Содержание
- 2. Plan of lecture Overview Etiology Epidemiology Pathogenesis Manifestations Diagnosis Therapy and Prevention
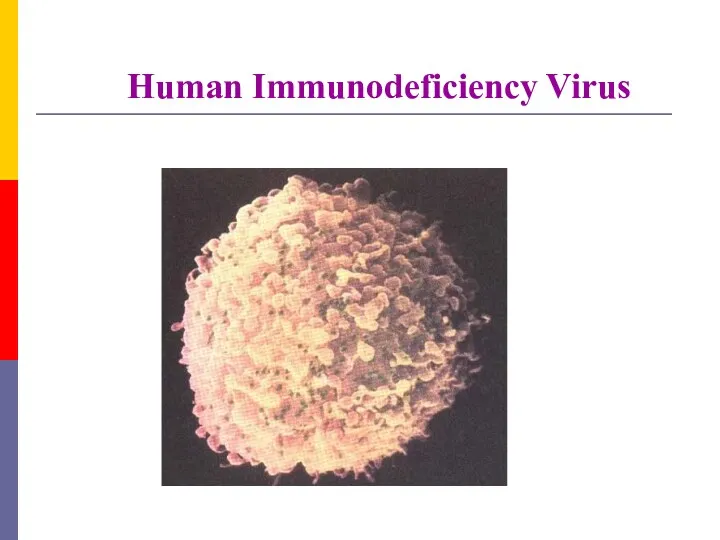
- 3. Human Immunodeficiency Virus
- 4. The first indication of new disease – Acquired Immunodificiency Syndrom (AIDS) began in the summer of
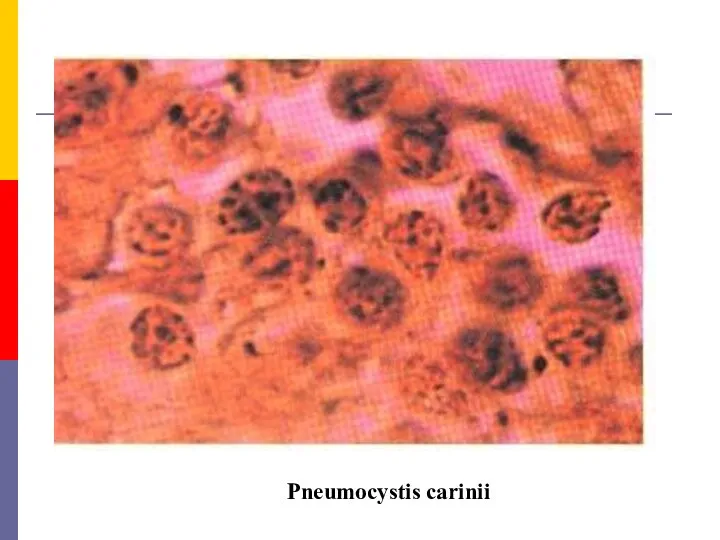
- 6. Pneumocystis carinii
- 7. Statistics The latest statistics on the world epidemic(UNAIDS/WHO) – 01.01.2012 People living with HIV/AIDS 33 million
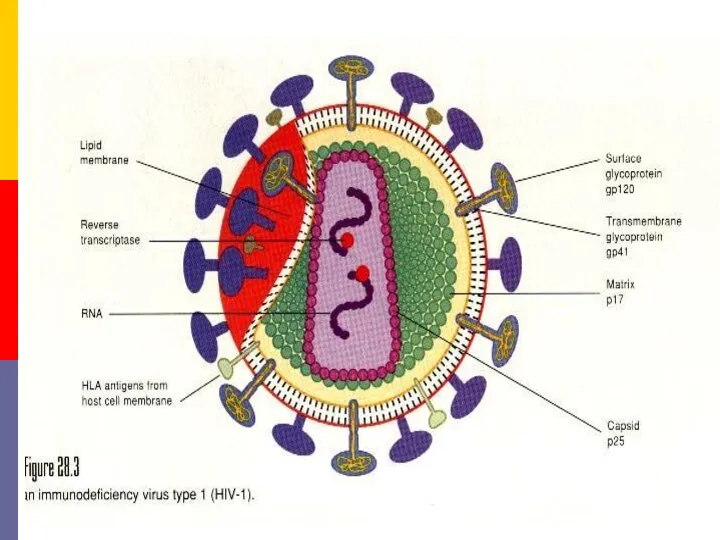
- 8. HIV, the etiologjcal agent of AIDS, belongs to the lentivirus subgroup of the family Retroviridae. Structure.
