Содержание
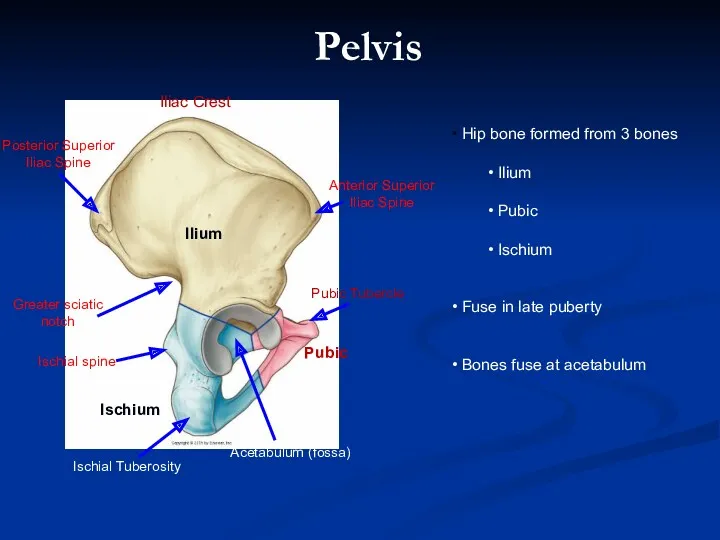
- 2. Ischium Pubic Ilium Hip bone formed from 3 bones Ilium Pubic Ischium Fuse in late puberty
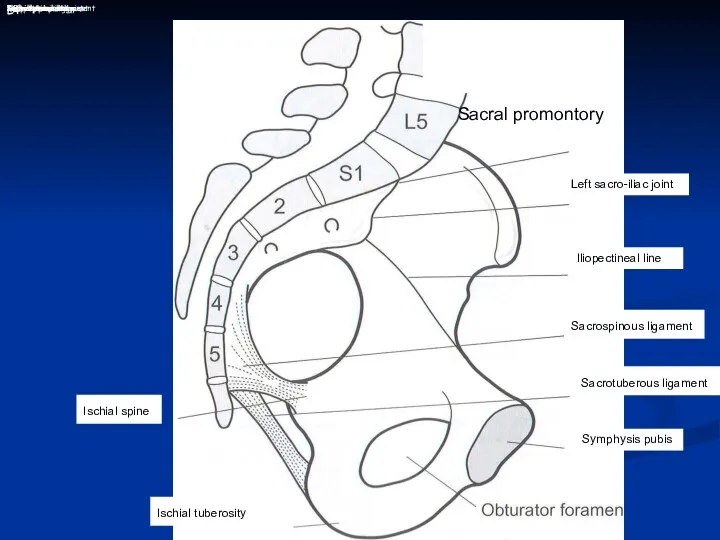
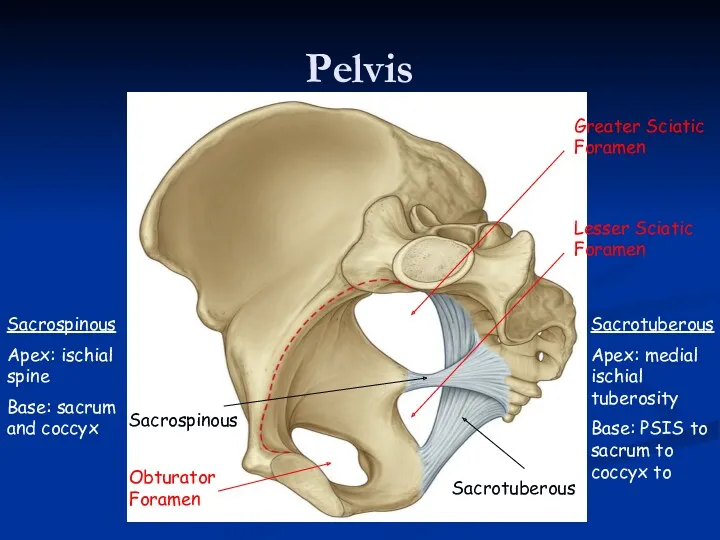
- 3. L4 Ischial spine Ischial tuberosity 48 Sacral promontory Left sacro-iliac joint Iliopectineal line Sacrospinous ligament Sacrotuberous
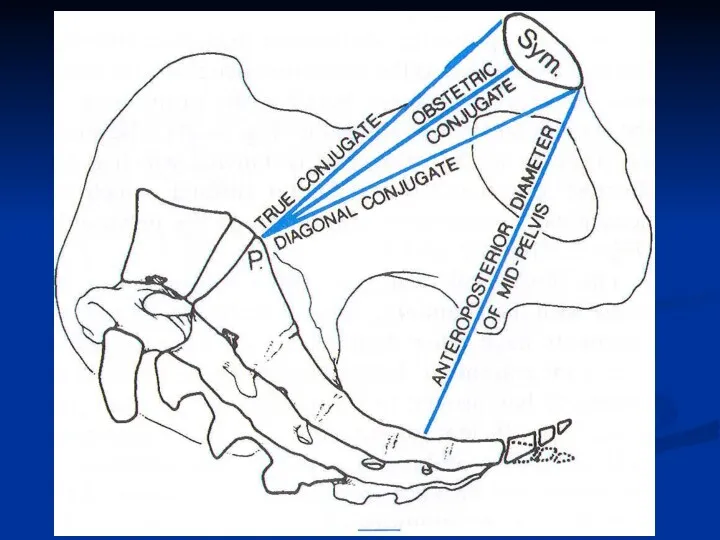
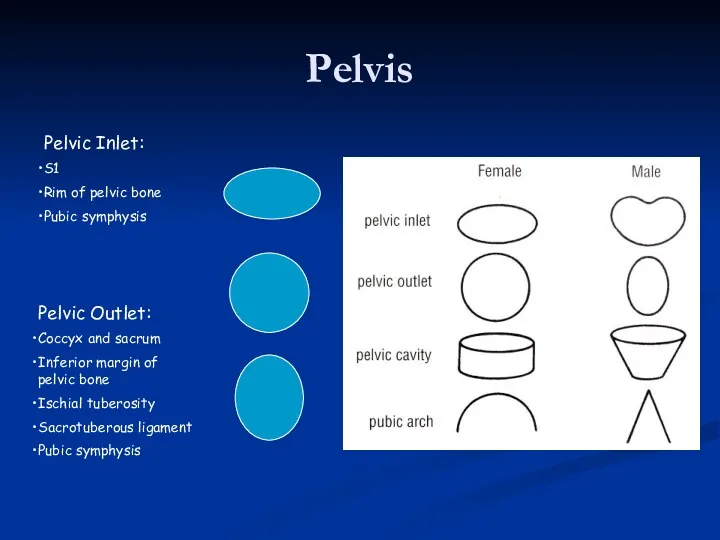
- 5. Pelvis Pelvic Inlet: S1 Rim of pelvic bone Pubic symphysis Pelvic Outlet: Coccyx and sacrum Inferior
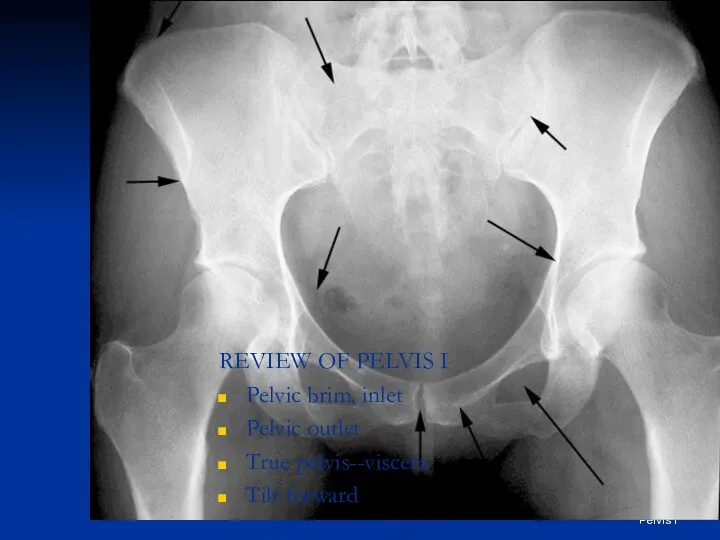
- 6. Frolich, Human Anatomy, Pelvis I REVIEW OF PELVIS I Pelvic brim, inlet Pelvic outlet True pelvis--viscera
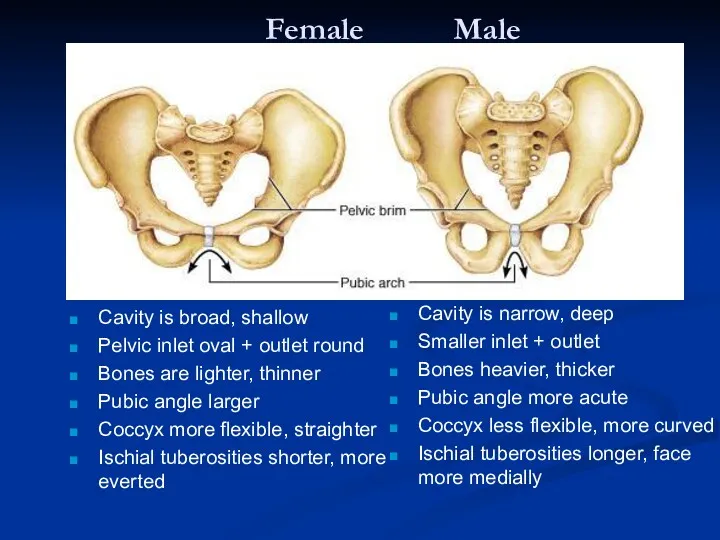
- 7. Female Male Cavity is broad, shallow Pelvic inlet oval + outlet round Bones are lighter, thinner
- 8. Pelvis Sacrospinous Sacrotuberous Sacrotuberous Apex: medial ischial tuberosity Base: PSIS to sacrum to coccyx to Sacrospinous
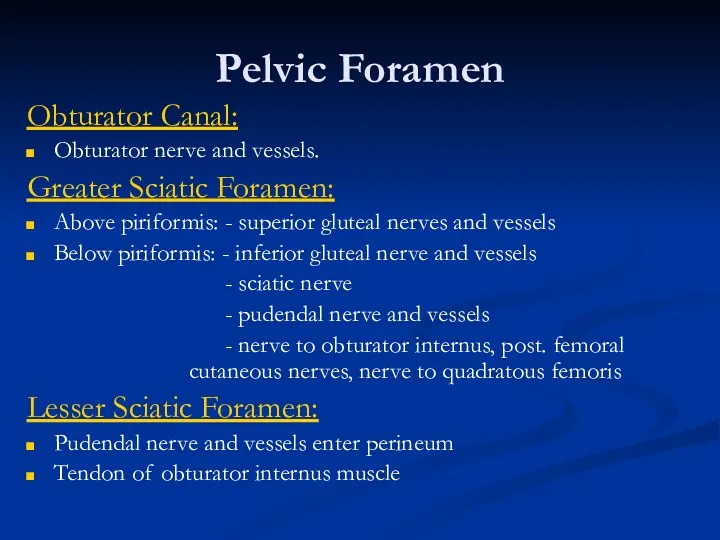
