Содержание
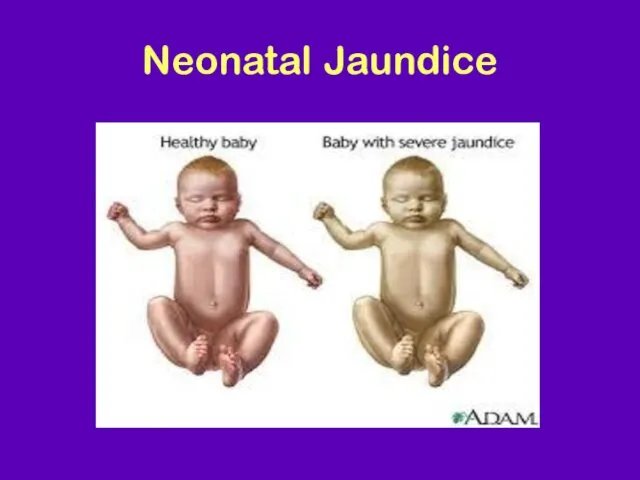
- 2. Neonatal Jaundice
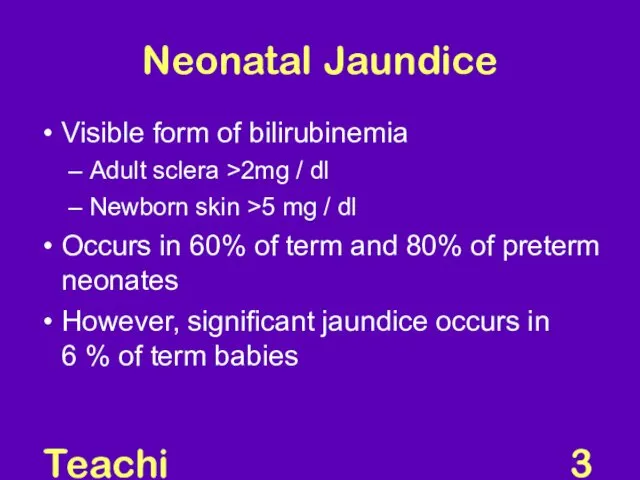
- 3. Teaching Aids: NNF Neonatal Jaundice Visible form of bilirubinemia Adult sclera >2mg / dl Newborn skin
- 4. Teaching Aids: NNF What is the Neonatal Jaundice? Neonatal Jaundice(also called Newborn jaundice) is a condition
- 5. Teaching Aids: NNF Causes of Jaundice according to time of appearance 1.Appearing at birth or within
- 6. Teaching Aids: NNF 2.Appearing between 24-72 hours of life Physiological Sepsis neonatorum Plycythemia Concealed hemorrhages:cephalhematoma,subarachnoid bleed,IVN.
- 7. Teaching Aids: NNF 3.Appearing after 72 hrs and within 1st week Sepsis Syphilis Toxoplasmosis 4.Jaundice apearing
- 8. Teaching Aids: NNF Special characteristic in neonates 1)More billirubin produced Much more hemolysis The life-length of
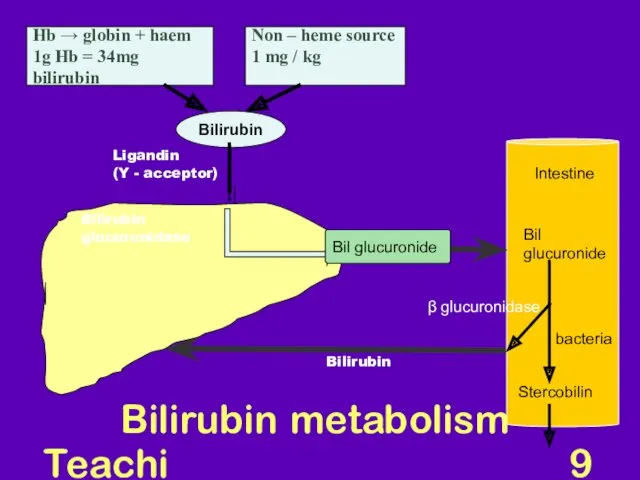
- 9. Teaching Aids: NNF Bilirubin metabolism Hb → globin + haem 1g Hb = 34mg bilirubin Non
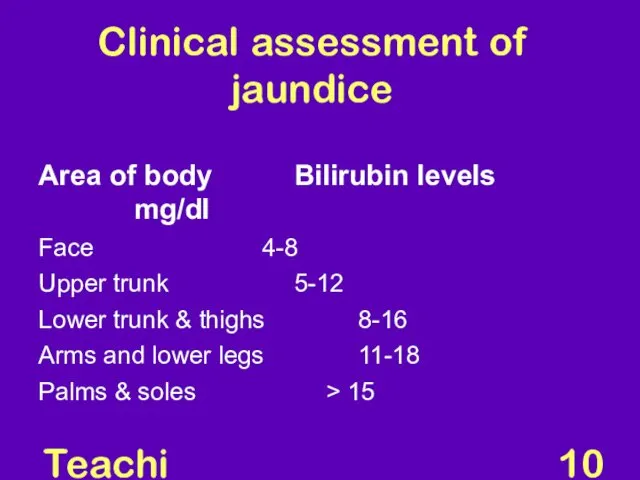
- 10. Teaching Aids: NNF Clinical assessment of jaundice Area of body Bilirubin levels mg/dl Face 4-8 Upper
- 11. Teaching Aids: NNF Physiological jaundice Characteristics Appears after 24 hours Maximum intensity by 4th-5th day in
- 12. Teaching Aids: NNF Why does physiological jaundice develop? Increased bilirubin load Defective uptake from plasma Defective
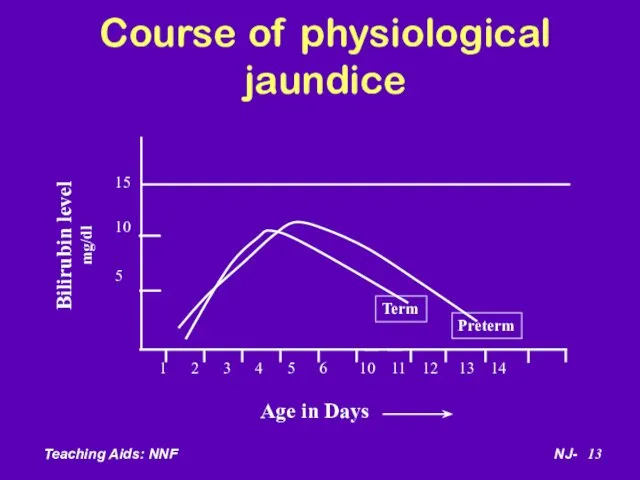
- 13. Course of physiological jaundice
- 14. Teaching Aids: NNF Pathological jaundice Appears within 24 hours of age Increase of bilirubin > 5
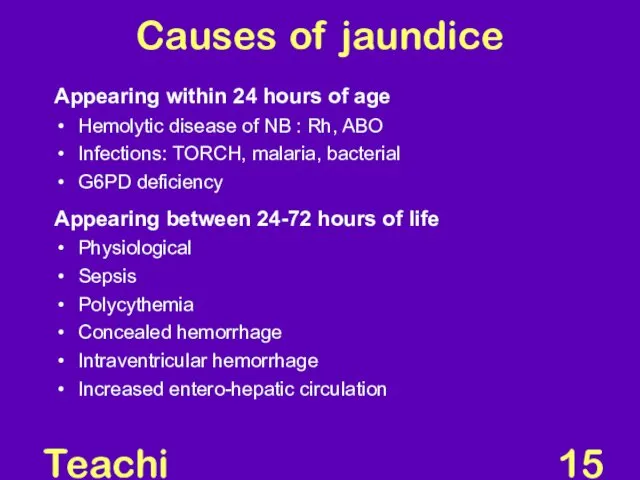
- 15. Teaching Aids: NNF Causes of jaundice Appearing within 24 hours of age Hemolytic disease of NB
