Содержание
- 2. «All is a poison, all is a medicine; either depends on the dose» Paracelsus (1493-1541)
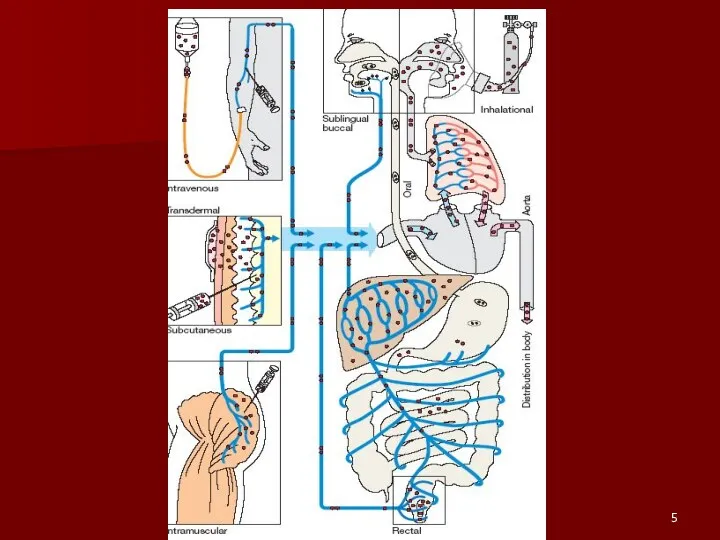
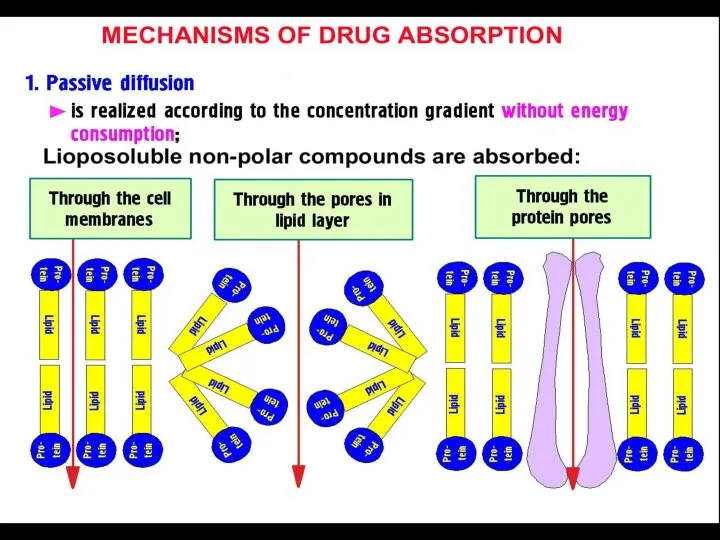
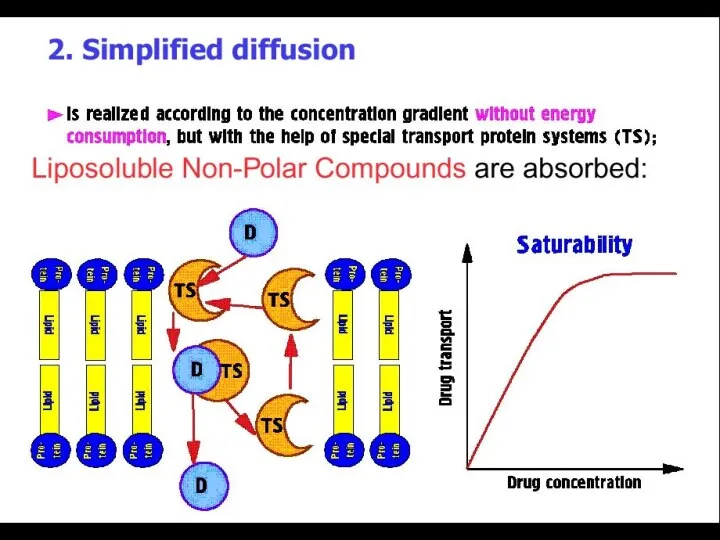
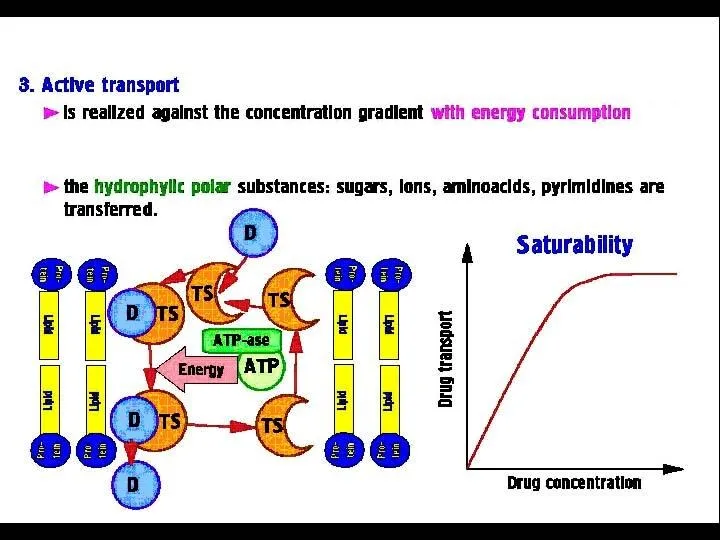
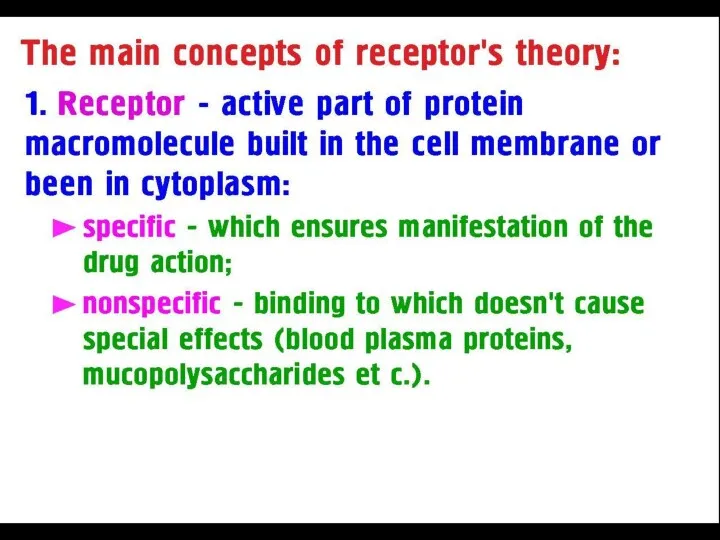
- 4. PHARMACOKINETICS PROCESSES: ► Absorption ►Distribution ►Binding /Localization /Storage ►Biotransformation ►Elimination
- 7. For most majority of drugs BIOAVAILABILITY is equal to 40-70% - Average level If Bioavailability
- 13. VOLUME of DESTRIBUTION (Vd) – a hypothetical volume of fluid into which the drug is disseminated
- 14. Volume of destruburion (Vd) – is a hypothetical volume of fluid into which the drug is
- 15. Vd is the ratio of the total amount of drug in the body to the concentration
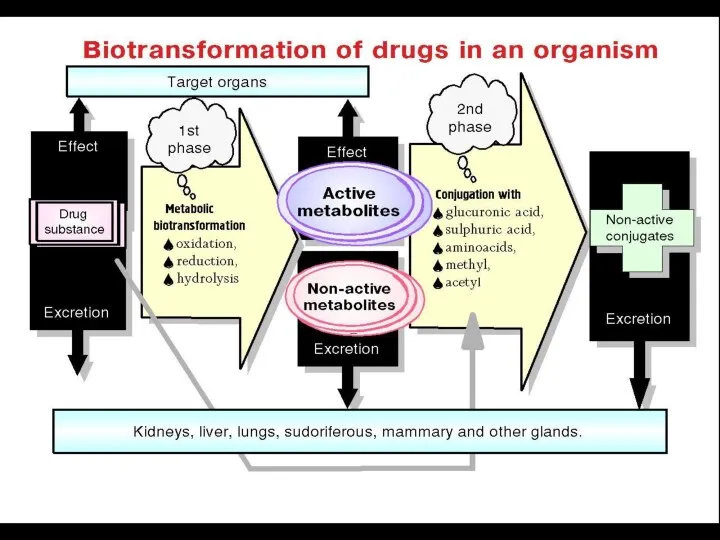
- 17. Phase I – Metabilic Biotransformation Lipophilic molecules => Polar Molecules by introducing or unmasking a polar
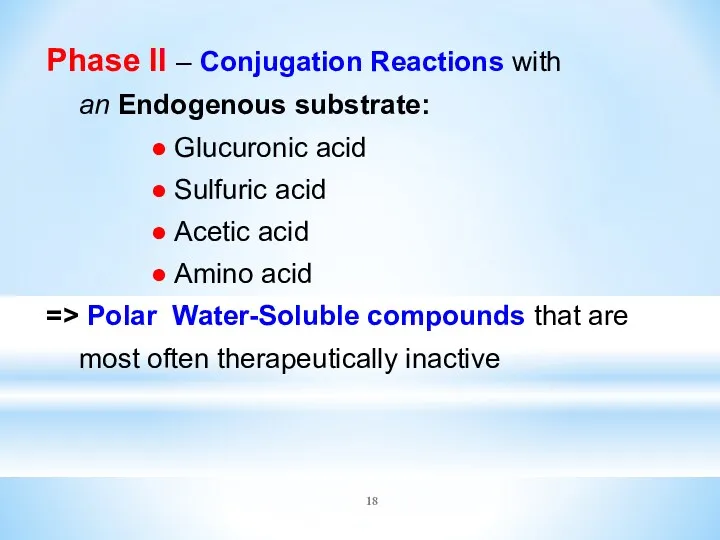
- 18. Phase II – Conjugation Reactions with an Endogenous substrate: ● Glucuronic acid ● Sulfuric acid ●
- 19. Enzyme Induction - the ability of some drugs to induce CYP-450 by: ? the rate of
- 20. Enzyme Inhibition - the ability of drugs to inhibit CYP-450 by: ? the rate of its
