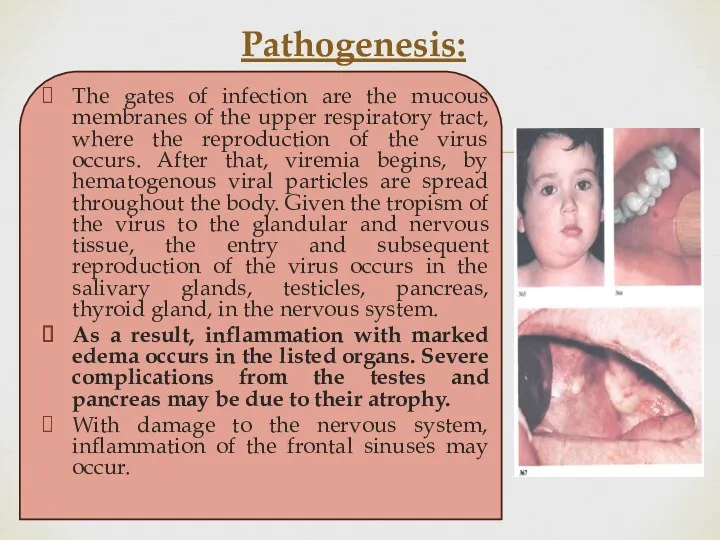
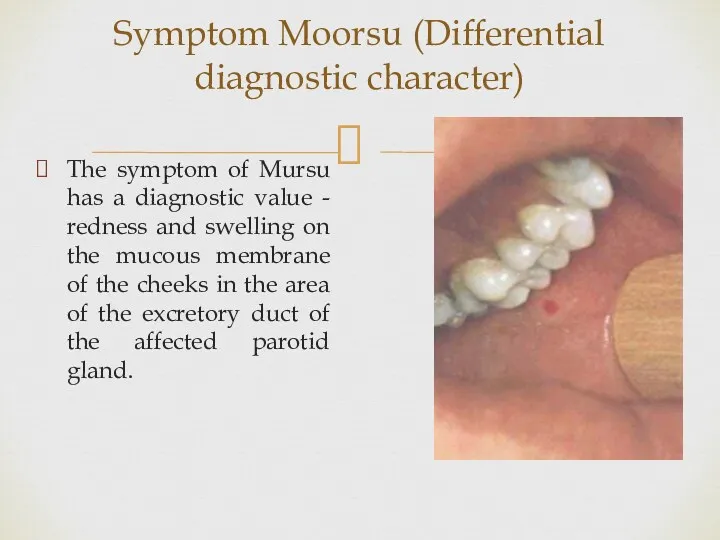
The gates of infection are the mucous membranes of the upper
respiratory tract, where the reproduction of the virus occurs. After that, viremia begins, by hematogenous viral particles are spread throughout the body. Given the tropism of the virus to the glandular and nervous tissue, the entry and subsequent reproduction of the virus occurs in the salivary glands, testicles, pancreas, thyroid gland, in the nervous system.
As a result, inflammation with marked edema occurs in the listed organs. Severe complications from the testes and pancreas may be due to their atrophy.
With damage to the nervous system, inflammation of the frontal sinuses may occur.
