Содержание
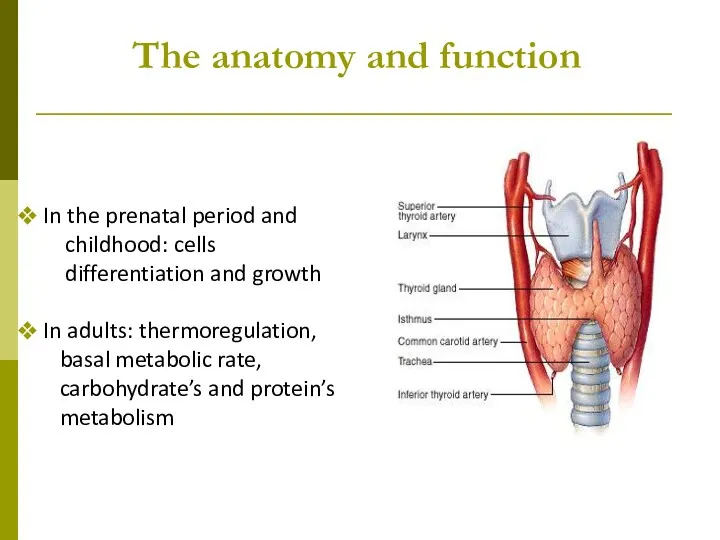
- 2. The anatomy and function In the prenatal period and childhood: cells differentiation and growth In adults:
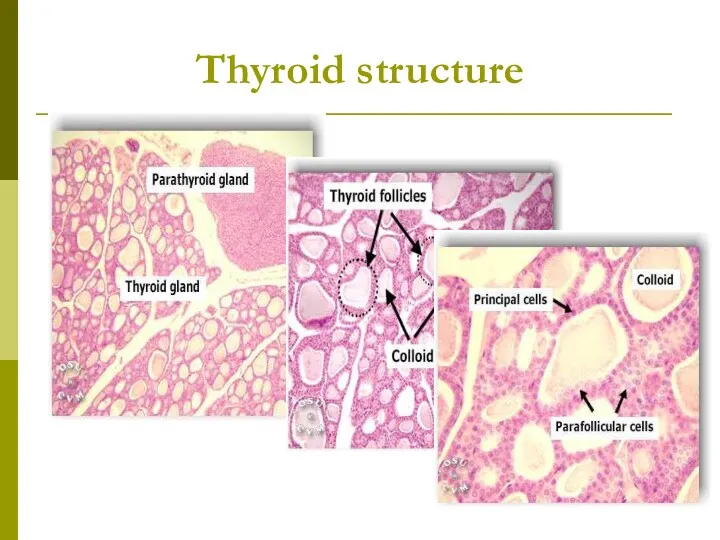
- 3. Thyroid structure
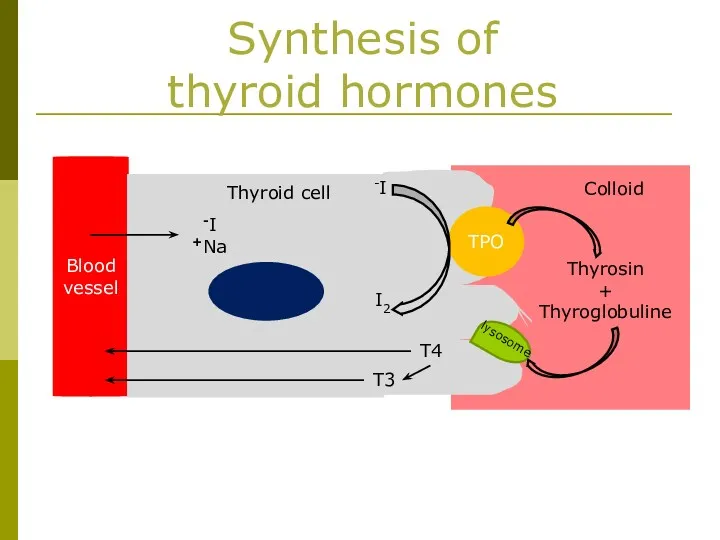
- 4. Blood vessel Thyroid cell I- Na+ TPO I- I2 Thyrosin + Thyroglobuline lysosome T4 T3 Synthesis
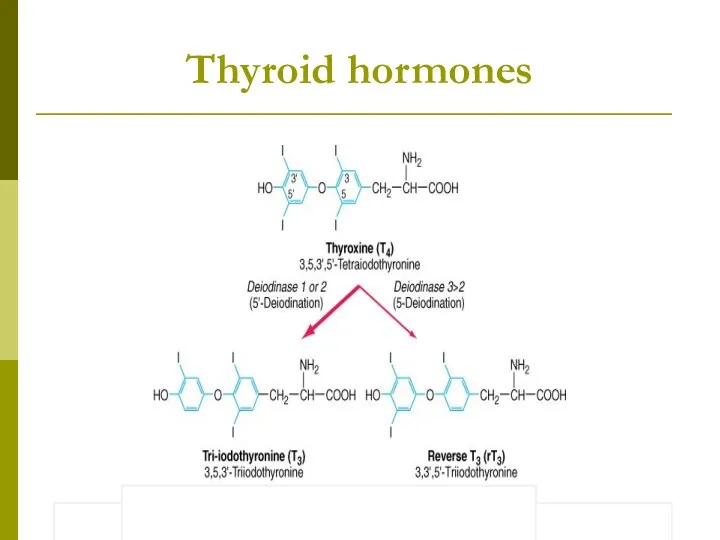
- 5. Thyroid hormones
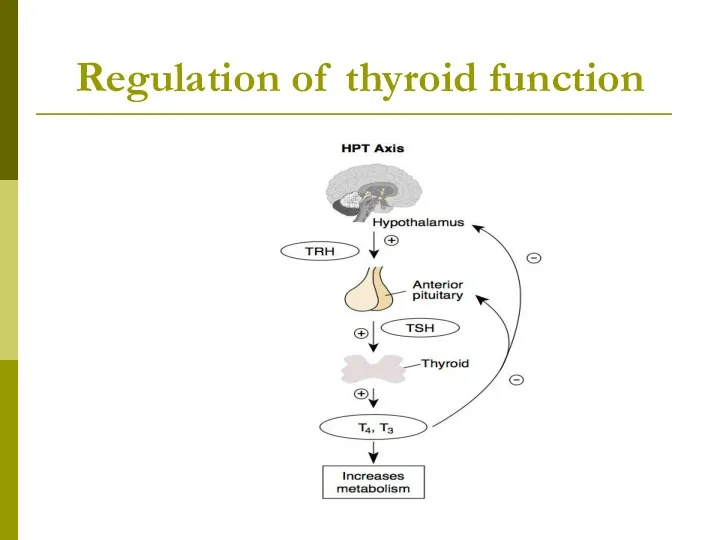
- 6. Regulation of thyroid function
- 7. Hyperthyroidism overproduction of thyroid hormones by the thyroid Thyrotoxicosis the condition of thyroid hormone excess, not
- 8. Subclinical hyperthyroidism: TSH low, FT4&FT3 normal, no symptoms Clinical hyperthyroidism: TSH low, FT4&FT3 high Classification
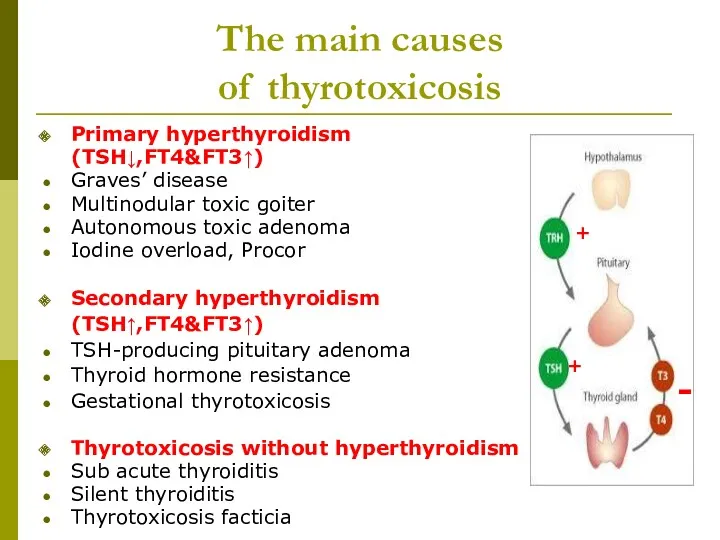
