Содержание
- 2. The tooth consists of: crown is the visible part of the tooth, above the gums; root
- 3. Enamel is the hardest and most highly mineralized substance of the body. It is one of
- 4. Dentin is the substance between enamel or cementum and the pulp chamber. It is secreted by
- 5. Cementum is a specialized bone like substance covering the root of a tooth. It is approximately
- 6. The dental pulp is the central part of the tooth filled with soft connective tissue. This
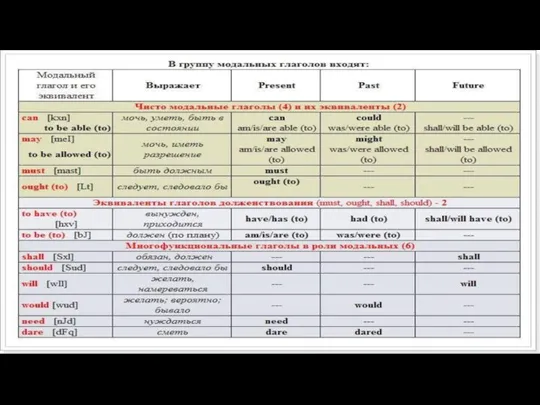
- 7. Модальные глаголы и их эквиваленты Модальные глаголы не выражают действие, а только отношение лица (подлежащего) к
- 8. 1. Модальный глагол May (might - в прошедшем времени) выражает предположение, просьбу, сомнение: May I come
- 9. 2. Модальный глагол Can (could - в прошедшем времени) выражает умственную или физическую возможность: The girl
- 12. Скачать презентацию
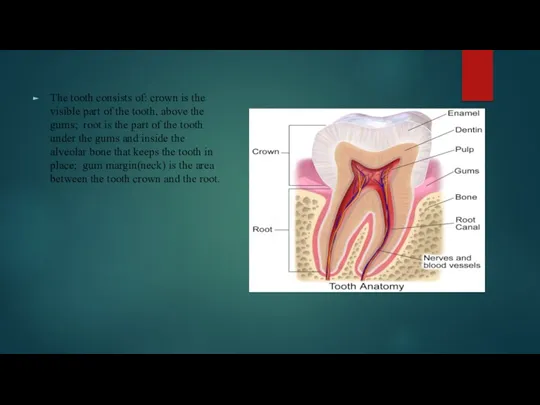
The tooth consists of: crown is the visible part of the
The tooth consists of: crown is the visible part of the
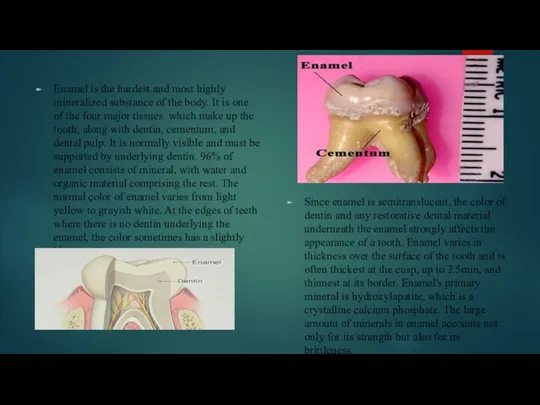
Enamel is the hardest and most highly mineralized substance of the
Enamel is the hardest and most highly mineralized substance of the
Since enamel is semitranslucent, the color of dentin and any restorative dental material underneath the enamel strongly affects the appearance of a tooth. Enamel varies in thickness over the surface of the tooth and is often thickest at the cusp, up to 2.5mm, and thinnest at its border. Enamel's primary mineral is hydroxylapatite, which is a crystalline calcium phosphate. The large amount of minerals in enamel accounts not only for its strength but also for its brittleness.
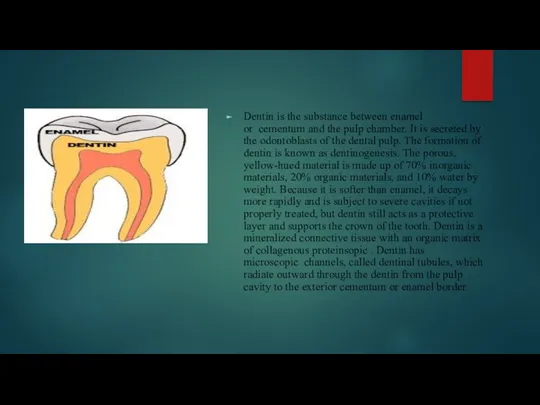
Dentin is the substance between enamel or cementum and the pulp
Dentin is the substance between enamel or cementum and the pulp
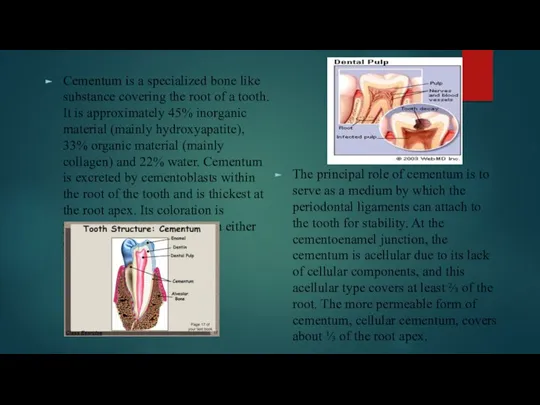
Cementum is a specialized bone like substance covering the root of
Cementum is a specialized bone like substance covering the root of
The principal role of cementum is to serve as a medium by which the periodontal ligaments can attach to the tooth for stability. At the cementoenamel junction, the cementum is acellular due to its lack of cellular components, and this acellular type covers at least ⅔ of the root. The more permeable form of cementum, cellular cementum, covers about ⅓ of the root apex.
