Содержание
- 2. Hypertension in Pregnancy High risk factors Etiology and pathophysiology Classification Diagnosis Treatment Prevention Future Implications
- 3. High risk factors Age - younger than 18 or older than 40 years Multiple pregnancy Has
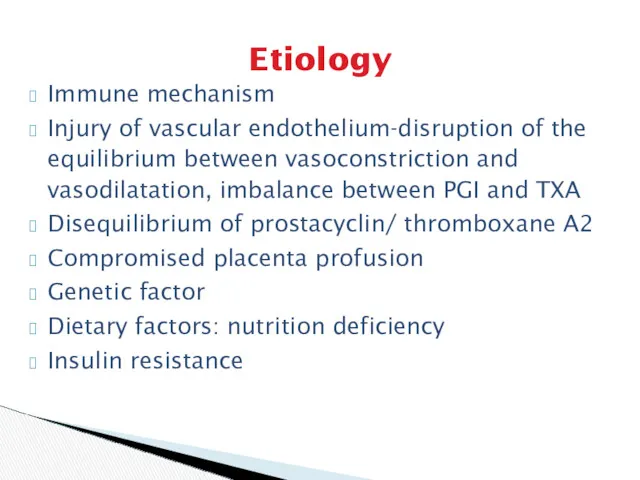
- 4. Etiology Immune mechanism Injury of vascular endothelium-disruption of the equilibrium between vasoconstriction and vasodilatation, imbalance between
- 5. Classification Chronic hypertension Gestational hypertension Preeclampsia (gestational hypertension with proteinuria) - mild preeclampsia - severe preeclampsia
- 6. О10 Хроническая артериальная гипертензия, (существовавшая ранее гипертензия, диагностированная до 20 недель беременности или сохраняющаяся через 6
- 7. Diagnosis: Hypertension Mild hypertension (either): SBP > 140 DBP > 90 Severe hypertension (either): SBP >
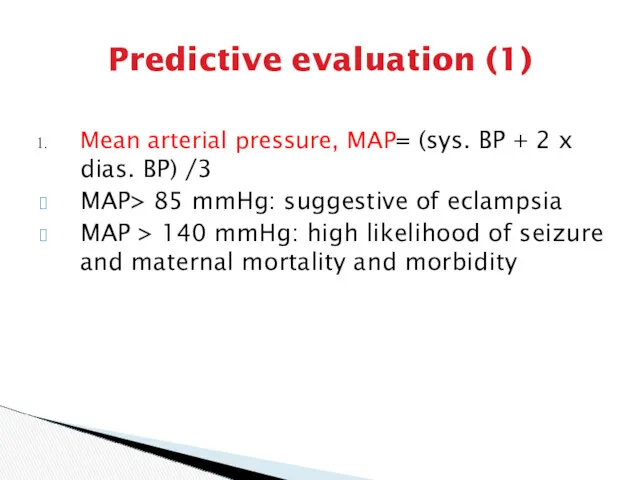
- 8. Predictive evaluation (1) Mean arterial pressure, MAP= (sys. BP + 2 x dias. BP) /3 MAP>
- 9. Classification Chronic hypertension proceeding pregnancy (essential or secondary to renal disease, endocrine disease or other causes)
- 10. Classification Gestational hypertension Presents after 20 week gestation Persists before 6 week postpartum BP ≥ 140/90
- 11. Mild preeclampsia – mild hypertension with proteinuria ±edema Легкая преэклампсия – легкая гипертензия в сочетании с
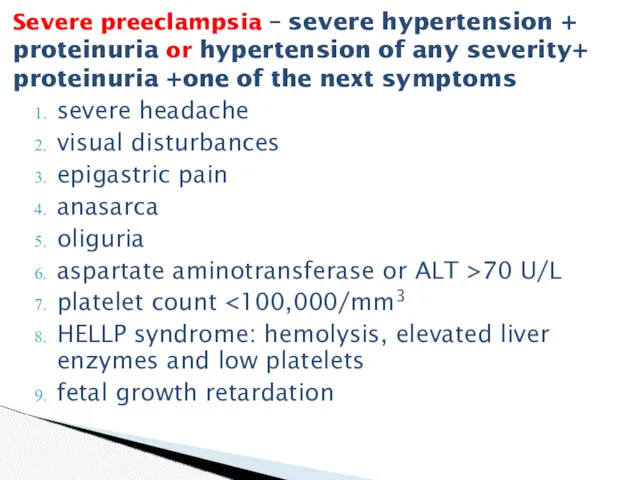
- 12. severe headache visual disturbances epigastric pain anasarca oliguria aspartate aminotransferase or ALT >70 U/L platelet count
- 13. сильная головная боль нарушение зрения боль в эпигастральной области и/или тошнота, рвота судорожная готовность генерализованные отёки