- 10. Types of HIV Virus HIV 1 Most common in sub-Saharan Africa and throughout the world Groups
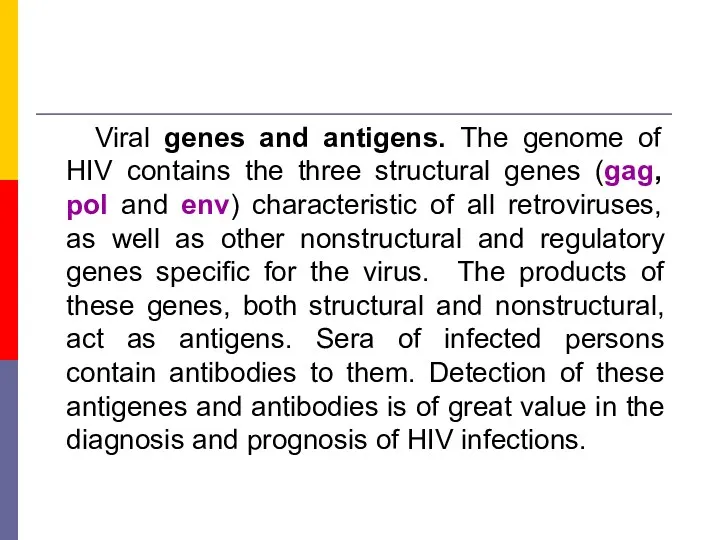
- 11. Viral genes and antigens. The genome of HIV contains the three structural genes (gag, pol and
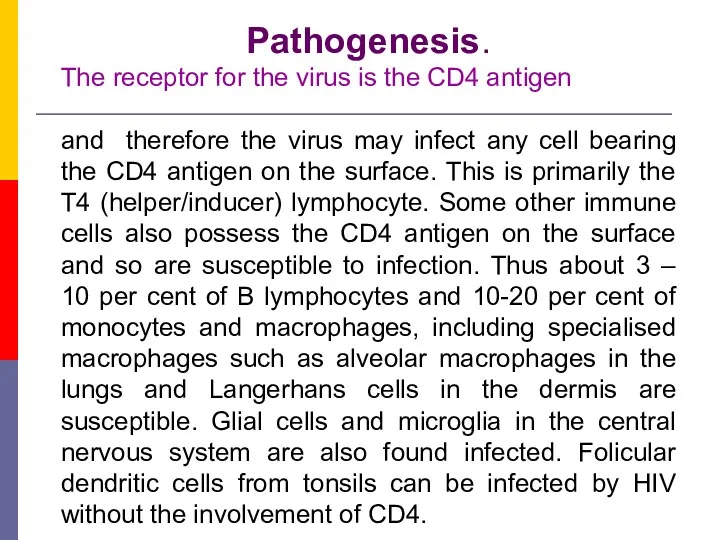
- 12. Pathogenesis. The receptor for the virus is the CD4 antigen and therefore the virus may infect
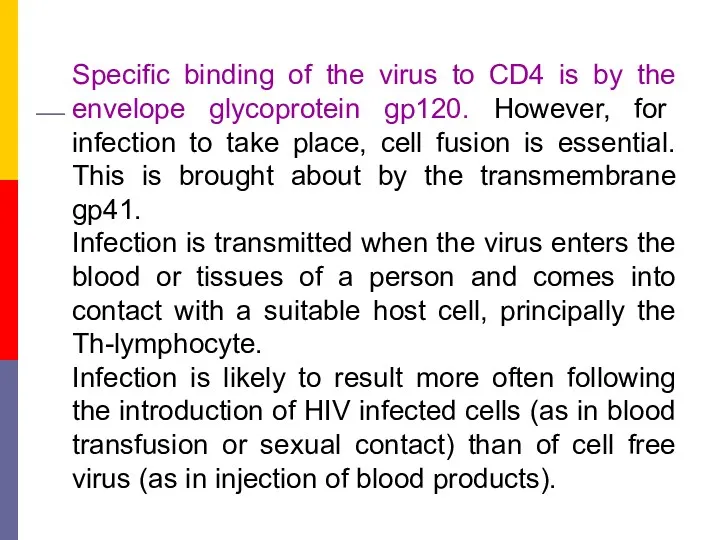
- 13. Specific binding of the virus to CD4 is by the envelope glycoprotein gp120. However, for infection
- 14. In an infected individual, HIV can be isolated from the blood, lymphocytes, cell free plasma, semen,
- 15. The primary pathogenic mechanism in HIV infection is the damage caused to the T4 lymphocyte. The
- 16. Window Period Time from initial infection with HIV until antibodies are detected by a single test
- 17. Disease Progression Severity of illness is determined by amount of virus in the body (increasing viral
- 18. What body fluid transmit HIV? blood semen vaginal fluid breast milk
