Содержание
- 2. Hormones are biologically active substances, produced by the endocrine glands. They regulate various functions of the
- 3. Types of hormonal therapy Specific: Replacement therapy for the treatment of the failure of endocrine gland.
- 4. Hormones drugs are obtained from the organs and urine of animals. In this case the activity
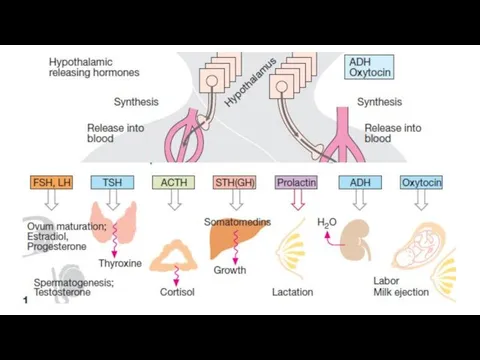
- 5. Hypothalamus and pituitary hormones. The hypothalamus produces releasing or inhibitory factors. They control the production and
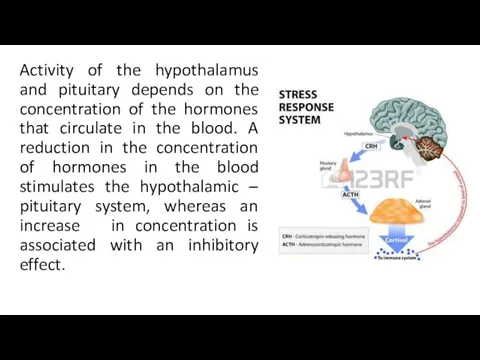
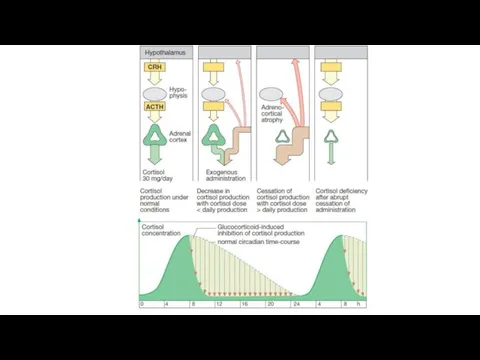
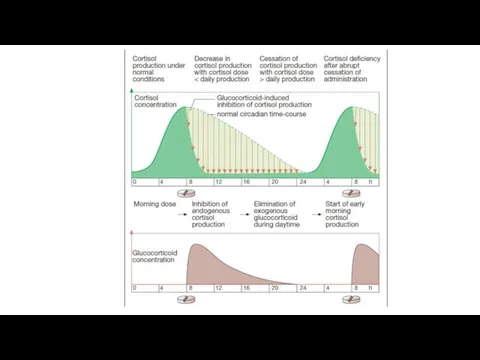
- 7. Activity of the hypothalamus and pituitary depends on the concentration of the hormones that circulate in
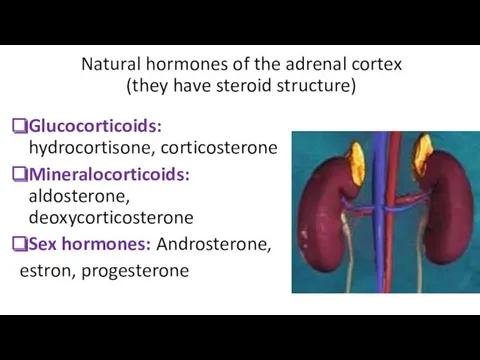
- 8. Natural hormones of the adrenal cortex (they have steroid structure) Glucocorticoids: hydrocortisone, corticosterone Mineralocorticoids: aldosterone, deoxycorticosterone
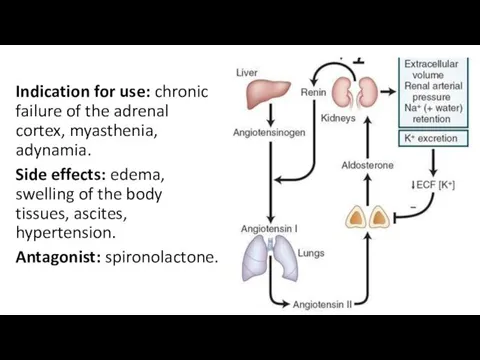
- 9. Mineralocorticoids interact with the receptors that are localized inside the cells. They enhance the synthesis of
- 10. Indication for use: chronic failure of the adrenal cortex, myasthenia, adynamia. Side effects: edema, swelling of
- 11. Glucocorticoids A. Natural: Hydrocortisone B. Synthetic Dehydrated: Prednisolone, Methylprednisolone Fluorinated: Dexamethasone Triamcinolone Difluorinated: Fluocinolone acetonide (Sinaflan)
