Содержание
- 2. COURSE CODE: MGT 4201 COURSE TITLE: Strategy and Business Policy –Section 3 CREDIT: 3 CLASS TIME
- 3. FACULTY: Monowar Mahmood MBA (International Business), Saint Mary’s University, Canada MA in HRM, University of Leeds,
- 4. COURSE/LEARNING OBJECTIVES To provide a basic understanding of the nature and dynamics of the strategy formulation
- 5. COURSE FORMAT/TEACHING METHODOLOGY The format of the course is based on a mix of theoretical discussion
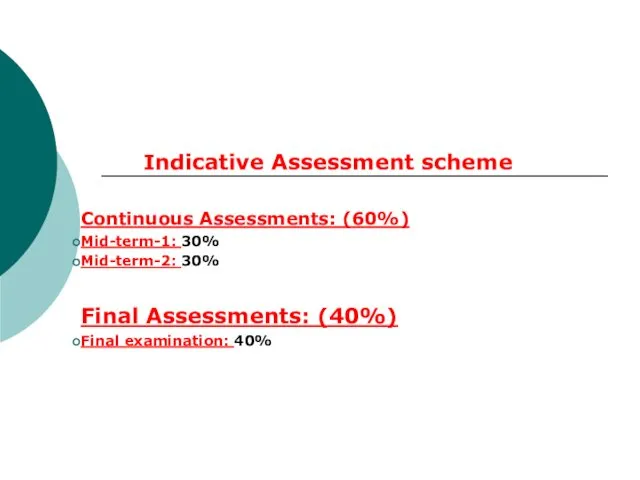
- 6. Indicative Assessment scheme Continuous Assessments: (60%) Mid-term-1: 30% Mid-term-2: 30% Final Assessments: (40%) Final examination: 40%
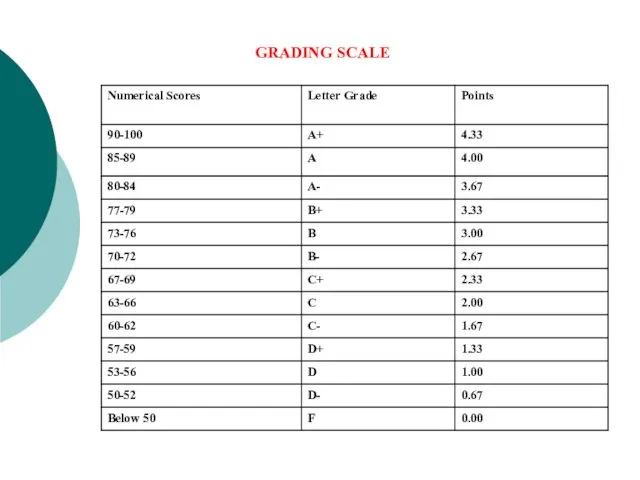
- 7. GRADING SCALE
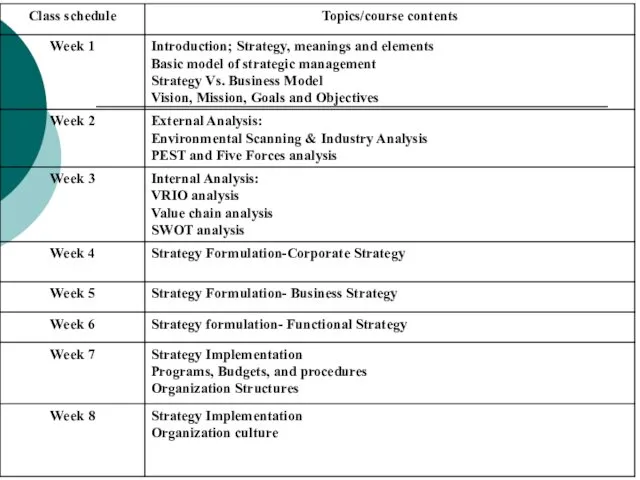
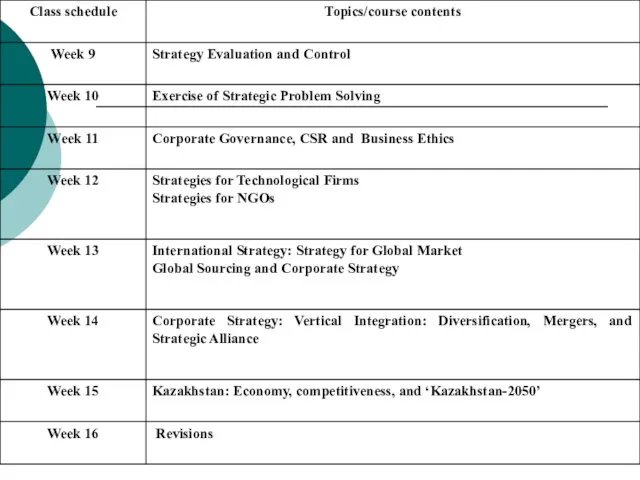
- 10. INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS Text: Thomas Wheelen & David Hunger (2017) Strategic Management and Business Policy, 15th Edition,
- 11. Use of mobile phone? How to manage the classes effectively?????
- 12. The Course Title: Strategy and Business Policy What is this course - all about ? Today’s
- 13. First, what is a Strategy? Your thought, your ideas, your assumptions
- 14. Are we talking about simple ‘plan’? If not a simple ‘plan’, then what are the differences
- 15. What organizations will do in future so that their performance will be better than their competitors.
- 16. Definition of Strategy Strategy is the long-term comprehensive master plan to gain competitive advantages (earning higher
- 17. Strategy- Level/Types/Categories Corporate Strategy (based on external analysis) Concentration Integration Diversification Etc. Business Strategy (based on
