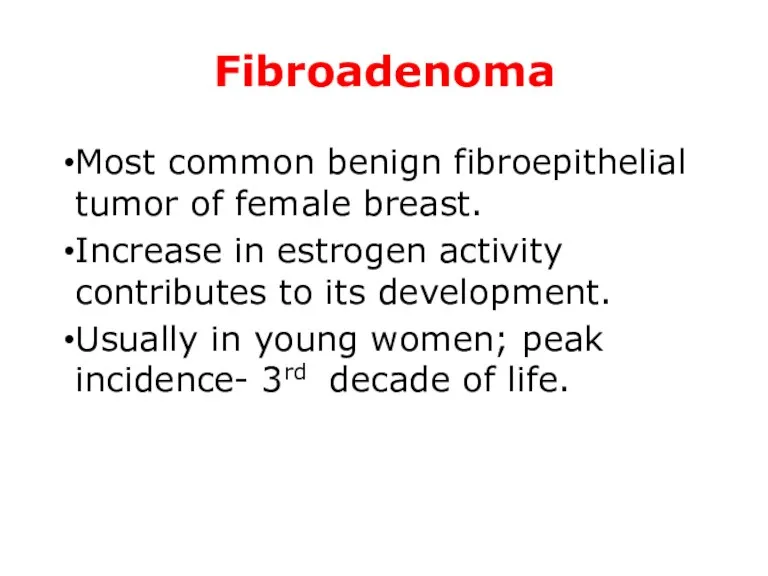
- 25. Fibroadenoma Most common benign fibroepithelial tumor of female breast. Increase in estrogen activity contributes to its
- 26. Morphology Gross: Discrete, usually solitary, freely movable nodule, 1-10 cm in diameter. Rarely multiple tumors and
- 27. Microscopy: Loose fibroblastic stroma containing ductlike, epithelium-lined spaces of various forms and sizes. Ductlike or glandular
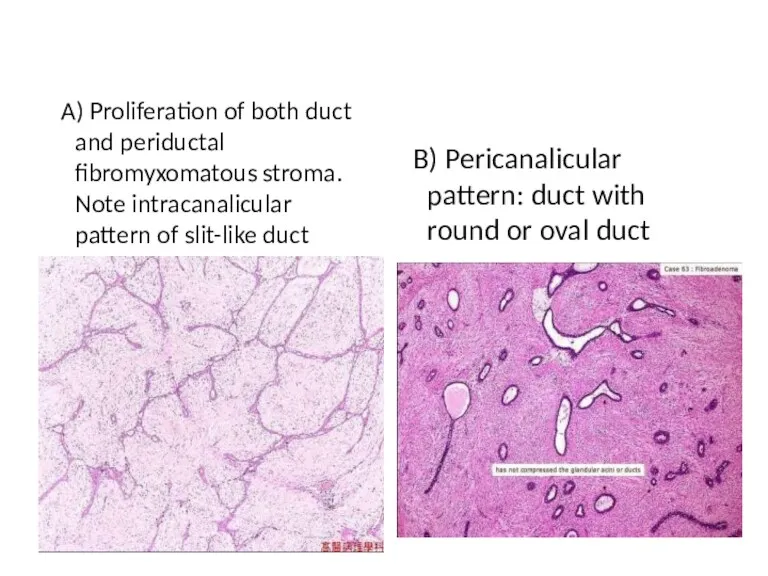
- 28. Two patterns: Pericanalicular fibroadenoma- Ductal spaces are open, round to oval, and regular. Intracanalicular fibroadenoma- Duct
- 29. A) Proliferation of both duct and periductal fibromyxomatous stroma. Note intracanalicular pattern of slit-like duct B)
- 30. Clinical features Present as solitary, discrete, movable painless masses. May enlarge late in menstrual cycle and
- 32. Скачать презентацию





















 Пневмония. Этиология. Принципы лечения
Пневмония. Этиология. Принципы лечения Острые нарушения мозгового кровообращения
Острые нарушения мозгового кровообращения Анатомо-фізіологічні особливості жувального апарату при повній втраті зубів
Анатомо-фізіологічні особливості жувального апарату при повній втраті зубів Микроорганизмы в окружающей среде
Микроорганизмы в окружающей среде Дейл Карнеги бойынша қарым-қатынас орнату
Дейл Карнеги бойынша қарым-қатынас орнату Презентация тема № 2 (из 17) Трепанация черепа, инструменты, ПХО 6 семестр Готово 02.02.23
Презентация тема № 2 (из 17) Трепанация черепа, инструменты, ПХО 6 семестр Готово 02.02.23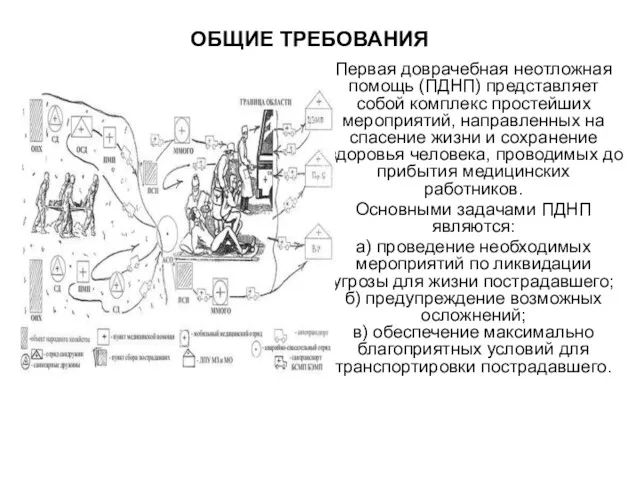 Первая доврачебная неотложная помощь
Первая доврачебная неотложная помощь Протеи. Причины возникновения инфекций, вызванных протеем
