Содержание
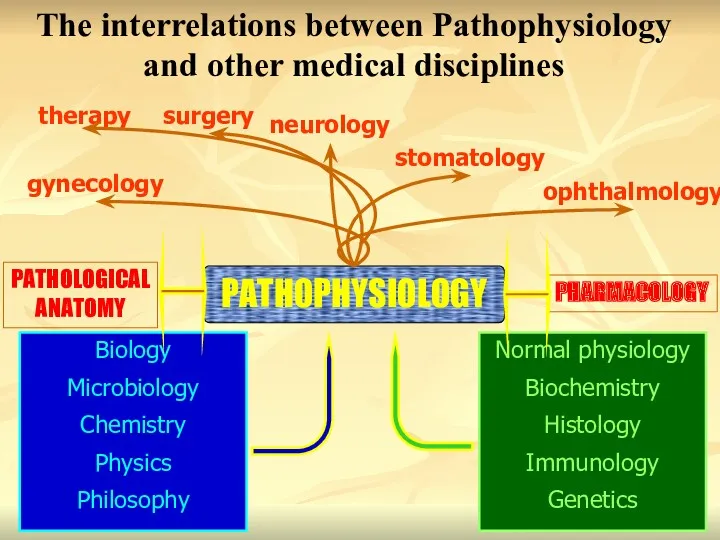
- 2. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY ophthalmology neurology surgery therapy gynecology stomatology PHARMACOLOGY PATHOLOGICAL ANATOMY Biology Microbiology Chemistry Physics Philosophy Normal
- 3. Head of Pathophysiology Department KOLESNIK Yuri Mikhailovich Rector of ZSMU, M.D., Ph.D., D.Sc., Professor, Honoured Science
- 4. Pathophysiology PATHOS – disease PHYSIS – essence LOGOS – knowledge Science studying the basic patterns of
- 5. Pathophysiology tasks Creation of the disease general conception (general nosology) Study of : reasons and conditions
- 6. Experimental therapy Working out of new methods of diseases treatment and prophylaxis Sanogenesis – mechanism of
- 7. The main methods of Pathophysiology Experimental modelling of: pathologic processes on animals; protective and adaptive reactions
- 8. Pathophysiological experiment It includes four stages: Planning the experiment; Carrying out of experiment (modelling and obtaining
- 9. The main methods of Pathophysiology Clinical examination of various diseases with different tests (clinical pathophysiology) to
- 10. Scientific work of department neuro-endocrine mechanisms of endocrine pancreas regulation the role of hypothalamic neuro-hormones in
- 11. Pathogenesis is the study of general mechanisms of diseases onset and development.
- 12. The role of etiologic factor in disease development Etiologic factor can “switch” some diseases (radiation sickness,
- 13. The main link of pathogenesis The main link of pathogenesis is that process that is absolutely
- 14. The role of local and general changes in the organism Local changes may start the disease
- 15. The role of pathogenic and adaptive reactions during disease development Pathogenesis of all the diseases and
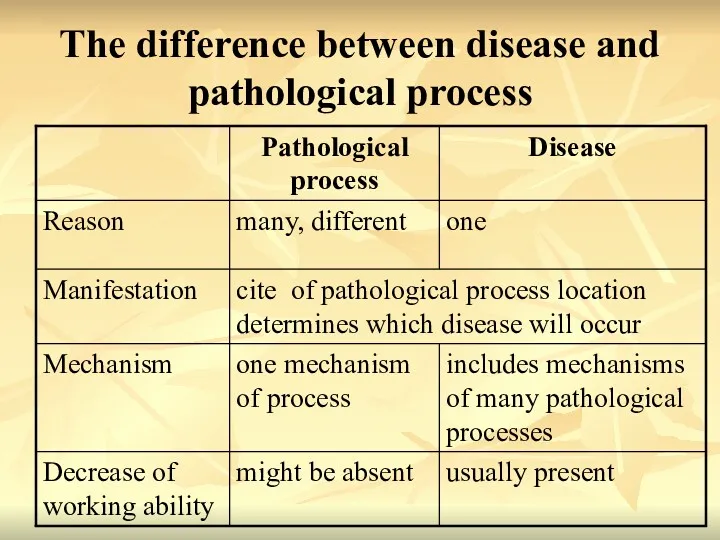
- 16. The difference between disease and pathological process
- 17. Civilization (lifestyle) diseases Positive consequences of civilization: resistance to infections, increased life duration. Negative consequences: ↑
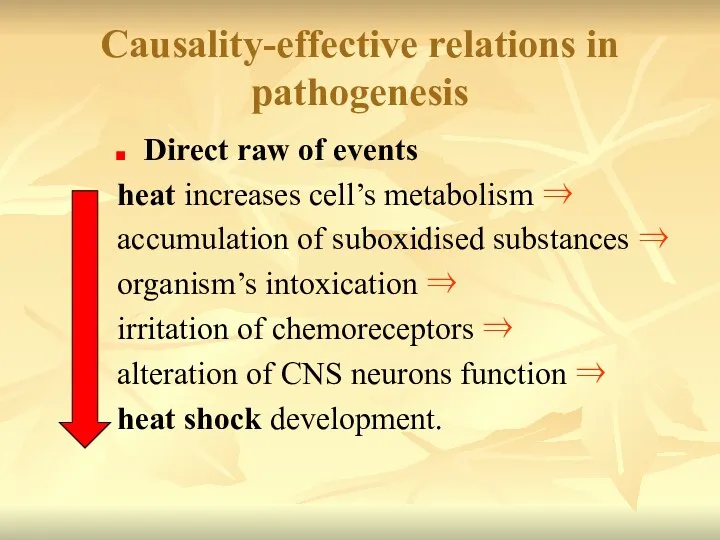