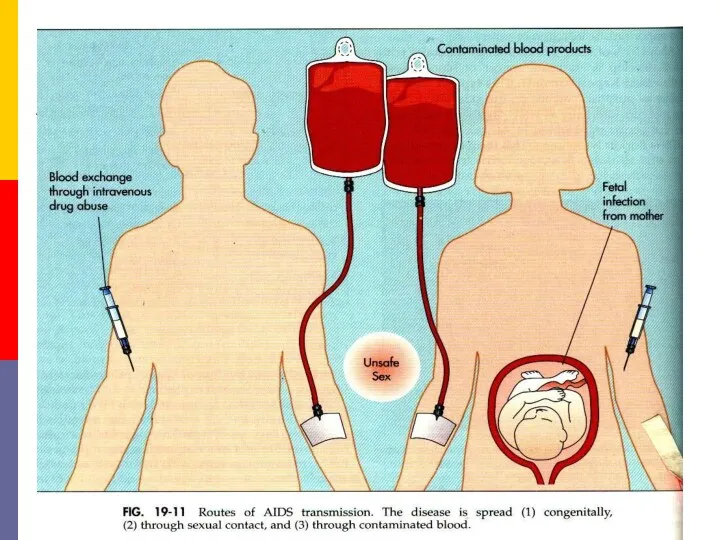
- 19. AIDS is primarily a sexually transmitted infection. In the USA it was transmitted predominantly among male
- 21. The second mode of transmission is through blood and blood products. Before the danger of HIV
- 23. This restriction also applies to the donation of semen, cornea, bone marrow, kidney and other organs
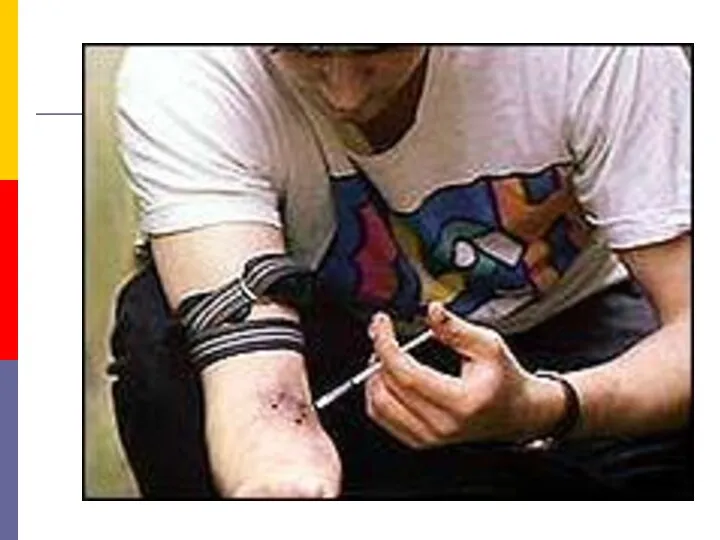
- 24. Contaminated needles can transmit the infection. This is particularly relevant in drug addicts who share syringes
- 26. The danger of needlestick injury is present in medical and paramedical personnel, though the chances of
- 27. Transmission of infection from mother to baby can take place before, during or after birth. As
- 28. Normal social and domestic contact does not transmit the infection. Shaking hands, hugging, putting cheeks together
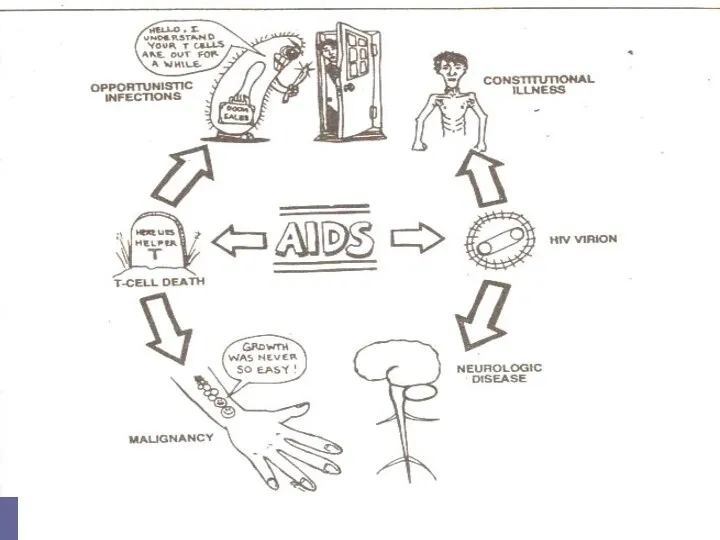
- 30. ACQUIRED DEFICIENCY SYNDROME (AIDS) Clinical features of HIV infection. AIDS is only the last stage in
