Содержание
- 2. 1. Control techniques 1.1. What? Techniques/tools which can be used ba a ‘controller’ or an ‘auditor’
- 3. 1. Control techniques 1.3. Audit risk = risk that material errors are not being discovered 1.4.
- 4. 1. Control techniques 1.4.1. Inventarisation Check whether the status of the assets as presented by the
- 5. 1. Control techniques 1.4.5. Interviewing employees/others To gain intelligence 1.4.6. Arithmetic Review Re-doing calculations 1.4.7. Analytical
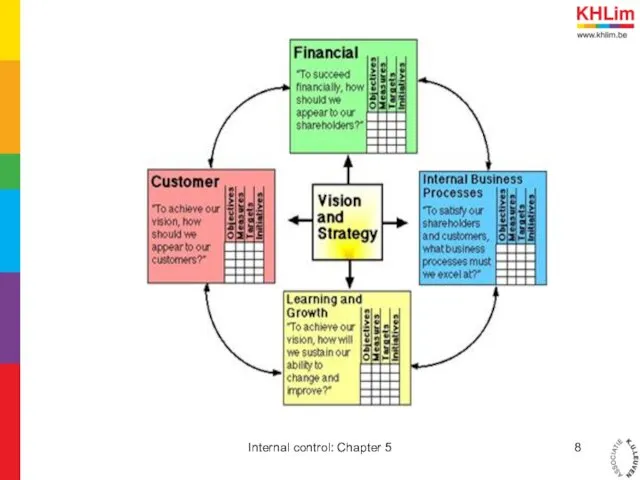
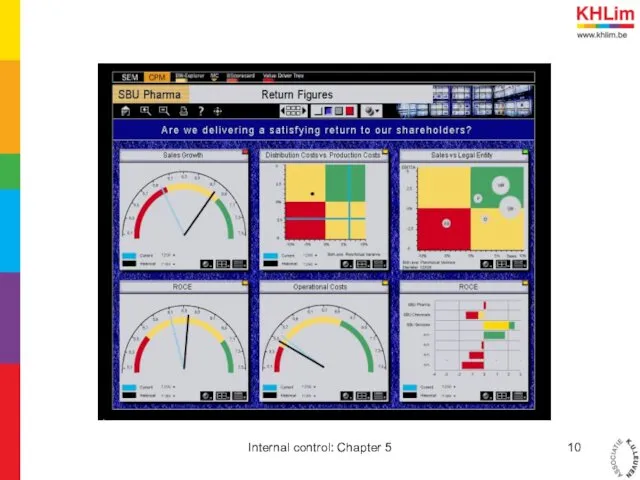
- 6. 2. Balanced scorecard 2.1. What are balanced scorecards Technique for strategic management Means of evaluation Not
- 7. 2. Balanced scorecards 2.3. Pro’s and con’s Focussing on certain area’s Finding good KPI’s is difficult
- 8. Internal control: Chapter 5
- 9. Internal control: Chapter 5
- 10. Internal control: Chapter 5
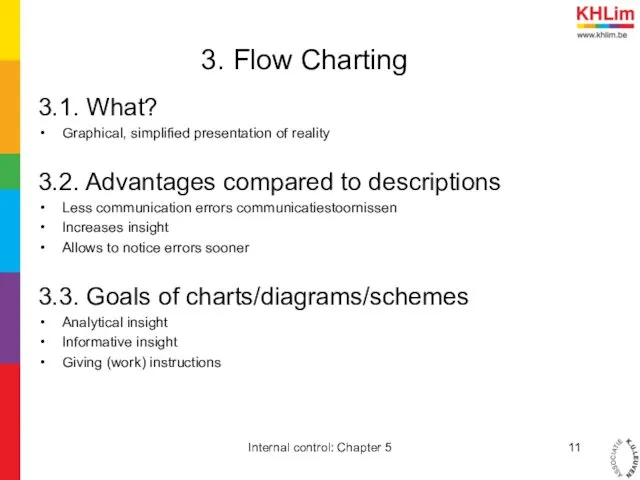
- 11. 3. Flow Charting 3.1. What? Graphical, simplified presentation of reality 3.2. Advantages compared to descriptions Less
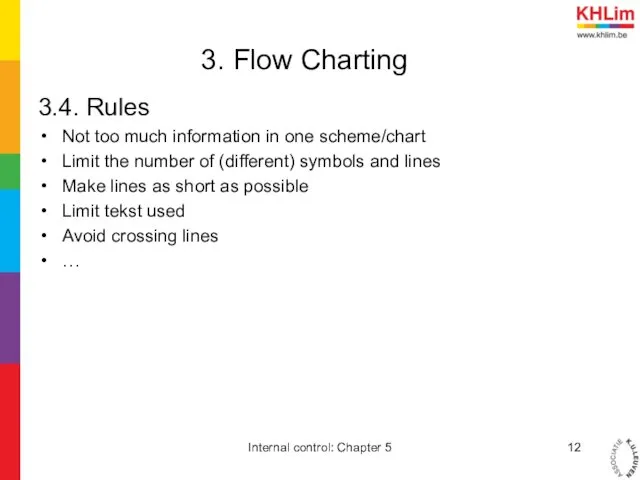
- 12. 3. Flow Charting 3.4. Rules Not too much information in one scheme/chart Limit the number of
- 13. 4. Sampling 4.1. In general To be useful a sample has to meet certain conditions: Non-statistical
- 14. 4. Sampling 4.3. Two types of sampling 4.3.1. Attribute sampling Binairy presentations Testing the effectiveness of
- 15. 4. Sampling 4.4. Sequences in the sampling process 4.4.1. Determine the objectives 4.4.2. Determine the population
- 16. 4. Sampling 4.4.4. Calculate the sample size Depends on: Population size Acceptable sample risk Variance of
- 18. Скачать презентацию











 Методы минимизации рисков
Методы минимизации рисков Совершенствование системы управления персоналом на предприятии. Дипломная работа
Совершенствование системы управления персоналом на предприятии. Дипломная работа Удосконалення управління на підприємствах готельноресторанного бізнесу: стратегічний підхід
Удосконалення управління на підприємствах готельноресторанного бізнесу: стратегічний підхід Метод PERT и управление проектами
Метод PERT и управление проектами Loeng 2. Riskihaldamine, hindamine, analuus
Loeng 2. Riskihaldamine, hindamine, analuus Классификация логистических проектов. (Модуль 2. Лекция 2.1)
Классификация логистических проектов. (Модуль 2. Лекция 2.1) Подготовка персонального тренера
Подготовка персонального тренера Project risk management