- 14. Blood (1) Volume: reduced plasma volume Normal physiologic volume expansion does not occur Generalized vasoconstriction and
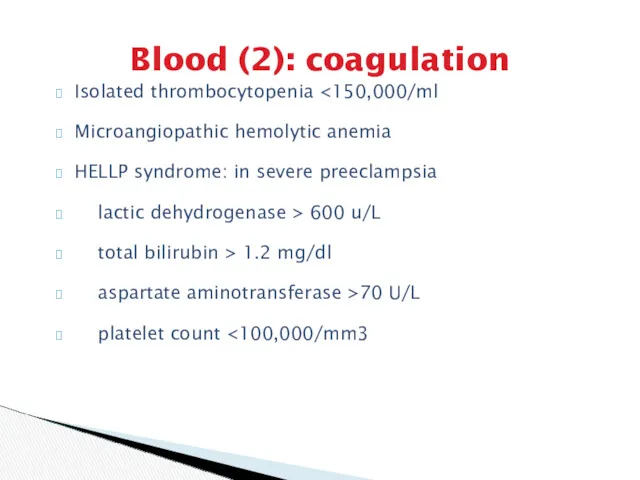
- 15. Blood (2): coagulation Isolated thrombocytopenia Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia HELLP syndrome: in severe preeclampsia lactic dehydrogenase >
- 16. Endocrine system Vascular sensitivity to catecholamines and other endogenous vasopressors such as antidiuretic hormone and angiotensin
- 17. Clinical findings (1) Symptoms and signs Hypertension Diastolic pressure ≥ 90 mmHg or Systolic pressure ≥
- 18. Clinical findings (2) Edema Weight gain: 1-2 lb/wk or 5 lb/wk is considered worrisome Degree of
- 19. Clinical findings (3) Differing clinical picture in preeclampsia-eclampsia crises: patient may present with Eclamptic seizures Liver
- 20. Clinical findings (4) Laboratory findings (1) Blood test: elevated Hb or HCT, in severe cases, anemia
- 21. Clinical findings (5) Laboratory findings (2) Retinal check Other tests: placenta function (ultrasound, kardiotokography, doppler), fetal
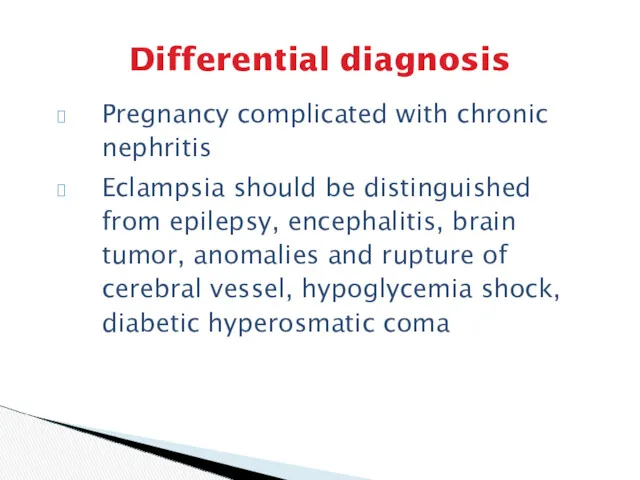
- 22. Differential diagnosis Pregnancy complicated with chronic nephritis Eclampsia should be distinguished from epilepsy, encephalitis, brain tumor,
- 23. Complications Preterm delivery Fetal risks: acute and chronic uteroplacental insufficiency Intrapartum fetal distress or stillbirth Oligohydramnios
- 24. Prevention Calcium supplementation: 1 g/24-hr effective in high risk group, not effective in low risk women
- 25. Treatment Mild preeclampsia Hospitalization or home regimen Bed rest (position and why) and daily weighing Blood
- 26. Severe preeclampsia Prevention of convulsion: magnesium sulfate or diazepam Control of maternal blood pressure: antihypertensive therapy
