Содержание
- 2. Plan Endocarditis Infective endocarditis Non-infective endocarditis Nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis Libman-Sacks endocarditis Diagnostics References
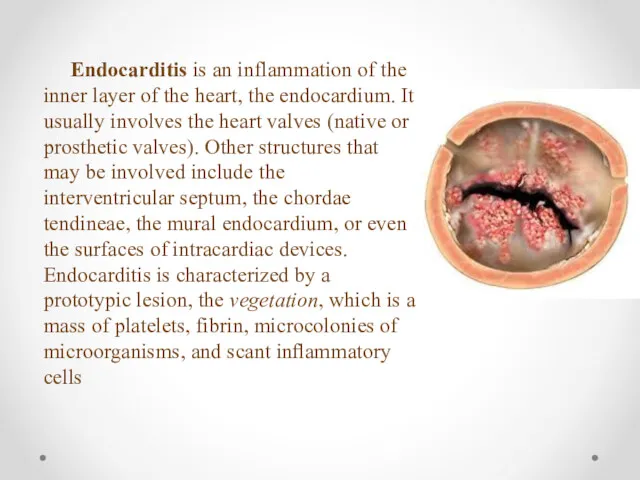
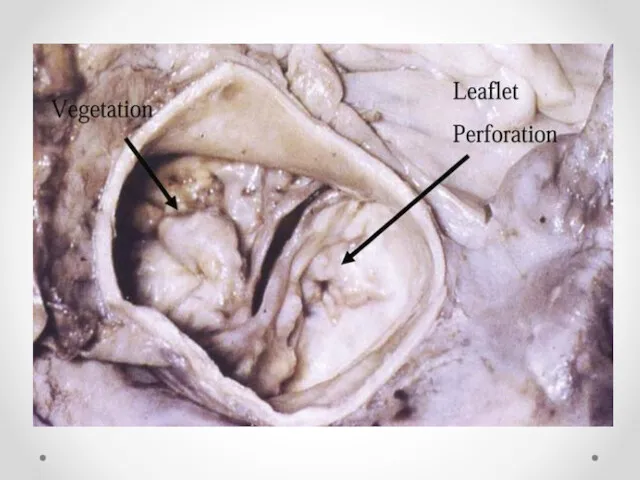
- 3. Endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner layer of the heart, the endocardium. It usually involves
- 4. There are multiple ways to classify endocarditis. The simplest classification is based on etiology: either infective
- 5. Infective endocarditis Since the valves of the heart do not receive any dedicated blood supply, defensive
- 7. Non-infective endocarditis Nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis Libman-Sacks endocarditis
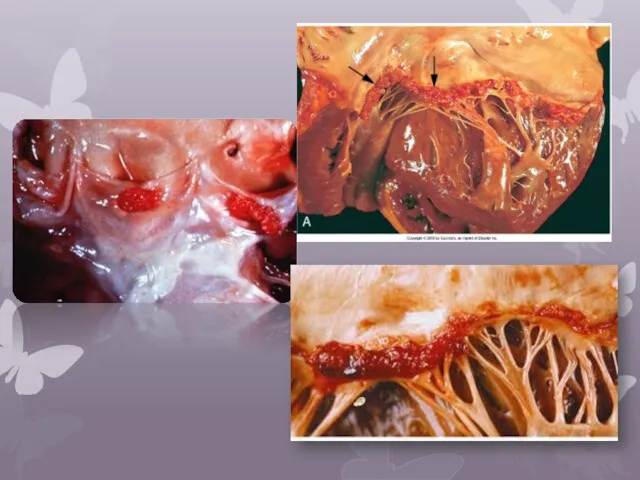
- 8. Nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis Nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis (NBTE), also called marantic endocarditis is most commonly found on
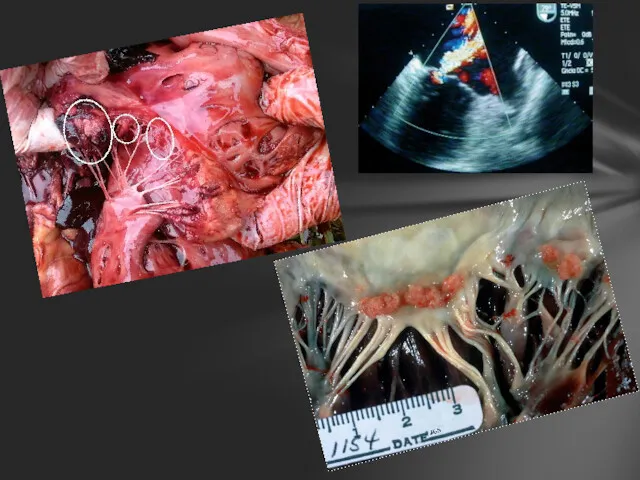
- 10. Another form of sterile endocarditis, is termed Libman-Sacks endocarditis; this form occurs more often in patients
- 12. DIAGNOSTICS Examination of suspected infective endocarditis includes a detailed examination of the patient, and especially careful
- 14. Thank you for your attention!!!