Протеи. Причины возникновения инфекций, вызванных протеем Жатыр мен қынаптың толықтай емес түсуі бар әйелдерде кольпорафиялық емнің және пессарий қоюдың нәтижелігін анықтау
Жатыр мен қынаптың толықтай емес түсуі бар әйелдерде кольпорафиялық емнің және пессарий қоюдың нәтижелігін анықтау Диагностика туберкулеза
Диагностика туберкулеза Стационардағы медбикенің қол жуу маңыздылығы
Стационардағы медбикенің қол жуу маңыздылығы Нормализация моторики органов артикуляции при дизартрии
Нормализация моторики органов артикуляции при дизартрии Неврологиялық ауруларды алдын-алу шаралары
Неврологиялық ауруларды алдын-алу шаралары Electrical Processes of the Heart
Electrical Processes of the Heart Хирургическое лечение эпилепсии и паркинсонизма
Хирургическое лечение эпилепсии и паркинсонизма Орнитоз (пситтакоз)
Орнитоз (пситтакоз) Комы. Патогенез развития коматозных состояний
Комы. Патогенез развития коматозных состояний Заболевание глотки
Заболевание глотки Тромботические микроангиопатии. Большая проблема или интересная задача
Тромботические микроангиопатии. Большая проблема или интересная задача Бактериальные инфекции
Бактериальные инфекции Гангренозный стоматит. Ангина Симановского-Плаута-Венсана
Гангренозный стоматит. Ангина Симановского-Плаута-Венсана Тіндердің шығу тегі мен дамуының заңдылықтары. Тіндердің жіктелуі
Тіндердің шығу тегі мен дамуының заңдылықтары. Тіндердің жіктелуі Хто вони: Рослини чи Тварини?
Хто вони: Рослини чи Тварини? Жатыр мойны қатерлі ісігі
Жатыр мойны қатерлі ісігі Pflege von Menschen mit Erkrankungen der Atemwege und Lunge
Pflege von Menschen mit Erkrankungen der Atemwege und Lunge Рентгенанатомия и рентгенпатология желудочно-кишечного тракта
Рентгенанатомия и рентгенпатология желудочно-кишечного тракта Аневризмы сосудов ГМ
Аневризмы сосудов ГМ A comparison of pill dispensers
A comparison of pill dispensers