Содержание
- 2. وزاده بسطة فى العلم والجسم (الجمع بين العلم والقوة الجسدية ) يا أبت استأجره إن خير
- 3. “ If we could give every individual the right amount of nourishment and exercises , not
- 4. Learning Objectives State an introduction Define sport medicine Classify sport injuries Enumerate risk factors Mention phases
- 5. Introduction Millions of people participate daily in sports. Sports not 100% safe. Shoulder more male. Knee
- 6. Over years tendons and ligaments elasticity decrease at age of 30 years. Muscle strength declines at
- 7. Fatalities Death is much more likely in sports than in boxing or football. equestrian
- 8. Air Sports and Mountaineering are the sports in which traumatic death are most common
- 9. Definition : Medical practices encompass the following elements:- preparation and training, prevention of injuries, diagnosis, treatment,
- 10. Classification: Acute: - Contact and non-contact. Chronic: - Overuse. Or: - According to their causes: -
- 11. Direct injuries: Caused by forces generated from outside the body, at the point of impact. Result
- 12. Indirect injuries: Caused by indirect force applied to the injured part away from the point of
- 13. Overuse injuries: Caused by repetitive microtrauma overloads the capacity of the tissue to repair itself. Result
- 14. Soft tissue injuries: - Acute. - Chronic. Include damage to : - Skin. - Muscle. -
- 15. Hard tissue injuries: Cause damage to : - Bones and teeth.
- 16. Sporting Injuries come from three main areas * Human (54%) - Muscles weakness and imbalance. -
- 17. Risk Factors of Sport Injuries 1- intrinsic (inherent to the athlete) Not modifiable (age, gender, genetics.)
- 18. PHASES OF HEALING
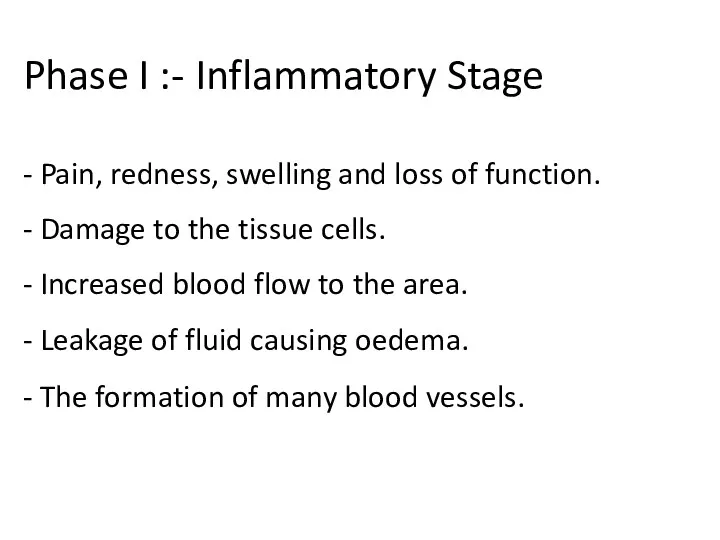
- 19. Phase I :- Inflammatory Stage - Pain, redness, swelling and loss of function. - Damage to
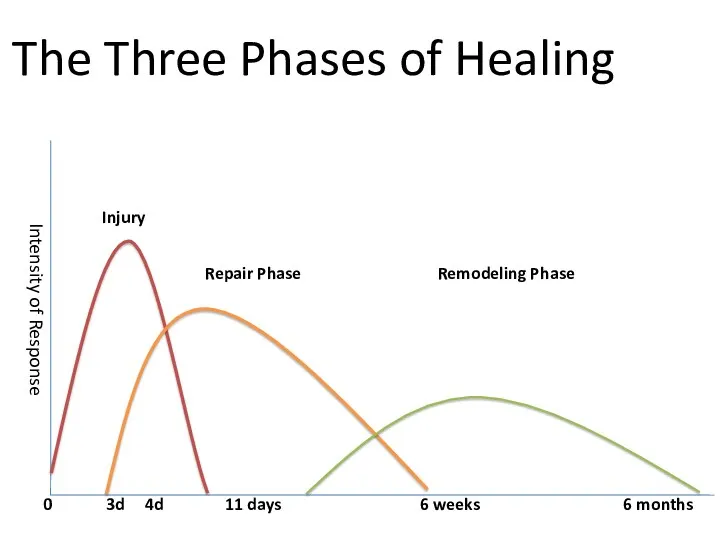
- 20. Phase II:- the repair and regenerative stage Three days to six weeks - The elimination of
- 21. Phase III:- the remodeling stage Six weeks to many months - Increased production of scar tissue.