- 9. Pelvic Foramen Obturator Canal: Obturator nerve and vessels. Greater Sciatic Foramen: Above piriformis: - superior gluteal
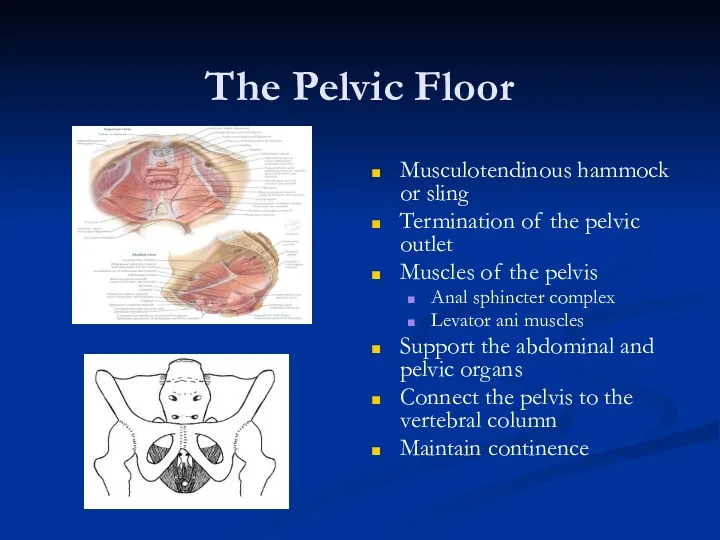
- 10. The Pelvic Floor Musculotendinous hammock or sling Termination of the pelvic outlet Muscles of the pelvis
- 11. The Function of Pelvic Floor Support pelvic and abdominal organs during stress of increased abdominal pressure
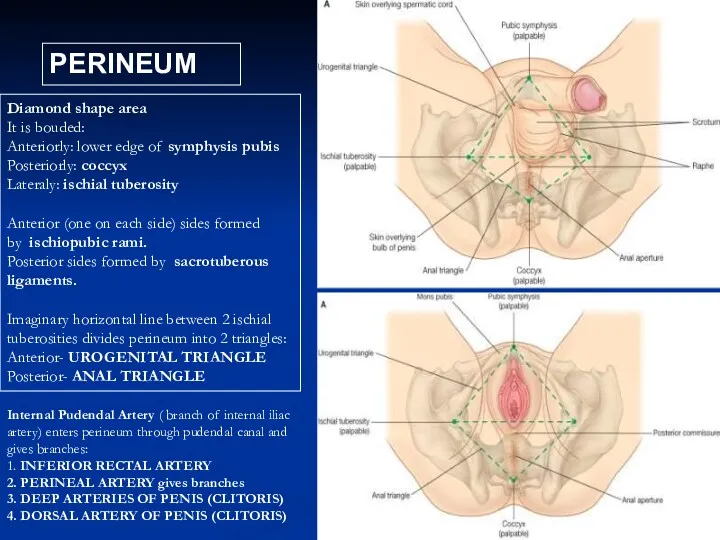
- 12. PERINEUM Diamond shape area It is bouded: Anteriorly: lower edge of symphysis pubis Posteriorly: coccyx Lateraly:
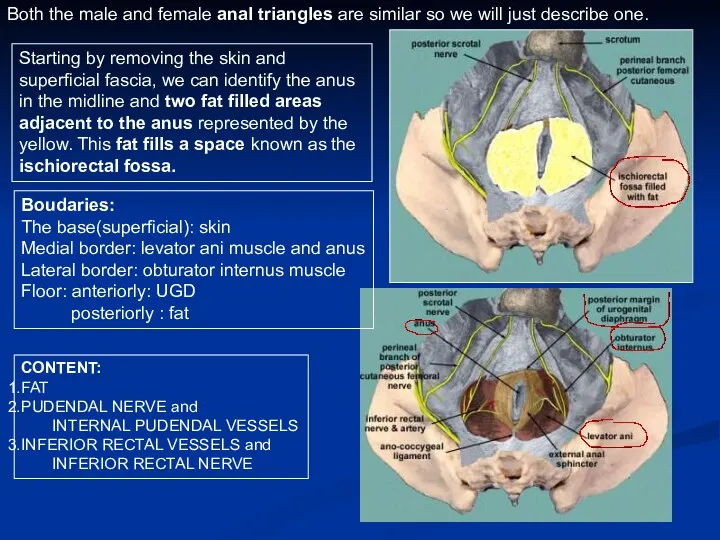
- 13. Both the male and female anal triangles are similar so we will just describe one. Starting
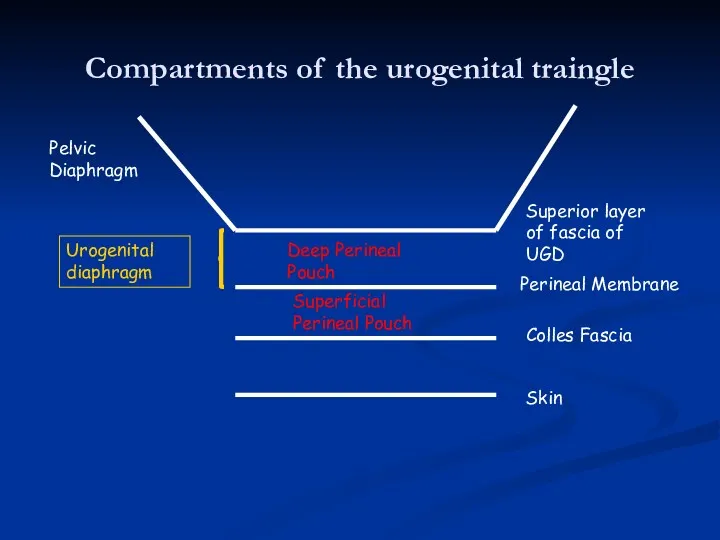
- 14. Compartments of the urogenital traingle Skin Colles Fascia Perineal Membrane Superior layer of fascia of UGD
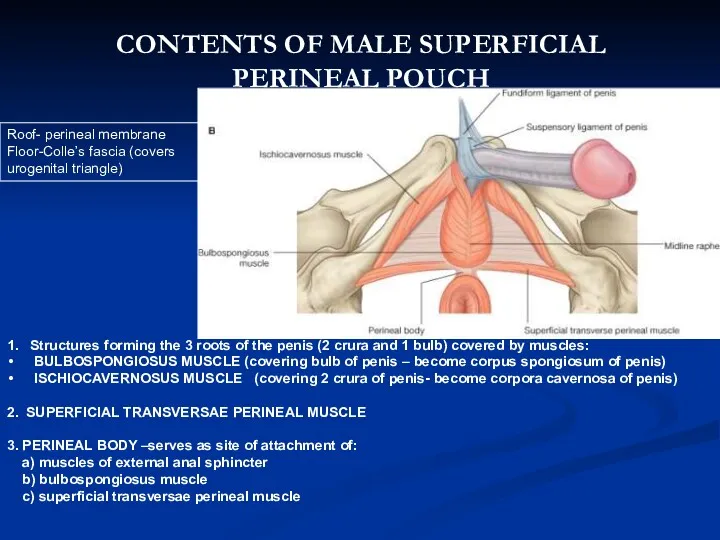
- 15. 1. Structures forming the 3 roots of the penis (2 crura and 1 bulb) covered by
