Содержание
- 2. Structure Clinical Manifestations Pathogenesis Epidemiology Diagnosis Control Overview
- 3. Definition of rickettsial disease Rickettsial disease in humans (spotted fevers, typhus or scrub typhus) is caused
- 4. The name Rickettsiaceae honors Haword Taylor Ricketts for his brilliant experiments. Ricketts, as well as another
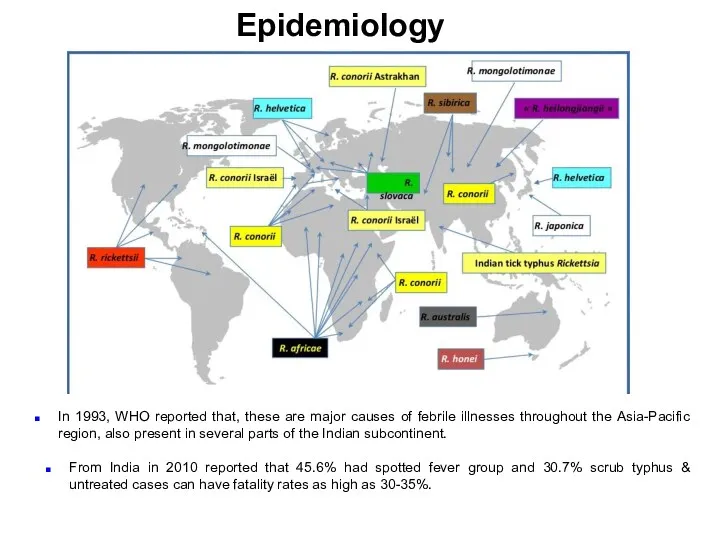
- 5. Epidemiology In 1993, WHO reported that, these are major causes of febrile illnesses throughout the Asia-Pacific
- 6. For India, the reported numbers are an underestimate due to lack of community based data and
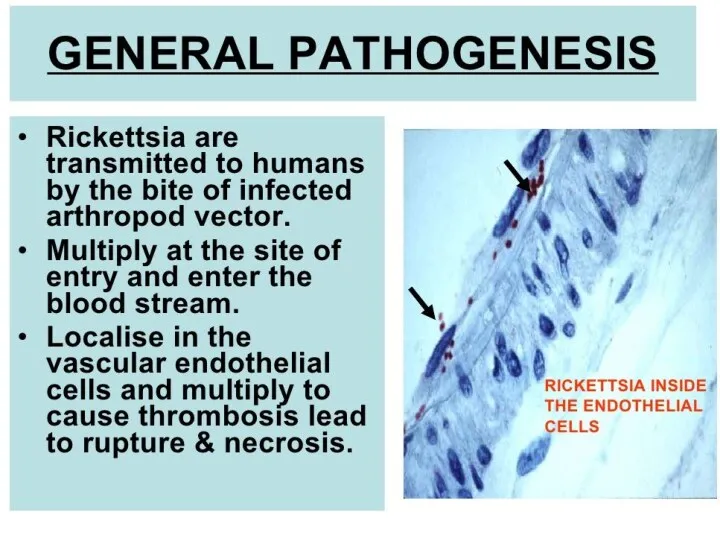
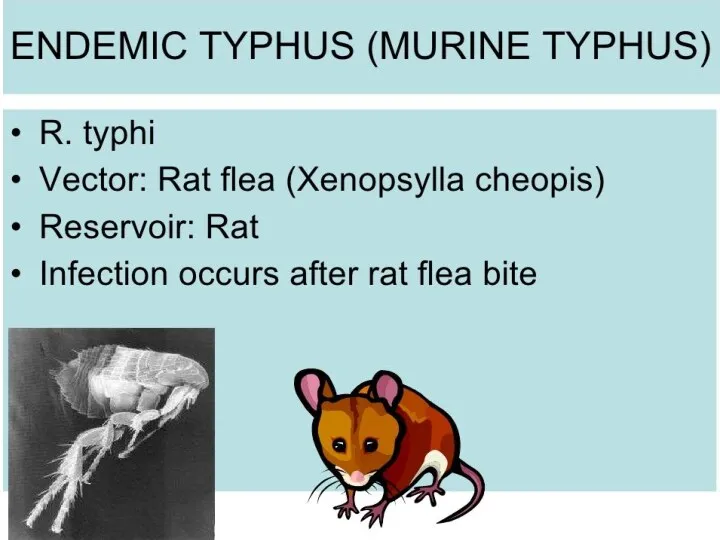
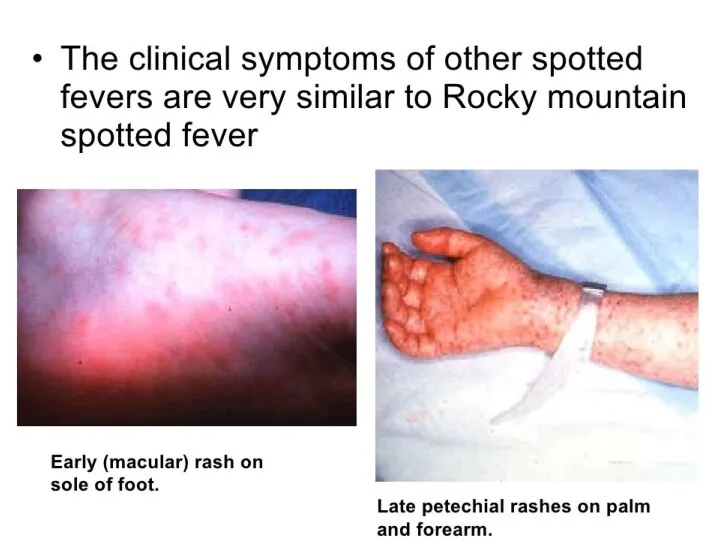
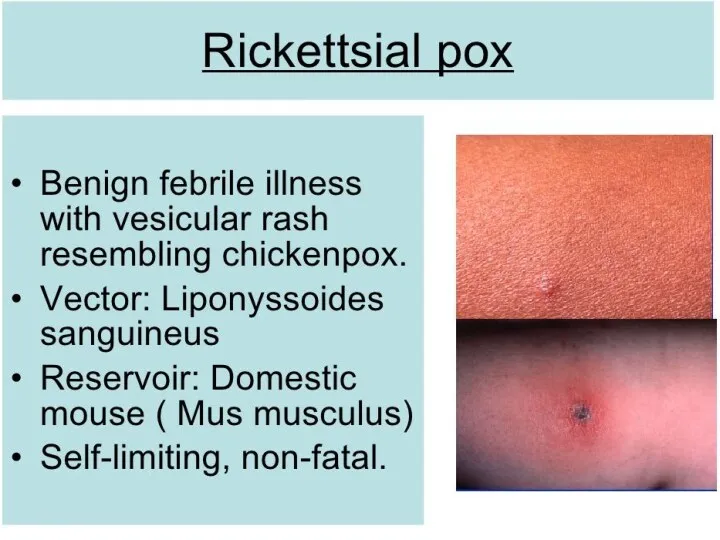
- 7. TRANSMISSION Vectors: fleas, lice, mites and ticks. The specific vectors that transmit each rickettsial pathogen. Transmission
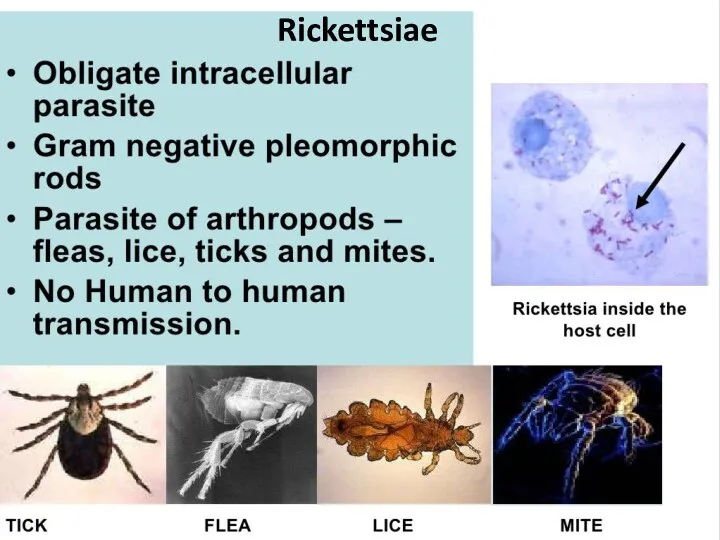
- 8. Rickettsiae
- 9. Rickettsia (11 species) Orientia Ehrlichia (2 species) Coxiella (1 species) Rickettsiae
- 19. C burnetii C.burnetii differs from other rickettsia in that it is enclosed in a persistent vacuole
- 20. Clinical Manifestations: Q Fever Entry: aerosol from infected placenta of sheep goats cattle Spread: blood stream
- 28. Скачать презентацию















 Interesting case