- 18. Causality-effective relations in pathogenesis Direct raw of events heat increases cell’s metabolism ⇒ accumulation of suboxidised
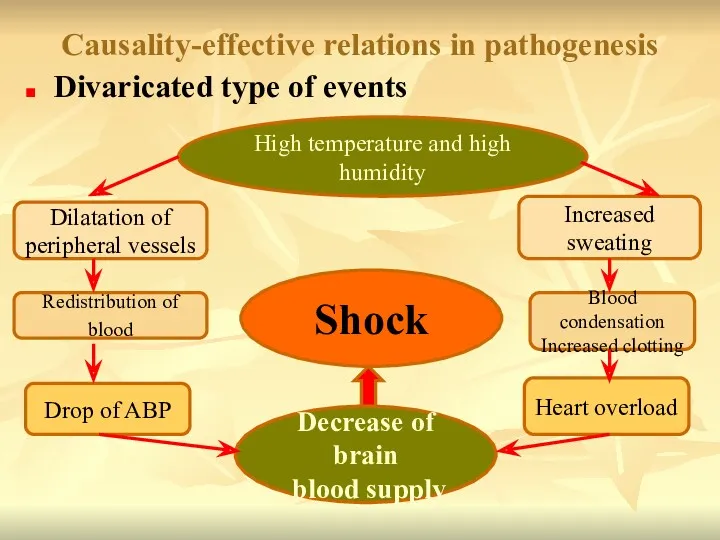
- 19. Causality-effective relations in pathogenesis Divaricated type of events Dilatation of peripheral vessels Drop of ABP Increased
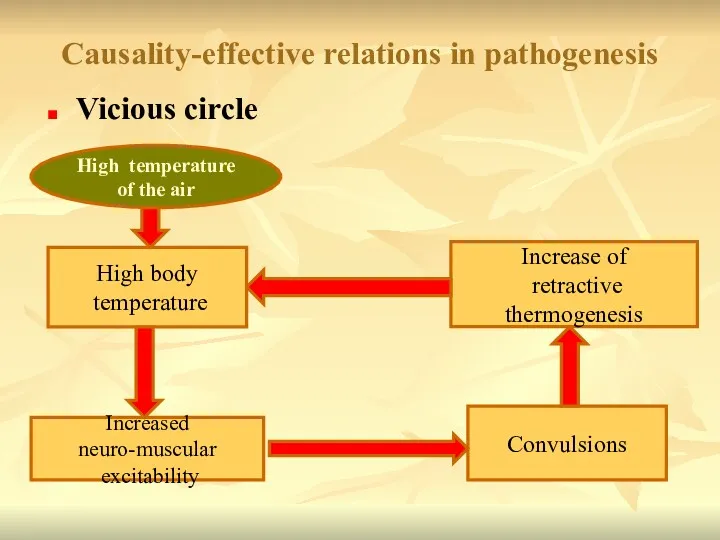
- 20. Causality-effective relations in pathogenesis Vicious circle High temperature of the air High body temperature Increased neuro-muscular
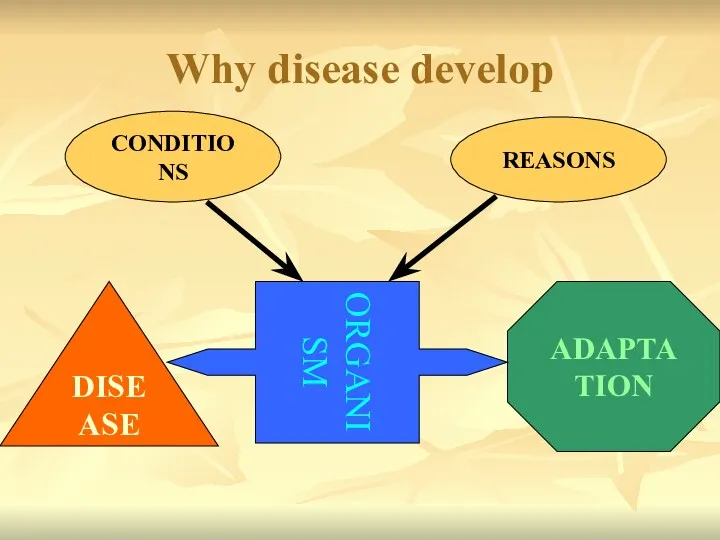
- 21. Why disease develop REASONS CONDITIONS DISEASE ADAPTATION ORGANISM
- 22. Organism responce Reactivity - ability to respond to internal and external factors. Resistance - stability of
- 23. Types of reactivity Levels: normal, increased, low, absent (anergy) Species reactivity (fish, bird, rat, dog, human)
- 24. Types of resistance Passive resistance – barrier systems, bactericidial agents, inborn immunity. Active resistance – adaptative
- 26. Скачать презентацию

















 ВІЛ-інфекція / СНІД-асоційовані інфекції та інвазії. Історія відкриття. Етіологія. Епідеміологія. Патогенез. Клінічні прояви
ВІЛ-інфекція / СНІД-асоційовані інфекції та інвазії. Історія відкриття. Етіологія. Епідеміологія. Патогенез. Клінічні прояви Медицинская физиотерапевтическая аппаратура (продолжение)
Медицинская физиотерапевтическая аппаратура (продолжение) Виды частичных съемных протезов. Способы их фиксации
Виды частичных съемных протезов. Способы их фиксации Іш сүзегі
Іш сүзегі Основы частной патологии органов дыхания
Основы частной патологии органов дыхания Трамвы живота
Трамвы живота Язвенно-некротический энтероколит - профилактика, диагностика, лечение
Язвенно-некротический энтероколит - профилактика, диагностика, лечение Гормональная контрацепция. Взвешенный выбор
Гормональная контрацепция. Взвешенный выбор Федеральное государственное бюро медико-социальной экспертизы
Федеральное государственное бюро медико-социальной экспертизы Эмоционально-неустойчивое расстройство личности
Эмоционально-неустойчивое расстройство личности Партнерские роды. Анатомия половой системы