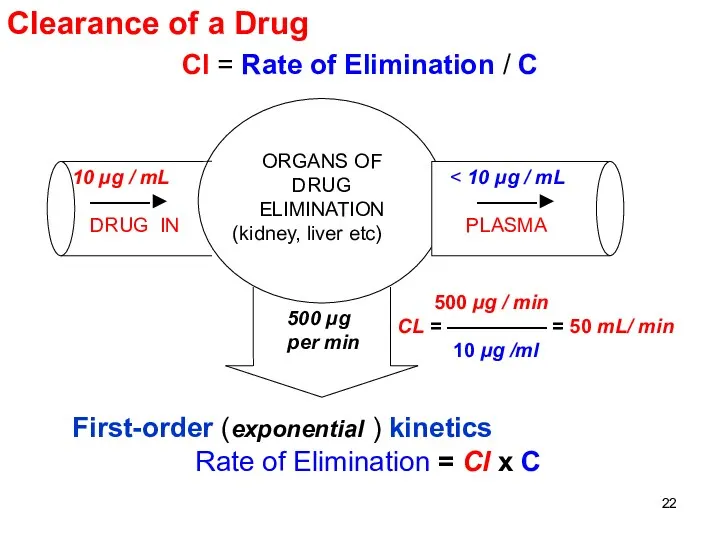
- 22. Clearance of a Drug Cl = Rate of Elimination / C First-order (exponential ) kinetics Rate
- 23. Steady State Plasma Concentration (Css) Dose Css = ———— or Dose = Css x Cl Cl
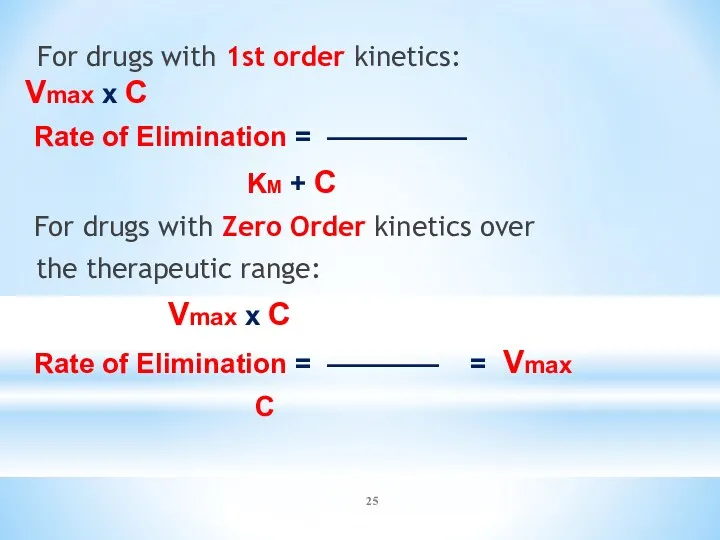
- 24. For drugs with Michaelis-Menten kinetics, elimination changes from 1st Order to Zero Order kinetics over the
- 25. For drugs with 1st order kinetics: Vmax x C Rate of Elimination = ————— KM +
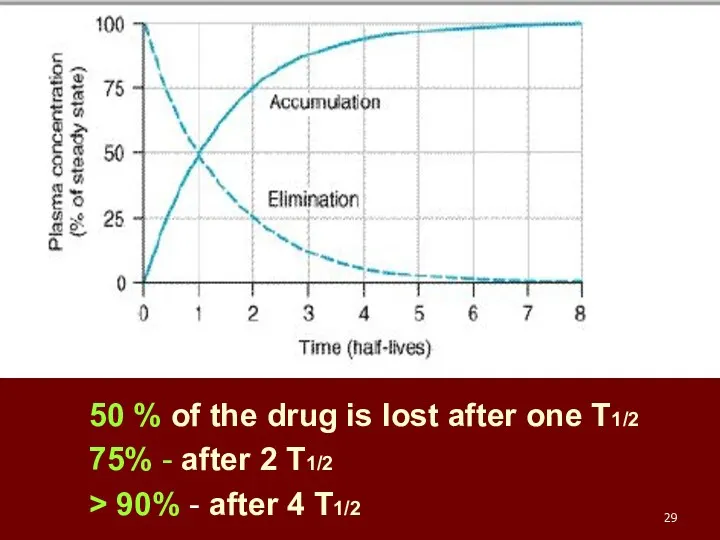
- 29. 50 % of the drug is lost after one T1/2 75% - after 2 T1/2 >
- 40. Placebo is an inert substance which is given in the garb of a medicine. Placebo causes
- 42. Скачать презентацию





















 Коррекция дисграфии у учащихся с общим недоразвитием речи III уровня в школе для детей с тяжёлыми нарушениями речи
Коррекция дисграфии у учащихся с общим недоразвитием речи III уровня в школе для детей с тяжёлыми нарушениями речи Өсіргіш заттар. Өсіргіш заттардың өсімдіктерге әсер ету механизмі. Ауксин әсері
Өсіргіш заттар. Өсіргіш заттардың өсімдіктерге әсер ету механизмі. Ауксин әсері Сердечные гликозиды. Негикозидные кардиотонические средства
Сердечные гликозиды. Негикозидные кардиотонические средства Акушериядағы қан кетулер. Босанғаннан кейінгі ҚК