- 9. The main causes of thyrotoxicosis Primary hyperthyroidism (TSH↓,FT4&FT3↑) Graves’ disease Multinodular toxic goiter Autonomous toxic adenoma
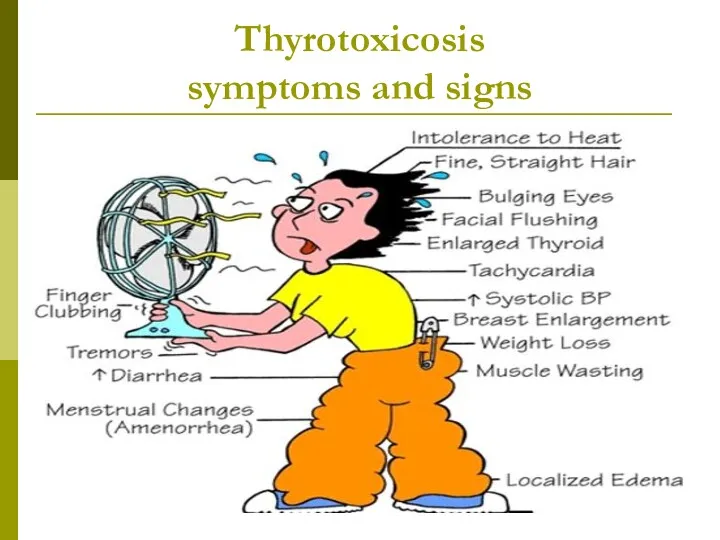
- 10. Thyrotoxicosis symptoms and signs
- 11. Apathetic thyrotoxicosis Old patients Weakness, weight loss Depression, pseudo-dementia Cardiac arrhythmias CHF exac. Pathological fractures
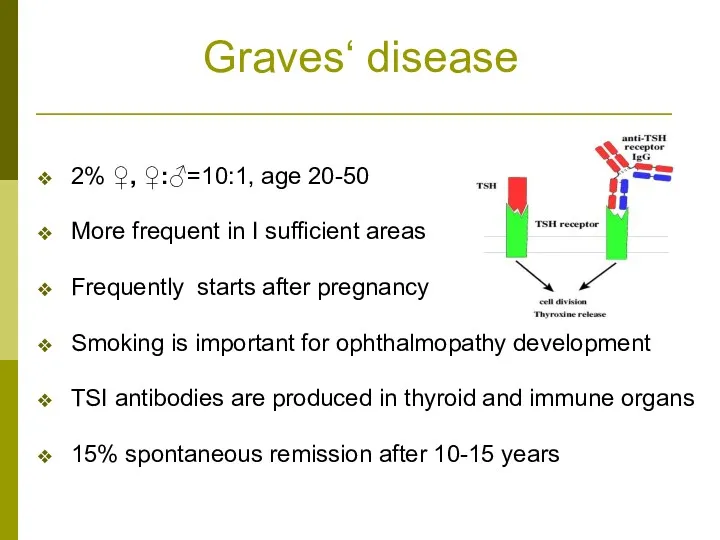
- 12. Graves‘ disease 2% ♀, ♀:♂=10:1, age 20-50 More frequent in I sufficient areas Frequently starts after
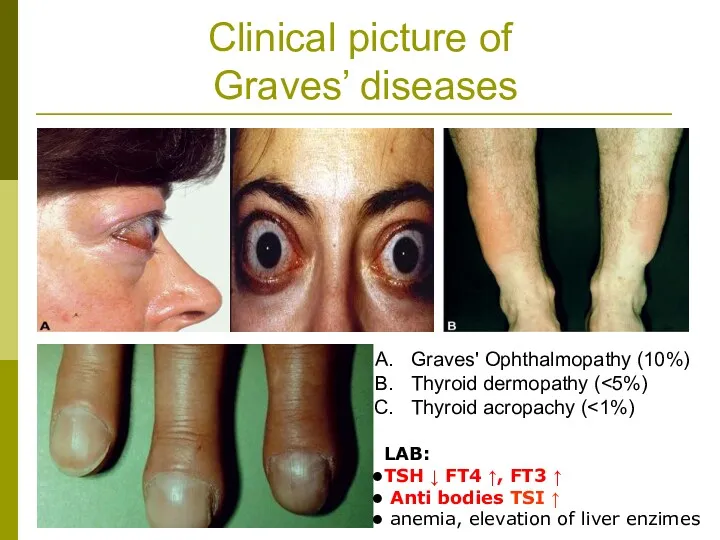
- 13. Clinical picture of Graves’ diseases Graves' Ophthalmopathy (10%) Thyroid dermopathy ( Thyroid acropachy ( LAB: TSH
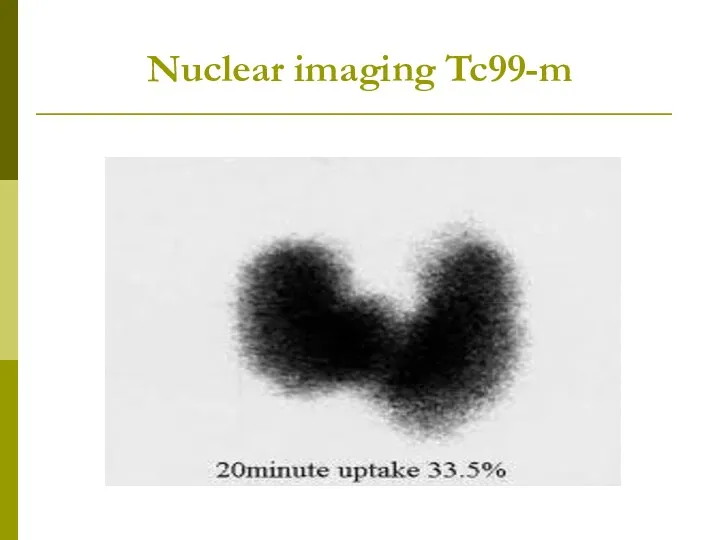
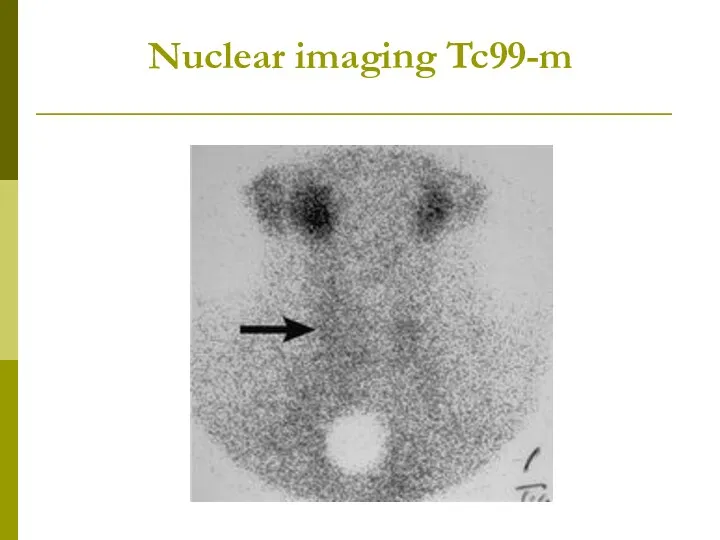