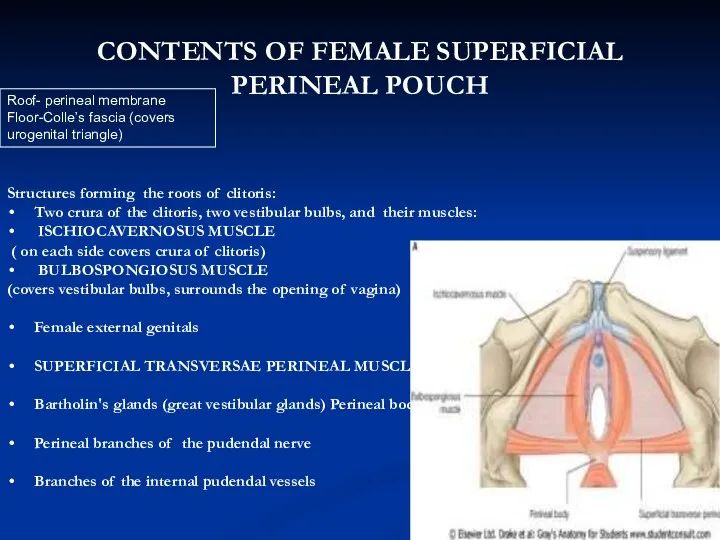
- 16. Structures forming the roots of clitoris: Two crura of the clitoris, two vestibular bulbs, and their
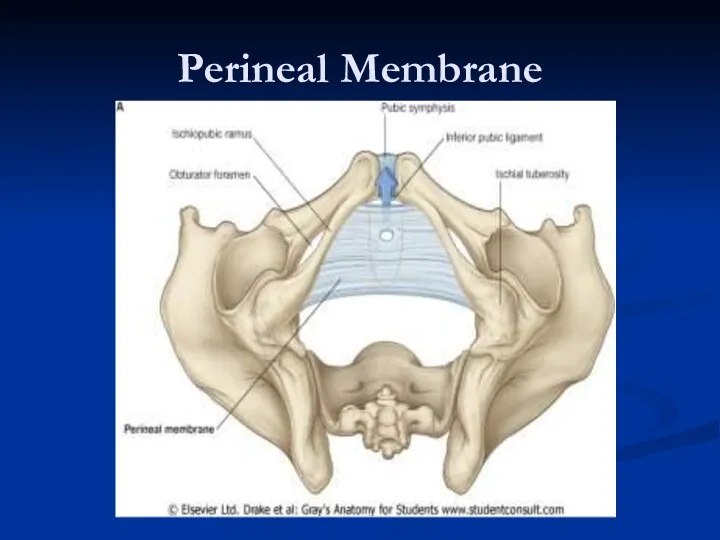
- 17. Perineal Membrane
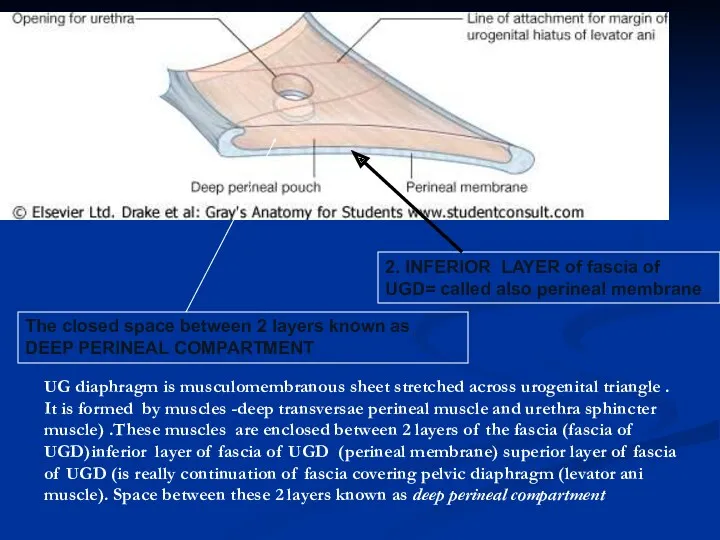
- 18. 2. INFERIOR LAYER of fascia of UGD= called also perineal membrane The closed space between 2
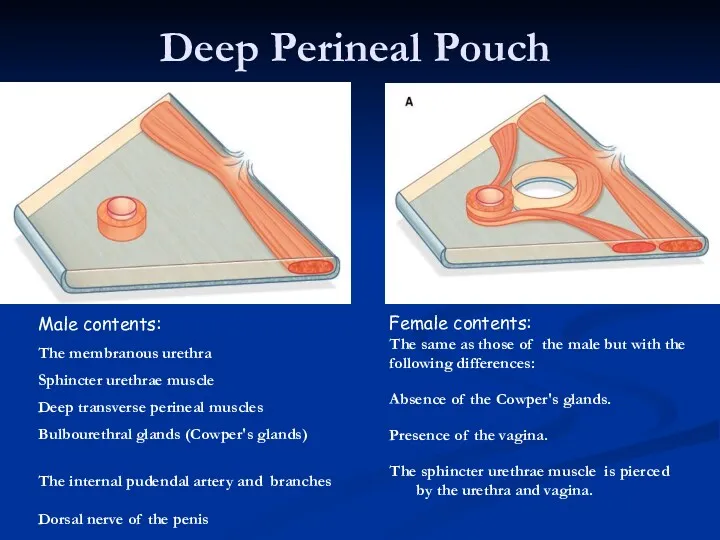
- 19. Deep Perineal Pouch Male contents: The membranous urethra Sphincter urethrae muscle Deep transverse perineal muscles Bulbourethral
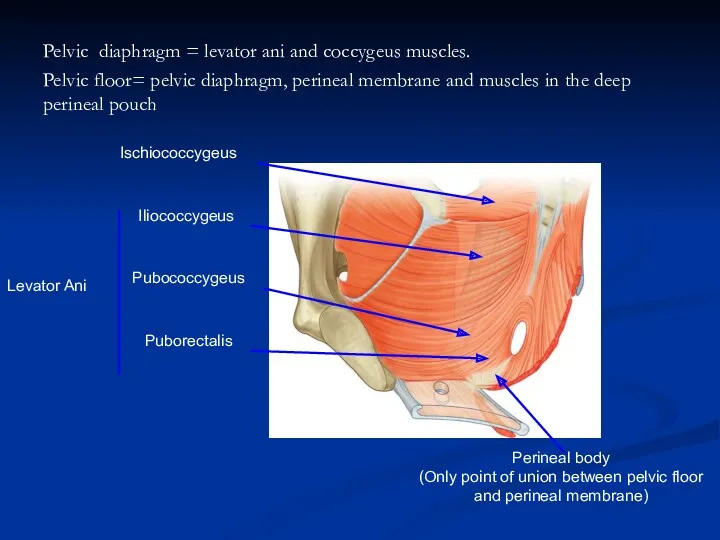
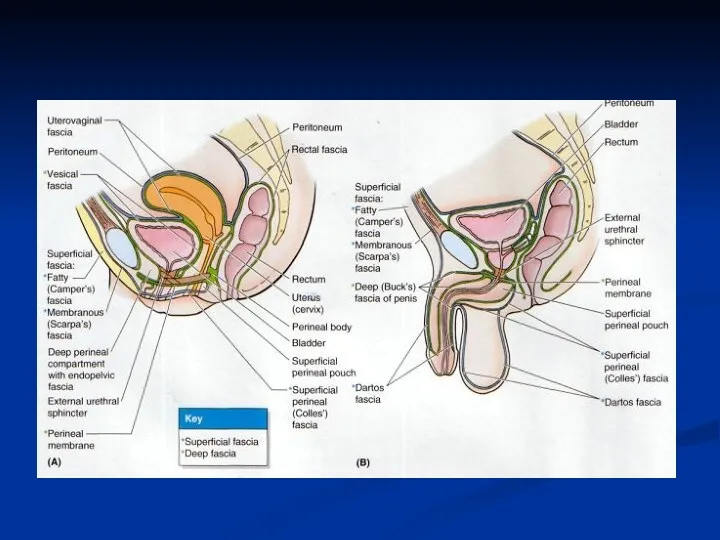
- 20. Pelvic diaphragm = levator ani and coccygeus muscles. Pelvic floor= pelvic diaphragm, perineal membrane and muscles
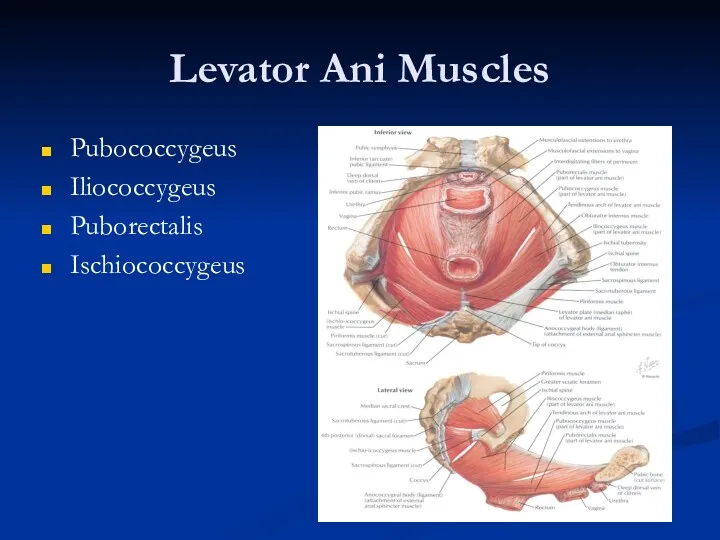
- 21. Levator Ani Muscles Pubococcygeus Iliococcygeus Puborectalis Ischiococcygeus
- 22. Puborectalis U-shaped, medial most located levator ani muscle Pulls the anorectal junction anteriorly, forming the anorectal
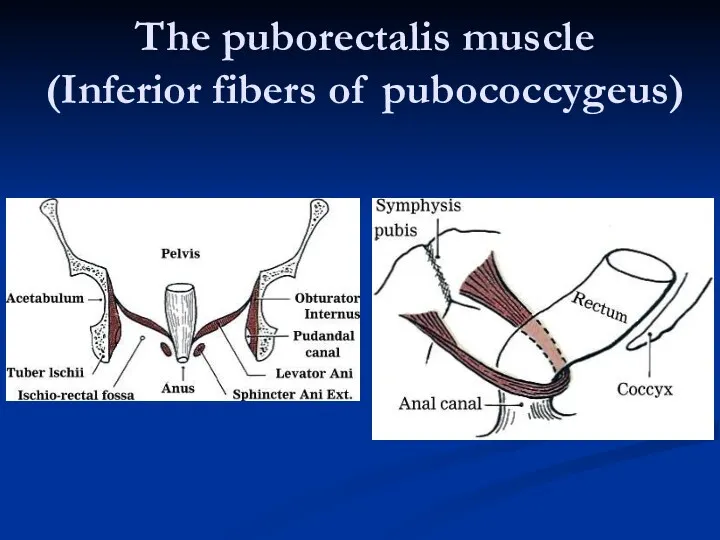