- 31. Acute HIV infection. Within a few weeks of infection with HIV, about 10-15 per cent of
- 32. Asymptomatic infection. All persons infected with HIV, whether they experience seroconversion illness or not, pass through
- 33. Persistant Generalised Liphadenopathy (PGL). This has been defined as the presence of enlarged lymph nodes, at
- 34. AIDS Related Complex (ARC). This group inc1udes patients with considerable immunodeficiency, suffering from various constitutional symptoms
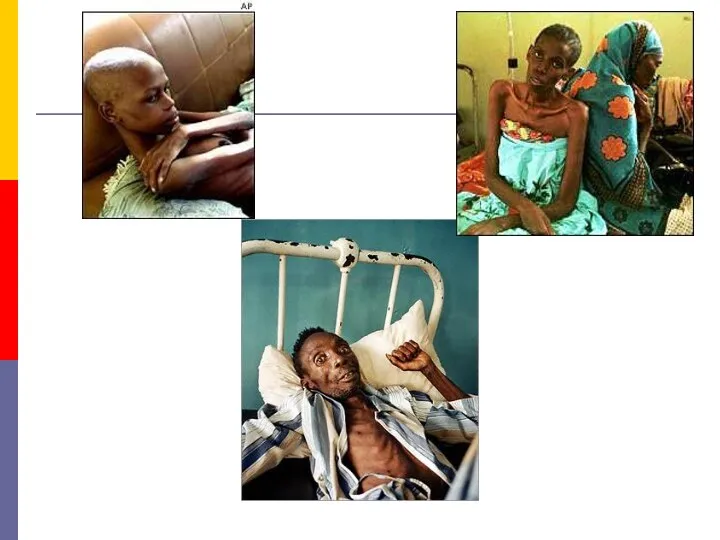
- 35. AIDS. This is the end stage disease representing the irreversible breakdown of immune defense mechanisms, leaving
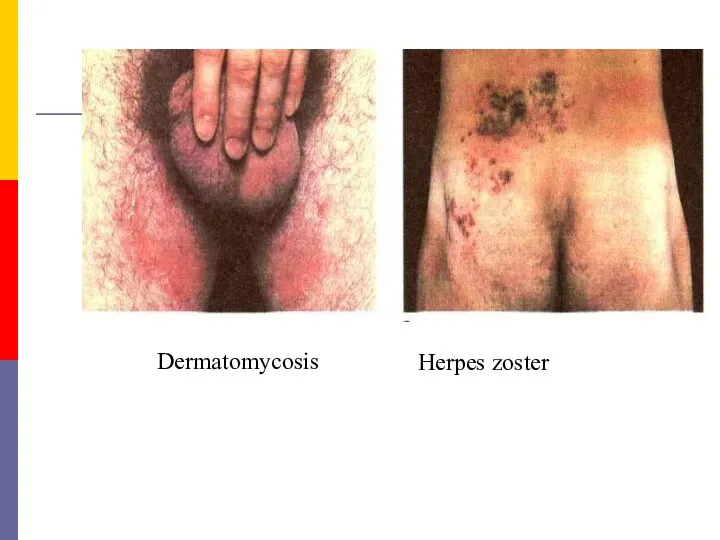
- 36. Dermatomycosis Herpes zoster
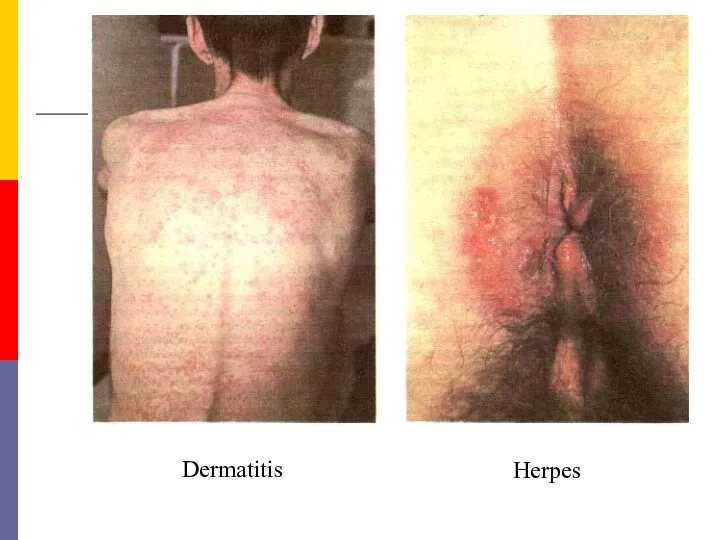
- 37. Dermatitis Herpes
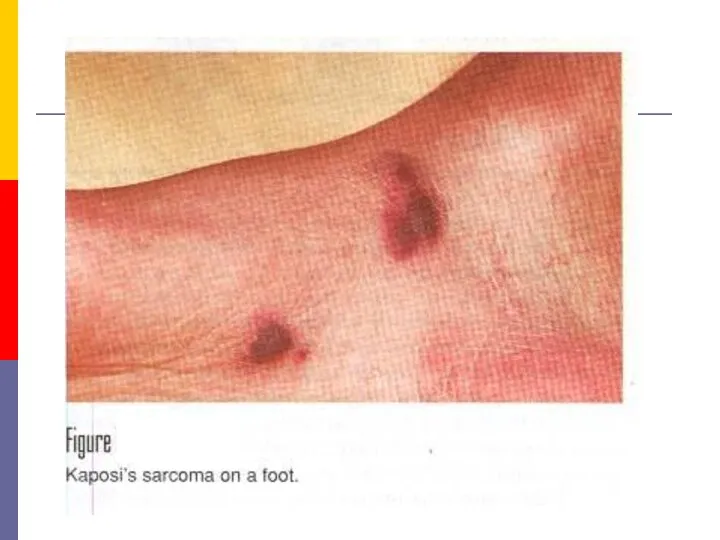
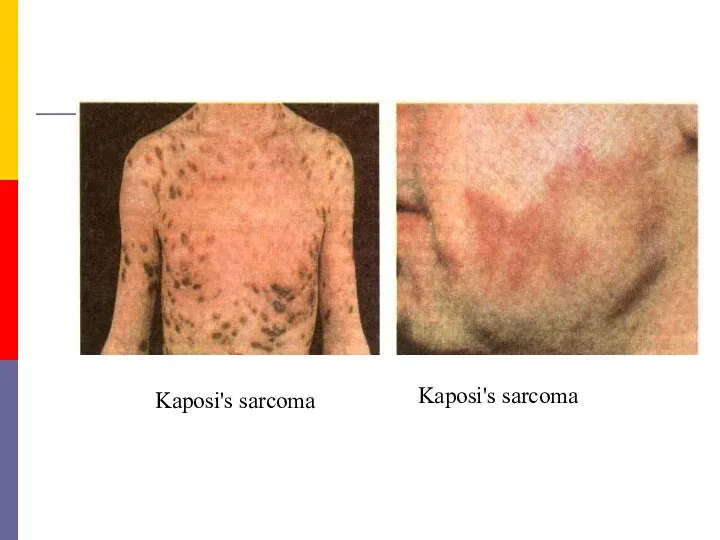
- 38. Kaposi's sarcoma Kaposi's sarcoma
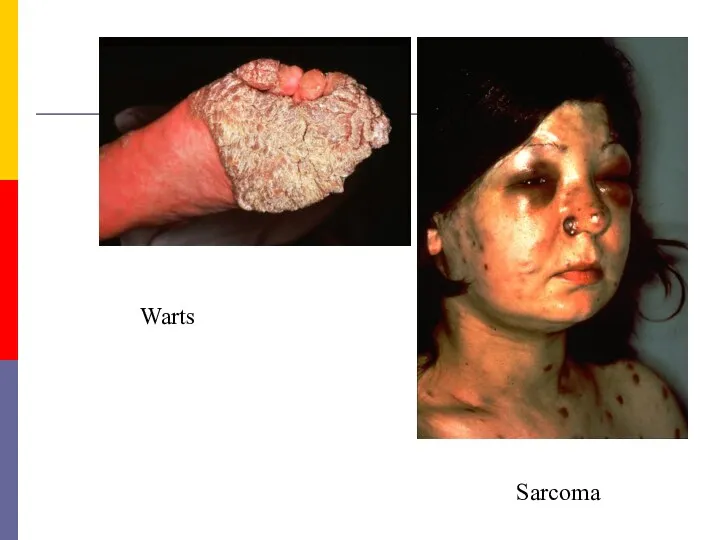