- 14. Nuclear imaging Tc99-m
- 15. Treatment of Graves’ disease Beta-blockers for tachycardia Anti-thyroid drugs (Mercaptizole, PTU) Radio-Iodine ablation Total/subtotal thyroidectomy Ophthalmopathy:
- 16. Multinodular toxic goiter Diffuse thyroid enlargement with autonimic nodules Clinical or subclinical hyperthyroidism Goiter is more
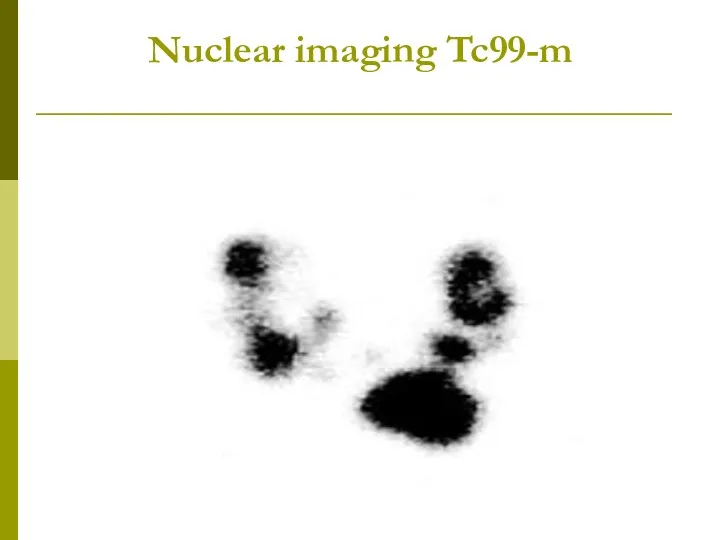
- 17. Nuclear imaging Tc99-m
- 18. Autonomous toxic adenoma Single autonomic thyroid nodule with causes thyrotoxicosis, rest of the thyroid is depressed
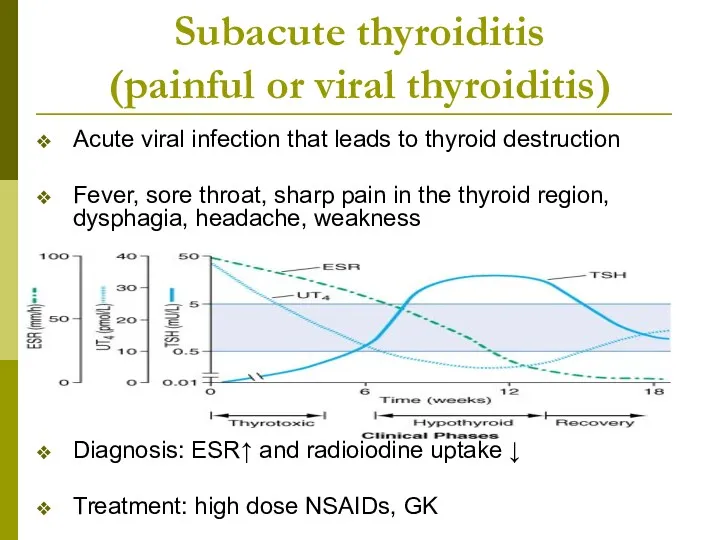
- 19. Subacute thyroiditis (painful or viral thyroiditis) Acute viral infection that leads to thyroid destruction Fever, sore
- 20. Nuclear imaging Tc99-m
- 21. Thyroid Storm (Thyrotoxic Crisis) Sever and life threating TTx Precipitated factor: infection, operation, trauma, labor RAF,