Акушериядағы қан кетулер. Босанғаннан кейінгі ҚК Артериальная гипертензия у детей и подростков
Артериальная гипертензия у детей и подростков Цукровий діабет. Лікування та реабілітація
Цукровий діабет. Лікування та реабілітація Человек. Гигиена пищеварительной системы
Человек. Гигиена пищеварительной системы Клинический случай
Клинический случай Внебольничная пневмония у взрослых: диагностика, лечение, профилактика
Внебольничная пневмония у взрослых: диагностика, лечение, профилактика Новые методы лечения морбидного ожирения: роль бариатрической хирургии
Новые методы лечения морбидного ожирения: роль бариатрической хирургии Диагностика ревматической лихорадки
Диагностика ревматической лихорадки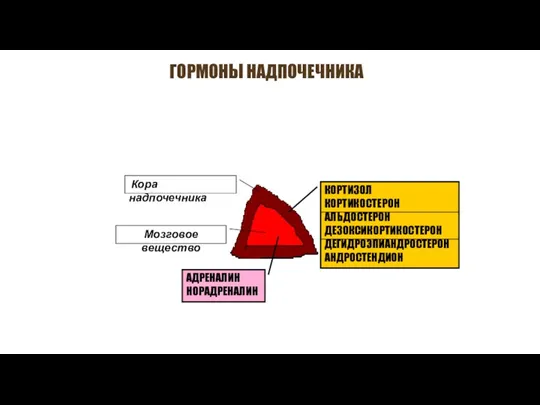 Гормоны надпочечника
Гормоны надпочечника Бактериальный вагиноз при беременности
Бактериальный вагиноз при беременности Аппликаторы Кузнецова
Аппликаторы Кузнецова Наркомания. Кодировка различных состояний, вызываемых злоупотреблением ПАВ (МКБ-10, 4-й знак)
Наркомания. Кодировка различных состояний, вызываемых злоупотреблением ПАВ (МКБ-10, 4-й знак) Опухоли. Классификация опухолей
Опухоли. Классификация опухолей Профилактика и диагностика врожденной патологии плода
