Содержание
- 2. Why molecular subtypes need to be characterized ? How is molecular characterization done ? What is
- 3. CHALLENGE- Despite surgery, cytotoxic chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, and/or regional radiotherapy, ~ 30% of patients will eventually
- 4. Histologic subtype Axillary lymph node status Tumor size Grade Age Comorbidities Standard Prognostic Factors
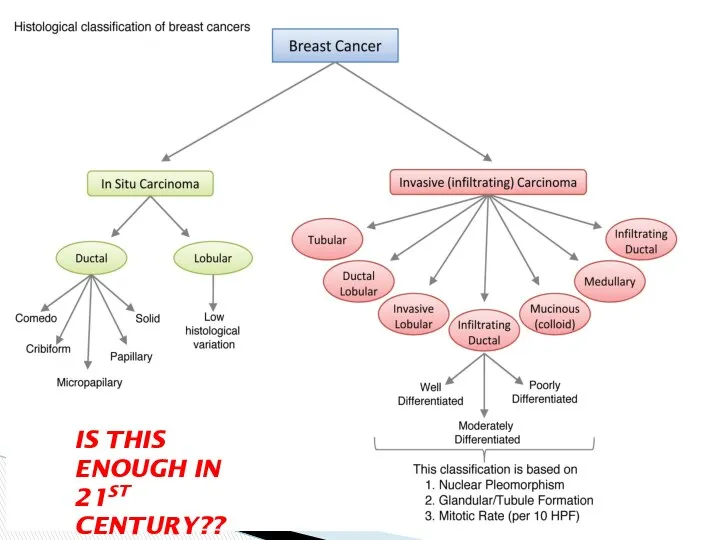
- 5. IS THIS ENOUGH IN 21ST CENTURY??
- 6. Historically, breast cancers were divided into hormone receptor positive and negative tumours. Up to half of
- 7. THUS, CLASSIFYING BREAST TUMOR HISTOLOGICALLY AND ON HORMONE SENSITIVITY IS IMPORTANT BUT NOT SUFFICIENT
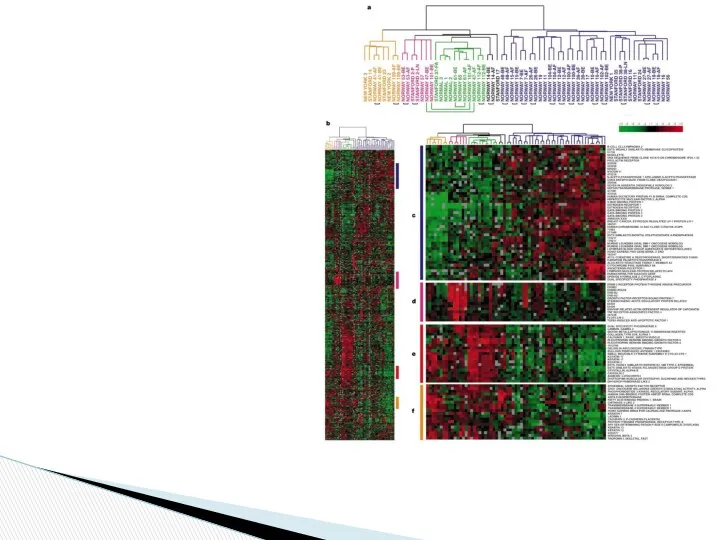
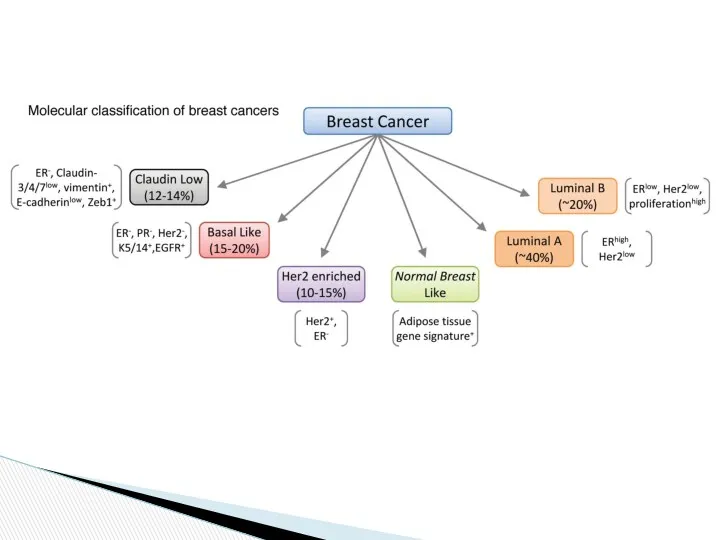
- 8. They characterized variation in gene expression patterns in a set of 65 surgical specimens of human
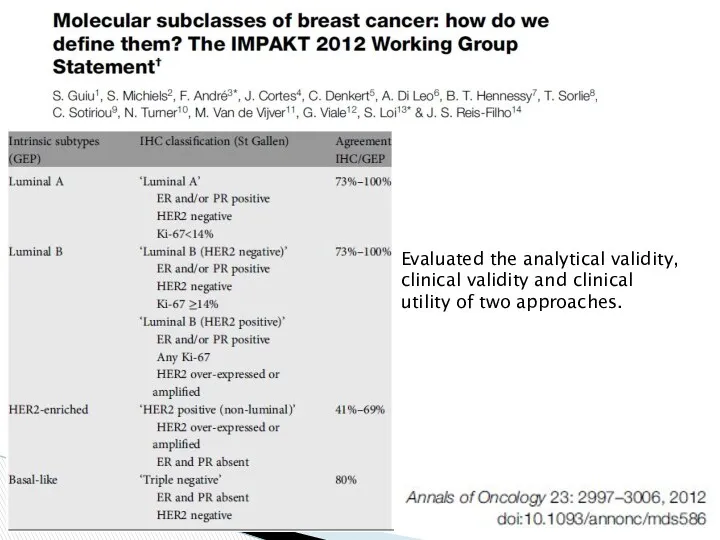
- 11. Evaluated the analytical validity, clinical validity and clinical utility of two approaches.
- 12. Goldhirsch et al. Ann Oncol June 2011. St Gallen 2011
- 14. Oxford Journals Medicine JNCI J Natl Cancer Inst Volume 101, Issue 10,2009 Pp. 736-750.
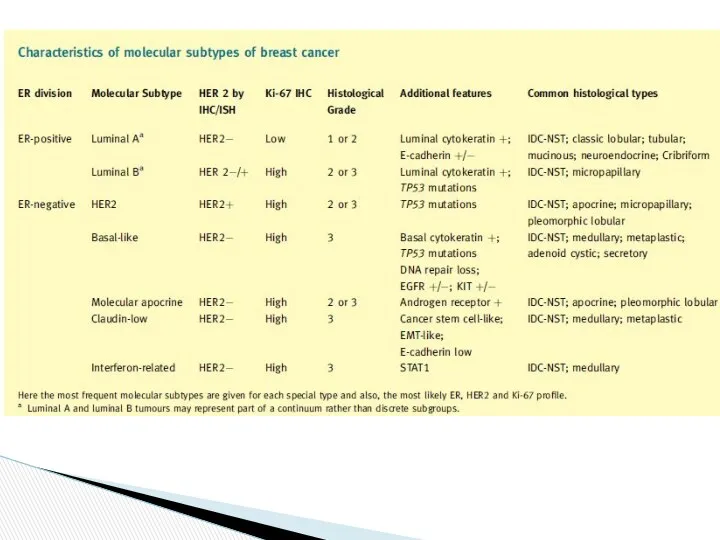
