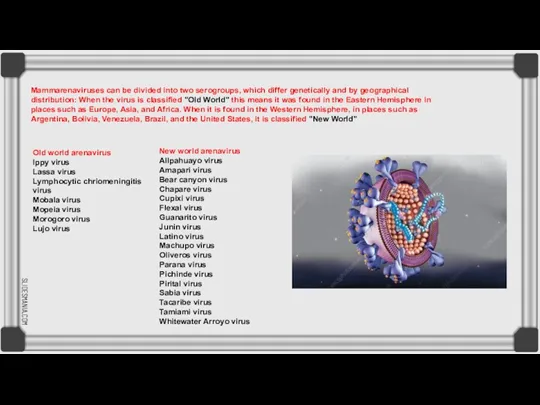
Old world arenavirus
Ippy virus
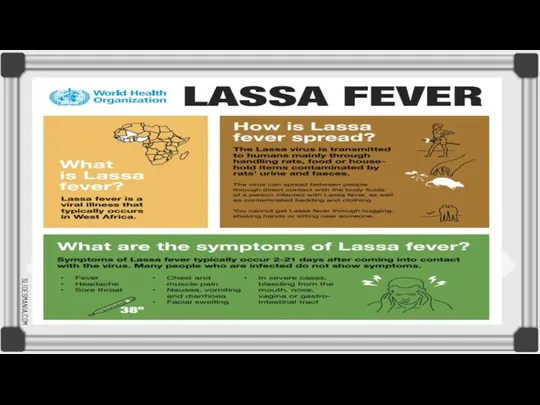
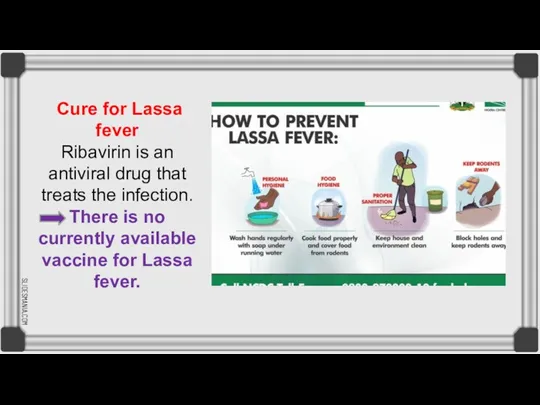
Lassa virus
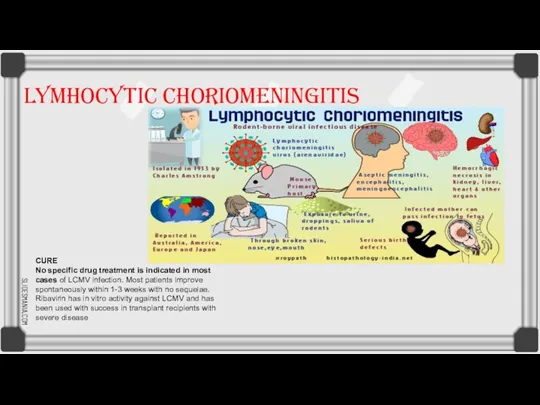
Lymphocytic chriomeningitis virus
Mobala virus
Mopeia
virus
Morogoro virus
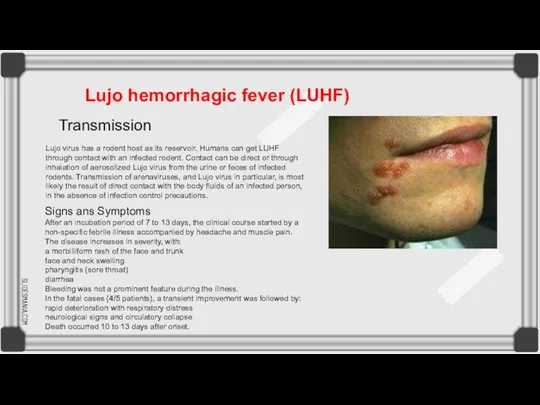
Lujo virus
New world arenavirus
Allpahuayo virus
Amapari virus
Bear canyon virus
Chapare virus
Cupixi virus
Flexal virus
Guanarito virus
Junin virus
Latino virus
Machupo virus
Oliveros virus
Parana virus
Pichinde virus
Pirital virus
Sabia virus
Tacaribe virus
Tamiami virus
Whitewater Arroyo virus
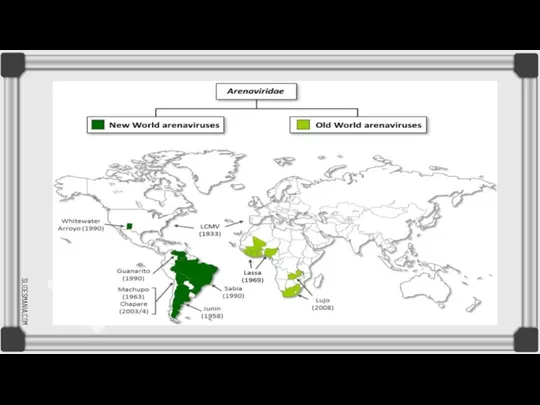
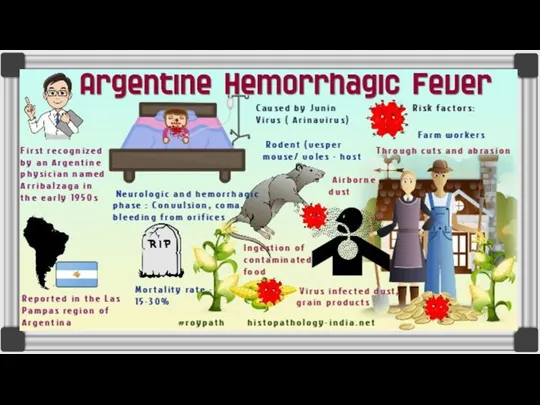
Mammarenaviruses can be divided into two serogroups, which differ genetically and by geographical distribution: When the virus is classified "Old World" this means it was found in the Eastern Hemisphere in places such as Europe, Asia, and Africa. When it is found in the Western Hemisphere, in places such as Argentina, Bolivia, Venezuela, Brazil, and the United States, it is classified "New World"


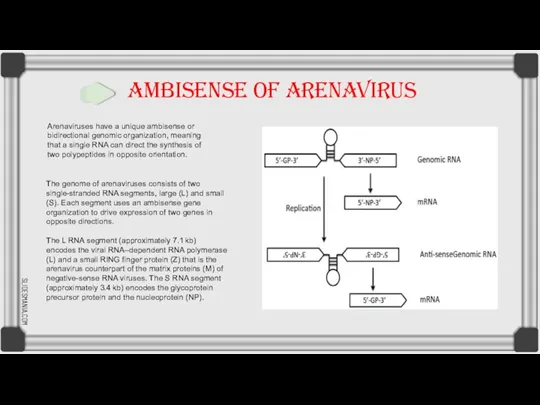




 Дизартрия. Определение дизартрии
Дизартрия. Определение дизартрии Первая помощь при синдроме длительного сдавления (СДС) или тяжелая компрессионная травма
Первая помощь при синдроме длительного сдавления (СДС) или тяжелая компрессионная травма Гастро-эзофагеальді рефлюкстік аурулардың патофизиологиясы
Гастро-эзофагеальді рефлюкстік аурулардың патофизиологиясы Наркотические анальгетики
Наркотические анальгетики Грыжи у детей
Грыжи у детей Зиянды факторлардың ұрыққа тигізетін әсері
Зиянды факторлардың ұрыққа тигізетін әсері Бас және мойынның хирургиялық аурулары және жарақаттары
Бас және мойынның хирургиялық аурулары және жарақаттары Спинной мозг. Кровоснабжение, ликвородинамика
Спинной мозг. Кровоснабжение, ликвородинамика Профилактика туберкулеза
Профилактика туберкулеза Определение тренирующего пульса. Тест 6-минутной ходьбы
Определение тренирующего пульса. Тест 6-минутной ходьбы Вещества вторичного биосинтеза
Вещества вторичного биосинтеза Тактика ведения больного ишемической болезнью сердца на фоне заболеваний органов пищеварения
