Содержание
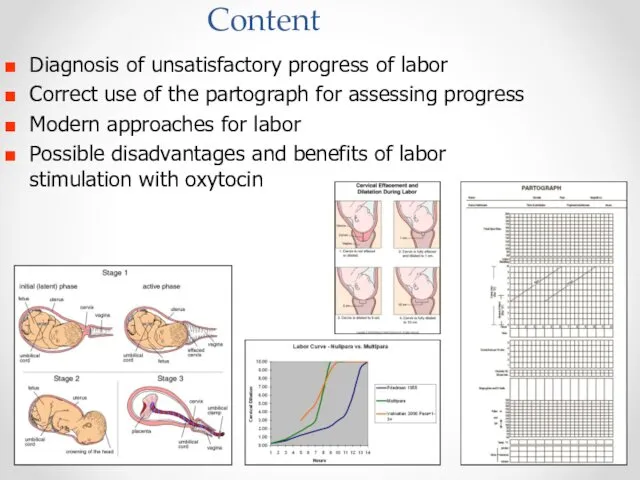
- 2. Content Diagnosis of unsatisfactory progress of labor Correct use of the partograph for assessing progress Modern
- 3. Prevention of the first cesarean section Approximately one in three pregnancies ends with a cesarean section,
- 4. The goal of WHO is to reduce the frequency of the caesarean section. Taking into account
- 5. Periods of labor: Definitions Childbirth is divided into 3 periods The first period: begins with regular
- 6. Unsatisfactory progress of labor: definition There is no consensus in determining the unsatisfactory progress of labor.
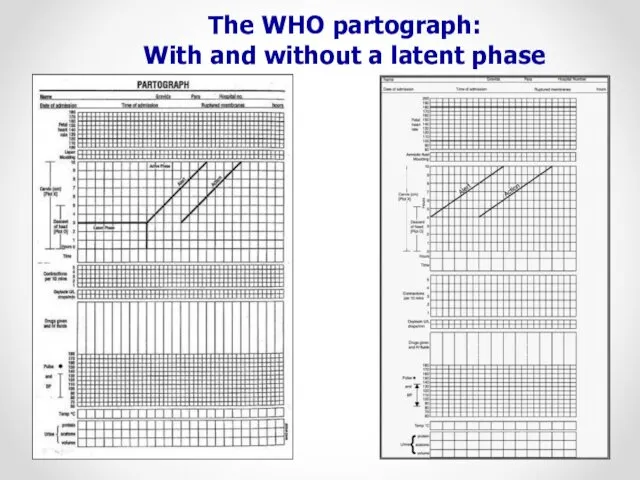
- 7. The WHO partograph: With and without a latent phase WHO 2007
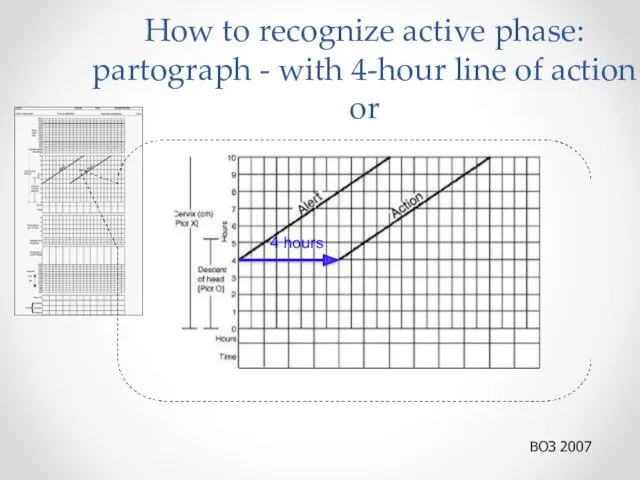
- 8. How to recognize active phase: partograph - with 4-hour line of action or 4 hours ВОЗ
- 10. Causes : 3 P ! Power: adequacy of uterine contractions Passage (birth canal): resistance to the
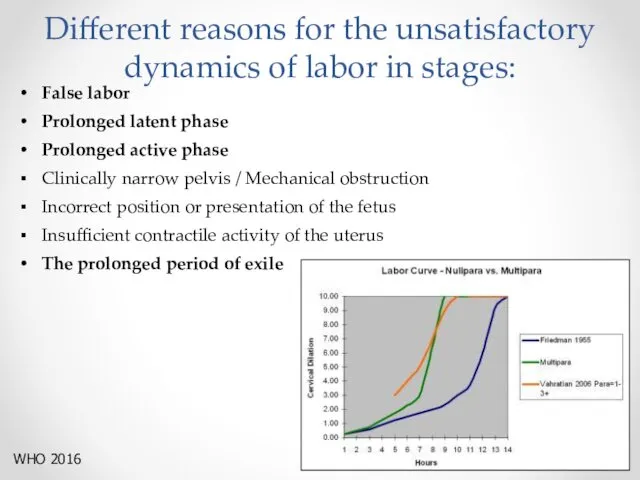
- 11. Different reasons for the unsatisfactory dynamics of labor in stages: False labor Prolonged latent phase Prolonged
- 12. Harbinger (precursors) of birth: definition Birth pains Predictive (precursor) Birth pains Uterine contractions occur at regular
- 13. Latent phase: determination Clinically latent phase of labor is difficult to recognize. Its duration can vary
- 14. Extended Latent Phase: Definition Many modern clinical guidelines and international communities do not provide a clear
- 15. Extended latent phase: maintenance There are differences in the tactics of conducting an Extended latent phase:
- 16. Extended active phase: determination (1) - The opening of the cervix less than 0.5-1 cm (at
- 17. To diagnose the slowing of the active phase of the first period of labor, all aspects
- 18. The opening of the cervix in 6 cm should be considered the beginning of the active
- 19. Evaluation of contractions : If they are effective, you should suspect a clinically narrow pelvis, a
- 20. Extended active phase: mismatch of the pelvis of the mother to the size of the fetus
- 21. Extended active phase: Mechanical obstacle (1) Identify Secondary cervical opening and lowering of the fetal part