- 18. How you will make better recommendations for corporate level strategies? This decision could/should bring better performance
- 19. How you will make better recommendations for corporate level strategies? You need to conduct/look at External
- 20. How you will make better recommendations for business level strategies? This decision could/should bring/be a source
- 21. How you will make better recommendations for business level strategies? You need to conduct/look at Internal
- 22. How you will make better recommendations for functional level strategies? You need to look at/follow corporate
- 23. For successful business operations, you need to formulate detailed and comprehensive strategies.
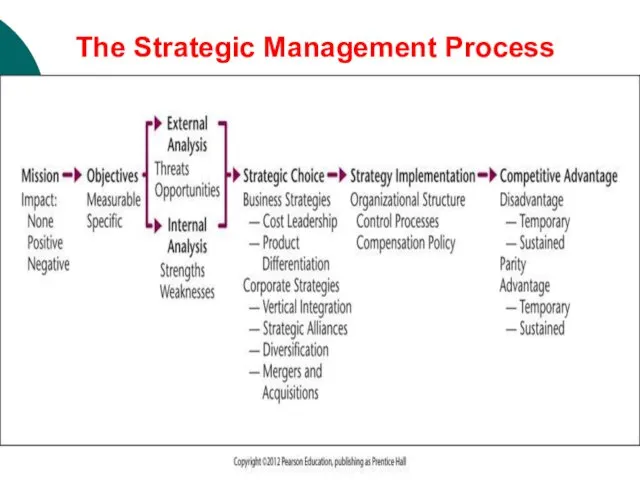
- 24. The Strategic Management Process
- 25. Final Thought: Definition of Strategy Strategy is the long-term comprehensive master plan (i.e., corporate, business, and
- 26. Strategy: Strategy is the long-term comprehensive master plan (i.e., corporate, business, and functional level) to gain/outperform
- 27. BUSINESS MODEL
- 28. BUSINESS MODEL The simplest definitions: A business model is the way in which a company generates
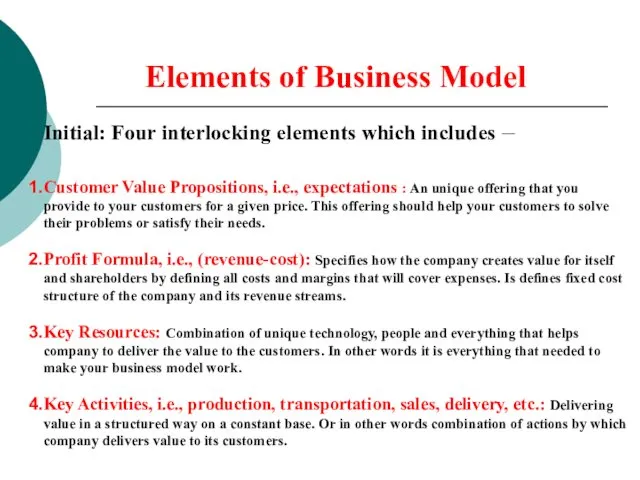
- 29. Elements of Business Model Initial: Four interlocking elements which includes – Customer Value Propositions, i.e., expectations
- 30. Elements of Business Model Later: Nine interlocking elements which includes – Customer Segment Value Propositions Customer
- 31. Elements of Business Model Customer segments - include different target customers for each product or service
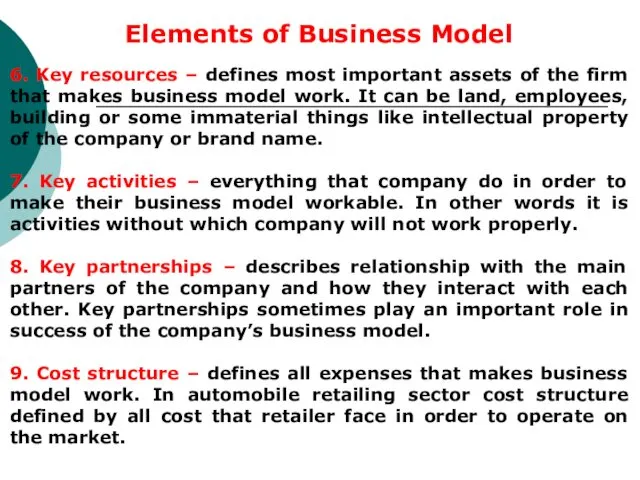
- 32. Elements of Business Model 6. Key resources – defines most important assets of the firm that
