Содержание
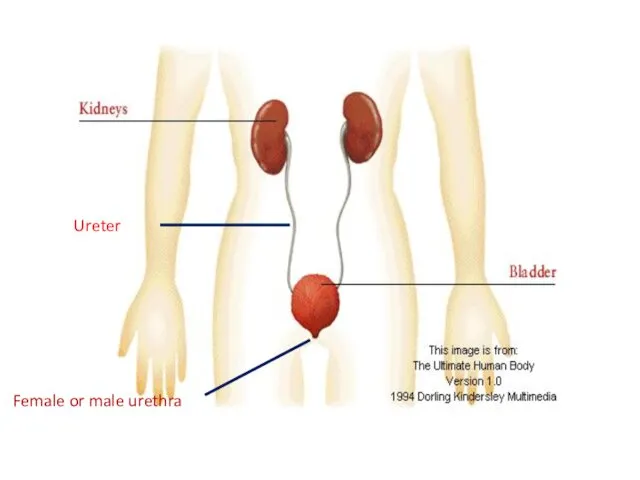
- 2. Ureter Female or male urethra
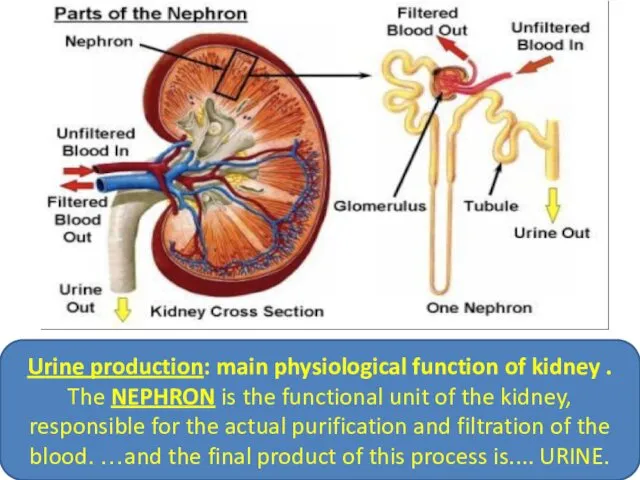
- 3. Urine production: main physiological function of kidney . The NEPHRON is the functional unit of the
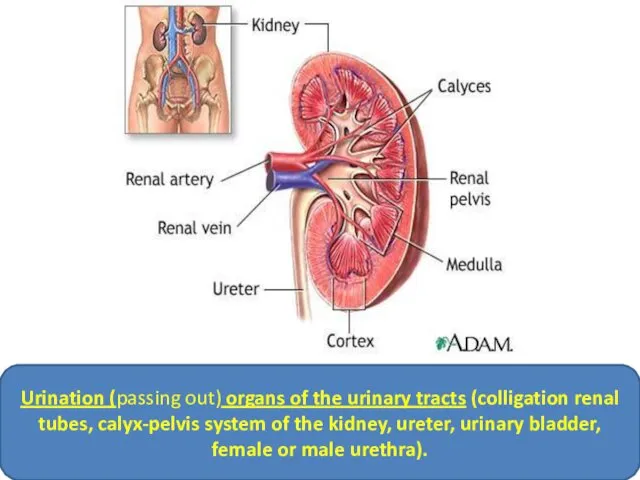
- 4. Urination (passing out) organs of the urinary tracts (colligation renal tubes, calyx-pelvis system of the kidney,
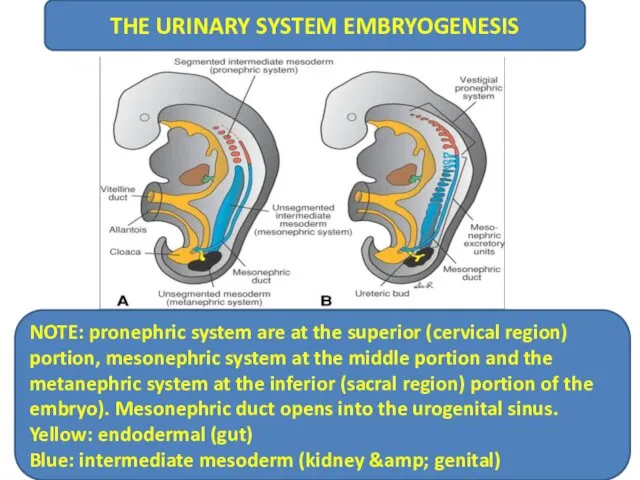
- 5. THE URINARY SYSTEM EMBRYOGENESIS NOTE: pronephric system are at the superior (cervical region) portion, mesonephric system
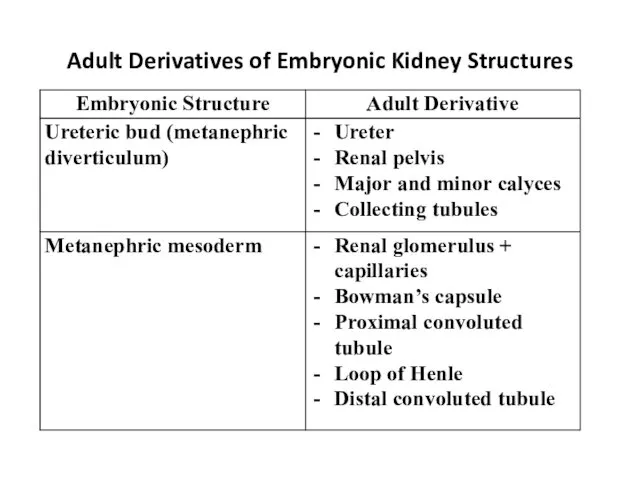
- 6. Adult Derivatives of Embryonic Kidney Structures
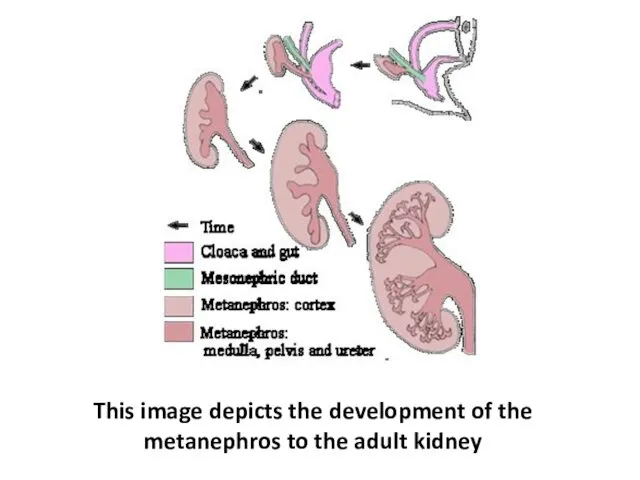
- 7. This image depicts the development of the metanephros to the adult kidney
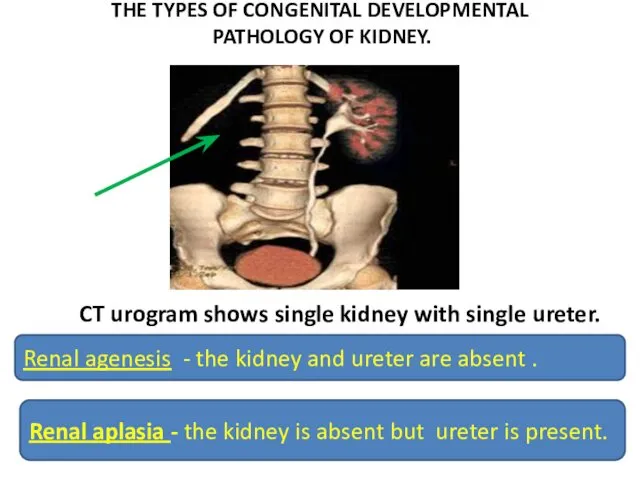
- 8. THE TYPES OF CONGENITAL DEVELOPMENTAL PATHOLOGY OF KIDNEY. CT urogram shows single kidney with single ureter.
