- Главная
- Менеджмент
- Modern theory of organization management

Содержание
- 2. Two types of Modern Organization Theory Modern Organizational Theories are classified into two types – Systems
- 4. Modern Organizational Theories – Systems Theory The Systems Theory was developed in the early 60s. With
- 6. Organization and its Environment There are two types of systems: Open Systems – which interact with
- 8. Main Parts of an Organization System Individual – An individual and his personality is the basic
- 9. Modern Organization Theory – Contingency Theory The contingency theory is simply an extension of the systems
- 11. Weber's ideal of bureaucracy Weber identified the following components of bureaucracy as essential Official jurisdiction on
- 12. Max Weber Max Weber believed that an ideal bureaucracy consists of six specific characteristics: hierarchy of
- 13. Criticism Weber's theories were purposed to set a stage for other organizations to follow, and the
- 15. Скачать презентацию
Слайд 2
Two types of Modern Organization Theory
Modern Organizational Theories are classified
Two types of Modern Organization Theory
Modern Organizational Theories are classified
into two types – Systems Theory and Contingency Theory. In this article, we will take an in-depth look at the Systems Theory along with its contributions and criticisms.
Слайд 3
Слайд 4
Modern Organizational Theories – Systems Theory
The Systems Theory was developed in
Modern Organizational Theories – Systems Theory
The Systems Theory was developed in
the early 60s. With a conceptual and analytical base, it attaches a great significance on empirical research data.
In simple terms, the theory considers organizations as systems. ”A system is an organized or complex whole – an assemblage or combination of things or parts which form a complex unitary whole”.
In simple terms, the theory considers organizations as systems. ”A system is an organized or complex whole – an assemblage or combination of things or parts which form a complex unitary whole”.
Слайд 5
Слайд 6
Organization and its Environment
There are two types of systems:
Open Systems –
Organization and its Environment
There are two types of systems:
Open Systems –
which interact with their environment. Also, all living systems are open systems.
Closed Systems – which have no interaction with their environment. Also, all non-living systems are closed systems.
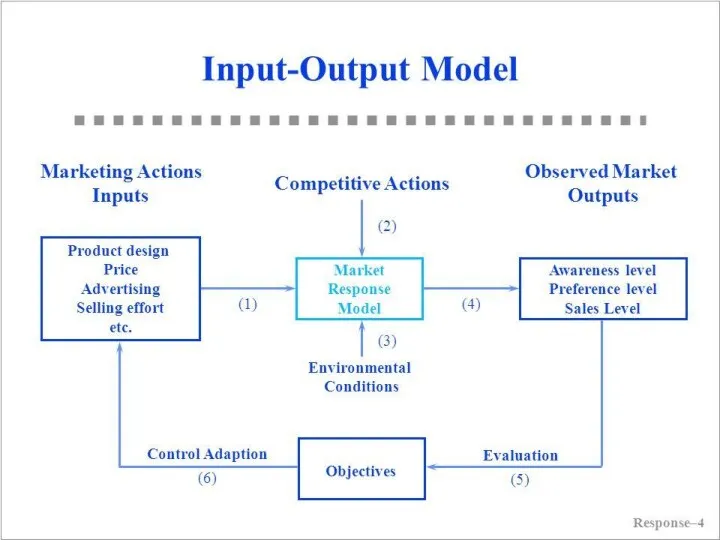
An organization is an Open System as it continuously interacts with its environment. Therefore, in order to understand an organization, one must identify its boundary. We can understand an organization’s interaction with its environment as an input-output model.
Closed Systems – which have no interaction with their environment. Also, all non-living systems are closed systems.
An organization is an Open System as it continuously interacts with its environment. Therefore, in order to understand an organization, one must identify its boundary. We can understand an organization’s interaction with its environment as an input-output model.