- 40. Warts Sarcoma
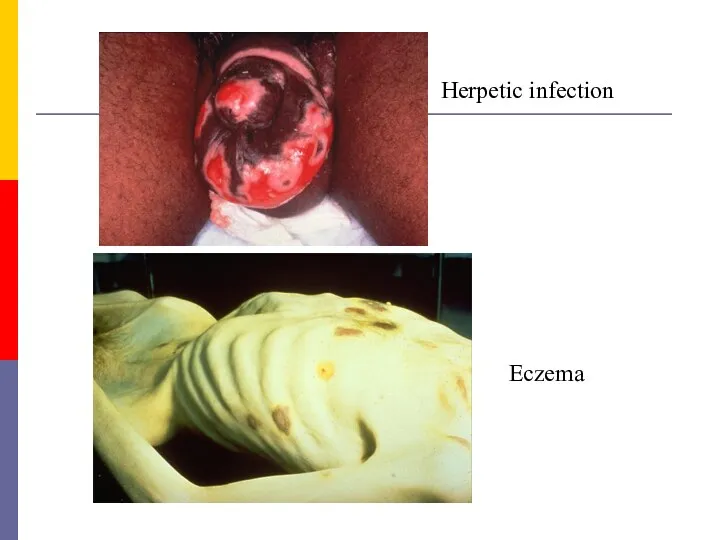
- 41. Herpetic infection Еczema
- 43. Dementia. HIV may cause direct cytopathogenic damage in tire central nervous system. It can cross the
- 44. There are many differences between adult and pediatric AIDS. Children develop humora1 immunodeficiency early, leading to
- 45. Laboratory diagnosis Laboratory procedures for the diagnosis of HIV infection include tests for immunodificiency as well
- 46. B. Specific tests for HIV infection. These inc1ude demonstration of HIV antigens and antibodies and isolation
- 47. If the infecting dose is small, as following a needlestick injury, the process may be considerably
- 48. 2. Virus isolation. Once infected with HIV, a person remains infected for life. The virus is
- 49. 3. Antibody detection. Demonstration of antibodies is the simplest and most widely employed technique for the
- 50. Once antibodies appear they increase in titre and broaden in spectrum for the next several months.