- 15. Express ER Most common. Luminal A possess a higher expression of the ER and oestrogen-associated genes
- 16. Express ER Variable HER2/neu expression Increased frequency of TP53 mutations Ki-67 proliferation index- high Luminal B
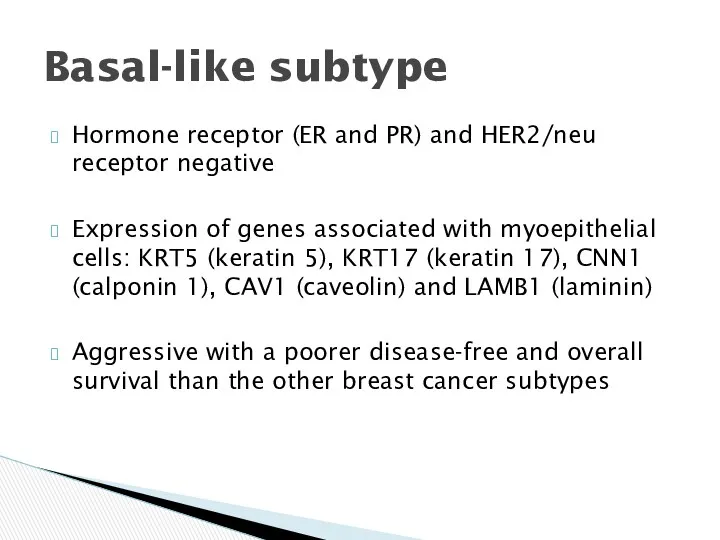
- 17. Hormone receptor (ER and PR) and HER2/neu receptor negative Expression of genes associated with myoepithelial cells:
- 18. Increased expression of genes located in the same region on chromosome 17q: human epidermal growth factor
- 19. In the past decade, microarray-based gene expression profiling has been extensively applied to the study of
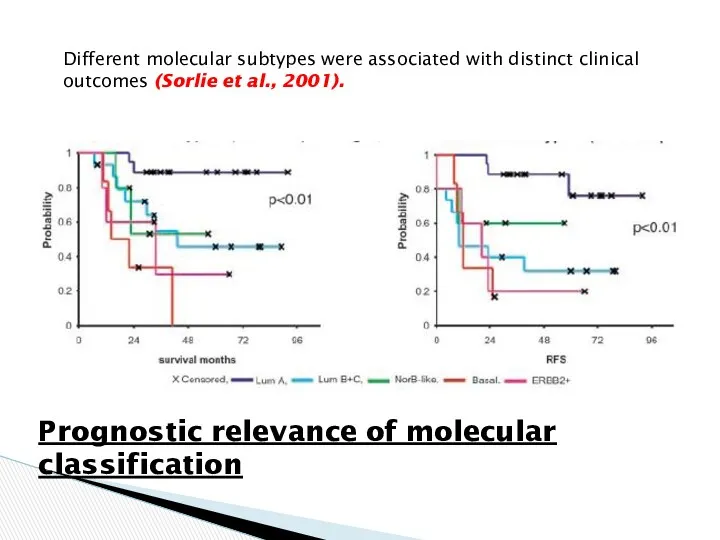
- 20. Different molecular subtypes were associated with distinct clinical outcomes (Sorlie et al., 2001). Prognostic relevance of
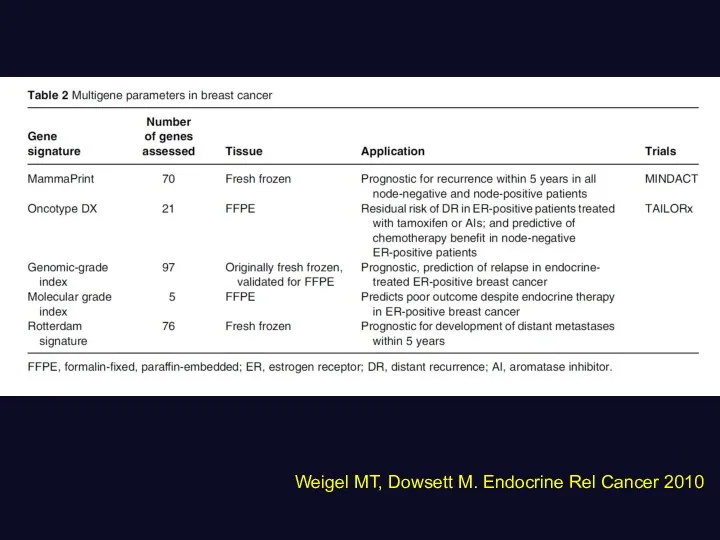
- 21. Weigel MT, Dowsett M. Endocrine Rel Cancer 2010
- 22. Predictive relevance of molecular classification Goldhirsch et al. Ann Oncol June 2011. St Gallen 2011
- 24. Скачать презентацию











 Дизартрия, коррекция. 1 этап
Дизартрия, коррекция. 1 этап Туберкулез кожи
Туберкулез кожи Гимназиялар мен лицейлерді жоспарлау мен құрылыс жүргізуде қойылатын гигиеналық талаптар. (Дәріс 16)
Гимназиялар мен лицейлерді жоспарлау мен құрылыс жүргізуде қойылатын гигиеналық талаптар. (Дәріс 16) Экспертиза при язвенной болезни