- 12. The introduction of 2 atoms of fluorine or chlorine into the molecules of glucocorticoids reduces their
- 13. Glucocorticoids bind to blood proteins. Hydrocortisone binds to blood proteins (transcortin and albumin) by 90%, the
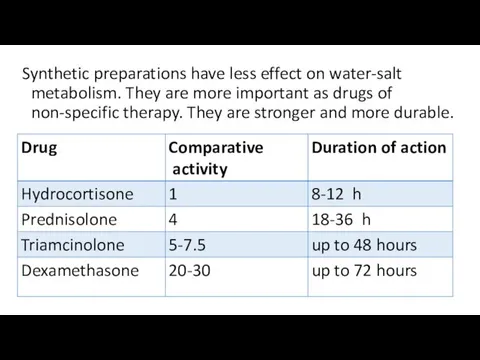
- 14. Synthetic preparations have less effect on water-salt metabolism. They are more important as drugs of non-specific
- 15. Effects on metabolism Glucocorticoids act intracellular. They interact with specific receptors in the cellular cytoplasm. The
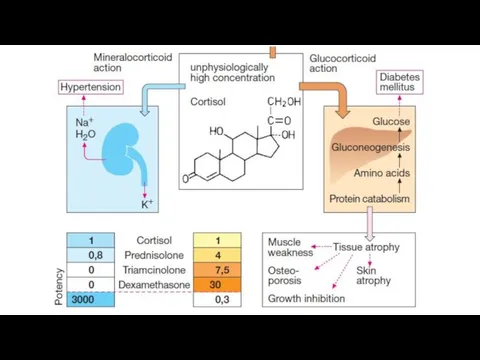
- 16. Carbohydrate metabolism: They increase glucose level in blood. They inhibit hexokinase, ↓the utilization of glucose, ↑gluconeogenesis,
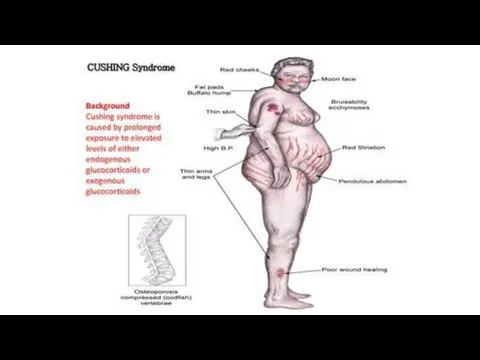
- 17. Fat metabolism. They cause the redistribution of fat (Cushing syndrome): accumulation of a considerable amount of
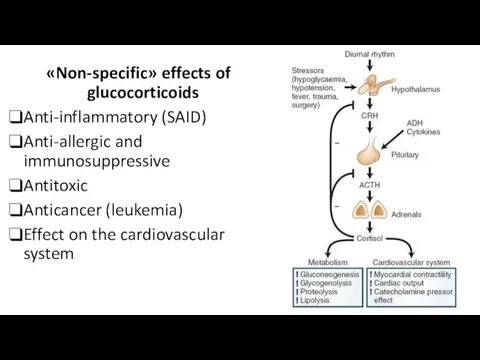
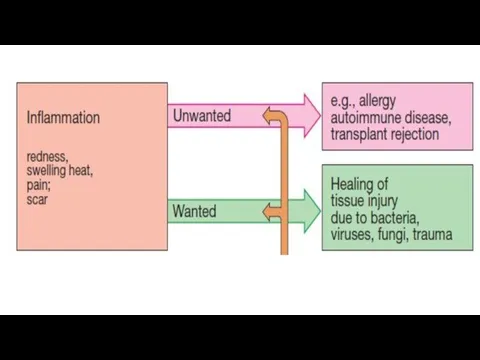
- 20. «Non-specific» effects of glucocorticoids Anti-inflammatory (SAID) Anti-allergic and immunosuppressive Antitoxic Anticancer (leukemia) Effect on the cardiovascular
- 21. Effects on the cardiovascular system: ↑blood volume; reduce release, but increase the breakdown of histamine; ↑the
- 22. Effects on hematopoiesis Glucocorticoids increase the amount of reticulocytes and erythrocytes. They are used for the