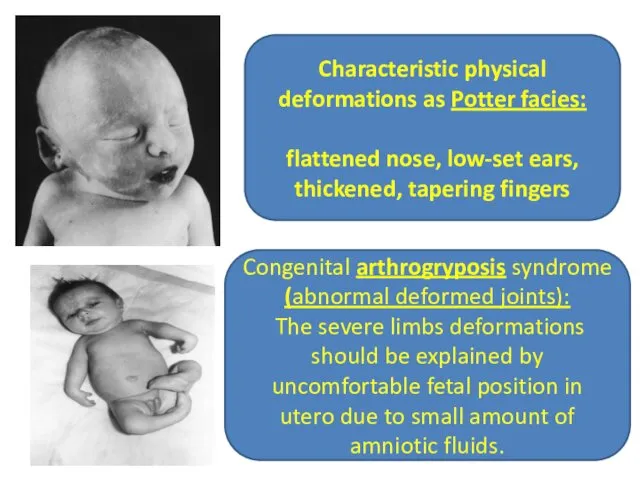
- 9. Characteristic physical deformations as Potter facies: flattened nose, low-set ears, thickened, tapering fingers Congenital arthrogryposis syndrome
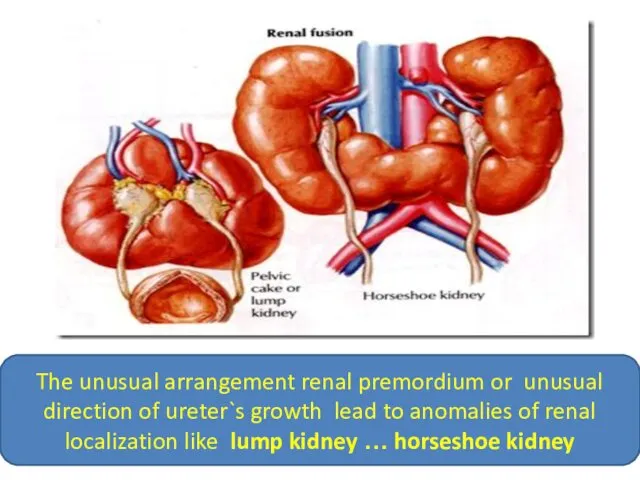
- 10. The unusual arrangement renal premordium or unusual direction of ureter`s growth lead to anomalies of renal
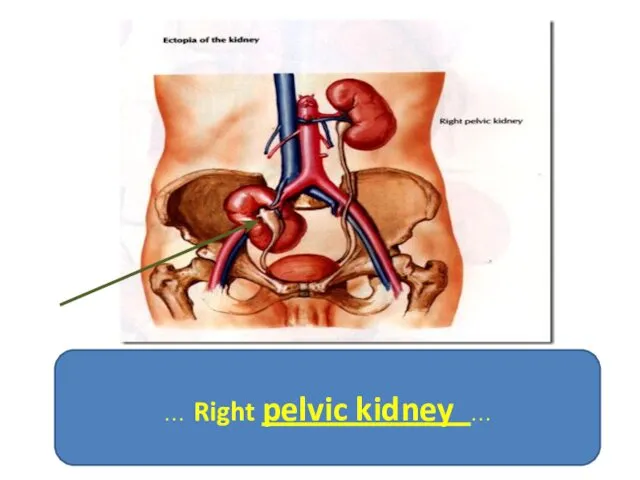
- 11. … Right pelvic kidney …
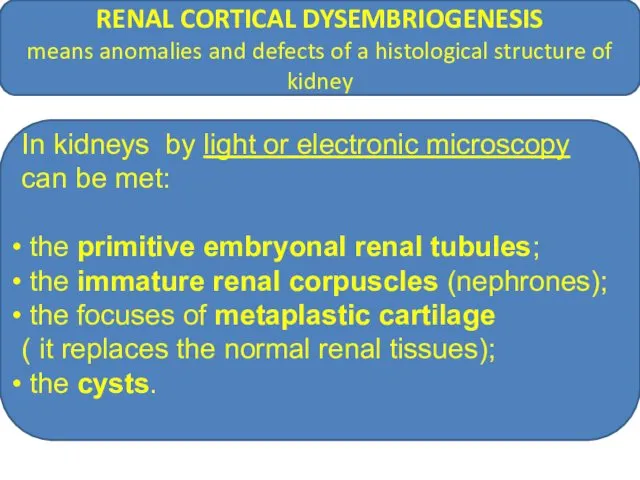
- 12. RENAL CORTICAL DYSEMBRIOGENESIS means anomalies and defects of a histological structure of kidney In kidneys by
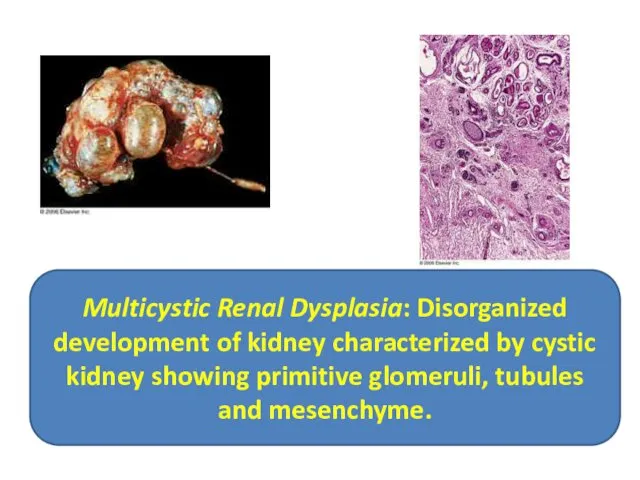
- 13. Multicystic Renal Dysplasia: Disorganized development of kidney characterized by cystic kidney showing primitive glomeruli, tubules and
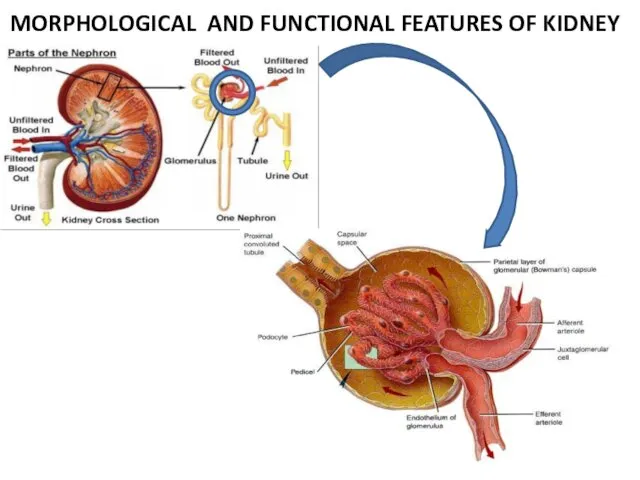
- 14. MORPHOLOGICAL AND FUNCTIONAL FEATURES OF KIDNEY
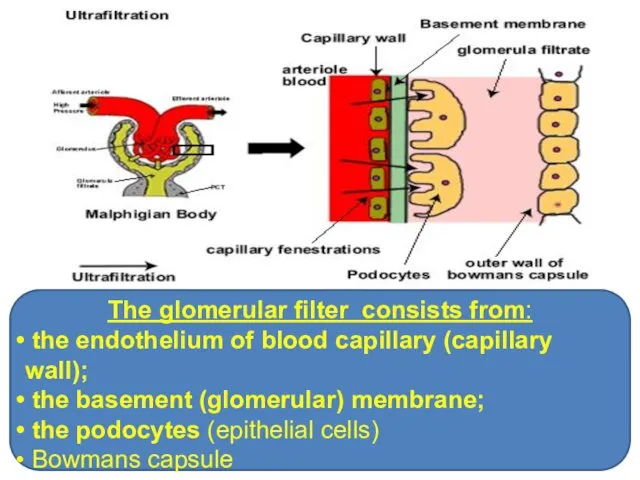