- 33. BUSINESS MODEL A good business model answers the questions: Who is the customer? What does the
- 34. Strategy is “how you will outperform the competitors” ( i.e., in terms of profitability or shareholders
- 35. In the business model development process, focus is primarily on customers. In strategy formulation process, focus
- 36. Business model is thinking about the financial viability of a company. If you are looking for
- 38. Professor W. Chan Kim Co-Author of Blue Ocean Strategy and Co-Director of the INSEAD Blue Ocean
- 39. Think About It One hundred years ago: Car industry Aviation industry Music recording TV Pharmaceuticals Management
- 40. Think About It (2) Thirty years ago: Cell phones Internet Biotechnology Coffee bars Mass discount retail
- 41. What is Blue Ocean Strategy? Best understood in contrast to the ‘red ocean’
- 42. The Red Ocean ‘the known market space’ “in red oceans, industry boundaries are defined and accepted,
- 43. The Blue Ocean ‘the unknown market space’ “untainted by competition…demand is created rather than fought over.
- 45. Six Contrasts
- 47. Скачать презентацию





































 Основной государственный экзамен по обществознанию – 2018
Основной государственный экзамен по обществознанию – 2018 Концепция системной модернизации высшего педагогического образования республики Казахстан
Концепция системной модернизации высшего педагогического образования республики Казахстан Профессиональное самоопределение
Профессиональное самоопределение Институт общественных наук и международных отношений
Институт общественных наук и международных отношений Семинар по индивидуальным проектам
Семинар по индивидуальным проектам Наука в современном обществ
Наука в современном обществ Работа с одарёнными детьми.