- 23. Hypothyroidism decreased level of thyroid hormones due to low thyroid function
- 24. Subclinical hypothyroidism: TSH high, FT4&FT3 normal, no symptoms Overt (clinical) hypothyroidism: TSH high, FT4&FT3 low Classification
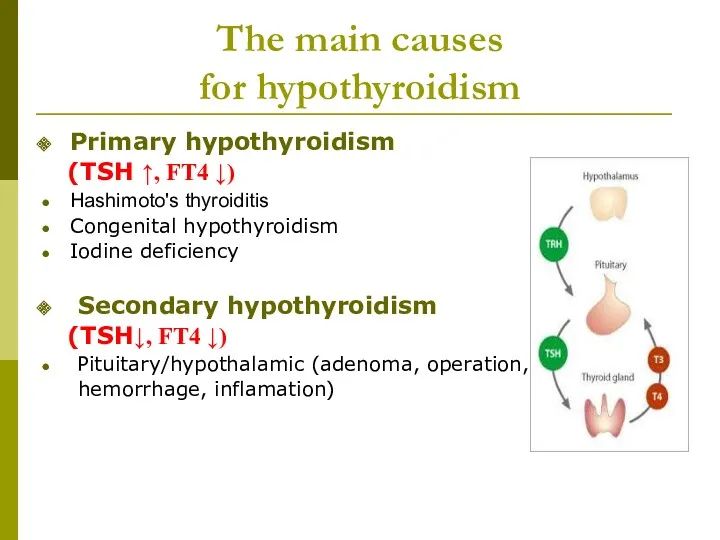
- 25. The main causes for hypothyroidism Primary hypothyroidism (TSH ↑, FT4 ↓) Hashimoto's thyroiditis Congenital hypothyroidism Iodine
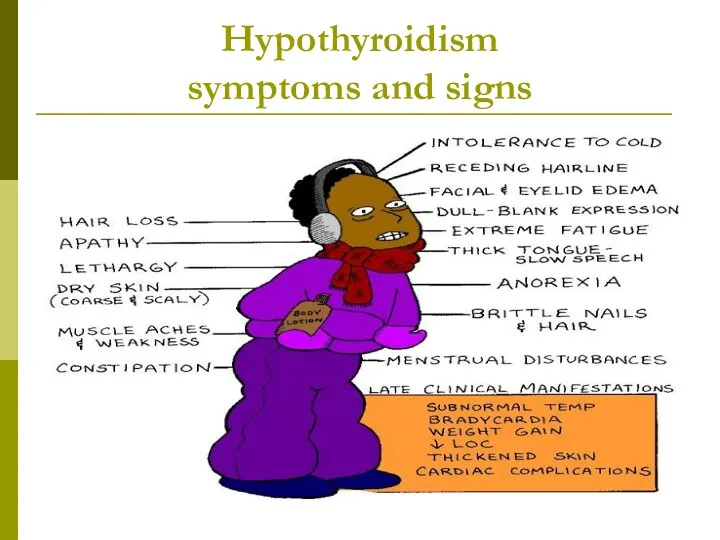
- 26. Hypothyroidism symptoms and signs
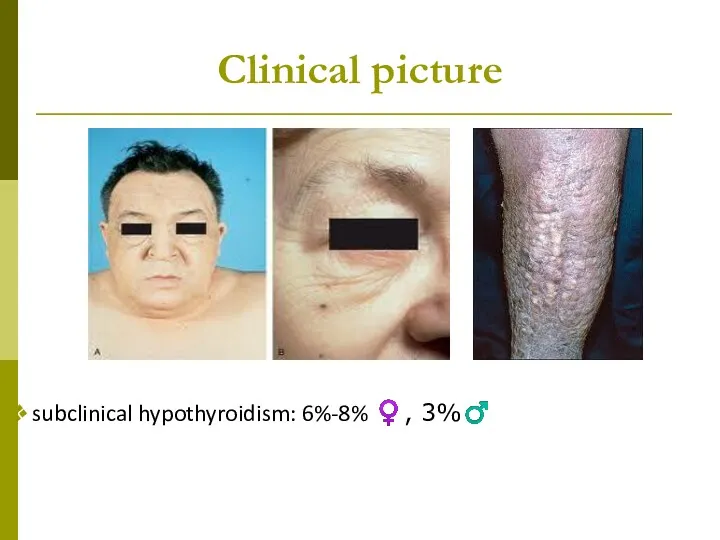
- 27. Clinical picture subclinical hypothyroidism: 6%-8% ♀, 3%♂
- 28. Endemic Iodine deficiency According to WHO: 2 billions people lives in I deficient areas More cases
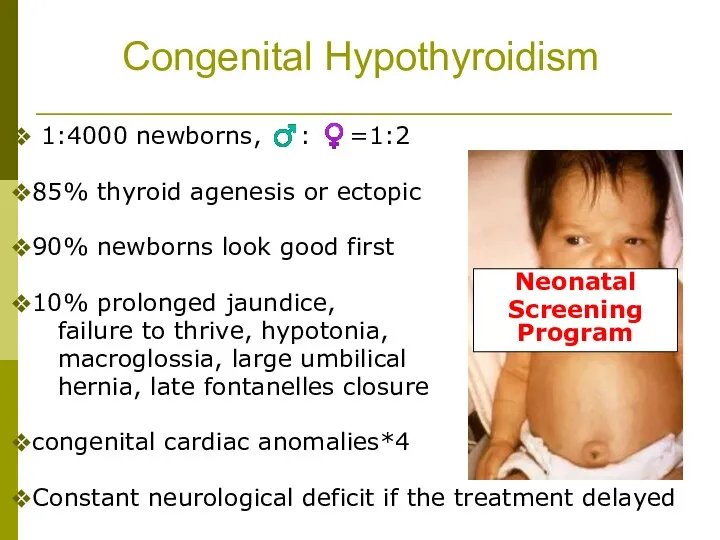