Project risk management Основы проектирования и оборудования заводов
Основы проектирования и оборудования заводов Структура и оценка затрат на персонал
Структура и оценка затрат на персонал Сущность и методология операционного менеджмента
Сущность и методология операционного менеджмента Введение в дисциплину Корпоративная социальная ответственность
Введение в дисциплину Корпоративная социальная ответственность Система менеджмента качества. Принципы менеджмента качества
Система менеджмента качества. Принципы менеджмента качества Тайм-менеджмент
Тайм-менеджмент Совершенствование качества обслуживая пассажиров АО Авиакомпании Россия в аэропорту Пулково (Санкт- Петербург)
Совершенствование качества обслуживая пассажиров АО Авиакомпании Россия в аэропорту Пулково (Санкт- Петербург) Инновационный процесс. Инновационный менеджмент (лекция 3)
Инновационный процесс. Инновационный менеджмент (лекция 3) Подбор персонала. Фриланс-рекрутинг
Подбор персонала. Фриланс-рекрутинг Разработка, организация производства топливных элементов
Разработка, организация производства топливных элементов Менеджмент организации
Менеджмент организации Организация работы службы спецавтотранспорта. Лекция 2
Организация работы службы спецавтотранспорта. Лекция 2 Роль и место руководителя в системе современного муниципального управления на примере администрации города Новочебоксарска
Роль и место руководителя в системе современного муниципального управления на примере администрации города Новочебоксарска Форсайт-сессия. Научно-образовательный потенциал Хабаровского края, как ресурс проектного управления
Форсайт-сессия. Научно-образовательный потенциал Хабаровского края, как ресурс проектного управления Чемпионат по стратегии и управлению бизнесом. Региональный кубок: выявление и развитие талантов для экономики региона
Чемпионат по стратегии и управлению бизнесом. Региональный кубок: выявление и развитие талантов для экономики региона Понятие и этапы планирования потребности в персонале
Понятие и этапы планирования потребности в персонале  Бөлінген мұрағаттарды жүргізу технологиясы
Бөлінген мұрағаттарды жүргізу технологиясы Отчет о проделанной работе. Test Manager/Test Designer/Tester
Отчет о проделанной работе. Test Manager/Test Designer/Tester Базовые принципы ведения переговоров
Базовые принципы ведения переговоров Процессуальные теории мотивации. Теория ожиданий, теория справедливости, теория Портера-Лоулера
Процессуальные теории мотивации. Теория ожиданий, теория справедливости, теория Портера-Лоулера