- 22. The Three Phases of Healing
- 23. Recognition of injuries 1- Life threatening conditions. 2- Non life threatening conditions.
- 24. Proper prehospital care minimizing the extent of injuries: -Identify injuries - Positioning. - Splinting. - Analgesics
- 25. 1. Head 2. Maxillofacial 3. C. Spine and neck 4. Chest 5. Abdomen 6. Perineum, rectum
- 26. Classification of muscloskeletal injuries: 1. Life threatening injuries. 2. limb threatening injuries. 3. Isolated, non-life- or
- 27. Morbidity and Mortality - Remember FEW musculoskeletal injuries are life threatening. - Do Not be distracted
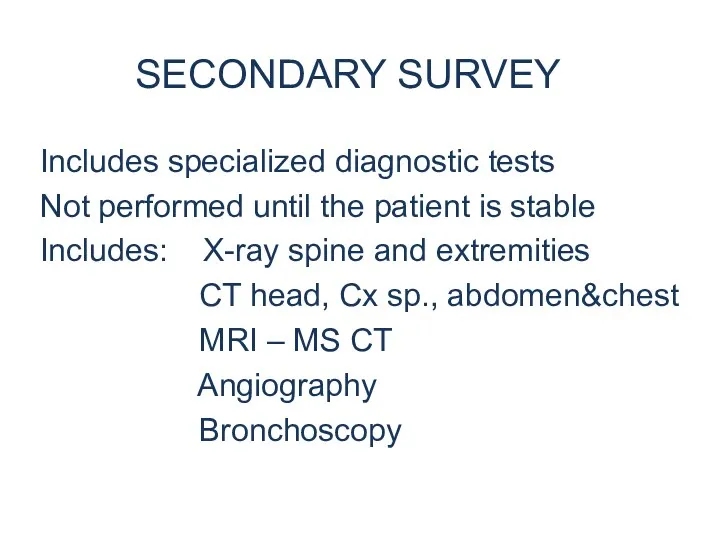
- 28. SECONDARY SURVEY Includes specialized diagnostic tests Not performed until the patient is stable Includes: X-ray spine
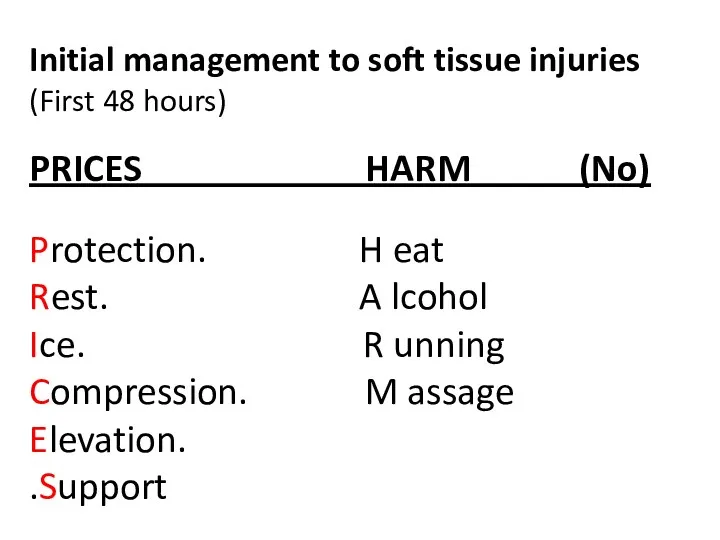
- 29. Initial management to soft tissue injuries (First 48 hours) PRICES HARM (No) Protection. H eat Rest.
