Содержание
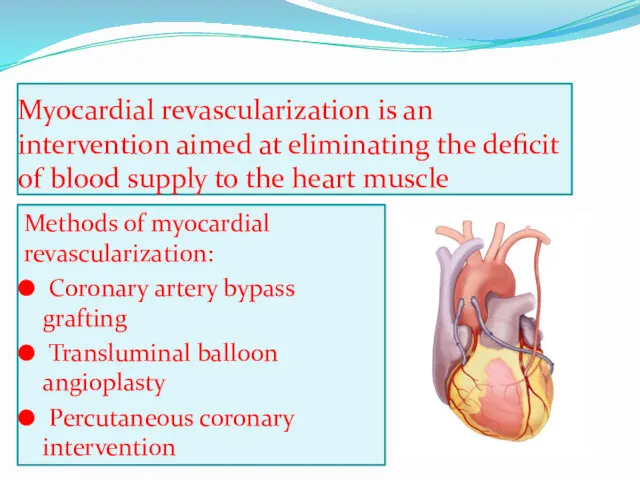
- 2. Myocardial revascularization is an intervention aimed at eliminating the deficit of blood supply to the heart
- 3. Main indications for myocardial revascularization: severe angina, poorly amenable to medical treatment stenosis of all coronary
- 4. Relative contraindications to myocardial revascularization: diffuse lesion of all coronary arteries a sharp decrease in left
- 5. Preparation of the patient for surgery The last meal in the evening, after midnight it is
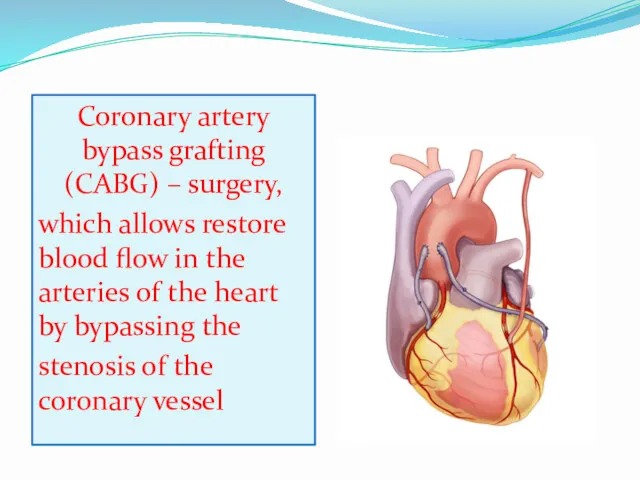
- 6. Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) – surgery, which allows restore blood flow in the arteries of
- 7. Methods for creating a workaround: mammarocoronary anastomosis coronary artery bypass with autovenous or autoarterial graft
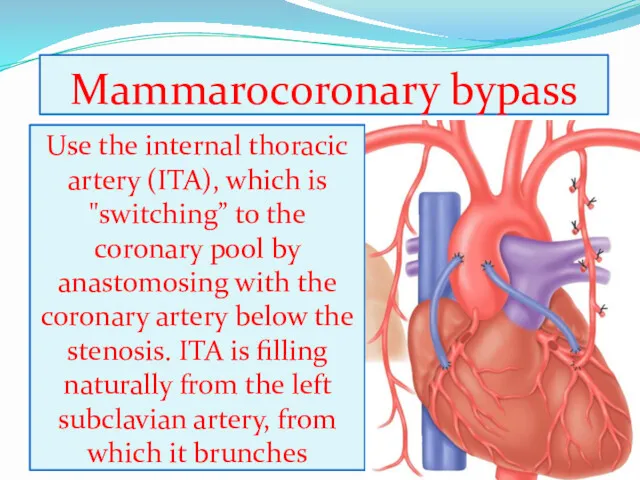
- 8. Mammarocoronary bypass Use the internal thoracic artery (ITA), which is "switching” to the coronary pool by
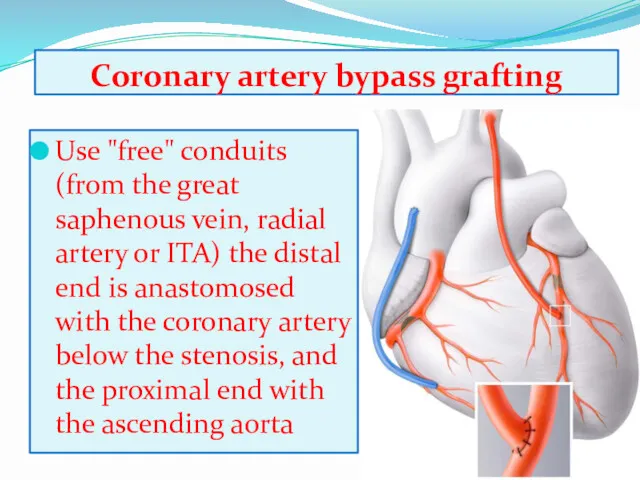
- 9. Coronary artery bypass grafting Use "free" conduits (from the great saphenous vein, radial artery or ITA)
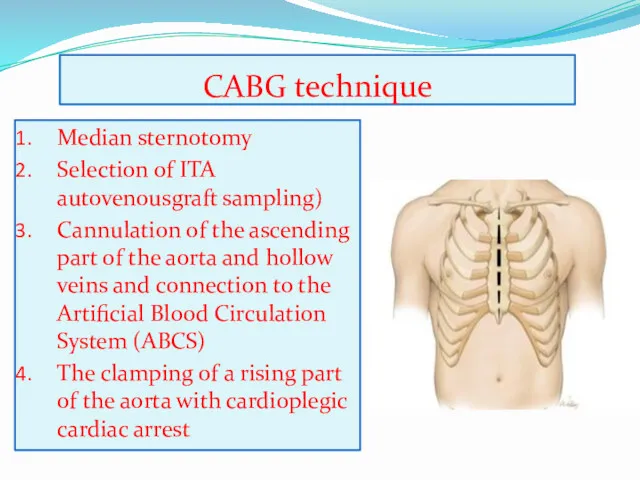
- 10. CABG technique Median sternotomy Selection of ITA autovenousgraft sampling) Cannulation of the ascending part of the
- 11. Imposition of distal anastomoses with coronary arteries Removing the clamp from the ascending part of the