- 51. Screening tests possess high sensitivity, have a broadly reactive spectrum, are simple to perform and can
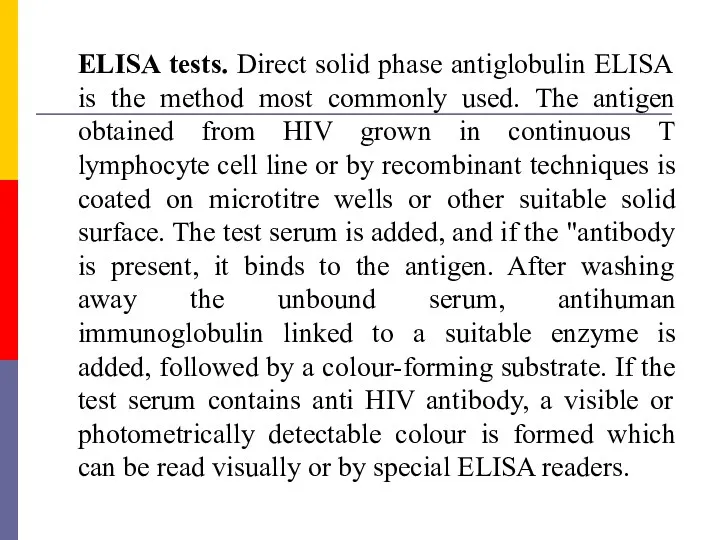
- 52. ELISA tests. Direct solid phase antiglobulin ELISA is the method most commonly used. The antigen obtained
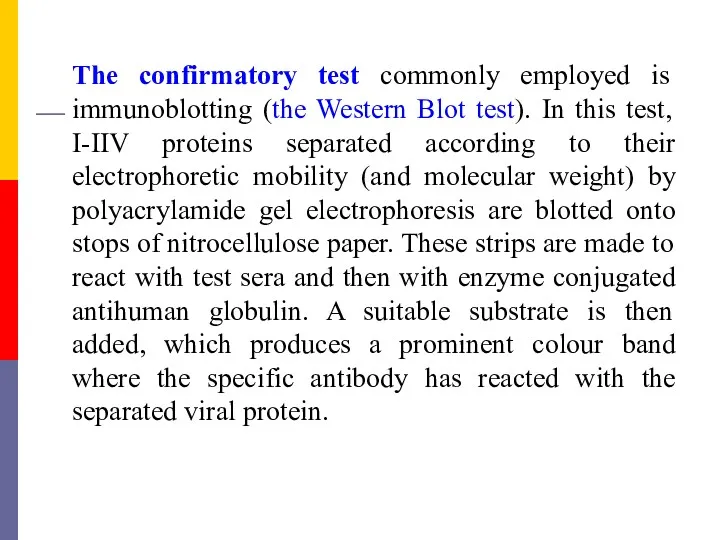
- 53. The confirmatory test commonly employed is immunoblotting (the Western Blot test). In this test, I-IIV proteins
- 54. The confirmatory test In a positive serum, bands will be seen with multiple proteins, typically with
- 55. Applications of serological tests. Serological tests for HIV infection are employed in the following situations. A
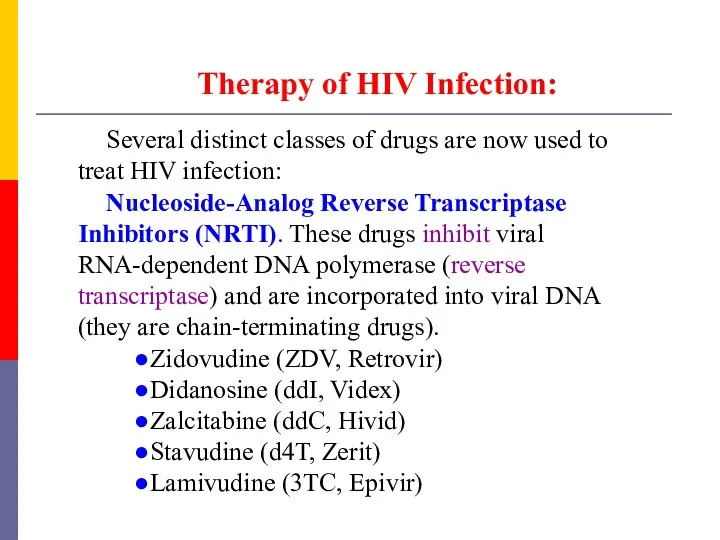
- 56. Therapy of HIV Infection: Several distinct classes of drugs are now used to treat HIV infection:
- 57. Therapy of HIV Infection: Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NNRTIs). In contrast to NRTIs, NNRTIs are not
- 58. Therapy of HIV Infection: Protease Inhibitors. These drugs are specific for the HIV-1 protease and competitively
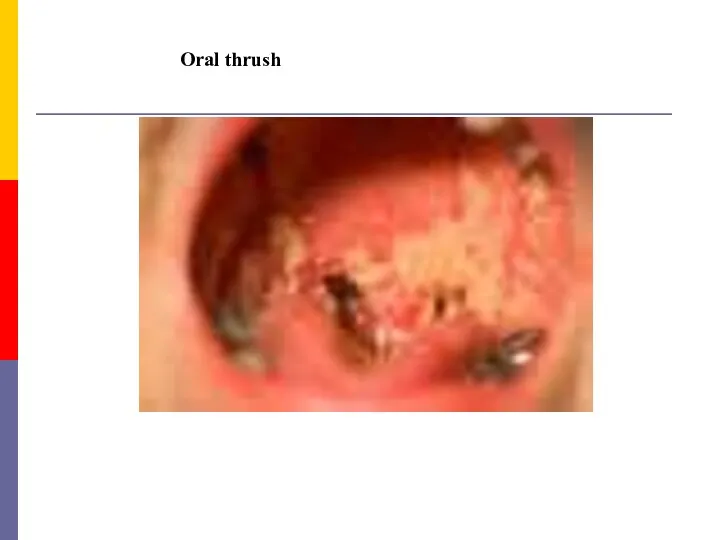
- 59. Oral thrush
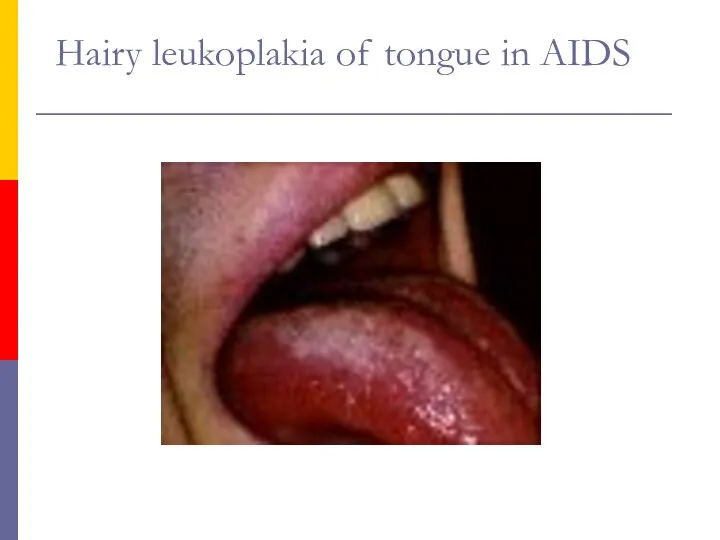
- 60. Hairy leukoplakia of tongue in AIDS
- 61. Candida and herpes simplex in AIDS
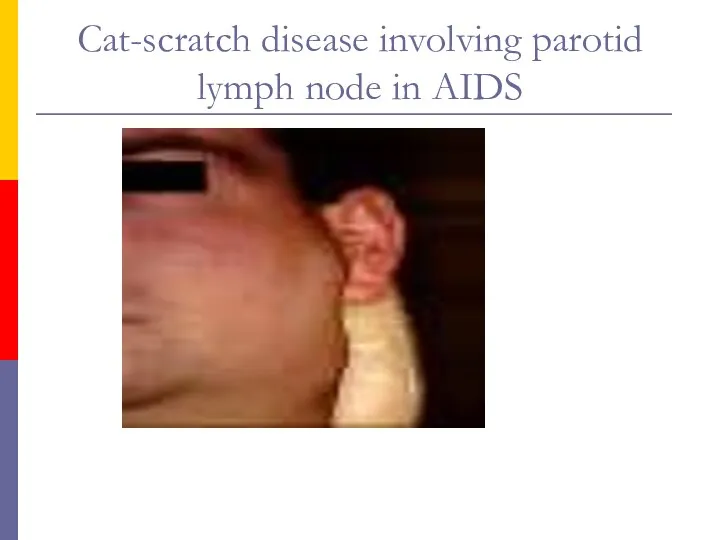