- 23. The puborectalis muscle (Inferior fibers of pubococcygeus)
- 24. Functional Anatomy Puborectalis and the anorectal angle allow for gross fecal continence Relieves pressure from the
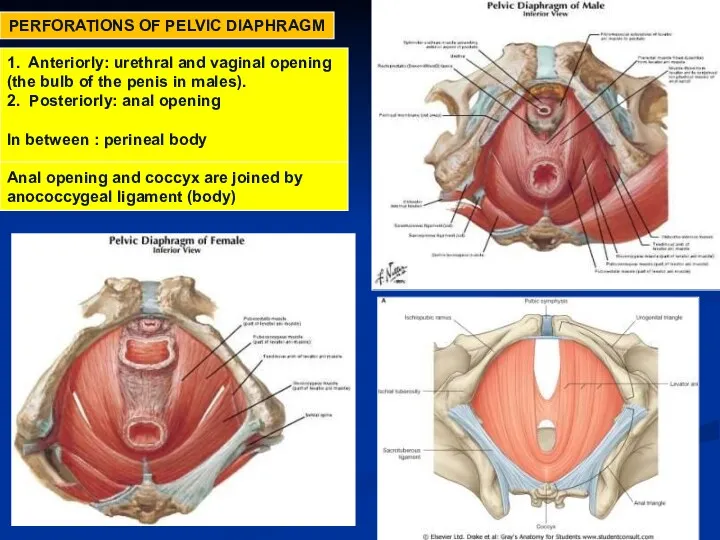
- 25. PERFORATIONS OF PELVIC DIAPHRAGM 1. Anteriorly: urethral and vaginal opening (the bulb of the penis in
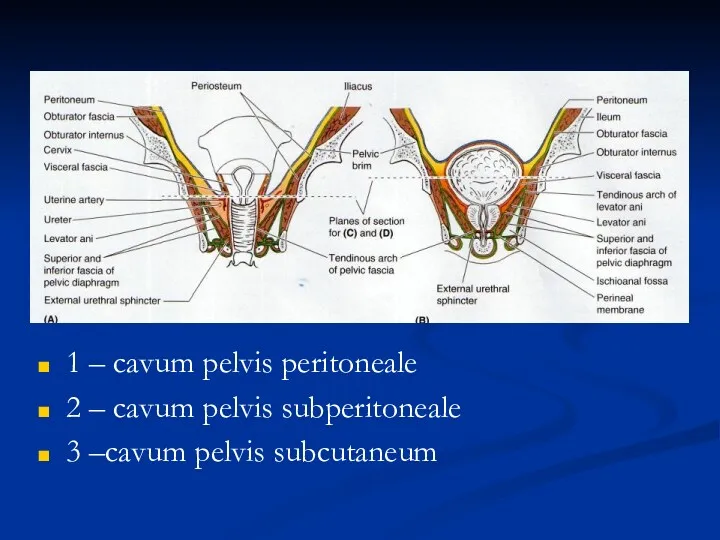
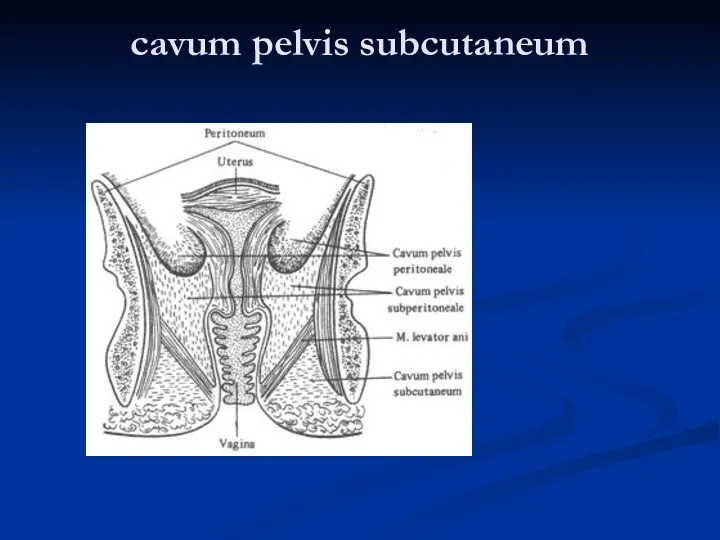
- 26. 1 – cavum pelvis peritoneale 2 – cavum pelvis subperitoneale 3 –cavum pelvis subcutaneum
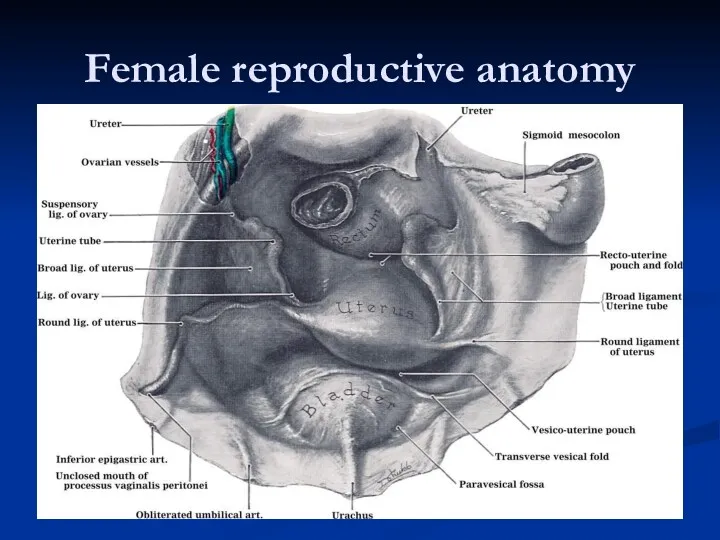
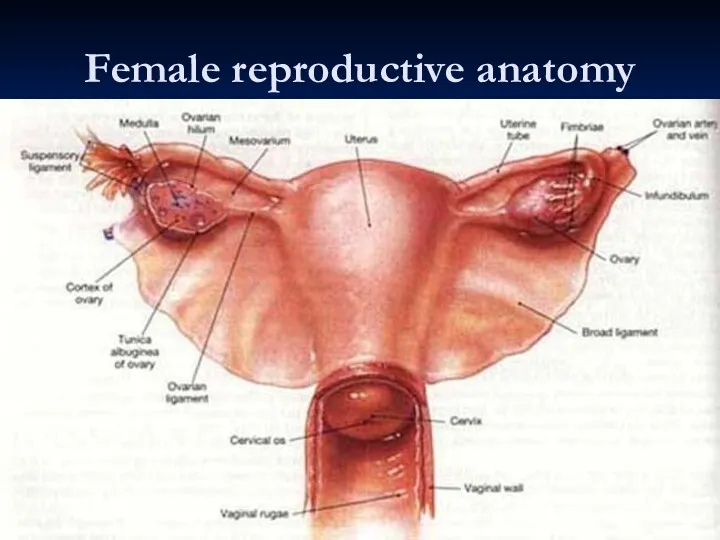
- 28. Female reproductive anatomy
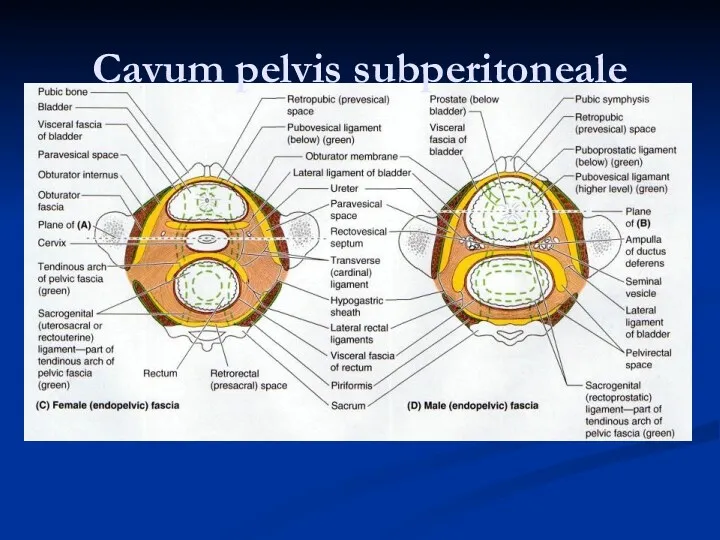
- 29. Cavum pelvis subperitoneale
- 30. cavum pelvis subcutaneum
- 31. Female reproductive anatomy
- 32. Uterine Support Uterine support thought to be by: Ligaments: - from the uterus to the pelvic
- 33. Ligaments Broad Ligament: Double fold of peritoneum extending laterally from the uterus towards the pelvic side
