Содержание
- 2. May 16, 2006 LIS580- Spring 2006 What is Control? The process of monitoring activities to ensure
- 3. Controlling as a Management Function Controlling Done well, it ensures that the overall directions of individuals
- 4. Controlling as a Management Function Controlling It helps maintain compliance with essential organizational rules and policies.
- 5. Controlling as a Management Function Cybernetic Control System One that is self-contained in its performance monitoring
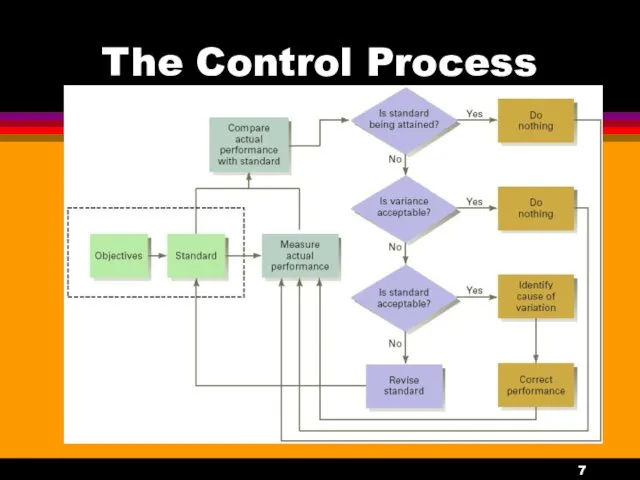
- 6. The Control Process Establish objectives and standards. Measure actual performance. Compare results with objectives and standards.
- 7. The Control Process
- 8. Establish Objectives and Standards The control process begins with planning and the establishment of performance objectives.
- 9. Establish Objectives and Standards There are two types of standards: Output Standards - measures performance results
- 10. Measuring Actual Performance Measurements must be accurate enough to spot deviations or variances between what really
- 11. Comparing Results with Objectives and Standards The comparison of actual performance with desired performance establishes the
- 12. Taking Corrective Action Taking any action necessary to correct or improve things. Management-by-Exception focuses managerial attention
- 13. Taking Corrective Action Management-by Exception can save the managers time, energy, and other resources, and concentrates
- 14. Effective Controls The Best Controls in Organizations are Strategic and results oriented Understandable Encourage self-control
- 15. Effective Controls The Best Controls in Organizations are Timely and exception oriented Positive in nature Fair
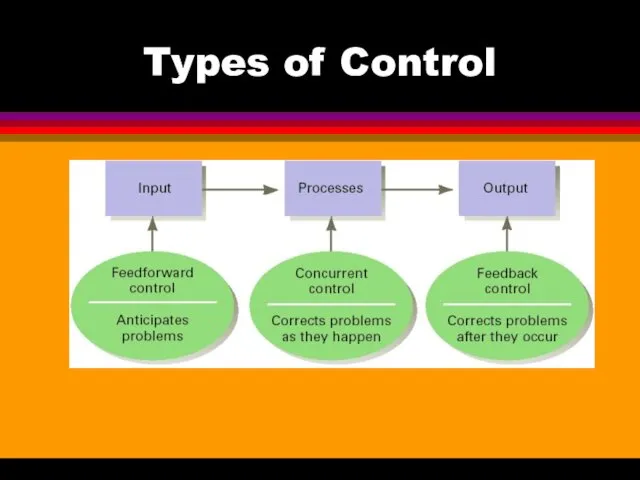
- 16. Types of Control
- 17. Types of Control Preliminary Sometimes called the feedforward controls, they are accomplished before a work activity
- 18. Types of Control Concurrent Focus on what happens during the work process. Sometimes called steering controls,
- 19. Types of Control Postaction Sometimes called feedback controls, they take place after an action is completed.
