Содержание
- 2. STRUCTURE OF COURSE LECTURES CLASSES - MCQ -DISCUSSION -REPORTS
- 3. MEDICINE(lat. medicina, fr. Medicare — to treat) – the science and practice of the diagnosis, treatment
- 4. History of medicine is more theoretical than practical science. It divides into 2 parts The General
- 5. The study of History of medicine follows the course of universal human history. There are 5
- 6. HISTORICAL SOURCES Comprise all the creations of human society that have been preserved to present day
- 7. 1. WRITTEN SOURCES
- 8. 2. MATERIAL SOURCES - the archaeological finds, the remains, tools, clothing, dishes etc
- 9. 3.ETHNOGRAPHIC SOURCES - - from Greek 'ethno' — nation and 'grapho' — to describe - cultural
- 10. 4. FOLKLORE SOURCES - - from 'folk' — nation, clan and 'lore' — traditional knowledge, wisdom
- 11. 5.LINGUISTIC SOURCES - -reflection of historical reality in verbal forms (e.g. terms, names etc)
- 12. 6. DOCUMENTARY AND PHOTOS - - recording or pictures of a historical events which can be
- 13. 7. AUDIO SOURCES - - a sound recording of historical events, which was made at the
- 14. QUESTIONS FOR REVISION The subject and purposes of the History of medicine. Define the term «medicine»
- 15. MEDICINE IN PREHISTORIC TIME
- 16. Historical period The defining characteristics Historical sources Ideas about causes of diseases Real causes of diseases
- 17. Historical period: 1. 2 mill. BC — 40 000 BC (formation) 2. 40 000 BC —
- 18. The defining characteristics - nomadic - could not write - primitive technology - first beliefs (spirits,
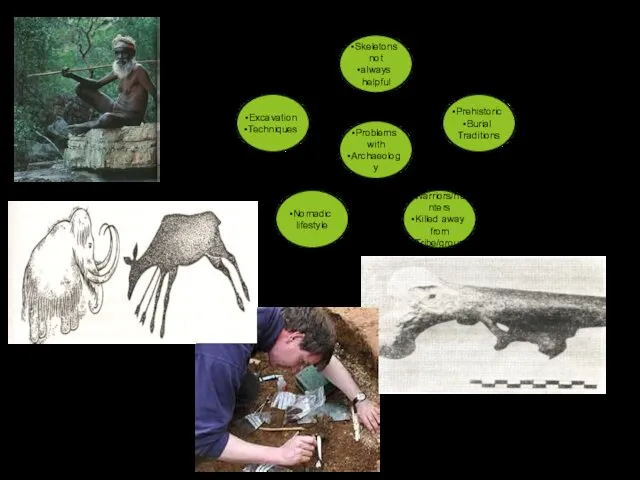
- 21. Sources The understanding of prehistoric medical practice is derived from paleopathology, the study of pictographs showing
- 22. Excavation Techniques Nomadic lifestyle Warriors/hunters Killed away from Tribe/group Prehistoric Burial Traditions Skeletons not always helpful
- 24. Лошадь,15-10 тысячелетие до н.э. Бизон,15-12 тысячелетие до н.э.
- 25. Погребение охотника на мамонтов
- 26. Ideas about causes of diseases influence of spirits influence of magic abstraction of the soul from
- 28. Totemism
- 29. Magic
- 30. Real causes of diseases in prehistoric time Transport and raising of massive rocks and stones Bad
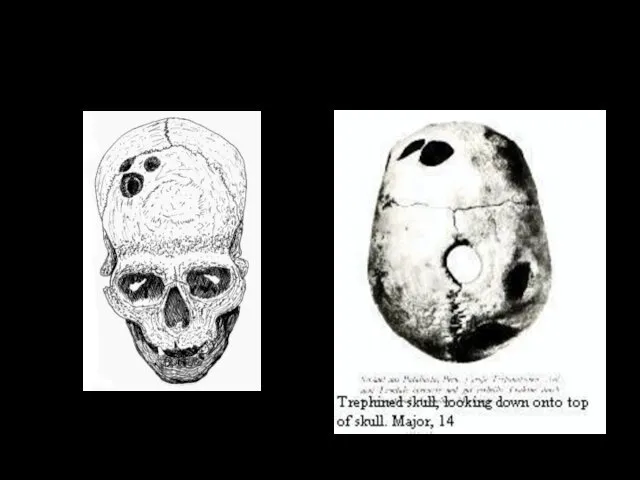
- 31. TREATMENT Incantations Rituals Magic Dancing Remedies Surgery (trephining, resetting dislocations and fractures, suturing wounds)
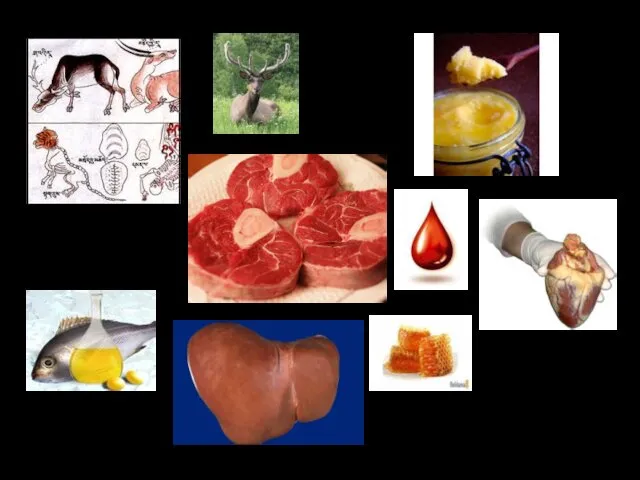
- 35. REMEDIES
- 36. HERBAL
- 37. PARTS OF ANIMALS
- 38. MINERALS
- 39. The word Shaman is an English translation of the Tungus word Saman. The Tungus are an
- 41. Healing the spirit is the primary function of a Shaman. This may include: Soul-extraction, Soul-retrieval, and
- 42. QUESTIONS FOR REVISION How prehistoric medicine reflected the ideas and practices of prehistoric society. What caused