Interesting case Заболевания дыхательной системы. Профилактика против заболеваний
Заболевания дыхательной системы. Профилактика против заболеваний Роль лучевых методов исследования в диагностике профессиональных заболеваний бронхолёгочной системы
Роль лучевых методов исследования в диагностике профессиональных заболеваний бронхолёгочной системы Передраки і рак губи, язика і слизової порожнини рота. Злоякісні пухлини щелеп. Злоякісні пухлини слинних залоз і шиї
Передраки і рак губи, язика і слизової порожнини рота. Злоякісні пухлини щелеп. Злоякісні пухлини слинних залоз і шиї Безусловные рефлексы новорожденных
Безусловные рефлексы новорожденных Механика.қатты денелердің айналмалы қозғалыс динамикасы,негізгі теңдеуі
Механика.қатты денелердің айналмалы қозғалыс динамикасы,негізгі теңдеуі Сопровождение лиц с нарушением зрения в образовательной среде ВУЗа
Сопровождение лиц с нарушением зрения в образовательной среде ВУЗа Эндоваскулярная хирургия в кардиологии
Эндоваскулярная хирургия в кардиологии Современные принципы антихеликобактерной терапии
Современные принципы антихеликобактерной терапии Молодёжь XXI века против СПИДа
Молодёжь XXI века против СПИДа Технология изготовления цельнолитой коронки на моляр
Технология изготовления цельнолитой коронки на моляр Рак молочной железы. Предраковые заболевания. Классификация РМЖ. Клиническая картина