- 16. Teaching Aids: NNF Causes of jaundice After 72 hours of age Sepsis Cephalhaematoma Neonatal hepatitis Extra-hepatic
- 17. Teaching Aids: NNF The general symptoms of Neonatal Jaundice Yellow skin Yellow eyes(sclera) Sleepiness Poor feeding
- 18. Teaching Aids: NNF Risk factors for jaundice JAUNDICE J - jaundice within first 24 hrs of
- 19. Teaching Aids: NNF Common causes Physiological Blood group incompatibility G6PD deficiency Bruising and cephalhaematoma Intrauterine and
- 20. Teaching Aids: NNF Approach to jaundiced baby Ascertain birth weight, gestation and postnatal age Assess clinical
- 21. Teaching Aids: NNF Workup Maternal & perinatal history Physical examination Laboratory tests (must in all)* Total
- 22. Teaching Aids: NNF Management Rationale: reduce level of serum bilirubin and prevent bilirubin toxicity Prevention of
- 23. Teaching Aids: NNF Principle of phototherapy Native bilirubin Photo isomers of bilirubin Insoluble Soluble 450-460nm of
- 24. Teaching Aids: NNF Phototherapy equipment White light tubes 6-8*/ 4 blue light tubes Cradle or incubator
- 25. Babies under phototherapy Baby under conventional phototherapy Baby under triple unit intense phototherapy
- 26. Teaching Aids: NNF Phototherapy Technique Perform hand wash Place baby naked in cradle or incubator Fix
- 27. Teaching Aids: NNF Phototherapy Frequent extra breast feeding every 2 hourly Turn baby after each feed
- 28. Teaching Aids: NNF Diffential Diagnoses Breast Milk Jaundice Cholestatis Dubin-Johnson Syndrome GalactoseMIA Hemolytic Disease of Newborn
- 29. Teaching Aids: NNF Side effects of phototherapy Increased insensible water loss Loose stools Skin rash Bronze
- 30. Teaching Aids: NNF Choice of blood for exchange blood transfusion ABO incompatibility Use O blood of