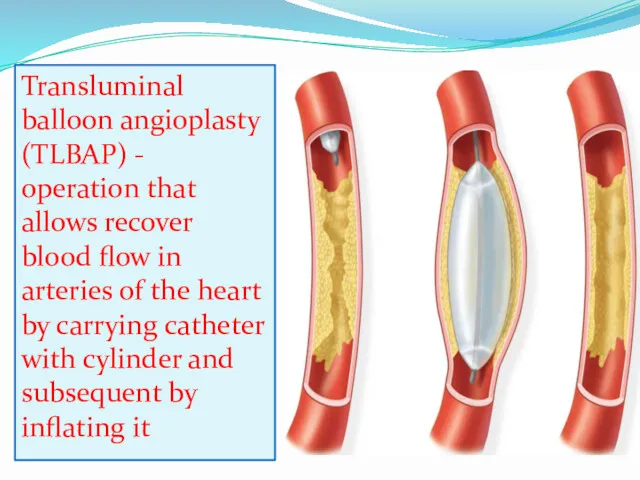
- 12. Transluminal balloon angioplasty (TLBAP) - operation that allows recover blood flow in arteries of the heart
- 13. The progress of the operation Restoration of patency of blood flow is carried out under radiological
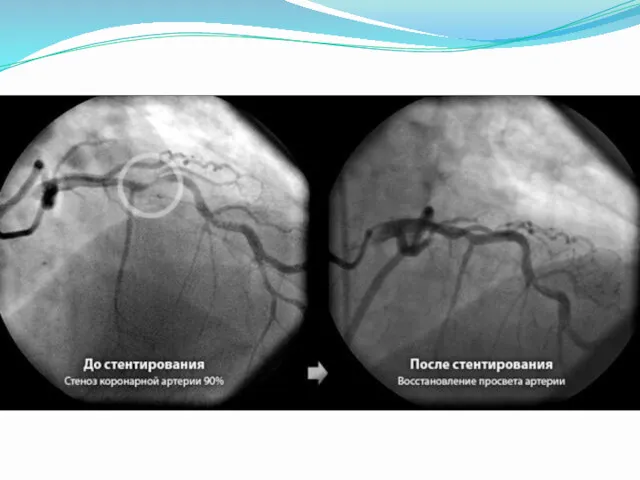
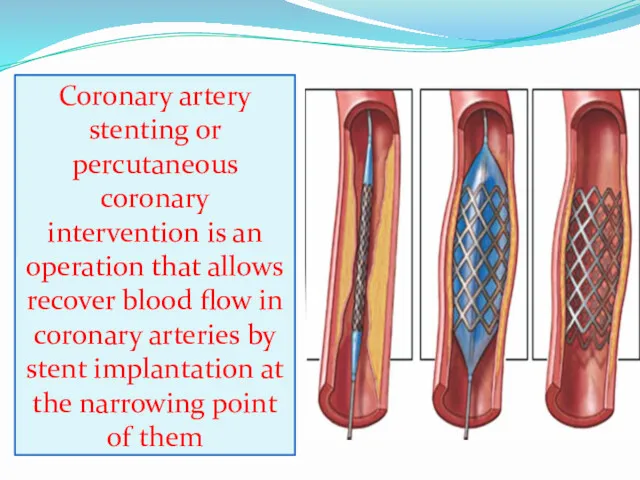
- 15. Coronary artery stenting or percutaneous coronary intervention is an operation that allows recover blood flow in
- 16. The progress of the operation A puncture is performed in the wrist or hip area The
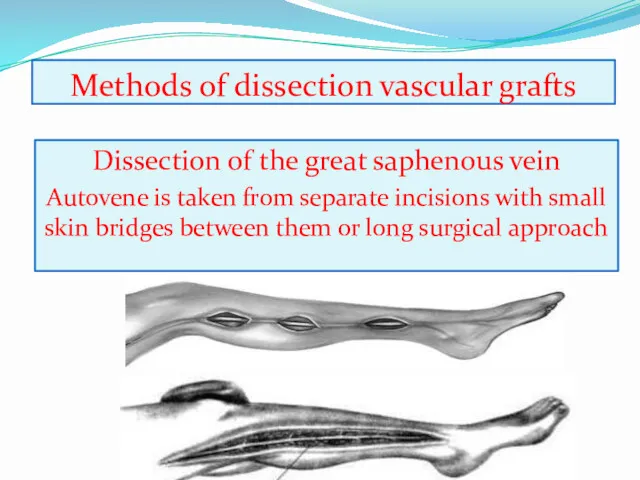
- 17. Methods of dissection vascular grafts Dissection of the great saphenous vein Autovene is taken from separate
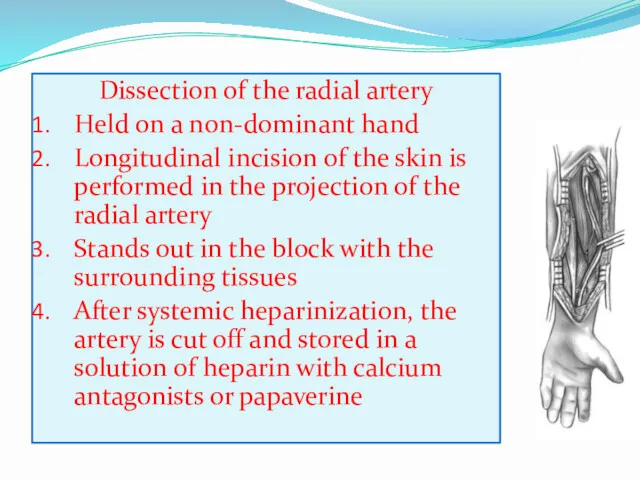
- 18. Dissection of the radial artery Held on a non-dominant hand Longitudinal incision of the skin is
- 19. Technique of internal thoracic artery dissection Sternotomy Asymmetric expansion of the wound with a retractor The
- 20. Technique of gastro-omentum artery dissection Sternotomy Upper median laparotomy The artery is visualized and isolated from
- 21. Lifestyle after surgery Dietary food Breathing exercises-the patient is offered a balloon, inflating which, the patient
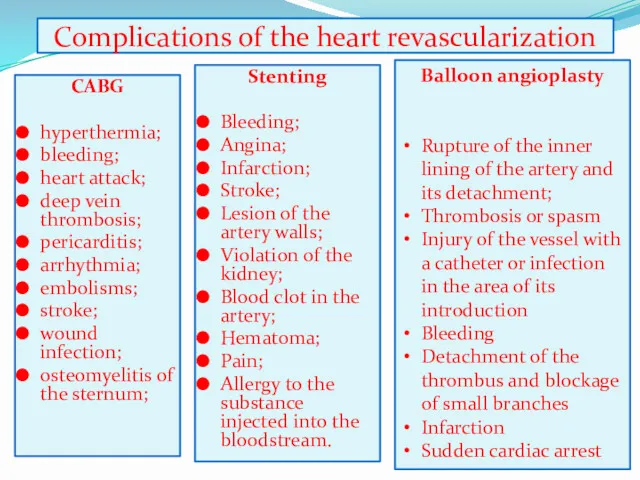
- 22. Complications of the heart revascularization CABG hyperthermia; bleeding; heart attack; deep vein thrombosis; pericarditis; arrhythmia; embolisms;