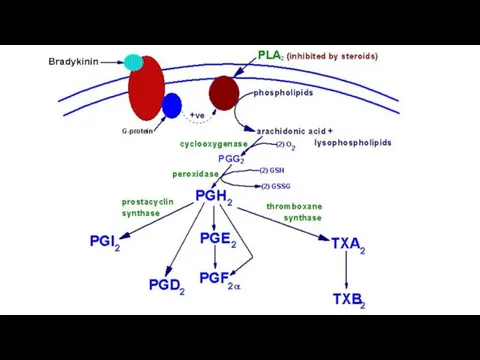
- 24. Anti-inflammatory effect Glucocorticoids induce biosynthesis of special proteins – lipocortins. They inhibit phospholipase A2. The production
- 26. Exudation. Glucocorticoids: reduce the development of edema; ↓the formation of mediators of inflammation, ↓ degranulation of
- 27. Proliferation. The drugs reduce scar formation because they: inhibit the synthesis of proteins; ↓migration of cellular
- 28. Immunosuppressive action. GCs: ↓ migration of stem cells, ↓production of T and B lymphocytes, their development
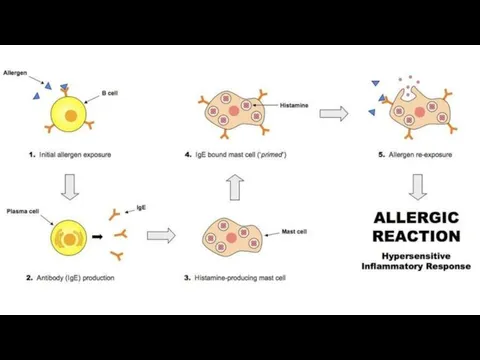
- 29. Anti-allergic effects. Glucocorticoids: ↓synthesis and block the Fc receptors on the surface of mast cells; ↓
- 31. Types of therapy with steroid anti-inflammatory drugs Substitutional therapy (adrenal insufficiency) Inhibiting therapy (adrenogenital syndrome) Pharmacodynamic
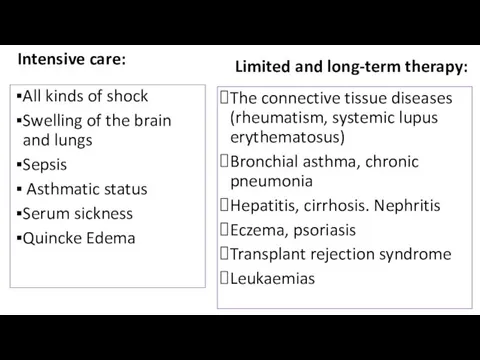
- 32. Intensive care: All kinds of shock Swelling of the brain and lungs Sepsis Asthmatic status Serum
- 33. Adverse effects: acute adrenal insufficiency; the Cushing syndrome; steroid diabetes mellitus; ulcerogenicity; slowing of wound’s regeneration,
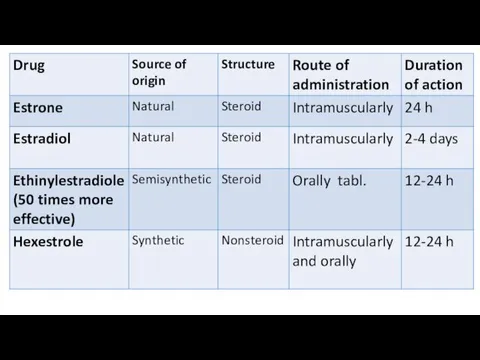
- 36. Anabolic steroids preparations created on the basis of male sex hormones, but have minimal androgenic activity.