- 15. The glomerular filter consists from: the endothelium of blood capillary (capillary wall); the basement (glomerular) membrane;
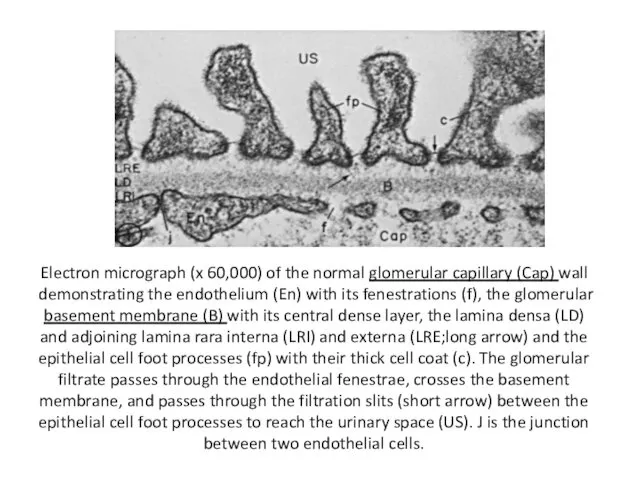
- 16. Electron micrograph (x 60,000) of the normal glomerular capillary (Cap) wall demonstrating the endothelium (En) with
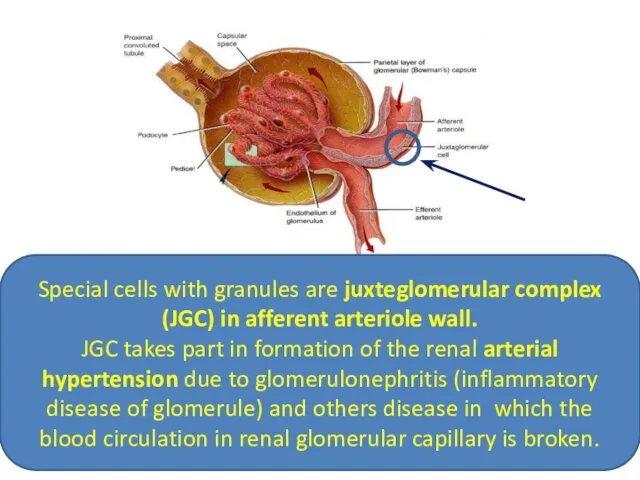
- 17. Special cells with granules are juxteglomerular complex (JGC) in afferent arteriole wall. JGC takes part in
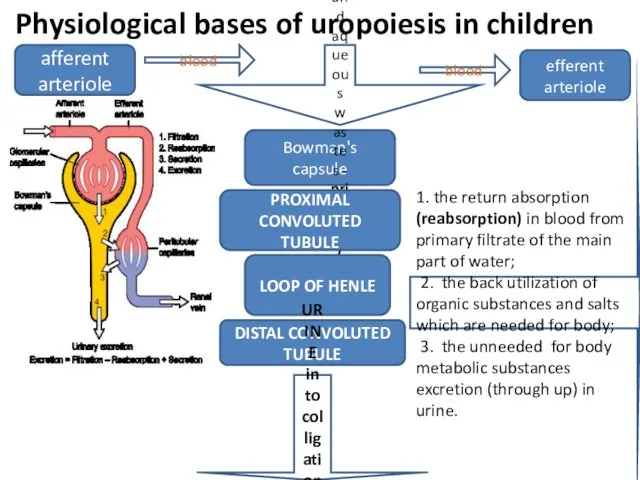
- 18. Physiological bases of uropoiesis in children blood Bowman's capsule afferent arteriole efferent arteriole blood filtered water
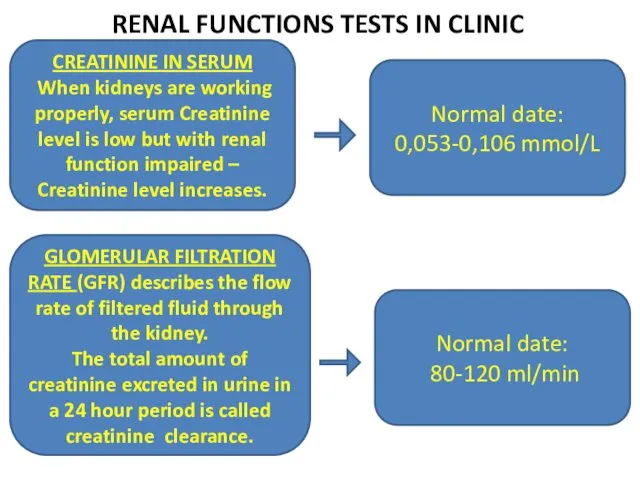
- 19. RENAL FUNCTIONS TESTS IN CLINIC CREATININE IN SERUM When kidneys are working properly, serum Creatinine level
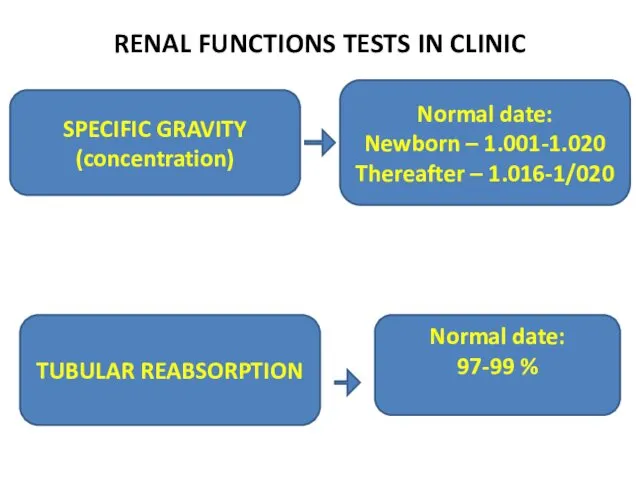
- 20. RENAL FUNCTIONS TESTS IN CLINIC SPECIFIC GRAVITY (concentration) Normal date: Newborn – 1.001-1.020 Thereafter – 1.016-1/020
