Содержание
- 2. Presentation of patient 33-year-old man He complained of pain in the right side of his chest
- 3. Medical history Patient underwent colonoscopy with biopsy 4 years ago because of chronic diarrhea and unexplained
- 4. Social history Is married, with 2 children under 10 years of age Works as a health
- 5. Family history Mother suffered from systemic lupus erythematosus without renal involvement Father and brother are well,
- 6. Physical examination Temperature - 36.9˚C Pulse - 110 beats per minute and regular Blood pressure -
- 7. Symptom-oriented examination? Chest Heart Lungs Abdomen Lower extremities Skin Joints Lymph nodes
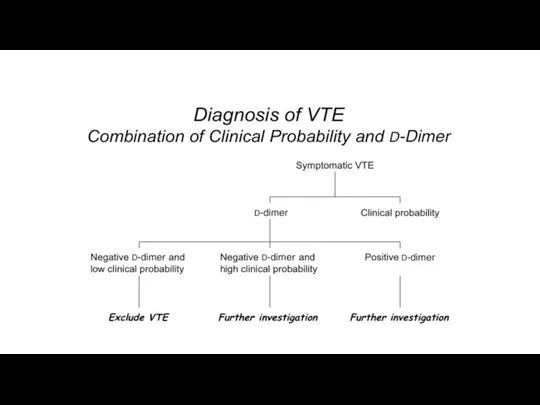
- 8. Which of the following tests are indicated to evaluate the patient’s symptoms? (3) 1. Cardiac ultrasonography
- 9. D-dimer level was elevated
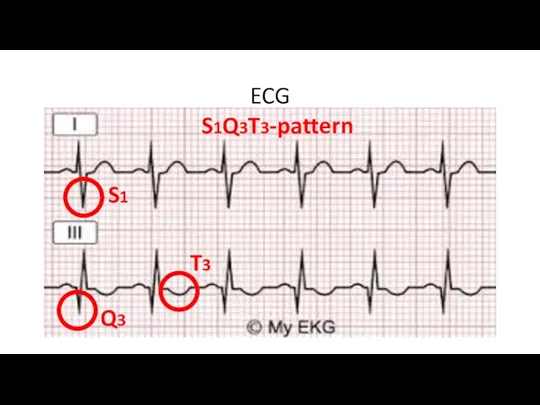
- 10. ECG S1 Q3 T3 S1Q3T3-pattern
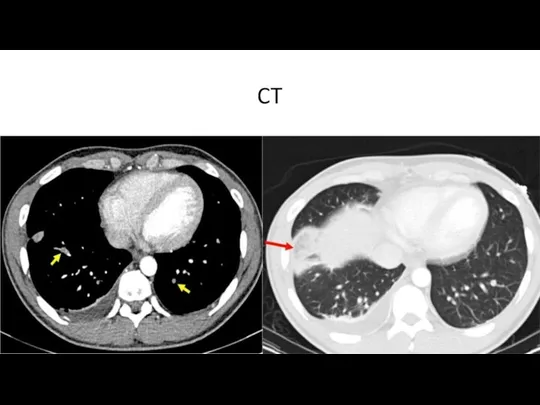
- 11. CT
- 12. Diagnosis The diagnosis of pulmonary embolism have been confirmed What should we do? Embolectomy Fibrinolytic therapy
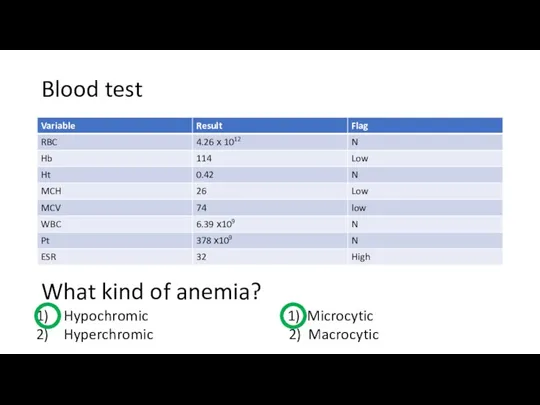