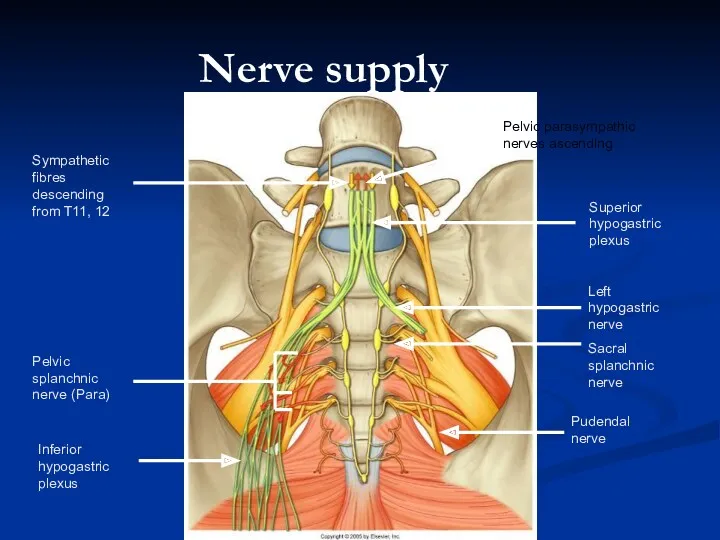
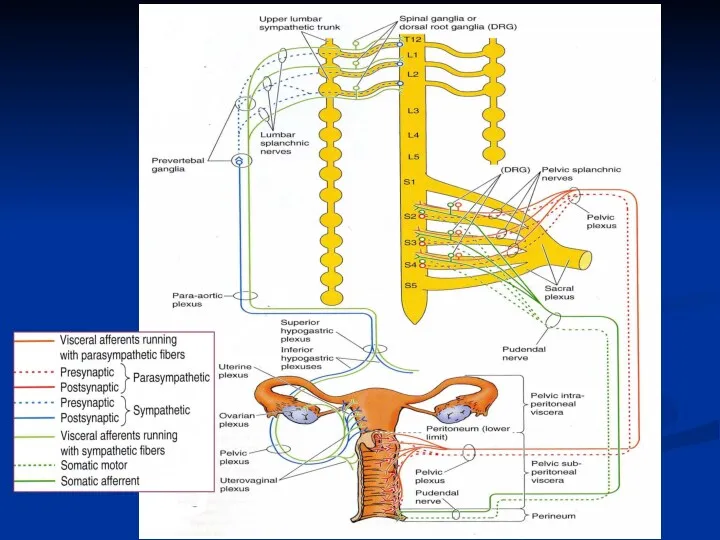
- 34. Nerve supply Pudendal nerve Left hypogastric nerve Sacral splanchnic nerve Superior hypogastric plexus Inferior hypogastric plexus
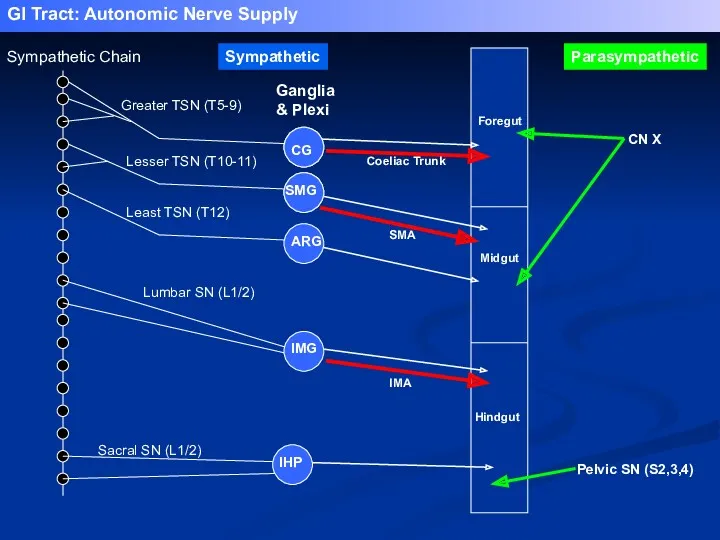
- 35. Greater TSN (T5-9) Lesser TSN (T10-11) Least TSN (T12) Lumbar SN (L1/2) Sacral SN (L1/2) Coeliac
- 37. Frolich, Human Anatomy, Pelvis I
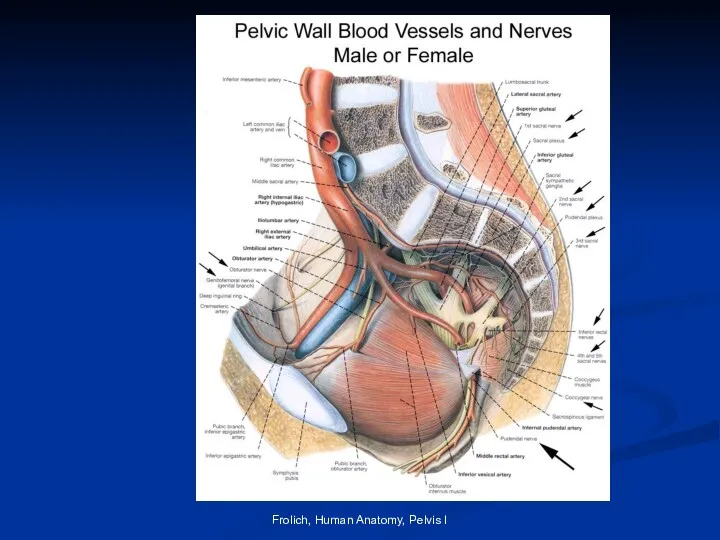
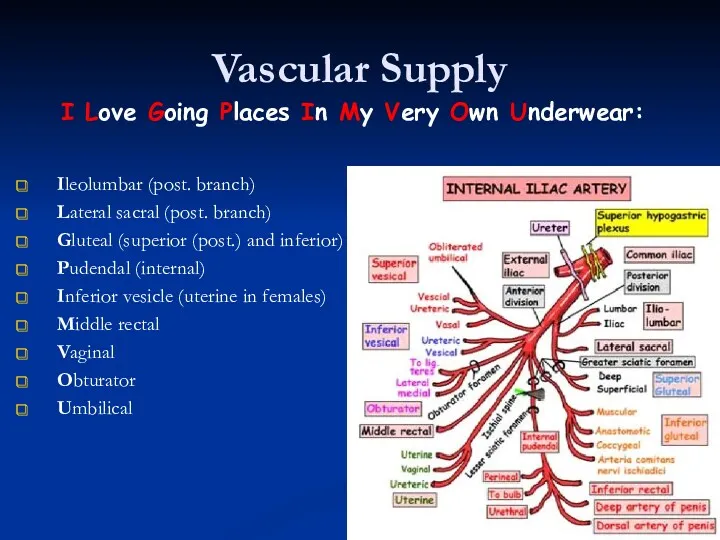
- 38. Vascular Supply Ileolumbar (post. branch) Lateral sacral (post. branch) Gluteal (superior (post.) and inferior) Pudendal (internal)
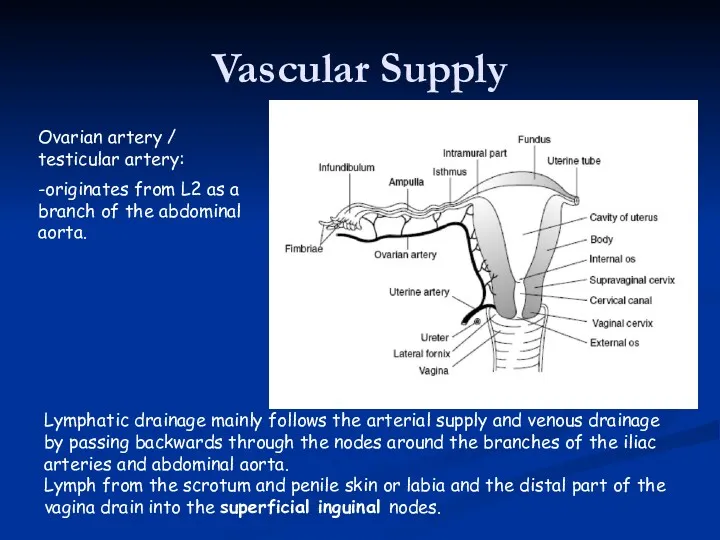
- 39. Vascular Supply Ovarian artery / testicular artery: -originates from L2 as a branch of the abdominal
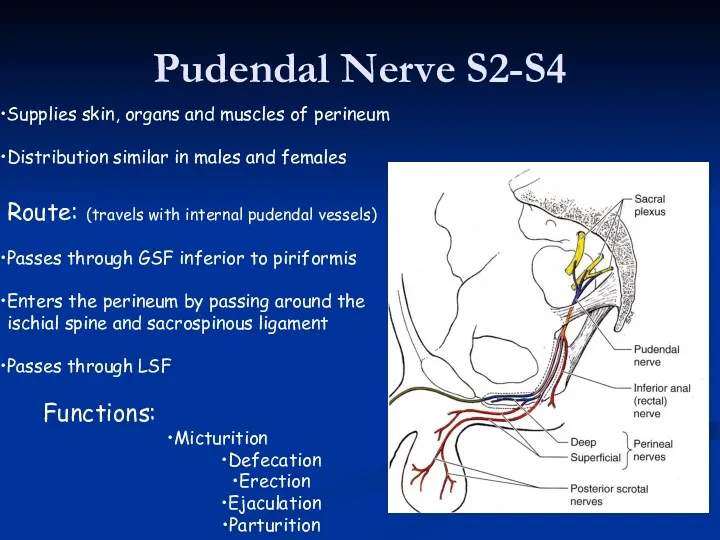
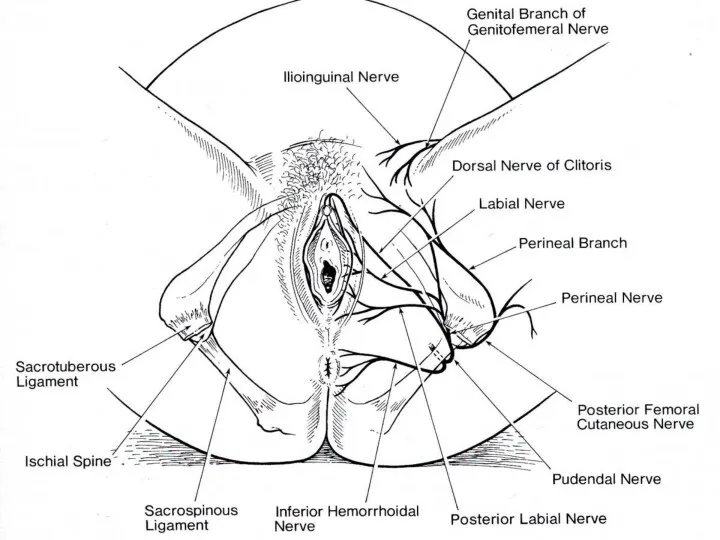
- 40. Pudendal Nerve S2-S4 Supplies skin, organs and muscles of perineum Distribution similar in males and females
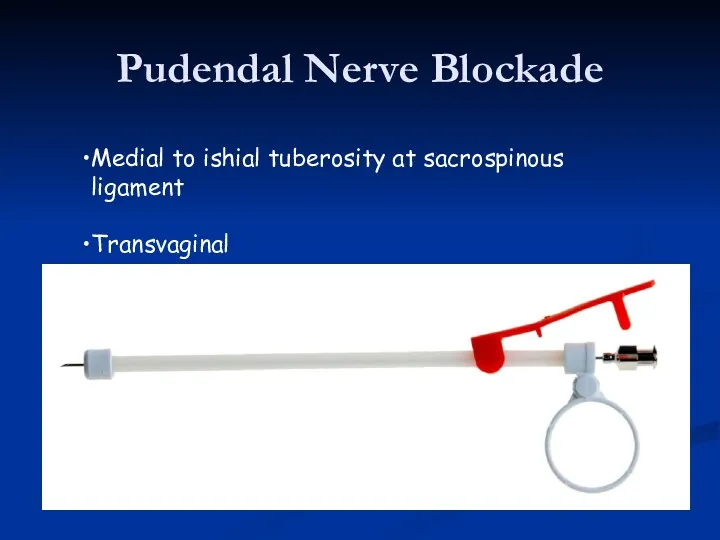