- 21. DIFFERENCES OF THE REABSORPTION AND SECRETIONS IN CHILD The water-remuving function of kidneys is very special.
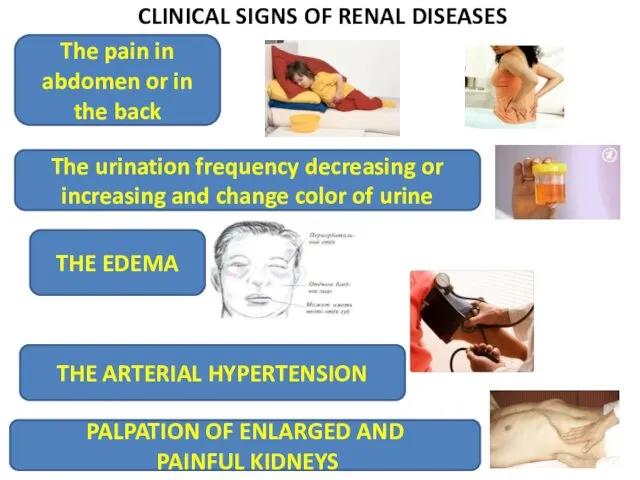
- 22. CLINICAL SIGNS OF RENAL DISEASES The pain in abdomen or in the back The urination frequency
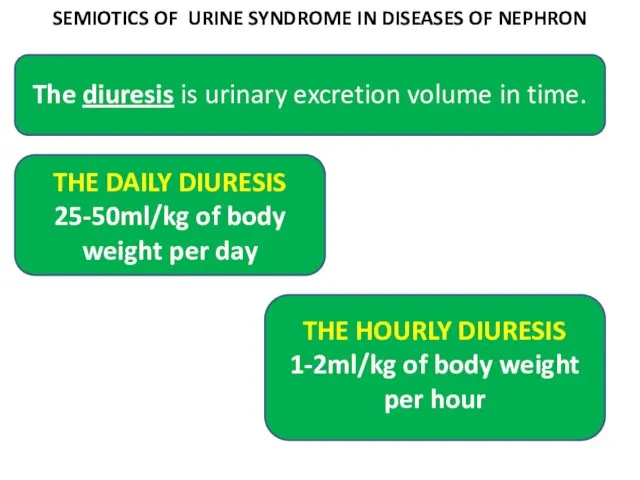
- 23. SEMIOTICS OF URINE SYNDROME IN DISEASES OF NEPHRON THE DAILY DIURESIS 25-50ml/kg of body weight per
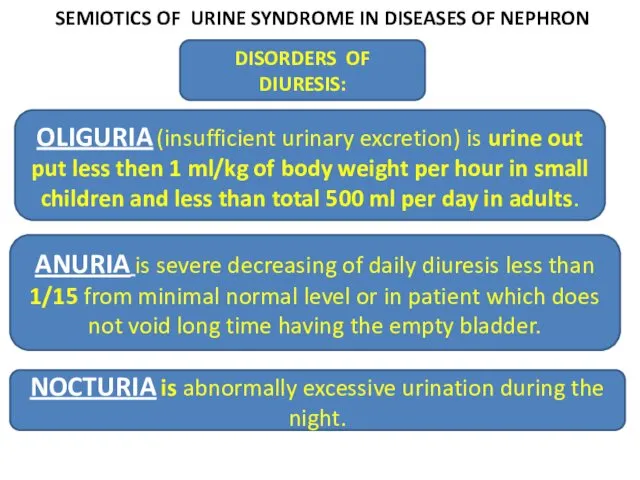
- 24. SEMIOTICS OF URINE SYNDROME IN DISEASES OF NEPHRON DISORDERS OF DIURESIS: OLIGURIA (insufficient urinary excretion) is
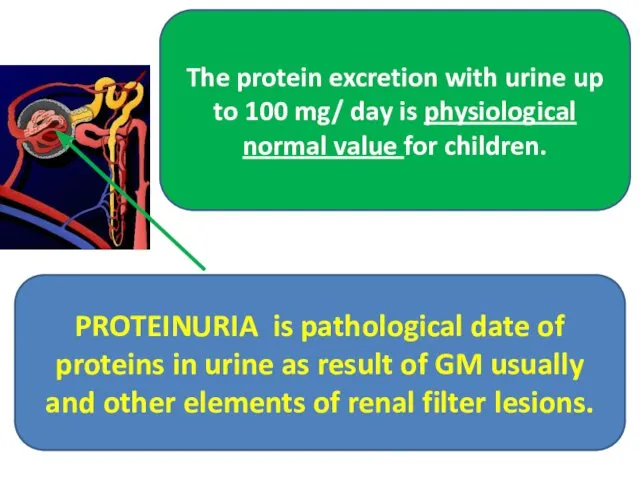
- 25. PROTEINURIA is pathological date of proteins in urine as result of GM usually and other elements
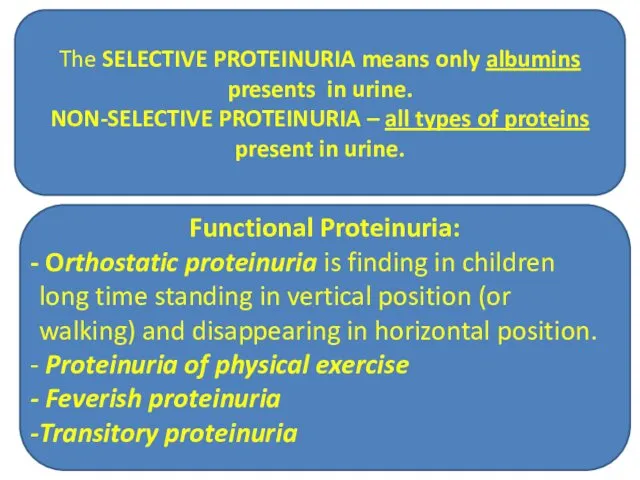
- 26. Functional Proteinuria: Orthostatic proteinuria is finding in children long time standing in vertical position (or walking)
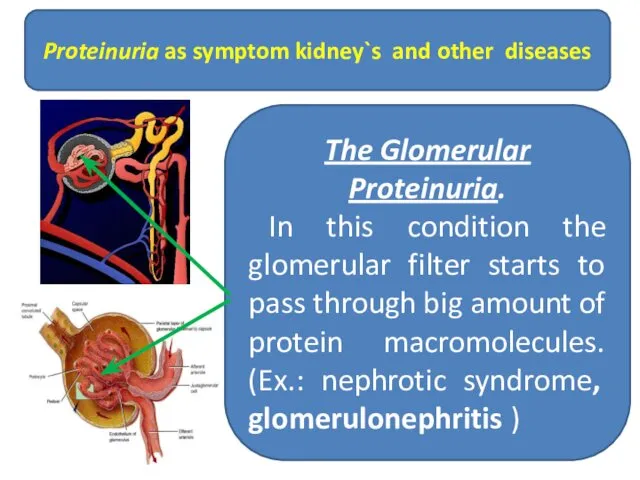