- 13. Blood test What kind of anemia? Hypochromic 1) Microcytic Hyperchromic 2) Macrocytic
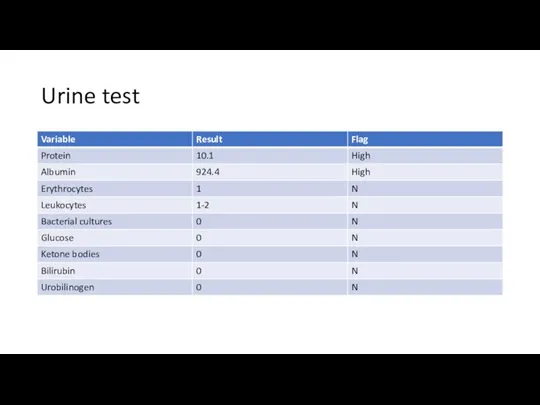
- 14. Urine test
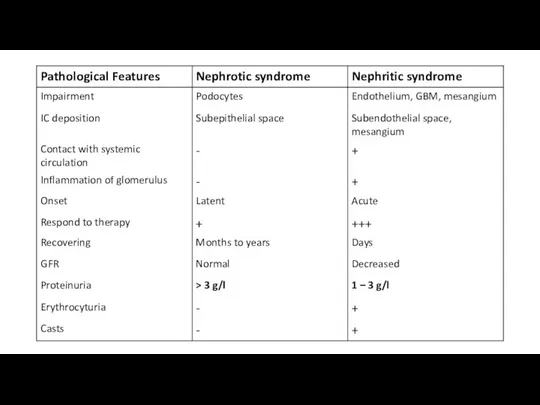
- 15. What is the most likely diagnosis according to urine test? Nephritic syndrome Nephrotic syndrome What is
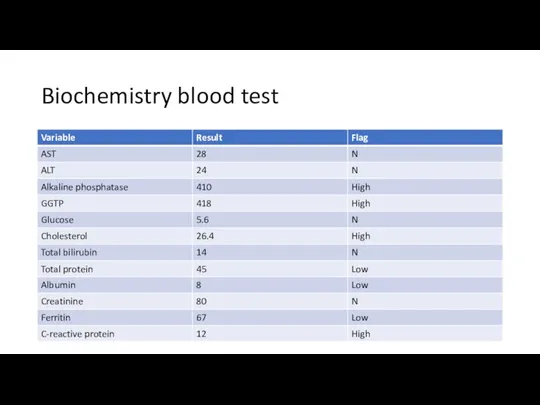
- 16. Biochemistry blood test
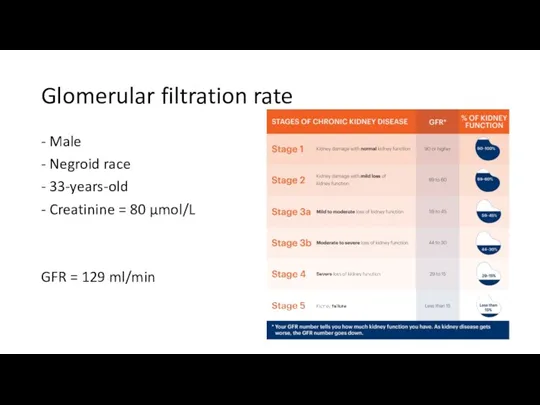
- 17. Glomerular filtration rate - Male - Negroid race - 33-years-old - Creatinine = 80 μmol/L GFR
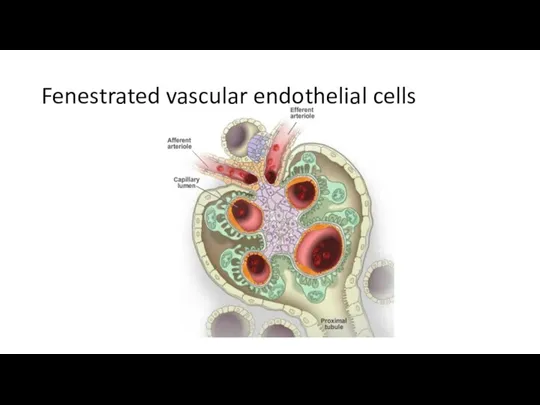
- 18. Fenestrated vascular endothelial cells
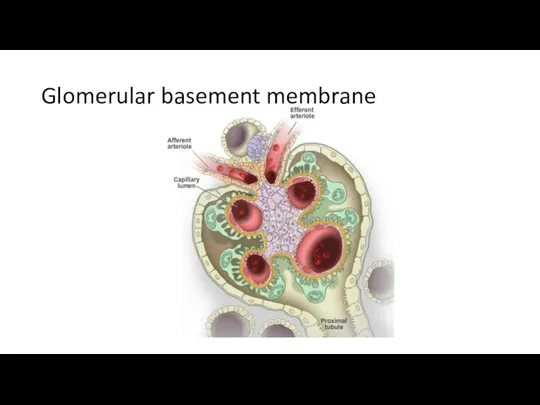
- 19. Glomerular basement membrane
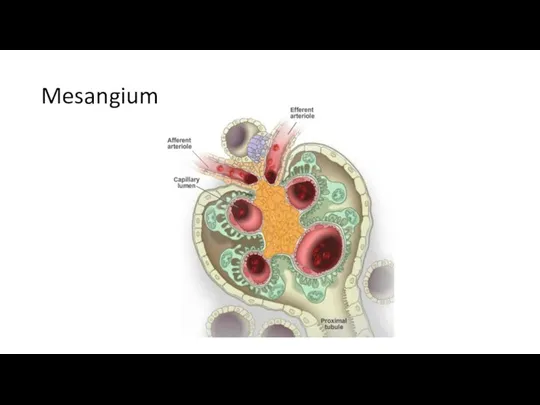
- 20. Mesangium
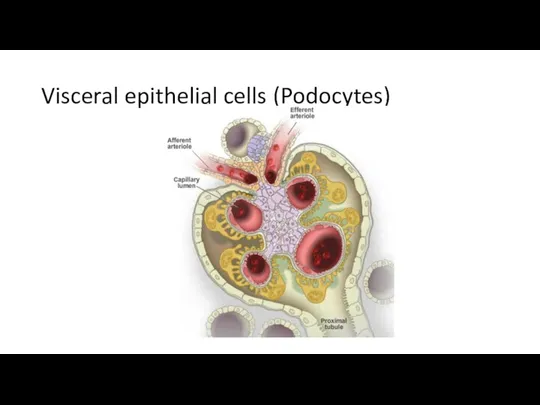
- 21. Visceral epithelial cells (Podocytes)
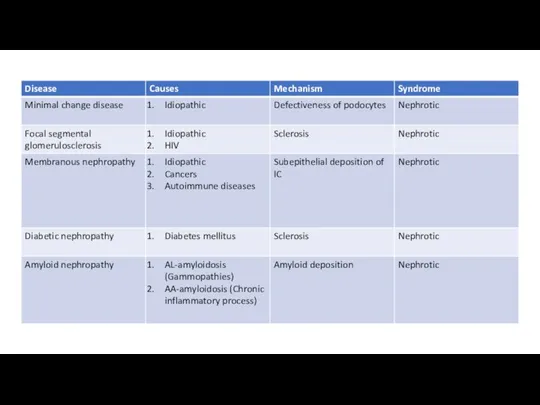
- 24. Minimal change disease Focal segmental glomerulocslerosis Membranous nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy Amyloid nephropathy Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis Mesangioproliferative glomerulonephritis
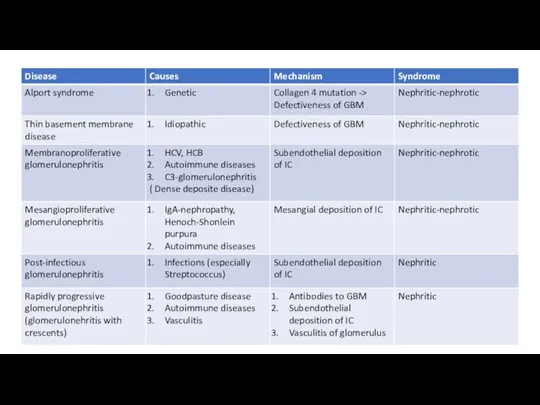
