Содержание
- 2. Public / private / home schooling Public education funded by the local → state → federal
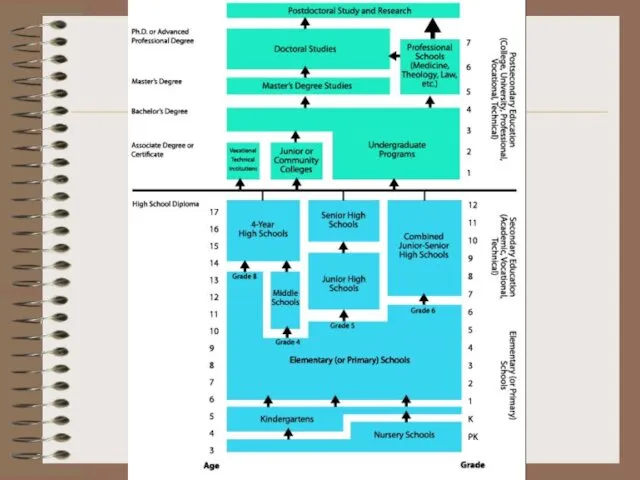
- 4. ELEMENTARY EDUCATION Admission - based on residency the curriculum in public elementary education is determined by
- 5. ELEMENTARY EDUCATION The No Child Left Behind Act of 2001 (NCLB) is a United States Act
- 7. SECONDARY EDUCATION Junior high school 7th, 8th, 9th grade students are given more independence, moving to
- 8. SECONDARY EDUCATION Senior high school (9th) 10th through 12th grade. The students in these grades are
- 9. SECONDARY EDUCATION Curriculum: mandatory subjects (studied for 2, 3 or 4 years): Science (biology, chemistry and
- 10. SECONDARY EDUCATION Curriculum: Electives Computers (word processing, programming, graphic design) Athletics (cross country, football, baseball, basketball,softball,
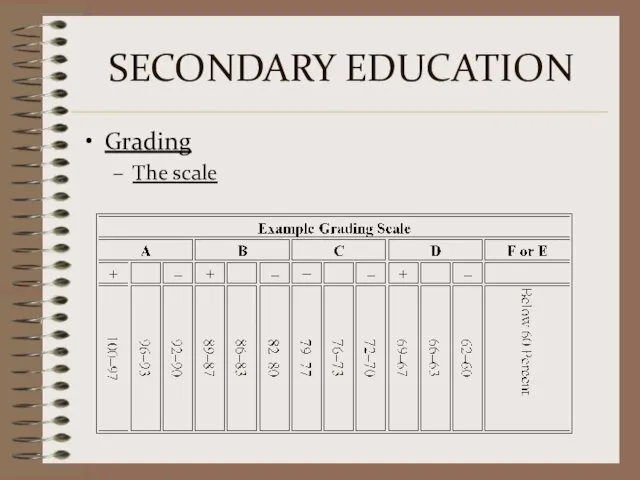
- 11. SECONDARY EDUCATION Grading The scale
- 12. SECONDARY EDUCATION Grading Report cards
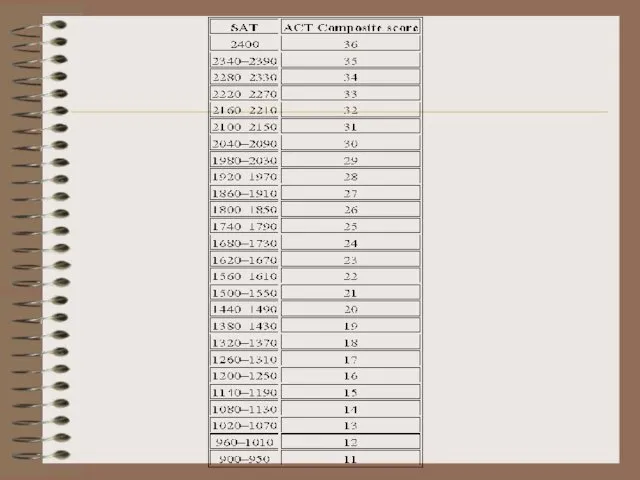
- 13. SECONDARY EDUCATION Testing yearly state tests to measure the "adequate yearly progress." (NCLB Act) SAT Reasoning
- 14. SECONDARY EDUCATION Testing The ACT (American College Testing) is a standardized test for high school achievement
- 16. HIGHER EDUCATION College/university distinction Private ones – more prestiguous Tuition varies from state to state. In
- 17. HIGHER EDUCATION Grant and scholarship programs (merit-based and need-based); government-sponsored and privately-sponsored community colleges (sometimes called
- 18. HIGHER EDUCATION Admissions based on: grades earned in high school, (the students' GPA) class ranking standardized
- 19. HIGHER EDUCATION undergraduate study: (1st year) freshman year (2nd year) sophomore year (3rd year) junior year
- 20. HIGHER EDUCATION The quality of American universities: Best: The Ivy League: Brown University, Columbia University, Cornell
- 21. A college at Princeton Univ. „Little Ivies” - old, small, exclusive, and academically competitive liberal arts
- 22. HIGHER EDUCATION The quality of American universities: public universities (state universities) rely on subsidies from their
- 23. according to Academic Ranking of World Universities
- 25. Скачать презентацию



















 Интеллектуальная игра для учащихся 8-11 классов
Интеллектуальная игра для учащихся 8-11 классов Школьные трудности и психологическое здоровье
Школьные трудности и психологическое здоровье Cтартовая ракетная установка с баржой (Морской старт)
Cтартовая ракетная установка с баржой (Морской старт) Презентация .Педагогический проект учителя истории на тему : Учить, не назидая, жизнь детей творя.
Презентация .Педагогический проект учителя истории на тему : Учить, не назидая, жизнь детей творя. Итоги демонстрационного экзамена как процедуры государственной итоговой аттестации