- 27. Proteinuria as symptom kidney`s and other diseases The Glomerular Proteinuria. In this condition the glomerular filter
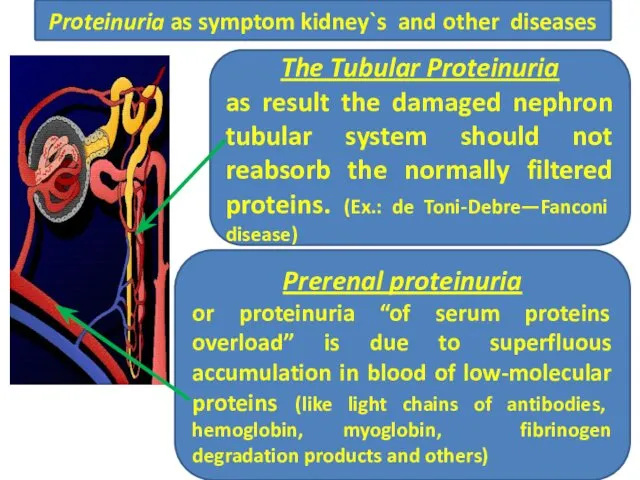
- 28. Prerenal proteinuria or proteinuria “of serum proteins overload” is due to superfluous accumulation in blood of
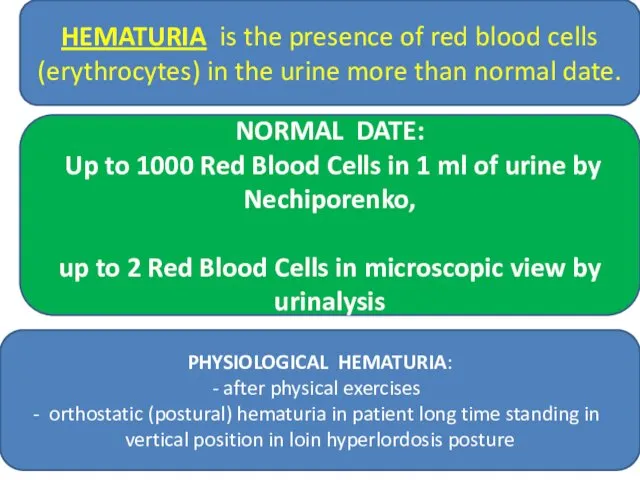
- 29. HEMATURIA is the presence of red blood cells (erythrocytes) in the urine more than normal date.
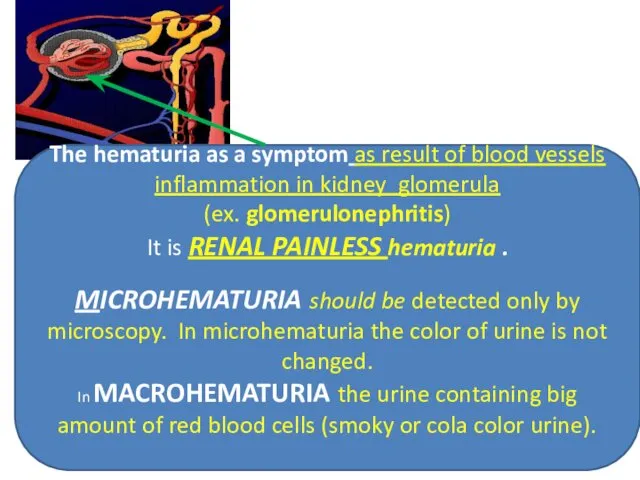
- 30. The hematuria as a symptom as result of blood vessels inflammation in kidney glomerula (ex. glomerulonephritis)
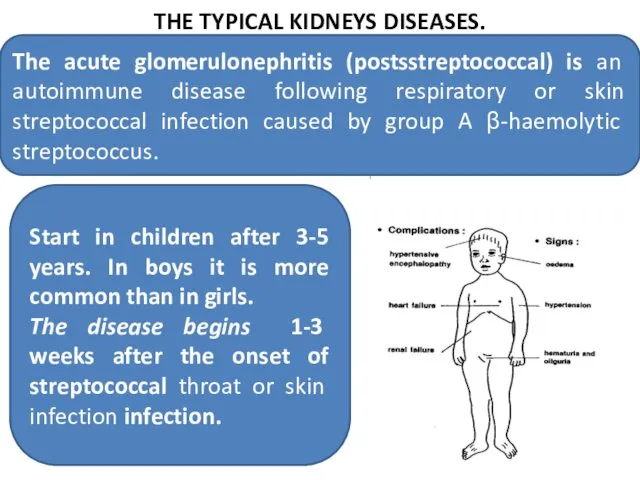
- 31. THE TYPICAL KIDNEYS DISEASES. The acute glomerulonephritis (postsstreptococcal) is an autoimmune disease following respiratory or skin
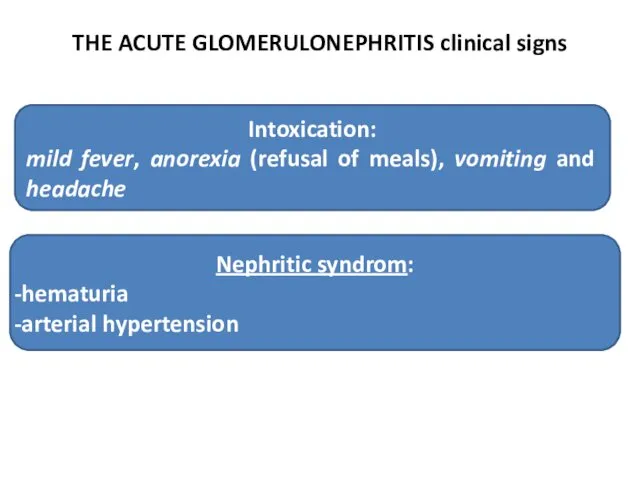
- 32. THE ACUTE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS clinical signs Intoxication: mild fever, anorexia (refusal of meals), vomiting and headache Nephritic