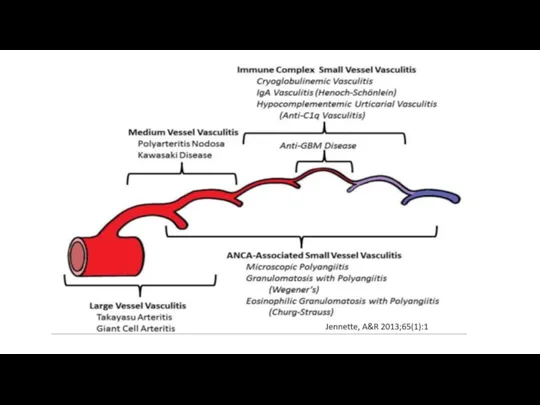
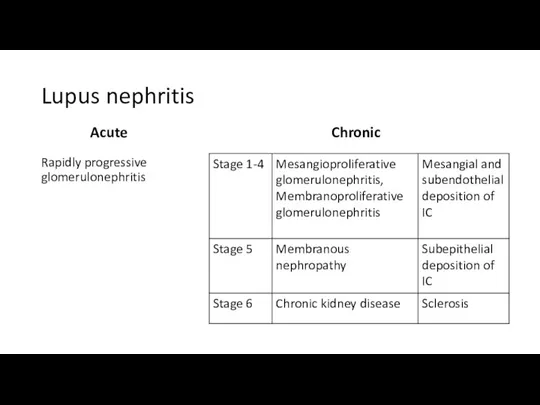
- 28. Lupus nephritis Acute Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis Chronic
- 29. Which of the following tests or procedures should be performed to further evaluate the cause of
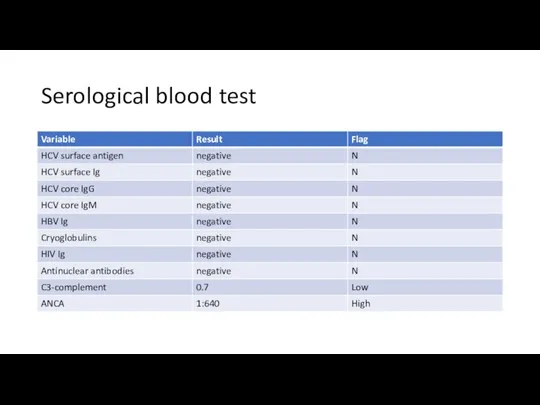
- 30. Serological blood test
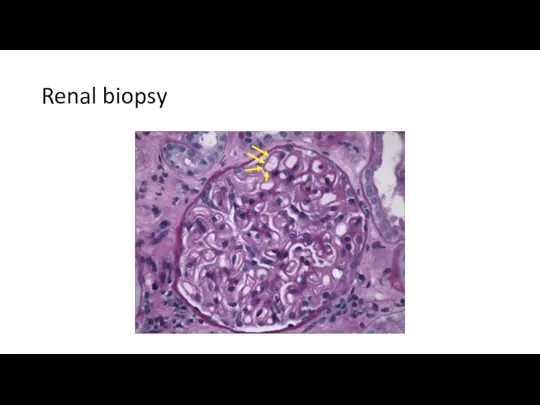
- 31. Renal biopsy
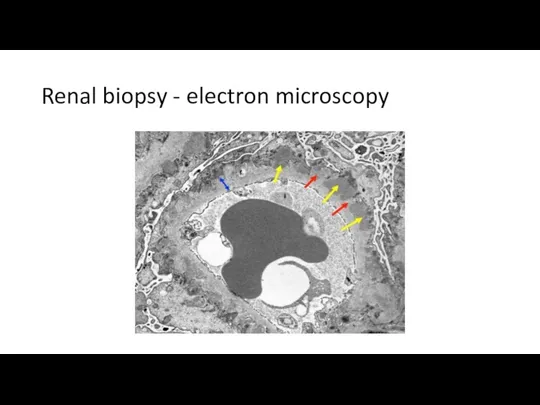
- 32. Renal biopsy - electron microscopy
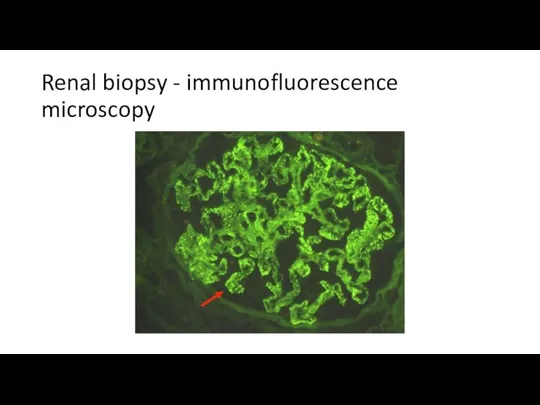
- 33. Renal biopsy - immunofluorescence microscopy
- 34. Renal biopsy The biopsy specimens reveal a membranous pattern of injury that is consistent with the
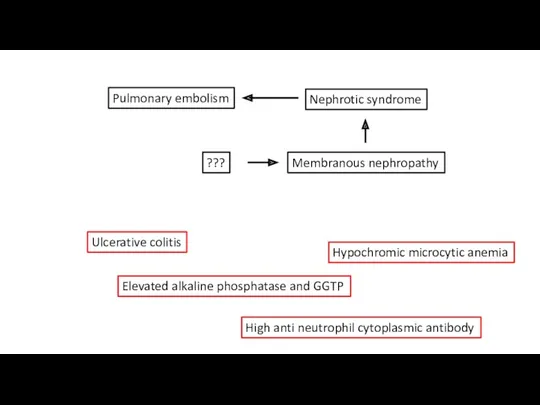
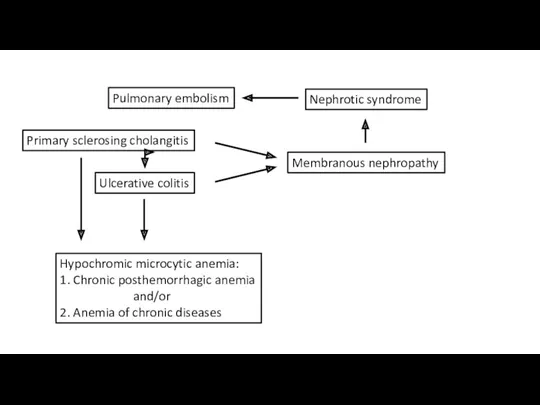
- 35. Pulmonary embolism Nephrotic syndrome Membranous nephropathy ??? Ulcerative colitis Elevated alkaline phosphatase and GGTP Hypochromic microcytic
- 36. The patient’s abnormal level of alkaline phosphatase is most suggestive of which one of the following
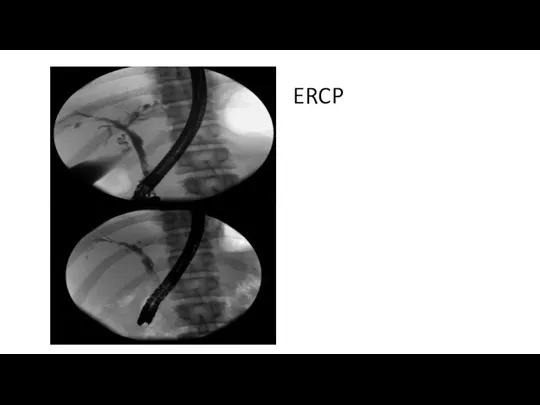
- 37. Which of the following procedures are now indicated? (2) 1) Cholangiopgraphy 2) Endoscopic ultrasonography of the