- 30. Evaluation of non-life threatening conditions 2 formats utilized: 1. H.O.P.S. ( History, Observation, Palpation, Special tests)
- 31. Multiple injuries: - Resuscitation. - 1st manage: * DX. * Fr. with vascular injuries. * Open
- 32. Assorted examples of sports injuries
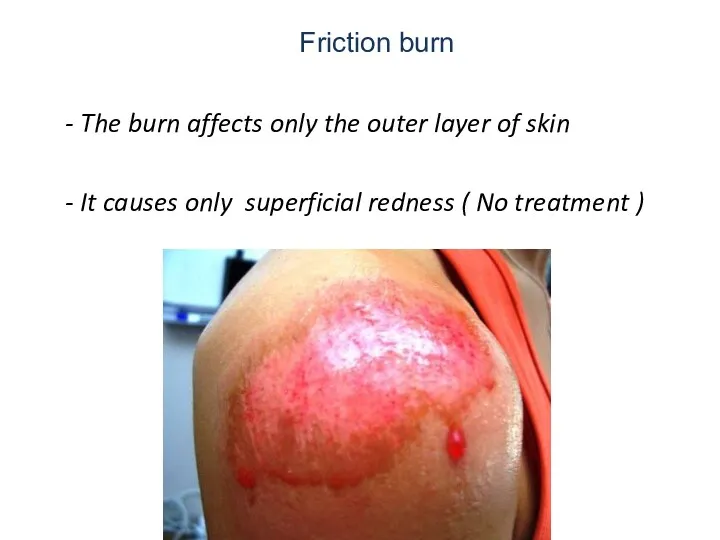
- 33. Friction burn - The burn affects only the outer layer of skin - It causes only
- 34. Muscle cramp Athletes may suffer cramp in a muscle during exertion Any factor which impairs circulation
- 35. Sharp pain in the upper abdomen ( rt . or lt . ) when sporting activity
- 36. Causes : Essentially unknown Some studies indicate mechanical effect may trigger it . The connective tissue
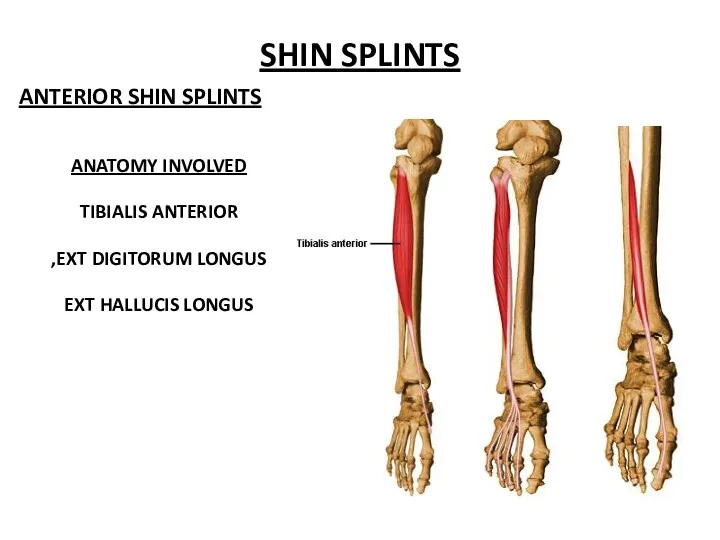
- 37. SHIN SPLINTS ANATOMY INVOLVED TIBIALIS ANTERIOR EXT DIGITORUM LONGUS, EXT HALLUCIS LONGUS ANTERIOR SHIN SPLINTS
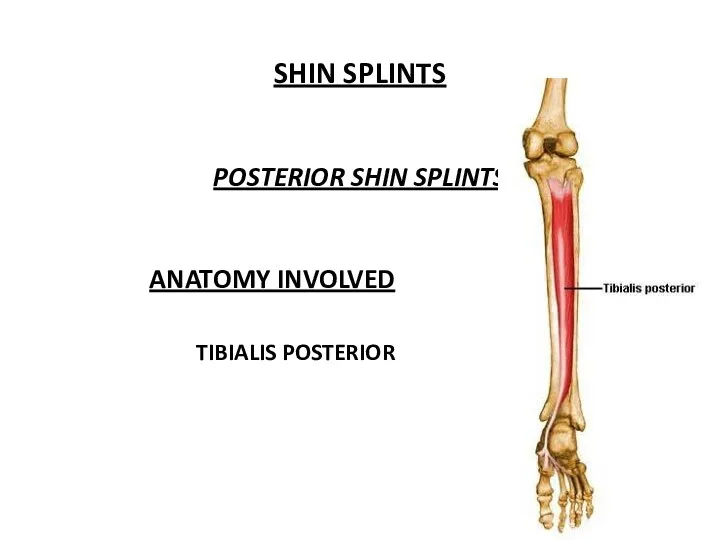
- 38. SHIN SPLINTS POSTERIOR SHIN SPLINTS ANATOMY INVOLVED TIBIALIS POSTERIOR
- 39. SHIN SPLINTS Common Causes Overuse Injury Aggressive Running, Jumping Activities Increase mileage or intensity too quickly
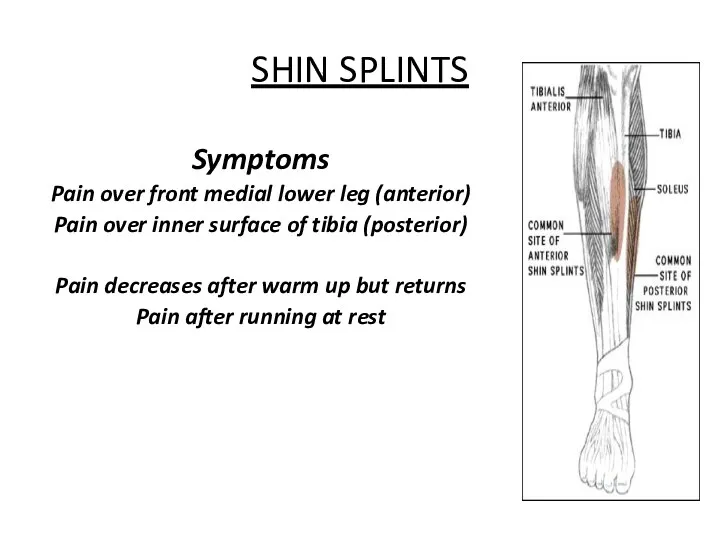
- 40. SHIN SPLINTS Symptoms Pain over front medial lower leg (anterior) Pain over inner surface of tibia