Слайд 7
Слайд 8
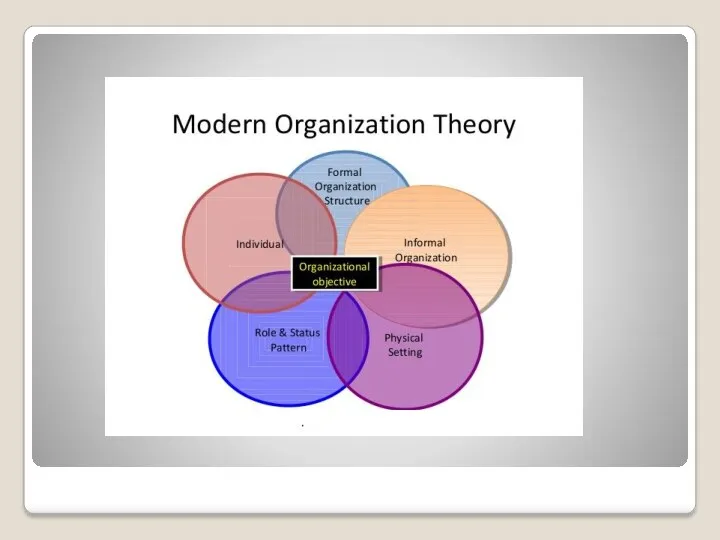
Main Parts of an Organization System
Individual – An individual and his personality
Main Parts of an Organization System
Individual – An individual and his personality
is the basic part of the system. Every individual’s attitude and motives determine his expectation when he participates in the organization system.
Formal Organization – A formal organization is the interrelated pattern of jobs which are designed to regulate the actions of individuals and other resources in the organization. Therefore, the individual must perform his job and the organization must fulfill his expectations on successful completion of the job. Usually, there is incongruency between the goals of the organization and those of its members.
Informal Organization – In any organization, an individual interacts significantly with the informal group to which he belongs. This informal group, typically, demands the individual to conform to its laid-down behavior patterns. The individual conforms in order to accomplish his goals by associating with the informal group. Further, since the two interact, they modify each other’s behavior.
Status and Roles – In every organization, individuals are expected to play certain roles. These roles determine their status. There are times when the demands on an individual from the formal and informal organizations contradict each other. At such times, there is a role conflict. Therefore, it is necessary that the two roles fuse together. This fusion process acts to wield divergent elements together in order to preserve the integrity of the organization.
Physical Setting – Another important component is the physical surroundings in which an individual performs a job. Therefore, it is important to carefully examine the interaction in the complex man-machine system. One cannot approach the problem in a purely technical manner and needs to consider the social, psychological, as well as physiological conditions of members. Only then can one fit the machines to men.
Formal Organization – A formal organization is the interrelated pattern of jobs which are designed to regulate the actions of individuals and other resources in the organization. Therefore, the individual must perform his job and the organization must fulfill his expectations on successful completion of the job. Usually, there is incongruency between the goals of the organization and those of its members.
Informal Organization – In any organization, an individual interacts significantly with the informal group to which he belongs. This informal group, typically, demands the individual to conform to its laid-down behavior patterns. The individual conforms in order to accomplish his goals by associating with the informal group. Further, since the two interact, they modify each other’s behavior.
Status and Roles – In every organization, individuals are expected to play certain roles. These roles determine their status. There are times when the demands on an individual from the formal and informal organizations contradict each other. At such times, there is a role conflict. Therefore, it is necessary that the two roles fuse together. This fusion process acts to wield divergent elements together in order to preserve the integrity of the organization.
Physical Setting – Another important component is the physical surroundings in which an individual performs a job. Therefore, it is important to carefully examine the interaction in the complex man-machine system. One cannot approach the problem in a purely technical manner and needs to consider the social, psychological, as well as physiological conditions of members. Only then can one fit the machines to men.