- 44. Скачать презентацию





































 Острая печеночная недостаточность
Острая печеночная недостаточность Головокружения: классификация, клиника
Головокружения: классификация, клиника Здоровье родителей и здоровье будущего ребёнка
Здоровье родителей и здоровье будущего ребёнка Препараты половых гормонов
Препараты половых гормонов Функциональные гастроинтестинальные заболевания. СРК
Функциональные гастроинтестинальные заболевания. СРК Өндірістік улардың әсерінің жалпы заңдылықтары
Өндірістік улардың әсерінің жалпы заңдылықтары Миофункциональный подход к лечению аномалий прикуса и челюстно-лицевого развития
Миофункциональный подход к лечению аномалий прикуса и челюстно-лицевого развития Егде және қарт жастағы (геронтологиялық аспект)адамдарының психосоматикалық бұзылыстары
Егде және қарт жастағы (геронтологиялық аспект)адамдарының психосоматикалық бұзылыстары Abortion is simulated interruption of pregnancy
Abortion is simulated interruption of pregnancy Қан айналымының бұзылуы
Қан айналымының бұзылуы Функциональная диспепсия. Современные принципы терапии
Функциональная диспепсия. Современные принципы терапии Лекарственные растения
Лекарственные растения Метаболизм белков: утилизация аммиака; Цикл мочевины. Патология белкового обмена
Метаболизм белков: утилизация аммиака; Цикл мочевины. Патология белкового обмена Podstawy chemioterapii nowotworów złośliwych
Podstawy chemioterapii nowotworów złośliwych Возрастные особенности кровеносных сосудов
Возрастные особенности кровеносных сосудов Стероидные и нестероидные противовоспалительные средства
Стероидные и нестероидные противовоспалительные средства Акушерские кровотечения во время беременности. Классификация
Акушерские кровотечения во время беременности. Классификация Типовые нарушения органно-тканевого кровообращения и микроциркуляции
Типовые нарушения органно-тканевого кровообращения и микроциркуляции Жұлынның қан тамырлық аурулары
Жұлынның қан тамырлық аурулары Цитомегаловирусты,герпестік,хламидиялық инфекция және жүктілік
Цитомегаловирусты,герпестік,хламидиялық инфекция және жүктілік Радиационная медицина. История развития. Радиоактивность. Радиационный фон
Радиационная медицина. История развития. Радиоактивность. Радиационный фон Нейротропные средства
Нейротропные средства Қан түзу ағзаларының визуалды диагностикасы
Қан түзу ағзаларының визуалды диагностикасы Тұрақты электротоктардың медицинада қолданылуы
Тұрақты электротоктардың медицинада қолданылуы Усік. Куйік. Электрожарақат
Усік. Куйік. Электрожарақат Репродуктивное здоровье женщин
Репродуктивное здоровье женщин Геморрой. Геморроидальные узлы
Геморрой. Геморроидальные узлы Амилоидоз почек. АА - амилоидоз. АL - амилоидоз
Амилоидоз почек. АА - амилоидоз. АL - амилоидоз