Pathogenesis:




 Травмы дистального отдела голени и голеностопного сустава
Травмы дистального отдела голени и голеностопного сустава Босанудан кейінгі кезеңде қан кетуде көрсетілетін шұғыл көмек алгоритмі
Босанудан кейінгі кезеңде қан кетуде көрсетілетін шұғыл көмек алгоритмі Тілменің қабынуы. Панариций, паронихия
Тілменің қабынуы. Панариций, паронихия Кровотечения в последовом и раннем послеродовом периоде
Кровотечения в последовом и раннем послеродовом периоде Жамбыл Жабаев
Жамбыл Жабаев Хвороби цивілізації
Хвороби цивілізації Issues Affecting ART Success: Adherence, ARV Toxicity, Drug Interactions
Issues Affecting ART Success: Adherence, ARV Toxicity, Drug Interactions Катаральный, гипертрофический гингивит. Лечение
Катаральный, гипертрофический гингивит. Лечение Доброкачественные и злокачественные новообразования вульвы
Доброкачественные и злокачественные новообразования вульвы Программа подготовки медицинского персонала по вопросам проведения медицинских осмотров водителей транспортных средств
Программа подготовки медицинского персонала по вопросам проведения медицинских осмотров водителей транспортных средств Первая помощь при укусах животных
Первая помощь при укусах животных Е-РОК - Тест розеткообразования — классический метод определения количества Тлимфоцитов в периферической крови
Е-РОК - Тест розеткообразования — классический метод определения количества Тлимфоцитов в периферической крови Реформування охорони здоров’я очима батьків дітей
Реформування охорони здоров’я очима батьків дітей Спинальный инсульт
Спинальный инсульт Препараты гормонов коры надпочечников
Препараты гормонов коры надпочечников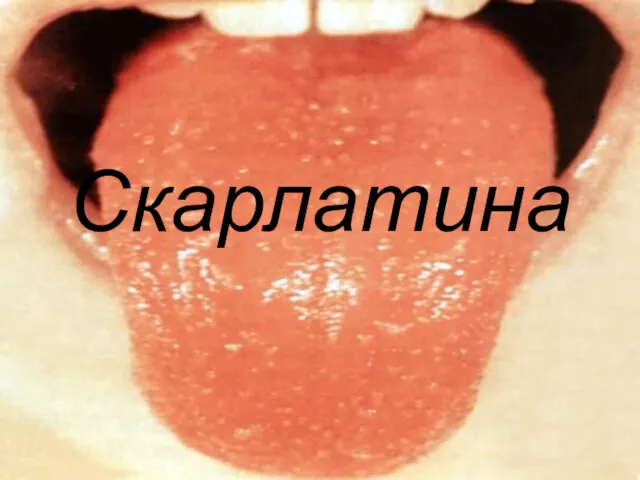 Скарлатина
Скарлатина Ісіктердің пайда болу механизмі
Ісіктердің пайда болу механизмі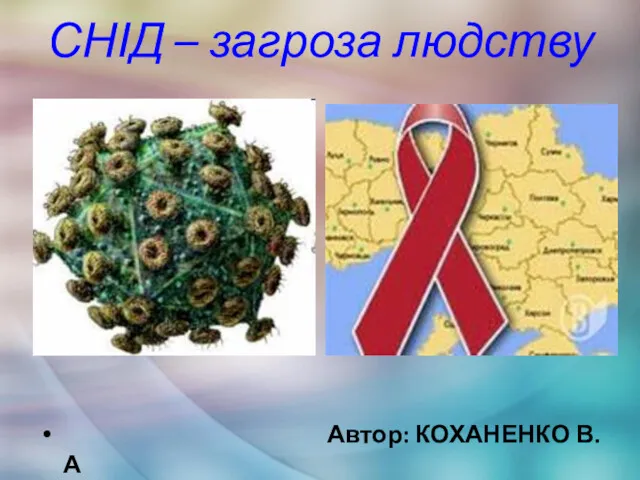 СНІД – загроза людству
СНІД – загроза людству Беременность и трихомониаз
Беременность и трихомониаз Лимфадениты челюстнолицевой области: этиология, патогенез, клиника, диагностика, лечение, профилактика
Лимфадениты челюстнолицевой области: этиология, патогенез, клиника, диагностика, лечение, профилактика Артериальная гипертензия у детей и подростков
Артериальная гипертензия у детей и подростков Профилактика чрезмерного употребления алкоголя
Профилактика чрезмерного употребления алкоголя Формулярная система: разработка формуляров на различных уровнях системы здравоохранения
Формулярная система: разработка формуляров на различных уровнях системы здравоохранения Гастростомия. Витсел әдісі
Гастростомия. Витсел әдісі Wie kann moderne gefäßprävention funktionieren
Wie kann moderne gefäßprävention funktionieren Үшкіл жүйке жүйесінің невралгиясын емдеудегі тиімді әдістерге талдау жасау
Үшкіл жүйке жүйесінің невралгиясын емдеудегі тиімді әдістерге талдау жасау Гемолитико-уремический синдром
Гемолитико-уремический синдром Неотожные состояния в педиатрии
Неотожные состояния в педиатрии