- 62. Cat-scratch disease involving parotid lymph node in AIDS
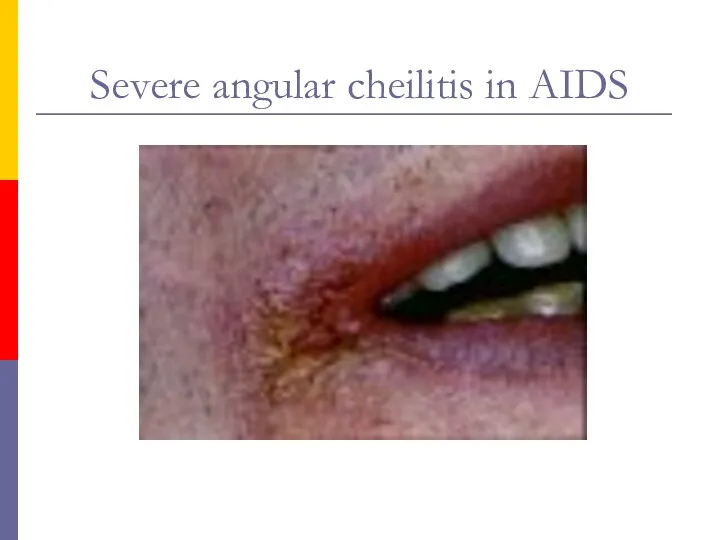
- 63. Severe angular cheilitis in AIDS
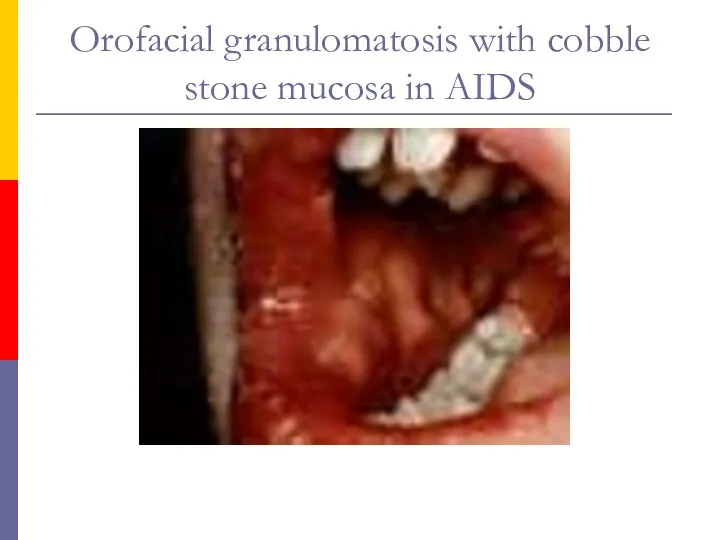
- 64. Orofacial granulomatosis with cobble stone mucosa in AIDS
- 65. Facial sarcoidosis in AIDS
- 68. Скачать презентацию




































 АФО нервной системы и органов чувств ребенка. НПР детей раннего детского возраста
АФО нервной системы и органов чувств ребенка. НПР детей раннего детского возраста Развитие медицины в Древнем Египте
Развитие медицины в Древнем Египте Pelvic аnatomy
Pelvic аnatomy Лимфомы. Лимфогранулематоз
Лимфомы. Лимфогранулематоз Нарушение сна и бодрствования
Нарушение сна и бодрствования Профилактика туберкулеза. Диспансерное наблюдение, группы учета. Вакцинация БЦЖ и ее осложнения
Профилактика туберкулеза. Диспансерное наблюдение, группы учета. Вакцинация БЦЖ и ее осложнения Гиперкинезы. Некоторые виды гиперкинезов
Гиперкинезы. Некоторые виды гиперкинезов История развития сестринского дела
История развития сестринского дела Микроорганизмы, возбудители антропозоонозных инфекций
Микроорганизмы, возбудители антропозоонозных инфекций Понятия о ВИЧ-инфекции и СПИДе
Понятия о ВИЧ-инфекции и СПИДе Анемиялар
Анемиялар Паращитовидные железы