Профилактика и диагностика врожденной патологии плода Классификация, клиника, диагностика рака щитовидной железы
Классификация, клиника, диагностика рака щитовидной железы Адамның психикалық қызметтерінің ерекшеліктері (зейін,түйсік,ой,сана,сөз)
Адамның психикалық қызметтерінің ерекшеліктері (зейін,түйсік,ой,сана,сөз) Обезболивание родов
Обезболивание родов Гипоксия и дыхательная недостаточность
Гипоксия и дыхательная недостаточность Жара және оның түрлері. Кесілген жаралар
Жара және оның түрлері. Кесілген жаралар Роль фельдшера в лечении бронхитов
Роль фельдшера в лечении бронхитов Физическое развитие детей
Физическое развитие детей Порядок проведения гемотрансфузионной терапии в клинической больнице
Порядок проведения гемотрансфузионной терапии в клинической больнице Сестринская помощь при проведении обследования пациентов с заболеваниями глаз. Методы исследования
Сестринская помощь при проведении обследования пациентов с заболеваниями глаз. Методы исследования Пломбировочные материалы. Систематика, требования предъявляемые к ним. Материалы для временных пломб и лечебных прокладок
Пломбировочные материалы. Систематика, требования предъявляемые к ним. Материалы для временных пломб и лечебных прокладок Методы исследования в акушерстве и гинекологии
Методы исследования в акушерстве и гинекологии