- 22. Extended active phase: Mechanical obstacle (2) Approach Vacuum extraction The fetus is alive, the full opening
- 23. Extended active phase: management of inadequate contractile activity of the uterus If the contractions are ineffective,
- 24. Extended active phase: prevention of inadequate contractile activity of the uterus Comfort during childbirth, including: Food
- 25. Stimulation of labor It is performed only after a clinical examination, the exclusion of the clinically
- 26. Principles of active management Active childbirth management includes: assistance in childbirth one on one; routine performance
- 27. Infusion of high doses of oxytocin in comparison with low doses High dose rate: reduces the
- 28. Infusion of oxytocin The effective dose of oxytocin varies significantly for each woman In most cases,
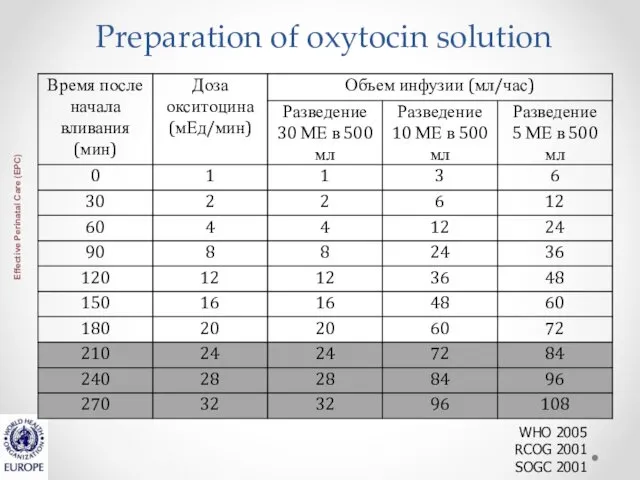
- 29. Preparation of oxytocin solution WHO 2005 RCOG 2001 SOGC 2001
- 30. Criteria for the effectiveness of rhythm stimulation 3-4 contractions in 10 minutes, each of which lasts
- 31. Criteria of inefficiency of stimulation of patrimonial activity Absence of adequate fights at the maximum rate
- 32. Complications of oxytocin infusion Tachysystole More than 5 contractions within 10 minutes Hypertension of the uterus
- 33. Extended second stage of labor: definition According to NICE: Primary: lack of dynamics for 3 hours
- 34. Extended second period of labor / insufficient dynamics (correction) Operative vaginal delivery in the second stage
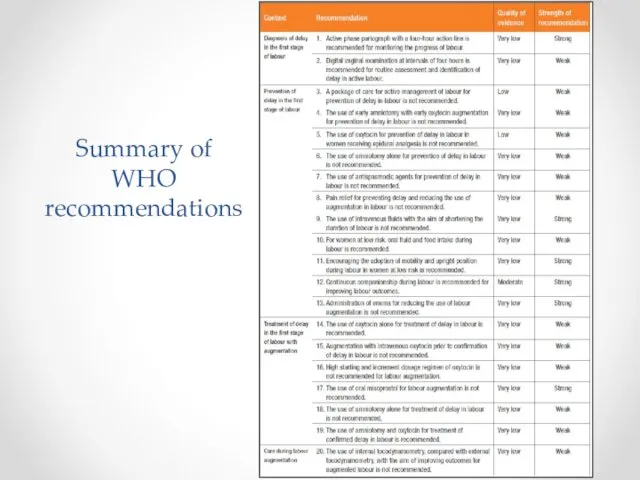
- 35. Summary of WHO recommendations
- 37. Скачать презентацию


























 Нейросифилис. Нейробруцеллез
Нейросифилис. Нейробруцеллез Клиническая психология
Клиническая психология Лучевая диагностика в урологии
Лучевая диагностика в урологии Спино-церебеллярная атаксия 1 типа
Спино-церебеллярная атаксия 1 типа Способы определения объема кровопотери
Способы определения объема кровопотери Оценка тяжести состояния раненого (пострадавшего) пациента
Оценка тяжести состояния раненого (пострадавшего) пациента Психодиагностиканың даму тарихы
Психодиагностиканың даму тарихы Организация наркологической службы в Российской Федерации
Организация наркологической службы в Российской Федерации Организация санитарно-противоэпидемического обеспечения в ЧС