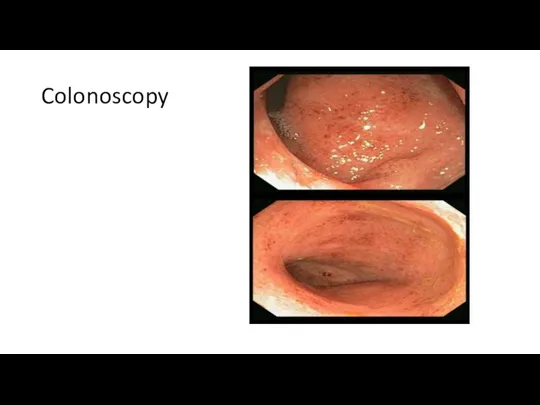
- 38. Colonoscopy
- 39. ERCP
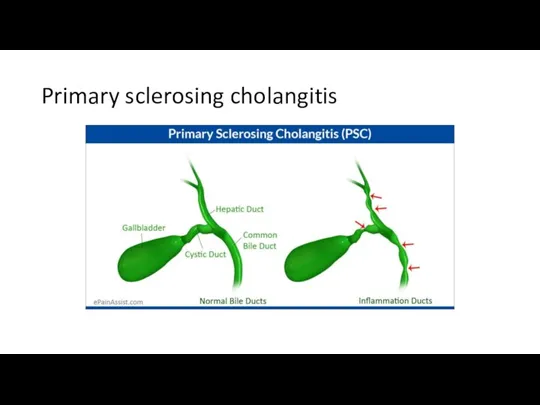
- 40. Primary sclerosing cholangitis
- 41. Primary sclerosing cholangitis Autoimmune disease Progressive inflammation and fibrosis of the intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts
- 42. Primary sclerosing cholangitis Elevated level of alkaline phosphatase is very common, even in early stages >
- 43. Pulmonary embolism Nephrotic syndrome Membranous nephropathy Primary sclerosing cholangitis Ulcerative colitis Hypochromic microcytic anemia: 1. Chronic
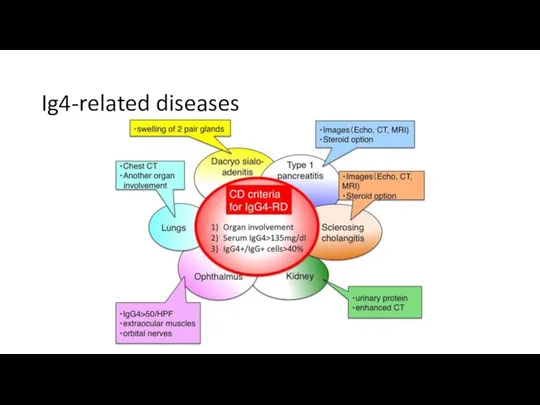
- 44. Ig4-related diseases
- 45. Outcomes The level of IgG4 was elevated The diagnosis has been changed to IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis
- 47. Скачать презентацию


















 Temporary fillings
Temporary fillings Диагностика и лечение инфаркта миокарда
Диагностика и лечение инфаркта миокарда Пиодермии. Определение
Пиодермии. Определение Ана сүтімен қоректендірудің маңызы
Ана сүтімен қоректендірудің маңызы Сосудистый шов