Работа с одарёнными детьми. Презентация Народные домашние способы лечения больных
Презентация Народные домашние способы лечения больных Конференция учителей иностранного языка
Конференция учителей иностранного языка Реализация курса внеурочной деятельности общеинтеллектуального направления Знакомимся с физикой в рамках реализации ФГОС ООО
Реализация курса внеурочной деятельности общеинтеллектуального направления Знакомимся с физикой в рамках реализации ФГОС ООО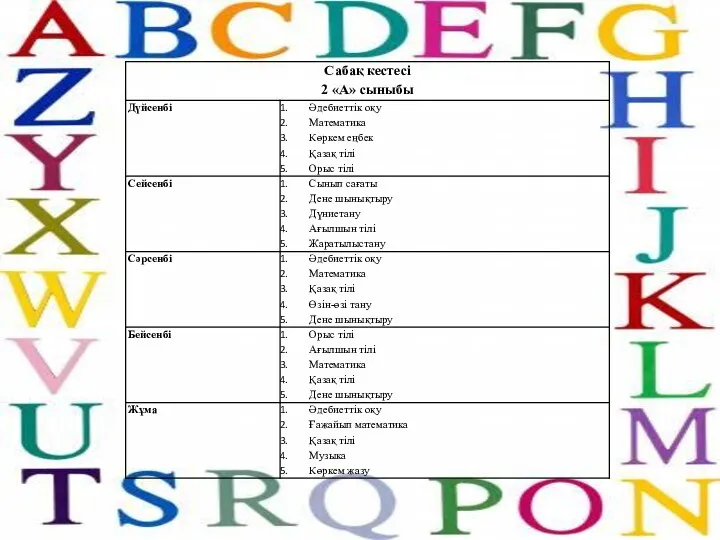 Сабақ кестесі
Сабақ кестесі кейс-метод
кейс-метод Основная образовательная программа подготовки специалистов в области физической культуры
Основная образовательная программа подготовки специалистов в области физической культуры Дуальное обучение в системе технического и профессионального образования казахстана. Содержание портфолио слушателя курсов
Дуальное обучение в системе технического и профессионального образования казахстана. Содержание портфолио слушателя курсов Правила выполнения презентаций
Правила выполнения презентаций Роль старшего вожатого в реализации нового Федерального государственного образовательного стандарта
Роль старшего вожатого в реализации нового Федерального государственного образовательного стандарта Наука и образование
Наука и образование Государственная политика в сфере образования 2021-2022
Государственная политика в сфере образования 2021-2022 Содержание образования и структура непрерывного образования
Содержание образования и структура непрерывного образования Зачисление в образовательное учреждение. Инструкция по подаче заявлений с использованием ЕПГУ 2021-2022
Зачисление в образовательное учреждение. Инструкция по подаче заявлений с использованием ЕПГУ 2021-2022 Целевой набор. ПАО Туполев
Целевой набор. ПАО Туполев Курс по алгебре для учеников 10-11 классов
Курс по алгебре для учеников 10-11 классов Календарный учебный график на 2022/2023 учебный год
Календарный учебный график на 2022/2023 учебный год Стратегическое планирование как инструмент управления образовательной организацией
Стратегическое планирование как инструмент управления образовательной организацией Образовательные услуги школы развития Дошколёнок на 2018-2019 год
Образовательные услуги школы развития Дошколёнок на 2018-2019 год Метод проектов в дошкольном учреждении.
Метод проектов в дошкольном учреждении. Основы учебно-исследовательской деятельности студентов
Основы учебно-исследовательской деятельности студентов Презентация. ФГОС НОО. Компетентностно – ориентированные задания как средство реализации системно – деятельностного подхода в стандартах второго поколения
Презентация. ФГОС НОО. Компетентностно – ориентированные задания как средство реализации системно – деятельностного подхода в стандартах второго поколения