Содержание
- 2. VIRAL HEPATITIS It is inflammation of the liver and divided into 5 types: Hepatitis A Hepatitis
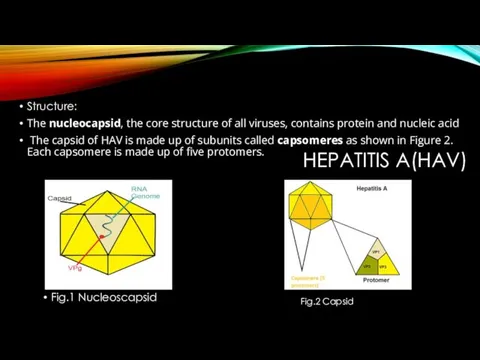
- 3. HEPATITIS A(HAV) Structure: The nucleocapsid, the core structure of all viruses, contains protein and nucleic acid
- 4. EPIDEMIOLOGY Natural infection is seen only in humans but chimpanzees have been seen to catch The
- 5. PREVENTION It can be prevented by vaccination good hygiene and sanitation Vaccines as: Havrix Fig.4
- 6. TREATMENT There is no treatment Syptomatic treatment : Initial therapy often consists of bed rest. The
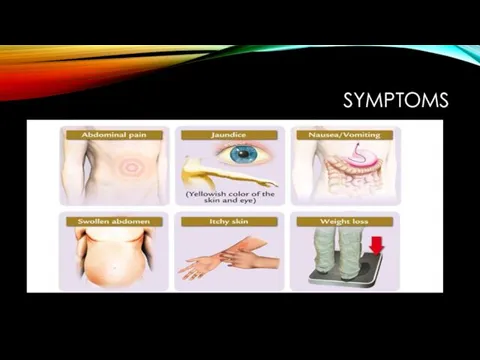
- 7. SYMPTOMS
- 8. DIAGNOSIS Fortunately, blood tests are widely available to accurately diagnose hepatitis A, including tests for antibodies,
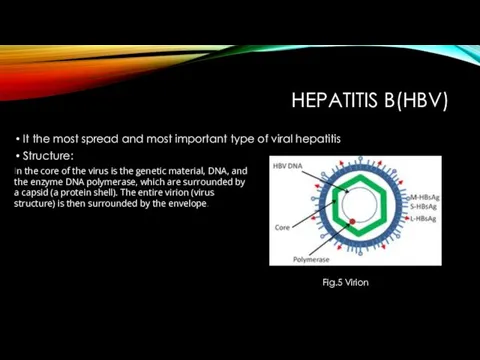
- 9. HEPATITIS B(HBV) It the most spread and most important type of viral hepatitis Structure: Fig.5 Virion
- 10. EPIDEMIOLOGY Natural infection occurs only in human,there is no animal reservoir Transmission :parenteral,sexual and perinatal It
- 11. PREVENTION It can be prevented by : Vaccination : Recombivax HB Not sharing needles or toothbrushes
- 12. TREATMENT No specific antiviral treatment is available for acute hepatitis B Synergistic approach of suppressing viral
- 13. SYMPTOMS
- 14. DISEASES Cirrhosis Liver cancer
- 15. DIAGNOSIS
- 16. HEPATITIS C Structure: The hepatitis C virus particle consists of a core of genetic material (RNA),
- 17. SYMPTOMS Hepatitis C infection causes acute symptoms in 15% of cases.Symptoms are generally mild and vague,
- 18. PREVENTION There are no vaccines for prevention
- 19. TREATMENT Long term infection can be treated by interferon alone or combined with ribavirin But short
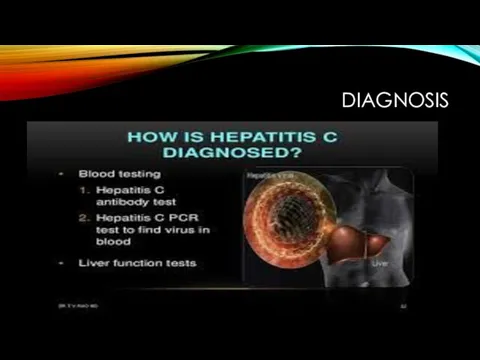
- 20. DIAGNOSIS
- 21. HEPATITIS E
- 22. PREVENTION Prevented by sanitation and vaccination
- 23. TREATMENT No treatment For people who have severe acute illness and who are not pregnant, treatment
- 24. SYMPTOMS Jaundice , fatigue, and nausea .