- 29. Congenital Hypothyroidism 1:4000 newborns, ♂: ♀=1:2 85% thyroid agenesis or ectopic 90% newborns look good first
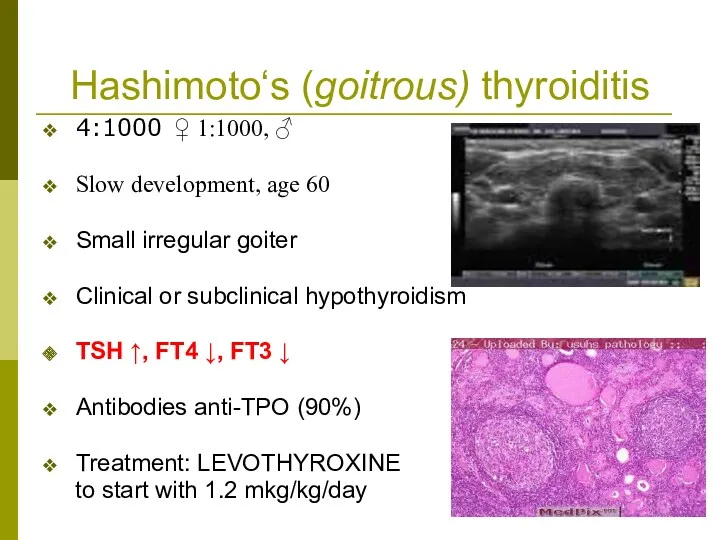
- 30. Hashimoto‘s (goitrous) thyroiditis 4:1000 ♀ 1:1000, ♂ Slow development, age 60 Small irregular goiter Clinical or
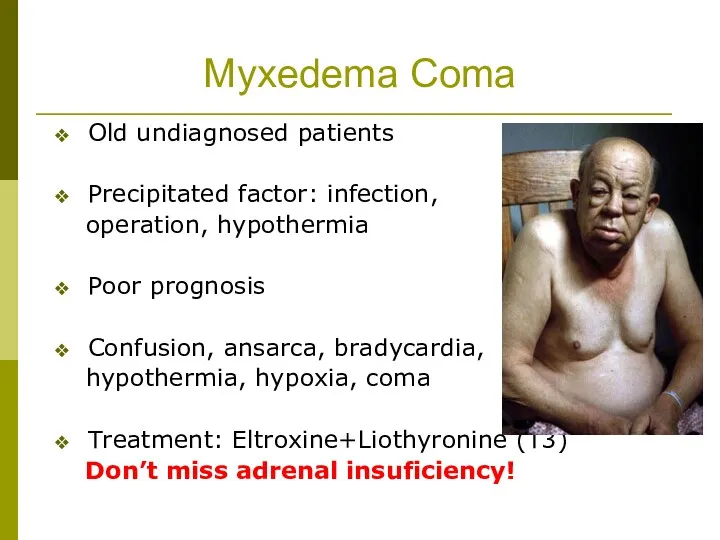
- 31. Myxedema Coma Old undiagnosed patients Precipitated factor: infection, operation, hypothermia Poor prognosis Confusion, ansarca, bradycardia, hypothermia,
- 32. Sick Euthyroid Syndrome Abnormal level of thyroid hormones without thyroidal disorder in critically ill patients TSH
- 34. Скачать презентацию












 8. العنف ضد المرأة
8. العنف ضد المرأة Состояние здоровья и качества жизни детей дошкольного возраста