Слайд 9
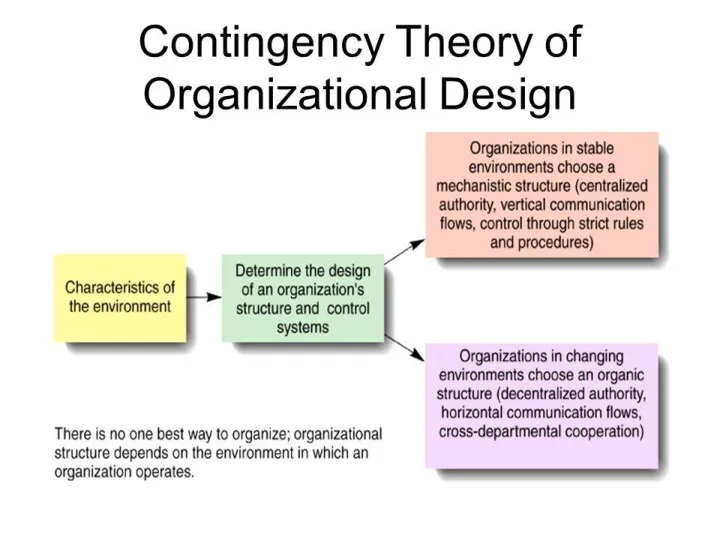
Modern Organization Theory – Contingency Theory
The contingency theory is simply an
Modern Organization Theory – Contingency Theory
The contingency theory is simply an
extension of the systems organizational theory. According to this theory, there is no particular managerial action or organizational design that is appropriate for all situations.
In fact, the design, as well as the managerial decision, depends on the situation. In other words, it is contingent on the situation and circumstances. Therefore, the Contingency Theory is also referred to as a situational theory.
Like in the systems organizational theory, the contingency theory considers an organization as a system which consists of several sub-systems.
Further, both these theories lay a lot of emphasis on maintaining and adapting activities for the growth and survival of the system.
They also deal with patterns of relationships and the interdependence among the elements of the system. However, there are some differences between the two.
In fact, the design, as well as the managerial decision, depends on the situation. In other words, it is contingent on the situation and circumstances. Therefore, the Contingency Theory is also referred to as a situational theory.
Like in the systems organizational theory, the contingency theory considers an organization as a system which consists of several sub-systems.
Further, both these theories lay a lot of emphasis on maintaining and adapting activities for the growth and survival of the system.
They also deal with patterns of relationships and the interdependence among the elements of the system. However, there are some differences between the two.
Слайд 10
Слайд 11
Weber's ideal of bureaucracy
Weber identified the following components of bureaucracy as
Weber's ideal of bureaucracy
Weber identified the following components of bureaucracy as
essential
Official jurisdiction on all areas is ordered by rules or laws already implemented.
There is an office hierarchy; a system of super- and sub-ordination in which higher offices supervise lower ones.
The management of the modern office is based upon written rules, which are preserved in their original form.
Office management requires training and specialization.
When the office is developed/established it requires the full working capacity of individuals.
Rules are stable and can be learned. Knowledge of these rules can be viewed as expertise within the bureaucracy (these allow for the management of society)
Official jurisdiction on all areas is ordered by rules or laws already implemented.
There is an office hierarchy; a system of super- and sub-ordination in which higher offices supervise lower ones.
The management of the modern office is based upon written rules, which are preserved in their original form.
Office management requires training and specialization.
When the office is developed/established it requires the full working capacity of individuals.
Rules are stable and can be learned. Knowledge of these rules can be viewed as expertise within the bureaucracy (these allow for the management of society)
Слайд 12
Max Weber
Max Weber believed that an ideal bureaucracy consists of six specific
Max Weber
Max Weber believed that an ideal bureaucracy consists of six specific
characteristics: hierarchy of command, impersonality, written rules of conduct, advancement based on achievement, specialized division of labor, and efficiency. This ultimate characteristic of Weberian bureaucracy, which states that bureaucracies are very efficient, is controversial and by no means accepted by all sociologists. There are certainly both positive and negative consequences to bureaucracy, and strong arguments for both the efficiency and inefficiency of bureaucracies.
Слайд 13
Criticism
Weber's theories were purposed to set a stage for other organizations
Criticism
Weber's theories were purposed to set a stage for other organizations
to follow, and the characteristics are so ideal that they may be impossible for any actual organization to succeed. He wanted to come up with a set of guidelines that would favor both efficiency and, most importantly, conditions that would make the workers top priority. It was common for earlier theorists to distort Weber's views, and today, people still make the same mistakes as they did when Weber's views first came into play. He has always been critiqued for the branches of his ideas that don't work in reality, but the point of his theory was not to actually create an organization, but to create an ideal model for other organizations to follow.