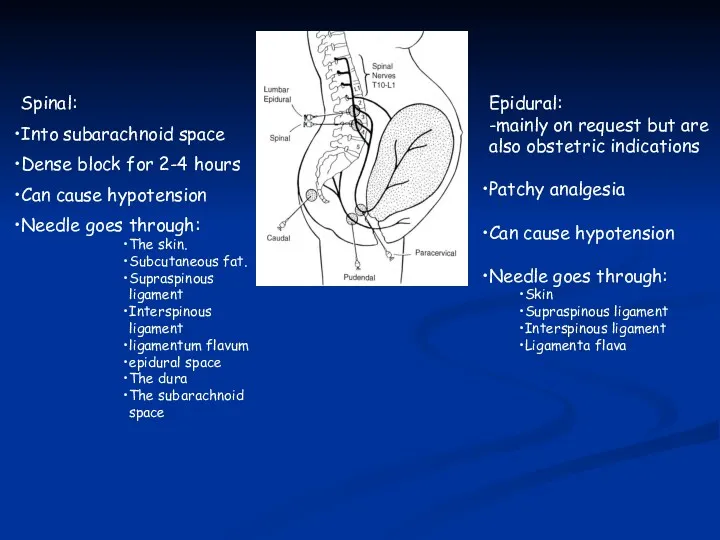
- 42. Pudendal Nerve Blockade Medial to ishial tuberosity at sacrospinous ligament Transvaginal
- 43. Spinal: Into subarachnoid space Dense block for 2-4 hours Can cause hypotension Needle goes through: The
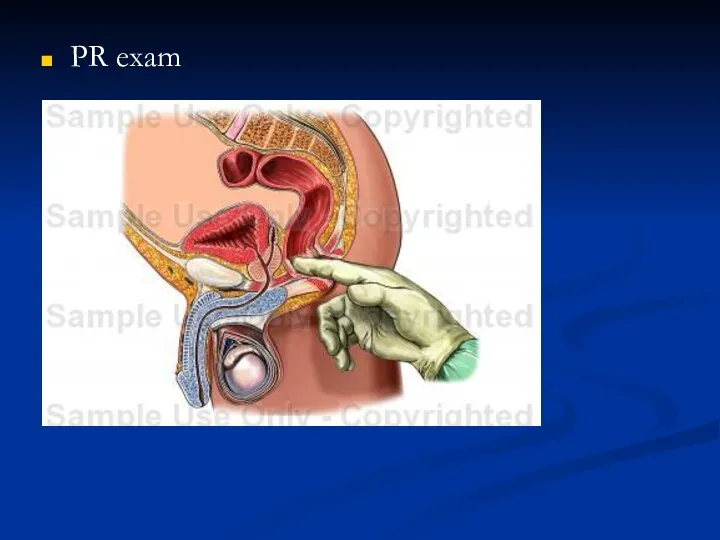
- 44. PR exam
- 46. Скачать презентацию





 Патология терморегуляции. Лекция № 8
Патология терморегуляции. Лекция № 8 Шетелдегі инклюзивті білім беру
Шетелдегі инклюзивті білім беру Планирование научного исследования в медицине
Планирование научного исследования в медицине Спинальная мышечная атрофия тип lll. Болезнь Кугельберга-Веландера
Спинальная мышечная атрофия тип lll. Болезнь Кугельберга-Веландера Prezentatsia_po_biologii_na_temu_Znachenie_pischi_i_eyo_sostav__8_klass
Prezentatsia_po_biologii_na_temu_Znachenie_pischi_i_eyo_sostav__8_klass Анемія. Етіологія і патогенез
Анемія. Етіологія і патогенез Борьба с вирусными заболеваниями (СПИД и другие)
Борьба с вирусными заболеваниями (СПИД и другие) Заманауи гепатопротекторлы заттар