Состояние здоровья и качества жизни детей дошкольного возраста Планирование выполнения операции Лабиринт III. Пациент, 67 лет
Планирование выполнения операции Лабиринт III. Пациент, 67 лет Система здравоохранения в Южной Корее
Система здравоохранения в Южной Корее Менингококковая инфекция
Менингококковая инфекция Здоровые родители - здоровый ребёнок
Здоровые родители - здоровый ребёнок Черепно-мозговая травма
Черепно-мозговая травма Балалардың церебральды салдануы
Балалардың церебральды салдануы Уход за новорождённым ребёнком после выписки из роддома
Уход за новорождённым ребёнком после выписки из роддома Генитальный эндометриоз
Генитальный эндометриоз Инфекционные болезни и их классификация
Инфекционные болезни и их классификация Врожденная миотония Томсена. Миотоническая дистрофия
Врожденная миотония Томсена. Миотоническая дистрофия Психические расстройства в результате употребления психодислептиков
Психические расстройства в результате употребления психодислептиков Припасовка металлического каркаса мостовидного протеза во рту. Подбор цвета облицовочного материала
Припасовка металлического каркаса мостовидного протеза во рту. Подбор цвета облицовочного материала Бөлменің радиациялық фоны. Радон мен оның өнімдерінің гигиеналық маңызы
Бөлменің радиациялық фоны. Радон мен оның өнімдерінің гигиеналық маңызы Доброякісні пухлини матки та яєчників. (Лекция 2)
Доброякісні пухлини матки та яєчників. (Лекция 2) Психологические особенности беременной женщины
Психологические особенности беременной женщины Доброкачественная гиперплазия предстательной железы (ДГПЖ)
Доброкачественная гиперплазия предстательной железы (ДГПЖ) Современная нейропсихология о локализации высших психических функций ВПФ. (Тема 2)
Современная нейропсихология о локализации высших психических функций ВПФ. (Тема 2) Инфаркт миокарда. Участие медицинской сестры
Инфаркт миокарда. Участие медицинской сестры Анализ вспышки заболеваемости корью в г. Екатеринбург в 2018 году
Анализ вспышки заболеваемости корью в г. Екатеринбург в 2018 году Фракционная мезотерапия
Фракционная мезотерапия Особенности кровоснабжения носа и придаточных пазух носа. Носовые кровотечения
Особенности кровоснабжения носа и придаточных пазух носа. Носовые кровотечения Гельминтозы
Гельминтозы Лекарственные средства
Лекарственные средства Нейроофтальмологические расстройства при ВИЧ-инфекции
Нейроофтальмологические расстройства при ВИЧ-инфекции Шовные материалы
Шовные материалы