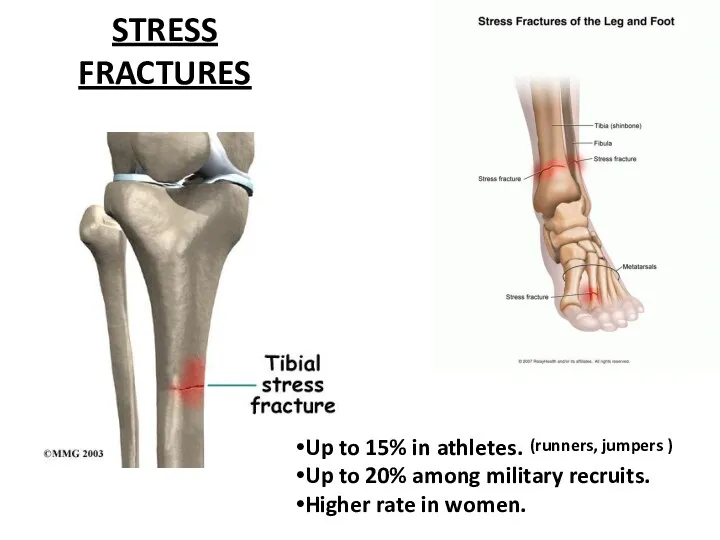
- 41. STRESS FRACTURES Up to 15% in athletes. Up to 20% among military recruits. Higher rate in
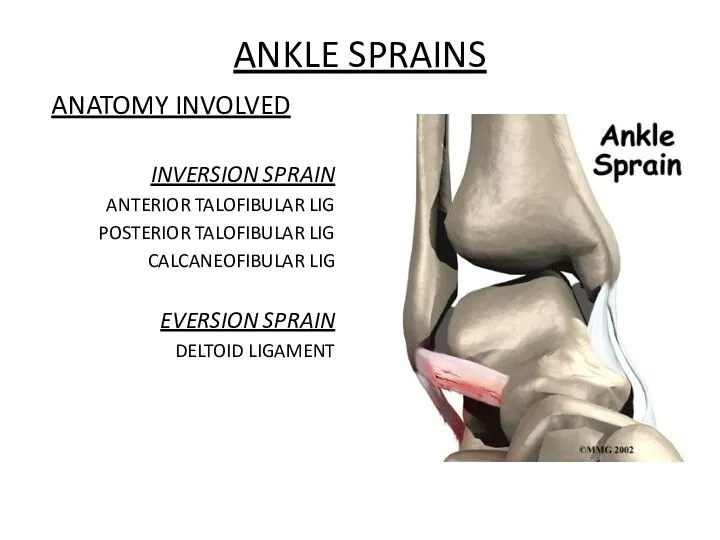
- 42. ANKLE SPRAINS ANATOMY INVOLVED INVERSION SPRAIN ANTERIOR TALOFIBULAR LIG POSTERIOR TALOFIBULAR LIG CALCANEOFIBULAR LIG EVERSION SPRAIN
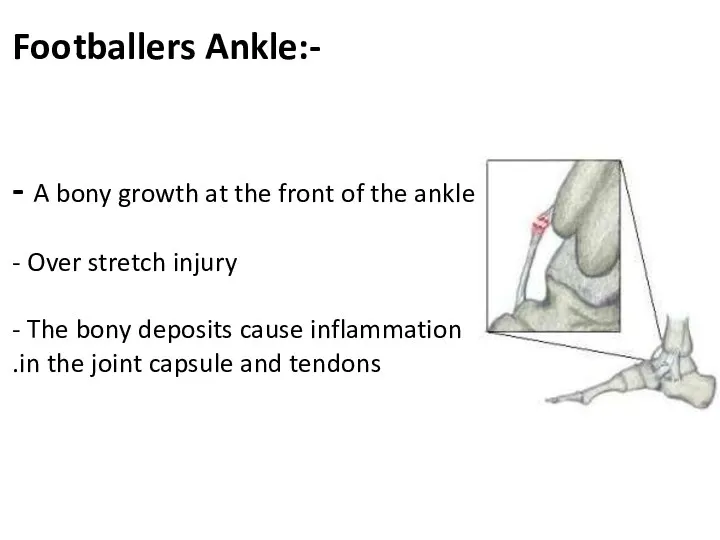
- 43. Footballers Ankle:- - A bony growth at the front of the ankle - Over stretch injury
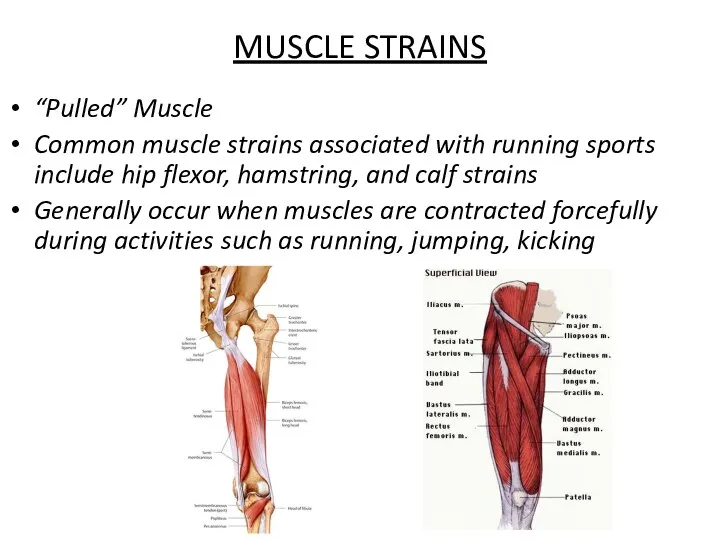
- 44. MUSCLE STRAINS “Pulled” Muscle Common muscle strains associated with running sports include hip flexor, hamstring, and
- 45. Sports Injuries regions Foot and ankle Injuries Plantar Fasciitis Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Broken Toe Sprained ankle
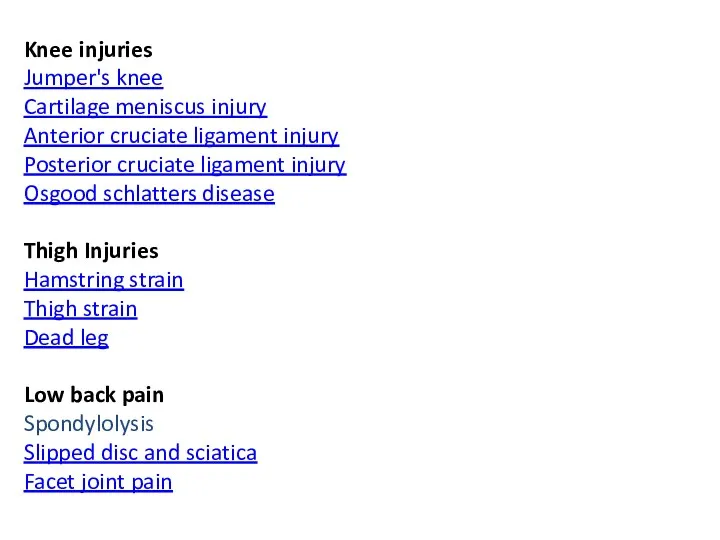
- 46. Knee injuries Jumper's knee Cartilage meniscus injury Anterior cruciate ligament injury Posterior cruciate ligament injury Osgood
- 47. Shoulder injuries Shoulder dislocation Rotator cuff injury AC joint sprain Frozen shoulder Elbow and wrist injuries
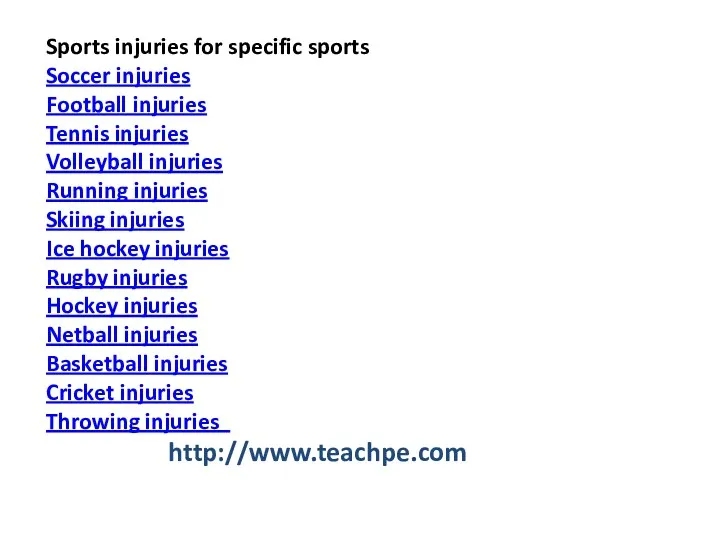
- 48. Sports injuries for specific sports Soccer injuries Football injuries Tennis injuries Volleyball injuries Running injuries Skiing