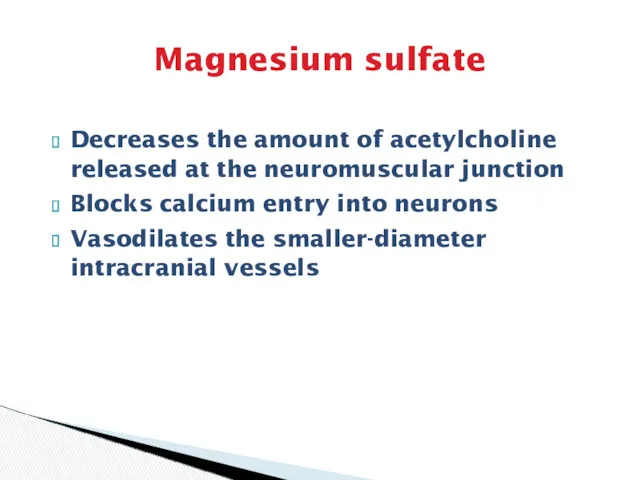
- 27. Magnesium sulfate Decreases the amount of acetylcholine released at the neuromuscular junction Blocks calcium entry into
- 28. Magnesium sulfate i.v. or i.m. Starting dose - 5g dry matter (20 ml 25% ) during
- 29. Toxicity Diminished or loss of patellar reflex Diminished respiration Muscle paralysis Blurred speech Cardiac arrest
- 30. Reversal of toxicity: Slow i.v. 10% 10,0 ml calcium gluconate Oxygen supplementation Cardiorespiratory support
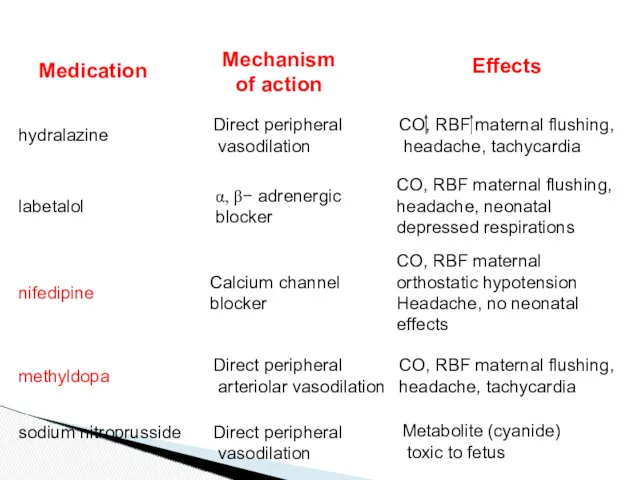
- 31. Antihypertensive therapy Medications: Hydrolazine: initial choice Labetolol Nifedipine Nimoldipine Methyldopa Sodium nitroprusside
- 32. Medication Mechanism of action Effects hydralazine Direct peripheral vasodilation CO, RBF maternal flushing, headache, tachycardia labetalol
- 33. Delivery Induction of labor Immature cervix ( Mature cervix (>6 points on the scale Bishop) –
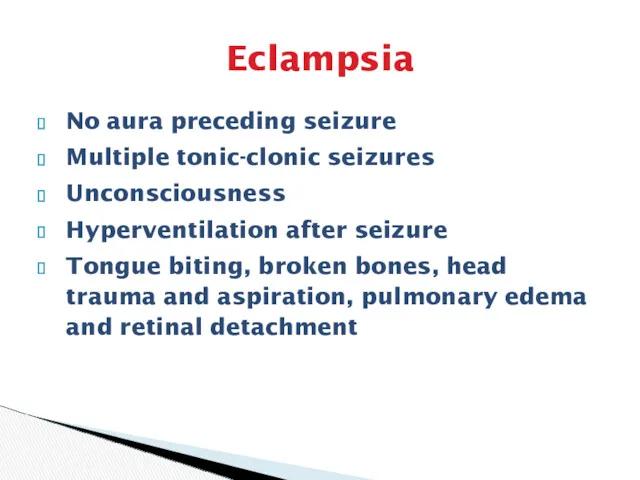
- 34. Eclampsia No aura preceding seizure Multiple tonic-clonic seizures Unconsciousness Hyperventilation after seizure Tongue biting, broken bones,
- 35. Delivery Control of seizure Control of hypertension: magnesium sulfate, diazepam, antihypertensive therapy Delivery during 12 hours
- 37. Скачать презентацию


























 Коклюш. Капельные инфекции
Коклюш. Капельные инфекции Холестаз при беременности
Холестаз при беременности Отравление наркотическими аналгетиками
Отравление наркотическими аналгетиками Проблема бессонницы с позиций традиционной китайской медицины
Проблема бессонницы с позиций традиционной китайской медицины Вирусты гепатиттер. Гепатит А
Вирусты гепатиттер. Гепатит А Наиболее распространенные варианты остеохондропатий