Заманауи гепатопротекторлы заттар Ортопедиялық стоматология
Ортопедиялық стоматология Комплексная программа организации летнего отдыха и оздоровления детей и подростков Беломорская волна
Комплексная программа организации летнего отдыха и оздоровления детей и подростков Беломорская волна Дети с особыми образовательными потребностями
Дети с особыми образовательными потребностями Непрерывное медицинское образование. Периодическая аккредитация
Непрерывное медицинское образование. Периодическая аккредитация Гравидограмма интерпритациясы
Гравидограмма интерпритациясы Экстрагенитальная патология и беременность
Экстрагенитальная патология и беременность Фізіологічні механізми та закономірності формування рухових навичок
Фізіологічні механізми та закономірності формування рухових навичок Физиология плода. Физиология беременности
Физиология плода. Физиология беременности Асфиксии новорождённых
Асфиксии новорождённых Герпетическая инфекция
Герпетическая инфекция Риккетсии. Хламидии
Риккетсии. Хламидии Общая и специальная подготовка полости рта перед протезированием
Общая и специальная подготовка полости рта перед протезированием Босанғаннан кейінгі ерте кезеңдегі қан кетудің себептері: травма,тромбин
Босанғаннан кейінгі ерте кезеңдегі қан кетудің себептері: травма,тромбин Антибиотики и химиотерапия. Химиотерапевтические препараты
Антибиотики и химиотерапия. Химиотерапевтические препараты Первая помощь при синдроме длительного сдавления (СДС) или тяжелая компрессионная травма
Первая помощь при синдроме длительного сдавления (СДС) или тяжелая компрессионная травма Мышцы верхних и нижних конечностей человека
Мышцы верхних и нижних конечностей человека Синдром диабетической стопы
Синдром диабетической стопы Острый аппендицит. История учения об аппендиците. Анатомо-физиологические особенности
Острый аппендицит. История учения об аппендиците. Анатомо-физиологические особенности Холера
Холера Острые респираторные вирусные инфекции
Острые респираторные вирусные инфекции