Сосудистый шов Иммунология даму тарихы. Иммунитет теориясы
Иммунология даму тарихы. Иммунитет теориясы Жедел гастрит
Жедел гастрит Принципы диагностики и лечения инфекционных заболеваний
Принципы диагностики и лечения инфекционных заболеваний железа
железа Острые эмболии и тромбозы магистральных артерий конечностей. Консервативное лечение. Показания и виды оперативных вмешательств
Острые эмболии и тромбозы магистральных артерий конечностей. Консервативное лечение. Показания и виды оперативных вмешательств Огнестрельные ранения. Хирургическая обработка огнестрельных ран
Огнестрельные ранения. Хирургическая обработка огнестрельных ран Шок. Патофизиология и принципы интенсивной терапии
Шок. Патофизиология и принципы интенсивной терапии Клинический случай
Клинический случай Вирусные дерматозы
Вирусные дерматозы Проводящая система сердца. ЭКГ
Проводящая система сердца. ЭКГ Особенности обеспечения проходимости дыхательных путей у детей. Интубация трахеи
Особенности обеспечения проходимости дыхательных путей у детей. Интубация трахеи Деваскурялизация матки при применении компрессионного шва по B-Linch
Деваскурялизация матки при применении компрессионного шва по B-Linch Гигиенические требования к выбору и планировке больничного участка. Системы строительства больниц, их преимущества и недостатки
Гигиенические требования к выбору и планировке больничного участка. Системы строительства больниц, их преимущества и недостатки Общая фармакология. Введение в фармакологию
Общая фармакология. Введение в фармакологию Боткин Сергей Петрович
Боткин Сергей Петрович Иық буынының жарақаттары
Иық буынының жарақаттары Респираторный дистресс-синдром взрослых
Респираторный дистресс-синдром взрослых Врождённые пороки развития женской половой системы
Врождённые пороки развития женской половой системы Анатомо-физиологические особенности строения полости рта новорожденного
Анатомо-физиологические особенности строения полости рта новорожденного Дифференциальный диагноз анемий
Дифференциальный диагноз анемий Сухожильный шов
Сухожильный шов Клинико-экономические исследования
Клинико-экономические исследования Дифференциальный диагноз суставного синдрома (один день из жизни врача общей практики)
Дифференциальный диагноз суставного синдрома (один день из жизни врача общей практики)