Экспертиза при язвенной болезни Классический массаж. Приемы
Классический массаж. Приемы Баланың физикалық және жүйке-психикалық дамуын бағалау
Баланың физикалық және жүйке-психикалық дамуын бағалау Массаж для лошадей. Применение и правила выполнения
Массаж для лошадей. Применение и правила выполнения Медициналық сақтандыру бағдарламалары. Әлемдегі сақтандыру медицинасының моделі
Медициналық сақтандыру бағдарламалары. Әлемдегі сақтандыру медицинасының моделі Инфузионная терапия в детском возрасте
Инфузионная терапия в детском возрасте Теория и практика того, как стать здоровее, легче, быстрее и сильнее
Теория и практика того, как стать здоровее, легче, быстрее и сильнее Перитонит. Классификация
Перитонит. Классификация Роль медицинской сестры в обеспечении качества жизни у пациентов с ишемической болезнью
Роль медицинской сестры в обеспечении качества жизни у пациентов с ишемической болезнью Тонзилор аппаратын қолдану созылмалы тонзилит емі кезінде тиімділігін анықтау
Тонзилор аппаратын қолдану созылмалы тонзилит емі кезінде тиімділігін анықтау Пороки развития центральной нервной системы
Пороки развития центральной нервной системы Экстракция. Медицина мен фармацияда эктракцияның қолданылуы
Экстракция. Медицина мен фармацияда эктракцияның қолданылуы Тромбофлебит глубоких вен
Тромбофлебит глубоких вен Зоонозды инфекция қоздырғыштары
Зоонозды инфекция қоздырғыштары Терапия. СД. Задача. Диагноз: гипертоническая болезнь 3 стадии
Терапия. СД. Задача. Диагноз: гипертоническая болезнь 3 стадии Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation
Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation Заболевания желчного пузыря и желчевыводящих путей
Заболевания желчного пузыря и желчевыводящих путей Этика взаимоотношений между субъектами фармации
Этика взаимоотношений между субъектами фармации О переводе государственных услуг в сфере здравоохранения в электронный вид
О переводе государственных услуг в сфере здравоохранения в электронный вид ЭКГ, ФКГ (электрокардиография)
ЭКГ, ФКГ (электрокардиография) Хроническая венозная недостаточность
Хроническая венозная недостаточность Сестринский процесс при хронических и острых расстройствах питания
Сестринский процесс при хронических и острых расстройствах питания Подготовка ВКР в формате основных направлений деятельности медицинской сестры
Подготовка ВКР в формате основных направлений деятельности медицинской сестры Наследственные болезни
Наследственные болезни Миома матки
Миома матки