Are We Listening?
“In my opinion current training/ curriculum do not provide
the necessary skills to work in truly remote environments where you may need to care for a variety of illness/ injury/ situations for extended periods of time with little/ no support.
Skills need to include advanced diagnosis and treatment, extended care, primary care, aero medical evacuation, crisis and emergency management, occupational hygiene and health, tropical/ exotic disease diagnosis and treatment, aspects of tactical medicine, rescue, training, OHS, cultural and community awareness, advanced pharmacology, telemedicine and so on.”
(LinkedIn)
“Ladies/Gentlemen, Is there such a thing called "Remote Paramedicine"? Can a new subject or at least a syllabus be developed or do we just have to translate what we already know to a specific environment with limited resources?”
“A Grad Dip Remote Para would be sensational.”
“Treating patients that are delivered in 15minutes to 1 hour to an ED, differs greatly in management to patients you must stabilise for hours, perhaps days via telemedicine. There is huge knowledge gap and a course similar to the UK offshore medic course would be beneficial.”
(LinkedIn)













 Острый гнойный средний отит. Мастоидит, антрит у детей. Хронический гнойный средний отит. Внутричерепные осложнения
Острый гнойный средний отит. Мастоидит, антрит у детей. Хронический гнойный средний отит. Внутричерепные осложнения Первая медицинская помощь
Первая медицинская помощь Цитологическая диагностика опухолей кожи. Строение кожи
Цитологическая диагностика опухолей кожи. Строение кожи Уборка помещений в больнице (для санитаров)
Уборка помещений в больнице (для санитаров) Типовые патологические процессы крови: анемии
Типовые патологические процессы крови: анемии Репродуктивті денсаулық
Репродуктивті денсаулық Балалардағы жедел аппендицит
Балалардағы жедел аппендицит Виды массажа в логопедической практике
Виды массажа в логопедической практике Заболевания кишечника
Заболевания кишечника Клиника, диагностика и лечение полинейропатии
Клиника, диагностика и лечение полинейропатии ГКУ Пермского края Центр психолого-педагогической, медицинской и социальной помощи
ГКУ Пермского края Центр психолого-педагогической, медицинской и социальной помощи Туберкулез и беременность
Туберкулез и беременность Вторичный метаболизм
Вторичный метаболизм Лечение сахарного диабета: инсулинотерапия
Лечение сахарного диабета: инсулинотерапия Славные люди нашего края. Андрей Иванович Козлов
Славные люди нашего края. Андрей Иванович Козлов Приклади хвороби органів ШКТ
Приклади хвороби органів ШКТ Клінічна анатомія та фізіологія зовнішнього дихання
Клінічна анатомія та фізіологія зовнішнього дихання Күйістілерді ценуроз бен эхинококкозға аллергиялық зерттеу
Күйістілерді ценуроз бен эхинококкозға аллергиялық зерттеу Спирография. Спирограмма
Спирография. Спирограмма Вплив природних чинників на здоров’я
Вплив природних чинників на здоров’я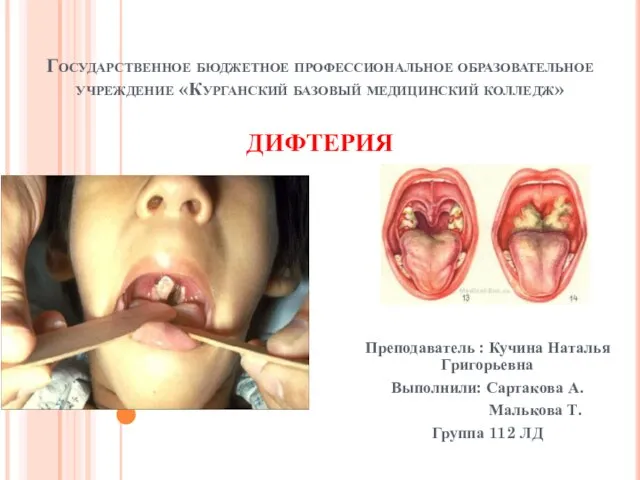 Дифтерия
Дифтерия Хирургическая инфекция
Хирургическая инфекция Лор ағзалардың құрылымы мен топографиясының жасқа байланысты ерекшеліктері
Лор ағзалардың құрылымы мен топографиясының жасқа байланысты ерекшеліктері Дисциплина: микробиология СРС. Антигены
Дисциплина: микробиология СРС. Антигены Миогимнастика как метод профилактики и лечения деформаций зубочелюстной системы ребенка
Миогимнастика как метод профилактики и лечения деформаций зубочелюстной системы ребенка Механизм действия перелитой крови
Механизм действия перелитой крови Поиск информации с использованием фильтров доказательной медицины. Систематические обзоры и мета-анализ статей
Поиск информации с использованием фильтров доказательной медицины. Систематические обзоры и мета-анализ статей Кариес и его профилактика
Кариес и его профилактика