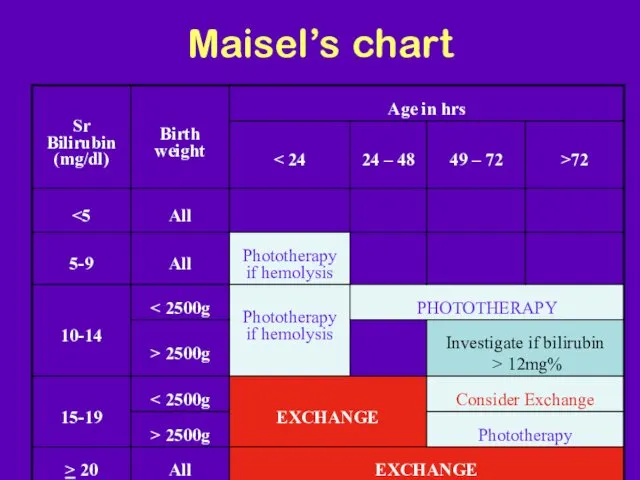
- 31. Maisel’s chart
- 32. Teaching Aids: NNF Prolonged indirect jaundice Causes Crigler Najjar syndrome Breast milk jaundice Hypothyroidism Pyloric stenosis
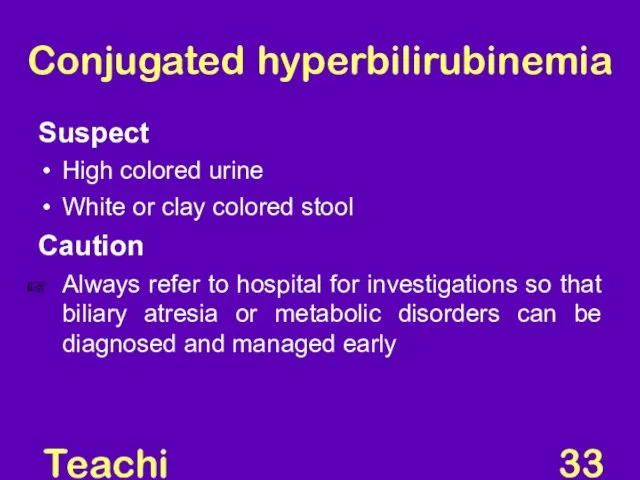
- 33. Teaching Aids: NNF Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia Suspect High colored urine White or clay colored stool Caution Always
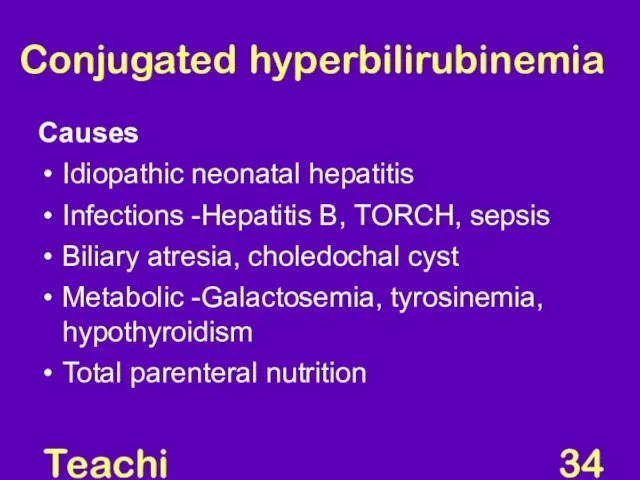
- 34. Teaching Aids: NNF Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia Causes Idiopathic neonatal hepatitis Infections -Hepatitis B, TORCH, sepsis Biliary atresia,
- 36. Скачать презентацию























 Микотоксины. Действие микотоксинов в истории
Микотоксины. Действие микотоксинов в истории Общие принципы лечения абсцессов и флегмон лица и шеи. Физиотерапия и реабилитация больных
Общие принципы лечения абсцессов и флегмон лица и шеи. Физиотерапия и реабилитация больных Диспансерное наблюдение за детьми с хроническими заболеваниями
Диспансерное наблюдение за детьми с хроническими заболеваниями Хронические расстройства питания у детей
Хронические расстройства питания у детей Наследственные заболевания человека
Наследственные заболевания человека Геморрагический шок
Геморрагический шок Гипогликемическая и гипергликемическая комы
Гипогликемическая и гипергликемическая комы Пути введения лекарственных средств
Пути введения лекарственных средств Обзор и принципы реанимации новорожденных
Обзор и принципы реанимации новорожденных Современные алгоритмы лечения сахарного диабета 2 типа
Современные алгоритмы лечения сахарного диабета 2 типа Нейропсихологическая диагностика
Нейропсихологическая диагностика Общая характеристика группы инфекционных болезней с воздушнокапельным механизмом передачи. Грипп