- 24. Скачать презентацию









 Эндокринологическая аллея. Остановка Музей изобразительных искусств
Эндокринологическая аллея. Остановка Музей изобразительных искусств Cтандарты в производстве медицинских изделий
Cтандарты в производстве медицинских изделий Язвенная болезнь желудка и 12-перстной кишки
Язвенная болезнь желудка и 12-перстной кишки Поражение мозжечка
Поражение мозжечка Фагоцитоз. Микрофаги и макрофаги
Фагоцитоз. Микрофаги и макрофаги Аяқ іріңі жаралары бар науқастарды емдеуде, озонды оттегі қоспаларын пайдалану тиімділігін бағалау
Аяқ іріңі жаралары бар науқастарды емдеуде, озонды оттегі қоспаларын пайдалану тиімділігін бағалау Информация для младшего мед. персонала противотуберкулёзного стационара
Информация для младшего мед. персонала противотуберкулёзного стационара Гипогликемия и гипергликемия у новорожденных
Гипогликемия и гипергликемия у новорожденных Гигиенические требования к выбору и планировке больничного участка. Системы строительства больниц, их преимущества и недостатки
Гигиенические требования к выбору и планировке больничного участка. Системы строительства больниц, их преимущества и недостатки Легионеллы. Морфология
Легионеллы. Морфология Стоматология. Жалобы на эстетический дефект
Стоматология. Жалобы на эстетический дефект Патологиялық анатомия. Ісіктер жөнінде жалпы ілім