- 25. DIAGNOSIS ElISA
- 26. HEPATITIS D Structure: It has an outer coat containing three kinds of HBV envelope protein -
- 27. PREVENTION Same vaccine used to treat hepatitis B
- 28. TREATMENT No treatment The drug myrcludex B, which inhibits virus entry into hepatocytes, is in clinical
- 29. SYMPTOMS Hepatitis D doesn’t always cause symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they often include: yellowing of
- 31. Скачать презентацию
























 Тактика ведения ВИЧ-инфицированных пациентов с туберкулезом. Лечение туберкулеза у ВИЧ-инфицированных
Тактика ведения ВИЧ-инфицированных пациентов с туберкулезом. Лечение туберкулеза у ВИЧ-инфицированных Невротикалық бұзылыстардың психогигиенасы және психопрофилактикасы
Невротикалық бұзылыстардың психогигиенасы және психопрофилактикасы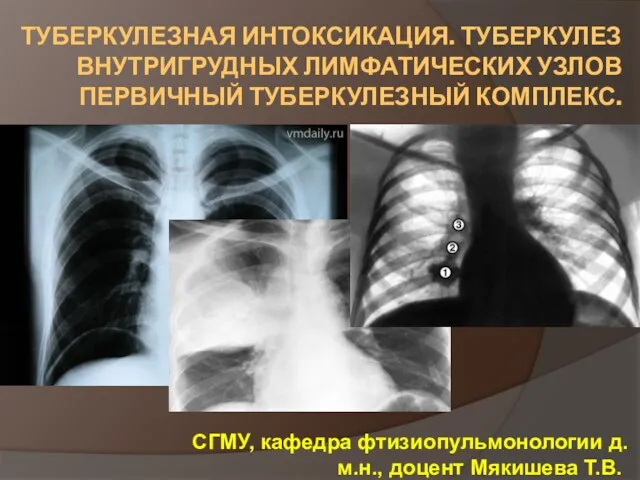 Туберкулезная интоксикация. Туберкулез внутригрудных лимфатических узлов. Первичный туберкулезный комплекс
Туберкулезная интоксикация. Туберкулез внутригрудных лимфатических узлов. Первичный туберкулезный комплекс Современные методы лечения сифилиса. Гонорея и инфекции, передаваемые половым путем
Современные методы лечения сифилиса. Гонорея и инфекции, передаваемые половым путем Иммунология. Популяции клеток. Лекция 2
Иммунология. Популяции клеток. Лекция 2 Электроэнцефалография
Электроэнцефалография Осуществление комплексного сестринского ухода за пациентами с бронхиальной астмой
Осуществление комплексного сестринского ухода за пациентами с бронхиальной астмой Особенности проведения тромболитической терапии
Особенности проведения тромболитической терапии ART әдісі
ART әдісі Кардиомиопатии. Классификация КМП
Кардиомиопатии. Классификация КМП Острая хирургическая патология во время беременности и родов
Острая хирургическая патология во время беременности и родов Оцінка стану новонародженого
Оцінка стану новонародженого Гормондардың биохимиясы. Гормондар және адаптациялық процестер
Гормондардың биохимиясы. Гормондар және адаптациялық процестер Эпилепсия. Классификация эпилепсии. Диагностические критерии. Неотложная помощь. Принципы лечения
Эпилепсия. Классификация эпилепсии. Диагностические критерии. Неотложная помощь. Принципы лечения Тамақтан улану кезіндегі алғашқы . Шұғыл әрекеттер
Тамақтан улану кезіндегі алғашқы . Шұғыл әрекеттер Болезнь Гентингтона
Болезнь Гентингтона Лечение больных туберкулезом. Практическое занятие
Лечение больных туберкулезом. Практическое занятие Иммобилизденген ферменттер
Иммобилизденген ферменттер Причины и механизм артериальной гиперемии
Причины и механизм артериальной гиперемии Тыныс жеткіліксіздігі
Тыныс жеткіліксіздігі Ауадаға бактерия санын есептеу. Судағы микроағзалардың санын есептеу
Ауадаға бактерия санын есептеу. Судағы микроағзалардың санын есептеу Жедел жүрек-қантамыр жетіспеушілік кезіндегі реанимация және интенсивті терапия
Жедел жүрек-қантамыр жетіспеушілік кезіндегі реанимация және интенсивті терапия Психиатриядағы шұғыл жағдайлар
Психиатриядағы шұғыл жағдайлар Двигательная система. Мышечное сокращение
Двигательная система. Мышечное сокращение Анатомия, физиология, гигиена детского организма
Анатомия, физиология, гигиена детского организма Переломы и травмы верхних конечностей
Переломы и травмы верхних конечностей Патология углеводного гомеостаза. Сахарный диабет
Патология углеводного гомеостаза. Сахарный диабет Нейроспид. История
Нейроспид. История