- 49. 10 Commandments for prevention 1- Know the rules of the game. 2- Normal muscle strength and
- 50. Warm up They should warm up with 5-10 minutes of light activity, stretching and specific skills
- 51. Stretching Performed during warm up and cool down. Athlete should NOT feel pain Hold stretch 30
- 52. Cool Down Athletes should gradually reduce activity for 5-10 minutes followed by stretching. Aims: - Prevents
- 53. Sporting Grounds Be sure of the following:- - level and firm - Free from obstructions. -
- 54. Sports are fun! The goal is a pain and injury free balanced fitness program for all
- 55. Learning Objectives State an introduction Define sport medicine Classify sport injuries Enumerate risk factors Mention phases
- 57. Скачать презентацию








































 Несеп зәр шығару жүйесі
Несеп зәр шығару жүйесі Жақ-бет аймағындағы микротамырлық хирургияның қолдану қағидалары
Жақ-бет аймағындағы микротамырлық хирургияның қолдану қағидалары Особо опасные инфекции (ООИ)
Особо опасные инфекции (ООИ) Патогенные анаэробы
Патогенные анаэробы Түрлі гистогенезді қатерлі ісіктер
Түрлі гистогенезді қатерлі ісіктер Нормальный менструальный цикл и его регуляция
Нормальный менструальный цикл и его регуляция Острые отравления наркотиками
Острые отравления наркотиками Малярия
Малярия Клиническая фармакология витаминов
Клиническая фармакология витаминов Отек Квинке
Отек Квинке Мениски. Шов менисков или резекция? Что выбрать при повреждениях менисков коленного сустава?
Мениски. Шов менисков или резекция? Что выбрать при повреждениях менисков коленного сустава? Уход за пациентами с заболеваниями сердечно-сосудистой системы
Уход за пациентами с заболеваниями сердечно-сосудистой системы Сүйек тінінің жасқа байланысты ерекшеліктері
Сүйек тінінің жасқа байланысты ерекшеліктері Анатомическое строение постоянных зубов
Анатомическое строение постоянных зубов Круглі черви – збудники захворювань людини
Круглі черви – збудники захворювань людини Факторы, влияющие на печень при ВИЧ-инфекции
Факторы, влияющие на печень при ВИЧ-инфекции Эпидемиология сахарного диабета (в РФ, субъектах РФ и других странах)
Эпидемиология сахарного диабета (в РФ, субъектах РФ и других странах) Психофизические особенности детей с задержкой психического развития и умственной отсталостью
Психофизические особенности детей с задержкой психического развития и умственной отсталостью Изосерологическая несовместимость крови матери и плода. Гемолитическая болезнь плода и новорождённого