One big misconception that people have had in the past is a question of Weber's morality due to their oversimplification of his characteristics of a pure bureaucracy. "There is dangerous risk of oversimplification in making Weber seem cold and heartless to such a degree that an efficiently-run Nazi death camp might appear admirable." In reality, Weber believed that by using human logic in his system, organizations could achieve improvement of human condition in various workplaces. Complexity in an organization yields the highest success, therefore simplifying it leads to the illusions of over-authority and intense hierarchical power that are inaccurate of Weber's beliefs.
One big misconception that people have had in the past is a question of Weber's morality due to their oversimplification of his characteristics of a pure bureaucracy. "There is dangerous risk of oversimplification in making Weber seem cold and heartless to such a degree that an efficiently-run Nazi death camp might appear admirable." In reality, Weber believed that by using human logic in his system, organizations could achieve improvement of human condition in various workplaces. Complexity in an organization yields the highest success, therefore simplifying it leads to the illusions of over-authority and intense hierarchical power that are inaccurate of Weber's beliefs.
- Предыдущая
ActivitiesСледующая -
Пейзаж настроения. Природа и художник








 Samsung. История развития. Схема управления. Система ценностей
Samsung. История развития. Схема управления. Система ценностей Dependency management. Visual Studio
Dependency management. Visual Studio Логистика производства
Логистика производства Контроль исполнения документов
Контроль исполнения документов Brand management and branding development tendency in small and medium enterprise: evidence from Kazakhstan
Brand management and branding development tendency in small and medium enterprise: evidence from Kazakhstan Особенности организации аутсорсинга на железнодорожном транспорте РФ
Особенности организации аутсорсинга на железнодорожном транспорте РФ Функции и принципы менеджмента
Функции и принципы менеджмента Теории мотивации. Содержательная и процессуальная теории мотивации
Теории мотивации. Содержательная и процессуальная теории мотивации Внепроизводственные методы обучения персонала
Внепроизводственные методы обучения персонала Основы профессиональной этики
Основы профессиональной этики Өндірістік логистикадағы материалдық ағымдарды басқарудың тартушы| жəне итеруші жүйелері. Тартушы жəне итеруші жүйелердің мəні
Өндірістік логистикадағы материалдық ағымдарды басқарудың тартушы| жəне итеруші жүйелері. Тартушы жəне итеруші жүйелердің мəні Анализ и оптимизация работы производства мясного цеха и технологического процесса приготовления блюд из мяса
Анализ и оптимизация работы производства мясного цеха и технологического процесса приготовления блюд из мяса Производственная инфраструктура предприятия
Производственная инфраструктура предприятия Закони, принципи, правила спілкування. (Лекція 1-2)
Закони, принципи, правила спілкування. (Лекція 1-2) Operations management in manufacturing and service industries. (Chapter 11)
Operations management in manufacturing and service industries. (Chapter 11) Mazda. Отдел по работе с клиентами
Mazda. Отдел по работе с клиентами PDF-отчет Презентация компании и проекта. Понятие МЛМ. Быстрый старт
PDF-отчет Презентация компании и проекта. Понятие МЛМ. Быстрый старт Work hard, play hard
Work hard, play hard Антикризисное регулирование состояния предприятий. (Лекция 8)
Антикризисное регулирование состояния предприятий. (Лекция 8) Типы лидерства. (Тема 4)
Типы лидерства. (Тема 4) Новое общественное управление
Новое общественное управление Лидерство. Стили лидерства
Лидерство. Стили лидерства Расчёт базовых показателей качества продукции
Расчёт базовых показателей качества продукции Анализ существующих решений проблематики, выявление ключевых достоинств и недостатков
Анализ существующих решений проблематики, выявление ключевых достоинств и недостатков Теория организации и организационное поведение
Теория организации и организационное поведение Методологические подходы к управлению деятельностью таможенных органов. Лекция 3
Методологические подходы к управлению деятельностью таможенных органов. Лекция 3 Отличие команд от рабочих групп. Выращивание команд. Жизненный цикл команды. (Тема 8)
Отличие команд от рабочих групп. Выращивание команд. Жизненный цикл команды. (Тема 8) Загальна характеристика управління проектами в туризмі
Загальна характеристика управління проектами в туризмі