Организация санитарно-противоэпидемического обеспечения в ЧС Философия сестринского дела. Этика в сестринском деле
Философия сестринского дела. Этика в сестринском деле Бастапқы медициналық-санитариялық көмек көрсету деңгейінде ұйымдастыру
Бастапқы медициналық-санитариялық көмек көрсету деңгейінде ұйымдастыру Pathology Of Hypertension
Pathology Of Hypertension Мультифакторлы аурулардың патогенез негіздері
Мультифакторлы аурулардың патогенез негіздері Reconstruction préprothétique par technique directe. Restaurer la dent deulpe
Reconstruction préprothétique par technique directe. Restaurer la dent deulpe Стерилизационные технологии
Стерилизационные технологии Вред алкоголя. Почему об этом нужно говорить
Вред алкоголя. Почему об этом нужно говорить Инструментальные методы исследования в работе врача общей практики (семейного врача). Электрокардиография. Нормальная ЭКГ
Инструментальные методы исследования в работе врача общей практики (семейного врача). Электрокардиография. Нормальная ЭКГ Менингококковая инфекция
Менингококковая инфекция Пищевые отравления
Пищевые отравления Физическая активность и здоровье
Физическая активность и здоровье Микроорганизмд ер
Микроорганизмд ер Даму мен өсудің негізгі заңдылықтары. Балалар мен жасөспірімдер дамуы мен өсуіне әсер ететін факторлар. (Дәріс 4)
Даму мен өсудің негізгі заңдылықтары. Балалар мен жасөспірімдер дамуы мен өсуіне әсер ететін факторлар. (Дәріс 4) Деятельность медицинской сестры по уходу за пациентами с железодефицитной анемией
Деятельность медицинской сестры по уходу за пациентами с железодефицитной анемией Гипо және гипергликемиялық кома. Қант диабетінің клиникалық ағымы, ерекшелігі
Гипо және гипергликемиялық кома. Қант диабетінің клиникалық ағымы, ерекшелігі Основы ЭКГ для врача общей практики
Основы ЭКГ для врача общей практики Профилактика катетер – ассоциированных инфекций кровотока (КАИК) и уход за центральным венозным катетером (ЦВК)
Профилактика катетер – ассоциированных инфекций кровотока (КАИК) и уход за центральным венозным катетером (ЦВК) Методы иммунопрофилактики
Методы иммунопрофилактики Клинические особенности пневмонии в зависимости от возбудителя
Клинические особенности пневмонии в зависимости от возбудителя