- 16. Скачать презентацию





 Лекарственные растения успокаивающего действия
Лекарственные растения успокаивающего действия Невідкладні стани. Анафілактична та алергічна реакція
Невідкладні стани. Анафілактична та алергічна реакція Органы чувств. Чувствительность
Органы чувств. Чувствительность Борьба с допингом на современном этапе
Борьба с допингом на современном этапе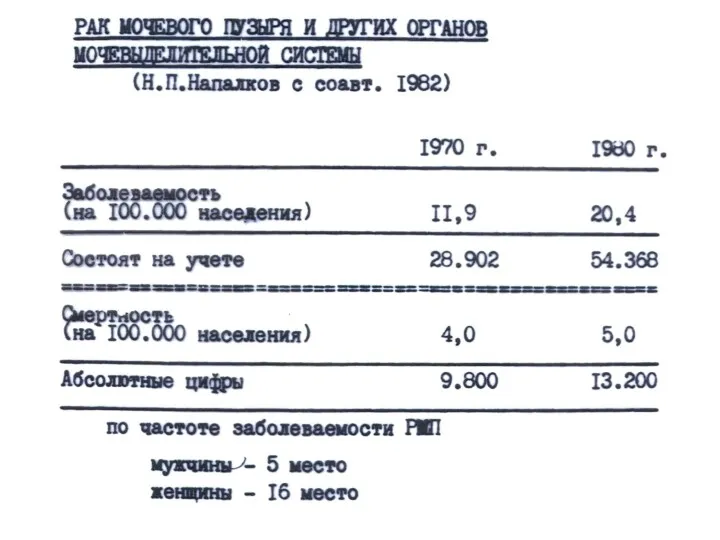 Рак мочевого пузыря
Рак мочевого пузыря Дыхательная гимнастика А. Н. Стрельниковой
Дыхательная гимнастика А. Н. Стрельниковой Рак шейки матки. Факторы риска, диагностика, стадирование, лечение и прогноз
Рак шейки матки. Факторы риска, диагностика, стадирование, лечение и прогноз Оптимизация обучения студентов медицинского университета
Оптимизация обучения студентов медицинского университета Медицина катастроф. Крупнейшие чрезвычайные ситуации в России в конце 80-х годов
Медицина катастроф. Крупнейшие чрезвычайные ситуации в России в конце 80-х годов Аномалии рефракции
Аномалии рефракции Связь телосложения и заболеваний человека
Связь телосложения и заболеваний человека Основы педиатрии. Введение. Педиатрия и гигиена - основные понятия и принципы
Основы педиатрии. Введение. Педиатрия и гигиена - основные понятия и принципы Ветеринарно-санитарная экспертиза яиц
Ветеринарно-санитарная экспертиза яиц Неврологические проявления острых порфирий
Неврологические проявления острых порфирий Клинические формы первичного туберкулеза. Дифференциальная диагностика туберкулеза с другими заболеваниями. Лекция 4
Клинические формы первичного туберкулеза. Дифференциальная диагностика туберкулеза с другими заболеваниями. Лекция 4 Всесвітній день боротьби зі СНІДом
Всесвітній день боротьби зі СНІДом Методы исследования сердечно-сосудистой системы
Методы исследования сердечно-сосудистой системы Денсаулық сақтау саласының кез-келген қаржыландыру және басқару нысанында. Модернизациясы
Денсаулық сақтау саласының кез-келген қаржыландыру және басқару нысанында. Модернизациясы Стрес. Гостра стресова реакція. Посттравматична стресова реакція
Стрес. Гостра стресова реакція. Посттравматична стресова реакція Профилактика заболеваний. СПИД
Профилактика заболеваний. СПИД Расстройства эмоциональной, двигательно-волевой сферы
Расстройства эмоциональной, двигательно-волевой сферы Акушерия гинекологиядағы шуғыл жағдайлар. Ауруханадан тыс босану
Акушерия гинекологиядағы шуғыл жағдайлар. Ауруханадан тыс босану Пузырчатка (Pemphigus acantholyticus)
Пузырчатка (Pemphigus acantholyticus) Септический шок
Септический шок Clinical manifestation of HIV-infection
Clinical manifestation of HIV-infection Введение в дисциплину. Общие основы физической реабилитации в травматологии и ортопедии
Введение в дисциплину. Общие основы физической реабилитации в травматологии и ортопедии Поздние осложнения сахарного диабета
Поздние осложнения сахарного диабета Наркомании, токсикомании. Выявление болезней зависимости в общесоматической сети
Наркомании, токсикомании. Выявление болезней зависимости в общесоматической сети