Паращитовидные железы Акупунктура. Акупунктураны медицинада қолдану. Биологиялық активті үктелер
Акупунктура. Акупунктураны медицинада қолдану. Биологиялық активті үктелер Желтушный синдром. Вирусный и токсический гепатит
Желтушный синдром. Вирусный и токсический гепатит Кариес и его профилактика
Кариес и его профилактика Клиника дифференцированных олигофрении
Клиника дифференцированных олигофрении ҚР 2016-2020 ж.арналған Денсаулық мемлекеттік бағдарламасы
ҚР 2016-2020 ж.арналған Денсаулық мемлекеттік бағдарламасы Ранняя помощь детям с ОВЗ
Ранняя помощь детям с ОВЗ Возбудители брюшного тифа и паратифов
Возбудители брюшного тифа и паратифов Патология слюнных желез
Патология слюнных желез Реабилитация пациентов при инфекционных и паразитарных заболеваниях
Реабилитация пациентов при инфекционных и паразитарных заболеваниях Трихофития
Трихофития Профессия Ветеринар
Профессия Ветеринар Угрожающее неотложное состояние у детей
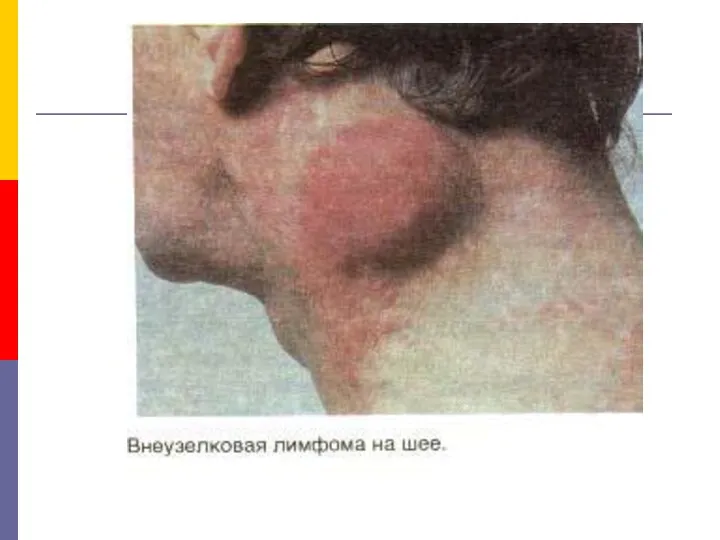
Угрожающее неотложное состояние у детей Неходжкинские лимфомы у ВИЧ-инфицированных больных
Неходжкинские лимфомы у ВИЧ-инфицированных больных Ревматоидный артрит
Ревматоидный артрит Анемиялардың патоморфологиясы
Анемиялардың патоморфологиясы Определение арт-терапии
Определение арт-терапии