Тактика ведения больного ишемической болезнью сердца на фоне заболеваний органов пищеварения Общая артрология
Общая артрология Группы крови. Методы определения групп крови и резус-фактора.Тема 4.1
Группы крови. Методы определения групп крови и резус-фактора.Тема 4.1 Профілактика захворювань незбалансованого харчування. Харчові добавки. Симптоми харчового отруєння
Профілактика захворювань незбалансованого харчування. Харчові добавки. Симптоми харчового отруєння Тромбоэмболия легочной артерии
Тромбоэмболия легочной артерии Трансплантология. Тері, бұлшық ет, сіңір, жүйке, сүйек тінді қуысты ағзалардың пластикасы
Трансплантология. Тері, бұлшық ет, сіңір, жүйке, сүйек тінді қуысты ағзалардың пластикасы Жалпы тәжірбиелі дәрігер жұмысын ұйымдастыру. Дәрігердің амбулаториялық менежмент негіздері
Жалпы тәжірбиелі дәрігер жұмысын ұйымдастыру. Дәрігердің амбулаториялық менежмент негіздері Клинико-электрографическая диагностика нарушений ритма
Клинико-электрографическая диагностика нарушений ритма Классификация противовирусных ЛС
Классификация противовирусных ЛС Негативний вплив комп’ютера на здоров’я людини. Захворювання опорно-рухового апарату
Негативний вплив комп’ютера на здоров’я людини. Захворювання опорно-рухового апарату Рекомендации ESC по диагностике и ведению пациентов с острой эмболией системы лёгочной артерии
Рекомендации ESC по диагностике и ведению пациентов с острой эмболией системы лёгочной артерии Рентгенологические проявления патологических процессов в легких
Рентгенологические проявления патологических процессов в легких Болезни желудочно-кишечного тракта
Болезни желудочно-кишечного тракта Диссеминированный туберкулез легких
Диссеминированный туберкулез легких Основные загрязнители пищи химической природы. Профилактика пищевых отравлений химической этиологии
Основные загрязнители пищи химической природы. Профилактика пищевых отравлений химической этиологии Особенности сестринского ухода за пациентами при лейкозах
Особенности сестринского ухода за пациентами при лейкозах Медицина в Западной Европе в период позднего средневековья
Медицина в Западной Европе в период позднего средневековья