- 37. Effects: Anabolic steroids increase protein synthesis, improve appetite, increase muscle and body mass, accelerate growth (in
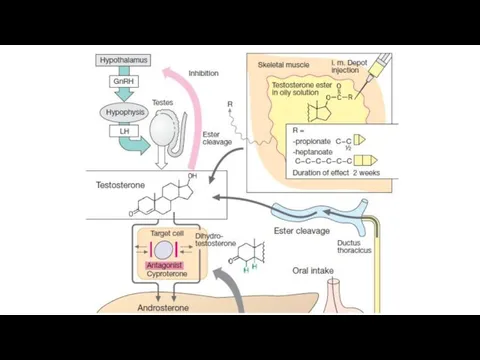
- 39. Male sex hormones (androgens) In male sex organs interstitial Leydig cells produce testosterone. It is converted
- 41. Drugs: Testosterone propionatis and testenate are produced in oil for muscular injections. Testosterone propionatis is administered
- 42. Indications for use Men: treatment of male sex organs dysfunction (delayed sexual development, impotence, castration), Female:
- 43. Antagonists 1. 5α-reductase inhibitors that supress testosterone conversion to dihydrotestosterone Finasteride blocks 5α-reductase and reduces the
- 44. The drugs block the testosterone – sensitive androgen receptors in the peripheral target tissues, suppresses spermatogenesis.
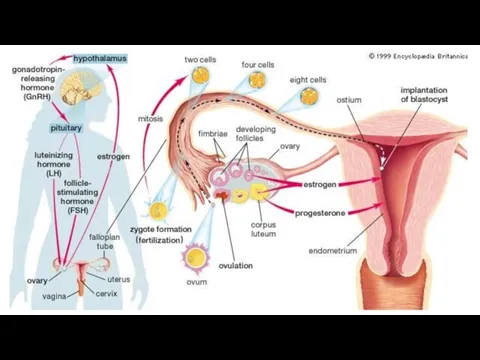
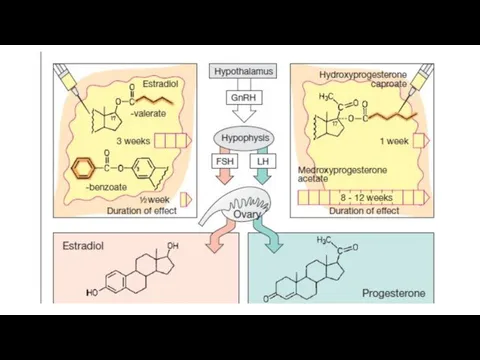
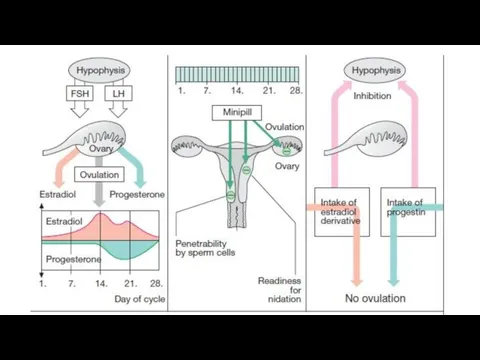
- 45. Female sex hormones, their drugs and antagonists Hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian system functions in the body of women. In
- 49. Drugs interact with specific estrogen receptors in the target organs (uterus, vagina, fallopian tubes, mammary glands,
- 50. Indications for use drugs of substitution therapy: sexual underdevelopment, amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea, infertility, early menopause, surgical removal
- 52. Clomiphene is antiestrogen. It passes through the BBB, interacts with the estrogenic receptors of the hypothalamus,
- 53. Gestagens and antigestagens
- 54. Effects: They prepare the uterus for implantation. They promotes the development of the placenta, reduces the
- 55. Indications for use: Violation of menstrual cycle, dysmenorrhea, dysfunctional uterine bleeding. The threat of miscarriage in
- 56. Mifepristone is antigestagen. It interacts with gestagen receptors and prevents the action of gestagens. It increases
- 58. Скачать презентацию




































 Острый рассеянный энцефаломиелит
Острый рассеянный энцефаломиелит Заболевания щитовидной железы
Заболевания щитовидной железы Этические аспекты генетики и эпидемиологии
Этические аспекты генетики и эпидемиологии Просветление. Рентгенопульмонология
Просветление. Рентгенопульмонология Вскармливание детей грудного возраста. Раздел 1.Лекция 6
Вскармливание детей грудного возраста. Раздел 1.Лекция 6 Затяжной субфебрилитет в амбулаторно-поликлинической практике
Затяжной субфебрилитет в амбулаторно-поликлинической практике Оказание ПМП при остановке сердца, искусственная вентиляция лёгких. Понятие первой помощи. Тема 4.1.1
Оказание ПМП при остановке сердца, искусственная вентиляция лёгких. Понятие первой помощи. Тема 4.1.1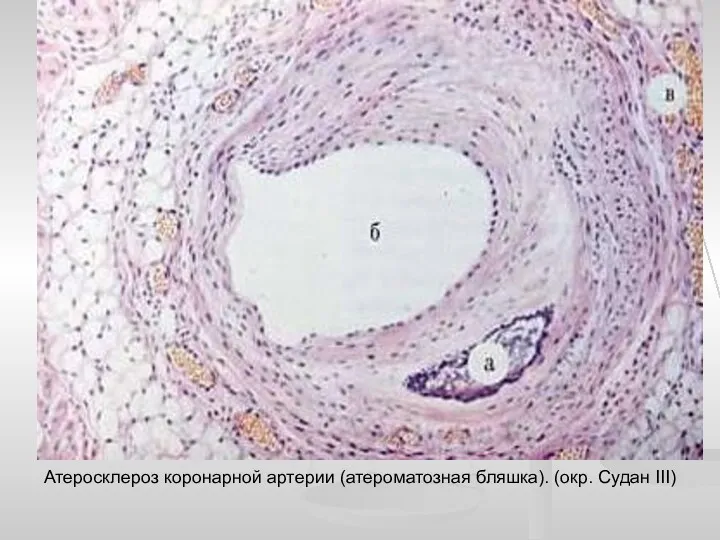 Атеросклероз коронарной артерии