Наиболее распространенные варианты остеохондропатий Хроническое воспаление. Гранулематозное и специфическое воспаление
Хроническое воспаление. Гранулематозное и специфическое воспаление Arenaviruses: unique virology. Diseases of the Old World and New World
Arenaviruses: unique virology. Diseases of the Old World and New World Особо опасные инфекции
Особо опасные инфекции Переломы нижней челюсти
Переломы нижней челюсти Патологические переломы
Патологические переломы Фармакокинетика и фармакодинамика
Фармакокинетика и фармакодинамика Моя специальность – врач
Моя специальность – врач Презентация ГУ8Т 2 З 1ВМП
Презентация ГУ8Т 2 З 1ВМП Болезнь Лайма
Болезнь Лайма Движения и их расстройство
Движения и их расстройство Возможности эффективного лечения больных с печеночной энцефалопатией
Возможности эффективного лечения больных с печеночной энцефалопатией Порядок аккредитации среднего медицинского персонала
Порядок аккредитации среднего медицинского персонала Сведения о деятельности службы медицины катастроф за 2017 год
Сведения о деятельности службы медицины катастроф за 2017 год Противоязвенные лекарственные средства
Противоязвенные лекарственные средства Кишечные инфекции. Эшерихиозы
Кишечные инфекции. Эшерихиозы Своды стопы. Плоскостопие
Своды стопы. Плоскостопие Анемии преждевременно рожденных детей
Анемии преждевременно рожденных детей Молекулярные аспекты нейропротекции
Молекулярные аспекты нейропротекции Регуляция и функции репродуктивной системы
Регуляция и функции репродуктивной системы Судебно-медицинская токсикология. Повреждения от действия отравляющих веществ
Судебно-медицинская токсикология. Повреждения от действия отравляющих веществ Haemophilia
Haemophilia Фармацевтикалық қызметті ұйымдастыру бойынша өндірістік тәжірибе
Фармацевтикалық қызметті ұйымдастыру бойынша өндірістік тәжірибе