- 34. Скачать презентацию

 Ветеринарные лекарственные формы. Особенности технологии
Ветеринарные лекарственные формы. Особенности технологии Grile de maxim 10
Grile de maxim 10 Здоровье подростков. Центр дружественного отношения к подросткам Вместе
Здоровье подростков. Центр дружественного отношения к подросткам Вместе Жүкті әйелге үйден патронаж жасап,карта толтыру
Жүкті әйелге үйден патронаж жасап,карта толтыру Адаптивные изменения функций почек при различных аномалиях
Адаптивные изменения функций почек при различных аномалиях Терапия ожирения. Групповой метод
Терапия ожирения. Групповой метод Эффективное применение ультразвуковых инструментов в современной эндодонтии
Эффективное применение ультразвуковых инструментов в современной эндодонтии Дисплазия коленного сустава
Дисплазия коленного сустава Средства физкультуры в регулировании работоспособности
Средства физкультуры в регулировании работоспособности Заманауи технологияларды қолдану арқылы жүрек ырғағының бұзылысын қалпына келтіру
Заманауи технологияларды қолдану арқылы жүрек ырғағының бұзылысын қалпына келтіру Психомотрное развитие детей. Этапы формирования психики ребенка
Психомотрное развитие детей. Этапы формирования психики ребенка Масаж і гімнастика дітей до 3 років
Масаж і гімнастика дітей до 3 років Сестринский уход при заболеваниях щитовидной железы
Сестринский уход при заболеваниях щитовидной железы Анатомия брюшины
Анатомия брюшины Инструментальная диагностика объемных образований головного мозга
Инструментальная диагностика объемных образований головного мозга Шизофрения. Физиология заболевания. Гипотеза Фанберга
Шизофрения. Физиология заболевания. Гипотеза Фанберга Диагностика беременности в женской консультации
Диагностика беременности в женской консультации Переломы нижней челюсти. Клиническая картина, диагностика и лечение
Переломы нижней челюсти. Клиническая картина, диагностика и лечение Недостаточность кровообращения: принципы фармакотерапии. Кардиотонические средства
Недостаточность кровообращения: принципы фармакотерапии. Кардиотонические средства Эпидемический процесс
Эпидемический процесс 1 жасқа дейінгі балаларды тамақтандырудың ерекшеліктері
1 жасқа дейінгі балаларды тамақтандырудың ерекшеліктері Эпидемиология и профилактика СПИДа
Эпидемиология и профилактика СПИДа Алгоритмы специализированной медицинской помощи больным сахарным диабетом
Алгоритмы специализированной медицинской помощи больным сахарным диабетом Жүрек-қантамыр жүйесі
Жүрек-қантамыр жүйесі Диабетикалық ретинопатия
Диабетикалық ретинопатия Пикфлоуметрия
Пикфлоуметрия Временная остановка наружного кровотечения. Ошибки на догоспитальном этапе
Временная остановка наружного кровотечения. Ошибки на догоспитальном этапе Гемоконтактные инфекции
Гемоконтактные инфекции