Общая характеристика группы инфекционных болезней с воздушнокапельным механизмом передачи. Грипп Вагинальные инфекции при беременности
Вагинальные инфекции при беременности Federal State Educational Institution of Higher Education
Federal State Educational Institution of Higher Education Синдром наличия жидкости и газа в плевральной полости. Плевриты
Синдром наличия жидкости и газа в плевральной полости. Плевриты Холера. Эпидемиология
Холера. Эпидемиология Хронический пылевой бронхит
Хронический пылевой бронхит Легочное сердце
Легочное сердце Инфекционный мононуклеоз у детей
Инфекционный мононуклеоз у детей Понятие гиподинамии, гипердинамии
Понятие гиподинамии, гипердинамии Действия ассистента, осуществляемые до прихода врача-стоматолога, после прихода врача-стоматолога и после окончания лечения
Действия ассистента, осуществляемые до прихода врача-стоматолога, после прихода врача-стоматолога и после окончания лечения Митральные пороки сердца
Митральные пороки сердца Критерии и качества стоматологических материалов. Система международных и национальных стандартов
Критерии и качества стоматологических материалов. Система международных и национальных стандартов Введение в венерологию. История развития венерологии. Инфекции, передающиеся половым путем
Введение в венерологию. История развития венерологии. Инфекции, передающиеся половым путем Доказательная профилактика. Скрининговые программы
Доказательная профилактика. Скрининговые программы Endocrine system
Endocrine system Современные подходы к лечению эндометриоидных кист яичников
Современные подходы к лечению эндометриоидных кист яичников Дисфункционалдық жатырдан қан кету
Дисфункционалдық жатырдан қан кету