Патологиялық анатомия. Ісіктер жөнінде жалпы ілім Местная хирургическая патология и ее лечение (раны)
Местная хирургическая патология и ее лечение (раны) Поздний гестоз беременных
Поздний гестоз беременных Врожденный сифилис
Врожденный сифилис Caries
Caries Туберкулинодиагностика
Туберкулинодиагностика Технология гомеопатических таблеток
Технология гомеопатических таблеток Оказание медицинской помощи при одноплодных родах в затылочном предлежании во внебольничных условиях
Оказание медицинской помощи при одноплодных родах в затылочном предлежании во внебольничных условиях Проблема биосовместимости (лекция 3)
Проблема биосовместимости (лекция 3) Суппозитории
Суппозитории Өкпе туберкулезінің рентгенодиагностикасы
Өкпе туберкулезінің рентгенодиагностикасы Гепатит В
Гепатит В Научно – обоснованная медицинская практика. Поиск доказательной информации. Базы данных
Научно – обоснованная медицинская практика. Поиск доказательной информации. Базы данных Гематологиялық анализаторлар. Анализ нәтижелеріне талдау жасау
Гематологиялық анализаторлар. Анализ нәтижелеріне талдау жасау Ротавирусы. Энтеровирусы. Рабдовирусы. Тогавирусы
Ротавирусы. Энтеровирусы. Рабдовирусы. Тогавирусы Орталық жүйке жүйесінің ноцецептивтік жүйесі. Неврологиядағы ауырсыну синдромы
Орталық жүйке жүйесінің ноцецептивтік жүйесі. Неврологиядағы ауырсыну синдромы Владимир Петрович Филатов 1875 – 1956
Владимир Петрович Филатов 1875 – 1956