Партнерские роды. Анатомия половой системы Эффективность лозартана по сравнению с атенололом в улучшении качества жизни мужчин и женщин в возрасте 25-40 лет
Эффективность лозартана по сравнению с атенололом в улучшении качества жизни мужчин и женщин в возрасте 25-40 лет Антибиотики. Пенициллины, цефалоспорины, карбапенемы, монобактамы, макролиды
Антибиотики. Пенициллины, цефалоспорины, карбапенемы, монобактамы, макролиды Диссеминированный туберкулез
Диссеминированный туберкулез Презентация Босанудың ІІІ кезеңін белсенді түрде жүргізу
Презентация Босанудың ІІІ кезеңін белсенді түрде жүргізу Мозговые оболочки. Церебро-спинальная жидкость и ее циркуляция. Ликвор. Люмбальная пункция
Мозговые оболочки. Церебро-спинальная жидкость и ее циркуляция. Ликвор. Люмбальная пункция Этиологические факторы обуславливающие появление деформации зубочелюстной системы
Этиологические факторы обуславливающие появление деформации зубочелюстной системы Маскированная депрессия
Маскированная депрессия Основные нейропсихологические синдромы в детском возрасте
Основные нейропсихологические синдромы в детском возрасте Pathology of pregnancy and delivery
Pathology of pregnancy and delivery Рассеянный склероз
Рассеянный склероз Травмы груди
Травмы груди Острое и хроническое воспаление поджелудочной железы
Острое и хроническое воспаление поджелудочной железы Жұлын – ми сұйықтығының айналысы
Жұлын – ми сұйықтығының айналысы Программа подготовки медицинского персонала по вопросам проведения медицинских осмотров водителей транспортных средств
Программа подготовки медицинского персонала по вопросам проведения медицинских осмотров водителей транспортных средств 1 жастан асқан балалардың тамақтануы
1 жастан асқан балалардың тамақтануы Оплодотворение. Этапы внутриутробного развития влияние патогенных факторов на эмбрион и плод
Оплодотворение. Этапы внутриутробного развития влияние патогенных факторов на эмбрион и плод Қышқыл-сілтінің тепетеңдігінің биохимиясы және клиникалық физиологиясы
Қышқыл-сілтінің тепетеңдігінің биохимиясы және клиникалық физиологиясы