- 20. Types of Controls Managers have two broad options with respect to control. They can rely on
- 21. Types of Control Internal Controls Allows motivated individuals to exercise self-control in fulfilling job expectations. The
- 22. Types of Control External Controls It occurs through personal supervision and the use of formal administrative
- 23. Qualities of an Effective Control System Prentice Hall, 2002
- 24. Organizational Control Systems Management Processes Strategy and objectives Policies and procedures Selection and training Performance appraisal
- 25. Organizational Control Systems Compensation and Benefits Attract talented people and retain them. Motivate people to exert
- 26. Organizational Control Systems Employee Discipline Discipline is defined as influencing behavior through reprimand. Progressive Discipline ties
- 27. The “Hot Stove Rule” Immediate Focus on activity not personality Consistent Informative Occur in a supportive
- 28. Organizational Control Systems Information and Financial Activity-based costing - the true cost of all products and
- 29. Operations Management and Control Purchasing Economic Order Quantity automatic reorder points Just-In-Time Scheduling
- 30. Operations Management and Control Project Management Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) - Identifies and controls
- 32. Скачать презентацию



























 Зарубежный опыт корпоративного управления
Зарубежный опыт корпоративного управления Основы безопасности полетов. Элементы атс
Основы безопасности полетов. Элементы атс Бизнес Сервис Центр Харьков. Инструкция по выставлению осуществленных рейсов ТЭК на оплату (блок документы)
Бизнес Сервис Центр Харьков. Инструкция по выставлению осуществленных рейсов ТЭК на оплату (блок документы) Організація, планування та оцінка консалтингової діяльності. (Тема 4)
Організація, планування та оцінка консалтингової діяльності. (Тема 4) Среды и инструменты для управления проектами
Среды и инструменты для управления проектами Internal control and deontology - Chapter 10 Deontology
Internal control and deontology - Chapter 10 Deontology Компетенции. Структура компетенции. Эффективная коммуникация
Компетенции. Структура компетенции. Эффективная коммуникация Научно-технический прогресс и инновационная деятельность. (Тема 1)
Научно-технический прогресс и инновационная деятельность. (Тема 1) Стратегическое управление в системе менеджмента
Стратегическое управление в системе менеджмента Деловые переговоры
Деловые переговоры Теории лидерства и их роль в менеджменте
Теории лидерства и их роль в менеджменте CDEK – логистический оператор, которого вы искали
CDEK – логистический оператор, которого вы искали Организация, структура и регулирование деятельности таможенных органов. (Тема 3)
Организация, структура и регулирование деятельности таможенных органов. (Тема 3) Теория организации и организационное поведение
Теория организации и организационное поведение Основы управления проектами. Лекция 1
Основы управления проектами. Лекция 1 Оценка использования трудовых ресурсов и обоснование путей их улучшения ОАО Витебские ковры
Оценка использования трудовых ресурсов и обоснование путей их улучшения ОАО Витебские ковры Авторитарлық стиль. Шешімді бір адам қабылдайды, ол жарлық, бұйрық түрінде келеді
Авторитарлық стиль. Шешімді бір адам қабылдайды, ол жарлық, бұйрық түрінде келеді Связи с общественностью – наука о гармонии рыночных отношений
Связи с общественностью – наука о гармонии рыночных отношений Основные виды децентрализованных структур: их достоинства и недостатки
Основные виды децентрализованных структур: их достоинства и недостатки Основные формы ФИДИК и OPBRC контрактов (Международная федерация инженеров-консультантов)
Основные формы ФИДИК и OPBRC контрактов (Международная федерация инженеров-консультантов) Управленческий процесс, функции и методы менеджмента
Управленческий процесс, функции и методы менеджмента Business process management. Concepts, languages, architectures. (Chapter 4)
Business process management. Concepts, languages, architectures. (Chapter 4) Стандарты хранения новых автомобилей
Стандарты хранения новых автомобилей Научно-исследовательский семинар Методология и методы медиаисследований. ОП Менеджмент в СМИ
Научно-исследовательский семинар Методология и методы медиаисследований. ОП Менеджмент в СМИ Управление материальными потоками (MM)
Управление материальными потоками (MM) Мотивационная программа Большие гонки - 2019 г компании ТК Мейджик Транс
Мотивационная программа Большие гонки - 2019 г компании ТК Мейджик Транс Анализ внешней и внутренней среды предприятия
Анализ внешней и внутренней среды предприятия Роль внутреннего аудита в корпоративном управлении компании
Роль внутреннего аудита в корпоративном управлении компании