Атеросклероз коронарной артерии Физиология беременности. Перинатальная охрана плода. Методы обследования в акушерстве
Физиология беременности. Перинатальная охрана плода. Методы обследования в акушерстве Наркологическая ситуация среди несовершеннолетних в Кировской области по итогам 2018 года
Наркологическая ситуация среди несовершеннолетних в Кировской области по итогам 2018 года Современный алгоритм диспансерного регламента для детей с врожденной патологией челюстно-лицевой области
Современный алгоритм диспансерного регламента для детей с врожденной патологией челюстно-лицевой области Воспалительные заболевания позвоночника
Воспалительные заболевания позвоночника Ревматические болезни (системные заболевания соединительной ткани)
Ревматические болезни (системные заболевания соединительной ткани) Организация амбулаторно-поликлинической помощи детям. Функциональные обязанности и показатели работы ВОП с детским населением
Организация амбулаторно-поликлинической помощи детям. Функциональные обязанности и показатели работы ВОП с детским населением Дефицит массы тела как фактор риска заболеваний
Дефицит массы тела как фактор риска заболеваний Общие вопросы наркологии
Общие вопросы наркологии Нейроциркуляторная дистония
Нейроциркуляторная дистония Заболевания век, слезных органов и орбиты. Конъюнктивит, трахома
Заболевания век, слезных органов и орбиты. Конъюнктивит, трахома Ұшқыш ингалянттарға тәуелділік
Ұшқыш ингалянттарға тәуелділік Корь
Корь Ортогнатическая хирургия при аномалиях величины и расположения челюстей
Ортогнатическая хирургия при аномалиях величины и расположения челюстей Продукт добровольного медицинского страхования Клещевой энцефалит
Продукт добровольного медицинского страхования Клещевой энцефалит Зубочелюстно-лицевая система – единый анатомо-функциональный комплекс. Особенности строения. Биодинамика движения нижней челюсти
Зубочелюстно-лицевая система – единый анатомо-функциональный комплекс. Особенности строения. Биодинамика движения нижней челюсти Разработка программы тренировок и питания для мужчины 42 года с целью коррекции фигуры
Разработка программы тренировок и питания для мужчины 42 года с целью коррекции фигуры Рак шкіри. Меланобластома
Рак шкіри. Меланобластома Қыздардағы гонорея. Потогенезінің, клиникасының, емінің ерекшеліктері. Троихомониаз. Микоплазмоз
Қыздардағы гонорея. Потогенезінің, клиникасының, емінің ерекшеліктері. Троихомониаз. Микоплазмоз Наследственные болезни накопления: Мукополисахаридозы. Муковисцидоз. Причина, патогенез, клиника, диагностика, лечение,прогноз
Наследственные болезни накопления: Мукополисахаридозы. Муковисцидоз. Причина, патогенез, клиника, диагностика, лечение,прогноз Халықтың радиациялық қауіпсіздігін қамтамасыз ету мен қоршаған ортаны радиоактивті заттардан қорғаудағы халықаралық
Халықтың радиациялық қауіпсіздігін қамтамасыз ету мен қоршаған ортаны радиоактивті заттардан қорғаудағы халықаралық