The dental pulp is the central part of the tooth filled
The dental pulp is the central part of the tooth filled
Модальные глаголы и их эквиваленты
Модальные глаголы не выражают действие, а только
Модальные глаголы и их эквиваленты
Модальные глаголы не выражают действие, а только
1. Модальный глагол May (might - в прошедшем времени) выражает предположение, просьбу, сомнение:
May I
1. Модальный глагол May (might - в прошедшем времени) выражает предположение, просьбу, сомнение: May I
Эквивалентом модального глагола may является to be allowed to. Употребляется в любом времени, а в будущем только оно и употребляется: When will you be allowed to see him? Когда ты сможешь увидеть его.
2. Модальный глагол Can (could - в прошедшем времени) выражает умственную или физическую возможность:
The
2. Модальный глагол Can (could - в прошедшем времени) выражает умственную или физическую возможность: The
Эквивалентом модального глагола Can является to be able to. Может употребляться в любом времени вместоcan, а в будущем времени только оно и употребляется: I had some free time yesterday, and was able to go to my friend. Вчера у меня было немного свободного времени и я смог навестить друга.



 Сердечно-сосудистые заболевания при ДТЗ
Сердечно-сосудистые заболевания при ДТЗ Загальна геріатрія. Особливості спостереження і догляду за хворими похилого та старечого віку
Загальна геріатрія. Особливості спостереження і догляду за хворими похилого та старечого віку Пластика деформаций лица лоскутами на ножке
Пластика деформаций лица лоскутами на ножке Антипсихотики (нейролептики)
Антипсихотики (нейролептики) Вирустар генетикасы. Вирустық геномның ұйымдасуы. Вирустық геномдардың репликациясы
Вирустар генетикасы. Вирустық геномның ұйымдасуы. Вирустық геномдардың репликациясы Инсулиновая помпа. Болюсное введение
Инсулиновая помпа. Болюсное введение Современные методы обследования больных с опухолями головы и шеи
Современные методы обследования больных с опухолями головы и шеи Прогноз и реабилитация больных в современной детской хирургии
Прогноз и реабилитация больных в современной детской хирургии Воспалительные заболевания позвоночника
Воспалительные заболевания позвоночника Заманауи эндодонттық аспаптар
Заманауи эндодонттық аспаптар Наследственные заболевания человека. Фенилкетонурия
Наследственные заболевания человека. Фенилкетонурия Острый аппендицит
Острый аппендицит Гипоксия
Гипоксия Введение в биологию
Введение в биологию Досье формата CTD
Досье формата CTD Система государственных учреждений, обеспечивающих контроль качества лекарственных средств
Система государственных учреждений, обеспечивающих контроль качества лекарственных средств Хирургические заболевания пищевода
Хирургические заболевания пищевода Зардап шеккендерге психологиялық көмек көрсету дағдыларын қалыптастыру
Зардап шеккендерге психологиялық көмек көрсету дағдыларын қалыптастыру Влияние биоритмов на проявление действия лекарственных средств. Понятие о хронофармакологии
Влияние биоритмов на проявление действия лекарственных средств. Понятие о хронофармакологии Жүйке жүйесі жұлын
Жүйке жүйесі жұлын Роль і значення лікарської етики і деонтології у загальній структурі соціального регулювання медичної діяльності
Роль і значення лікарської етики і деонтології у загальній структурі соціального регулювання медичної діяльності Категория Косметология
Категория Косметология Мониторинг и поддержание дыхания. Капнография
Мониторинг и поддержание дыхания. Капнография Наблюдение здорового ребенка на педиатрическом участке. Группы риска детей раннего возраста
Наблюдение здорового ребенка на педиатрическом участке. Группы риска детей раннего возраста Свойства материалов и их влияние на ткани зуба. Материаловедение. Лекция № 1. Тема 2
Свойства материалов и их влияние на ткани зуба. Материаловедение. Лекция № 1. Тема 2 Контроль работоспособности при занятиях футболом
Контроль работоспособности при занятиях футболом Cестринский уход за новорождёнными при многоплодной беременности
Cестринский уход за новорождёнными при многоплодной беременности Наиболее значимые для наркологической службы регламентирующие документы
Наиболее значимые для наркологической службы регламентирующие документы