Изосерологическая несовместимость крови матери и плода. Гемолитическая болезнь плода и новорождённого Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. - один из лидеров мировой фармацевтической отрасли
Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. - один из лидеров мировой фармацевтической отрасли Әріптестермен өзара қарым-қатынастың ерекшеліктері
Әріптестермен өзара қарым-қатынастың ерекшеліктері Мамандандырылған және арнайы мамандандырылған медициналық көмек
Мамандандырылған және арнайы мамандандырылған медициналық көмек Средства, влияющие на тонус миометрия. Оральные контрацептивы
Средства, влияющие на тонус миометрия. Оральные контрацептивы Ембріогенез, його клінічне значення. Артеріальні особливості гіпертензії. Анатомо-фізіологічні функціонування;
Ембріогенез, його клінічне значення. Артеріальні особливості гіпертензії. Анатомо-фізіологічні функціонування; Внутрибольничные инфекции. Меры профилактики
Внутрибольничные инфекции. Меры профилактики Знать, чтобы жить…. Что такое ВИЧ и СПИД?
Знать, чтобы жить…. Что такое ВИЧ и СПИД? Хондропротекторы. Биофосфонаты. Препараты кальция
Хондропротекторы. Биофосфонаты. Препараты кальция Гормональна контрацепція
Гормональна контрацепція