Рак молочной железы. Предраковые заболевания. Классификация РМЖ. Клиническая картина Противосудорожные средства
Противосудорожные средства Лекция 1 Перикардит
Лекция 1 Перикардит Мониторинг в медицине. Анестезия и гемодинамика
Мониторинг в медицине. Анестезия и гемодинамика Оценка функционального состояния пациента
Оценка функционального состояния пациента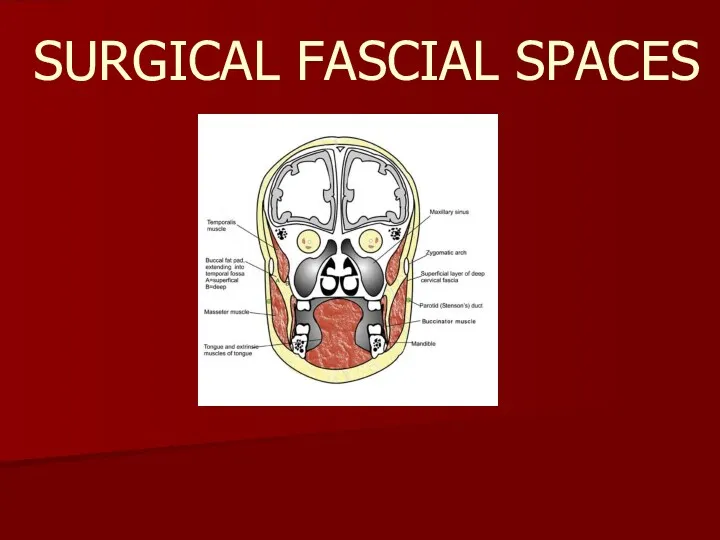 Surgical fascial spaces
Surgical fascial spaces Антипсихотические средства. Антидепрессанты. Анксиолитики. Седативные препараты
Антипсихотические средства. Антидепрессанты. Анксиолитики. Седативные препараты Ботулизм. Эпидемиология ботулизма
Ботулизм. Эпидемиология ботулизма Анемии (железодефицитные, билководефицитные, фолиеводефицитные)
Анемии (железодефицитные, билководефицитные, фолиеводефицитные) ХТІ, сальмонельоз, ботулізм
ХТІ, сальмонельоз, ботулізм Обезболивающие препараты: польза и вред
Обезболивающие препараты: польза и вред Патология красной крови. Диагностика анемий. Терминология. Классификация
Патология красной крови. Диагностика анемий. Терминология. Классификация Вирусные гепатиты В, С, D
Вирусные гепатиты В, С, D Лапароскопическая холецистэктомия
Лапароскопическая холецистэктомия Балалардағы пародонт аурулары кезіндегі гигиена ролі
Балалардағы пародонт аурулары кезіндегі гигиена ролі Ятрогенные расстройства
Ятрогенные расстройства Кровотечение
Кровотечение