Итоги демонстрационного экзамена как процедуры государственной итоговой аттестации Сравнительный анализ коммерческих зарубежных и отечественных учебных заведений
Сравнительный анализ коммерческих зарубежных и отечественных учебных заведений Использование ИКТ как средство развития ценностно-смысловых компетенций.
Использование ИКТ как средство развития ценностно-смысловых компетенций. Предметные олимпиады школьников – путь в будущее
Предметные олимпиады школьников – путь в будущее Всероссийская олимпиада школьников по технологии
Всероссийская олимпиада школьников по технологии What? Where? When?
What? Where? When? Послы Русского народа: Амбассадоры культурного кода или молодые дипломаты?
Послы Русского народа: Амбассадоры культурного кода или молодые дипломаты? Нормативні вимоги до освітньо-виховного процесу у вищій школі
Нормативні вимоги до освітньо-виховного процесу у вищій школі Система образования Китая
Система образования Китая Презентация Метод проблемного диалога и его применение на уроках русского языка и литературы в контексте ФГОС нового поколения
Презентация Метод проблемного диалога и его применение на уроках русского языка и литературы в контексте ФГОС нового поколения Самоконтроль в учреждении образования, или как управлять качеством образования
Самоконтроль в учреждении образования, или как управлять качеством образования Индивидуальный подход как основа физического развития одаренных детей в условиях введения ФГОС дошкольного образования
Индивидуальный подход как основа физического развития одаренных детей в условиях введения ФГОС дошкольного образования Формирование УУД
Формирование УУД Значение дисциплины Проектно-исследовательская деятельность в подготовке специалиста индустрии гостеприимства
Значение дисциплины Проектно-исследовательская деятельность в подготовке специалиста индустрии гостеприимства Урок математики. Вимоги до уроку
Урок математики. Вимоги до уроку Оқушылардың шығармашылық қызуғышылығын қалыптастыру
Оқушылардың шығармашылық қызуғышылығын қалыптастыру Конкурсное задание Методический семинар
Конкурсное задание Методический семинар Презентация-отчет по ознакомлению детей 2-ой мл.группы с бытом и культурой Архангельской губернии.
Презентация-отчет по ознакомлению детей 2-ой мл.группы с бытом и культурой Архангельской губернии. Advance blended learning with NEDlines.org
Advance blended learning with NEDlines.org Eton college. History
Eton college. History Анализ результатов ОГЭ и ЕГЭ 2014 г. по физике в Мурманской области
Анализ результатов ОГЭ и ЕГЭ 2014 г. по физике в Мурманской области Оформление дипломной работы ПЭР
Оформление дипломной работы ПЭР Современный этап развития отечественной системы специального образования
Современный этап развития отечественной системы специального образования Название проекта. Дополнительная информация
Название проекта. Дополнительная информация