REGIONAL EDUCATIONAL LEGISLATION
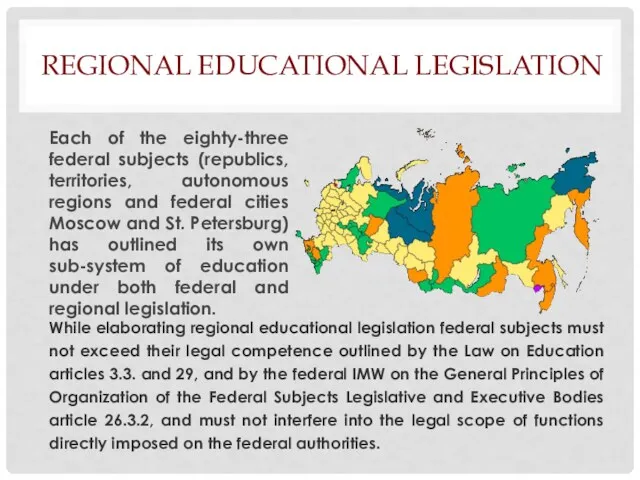
While elaborating regional educational legislation federal subjects must not
exceed their legal competence outlined by the Law on Education articles 3.3. and 29, and by the federal IMW on the General Principles of Organization of the Federal Subjects Legislative and Executive Bodies article 26.3.2, and must not interfere into the legal scope of functions directly imposed on the federal authorities.
Each of the eighty-three federal subjects (republics, territories, autonomous regions and federal cities Moscow and St. Petersburg) has outlined its own sub-system of education under both federal and regional legislation.








 Государственная итоговая аттестация 9 классов 2019 года
Государственная итоговая аттестация 9 классов 2019 года Национальная система учительского роста
Национальная система учительского роста Направления деятельности органов студенческого самоуправления
Направления деятельности органов студенческого самоуправления Сучасна система освіти у Франції
Сучасна система освіти у Франції Современные направления развития образования в России
Современные направления развития образования в России Итоговое сочинение 2017-2018
Итоговое сочинение 2017-2018 Шаблон презентации на защиту проекта
Шаблон презентации на защиту проекта Образование, как процесс приобретения знаний и умений
Образование, как процесс приобретения знаний и умений Inter-action - ақпараттық-білім беру порталы
Inter-action - ақпараттық-білім беру порталы Novosibirsk State Technical University
Novosibirsk State Technical University Оценочная деятельность в условиях реализации ФГОС НОО и ООО
Оценочная деятельность в условиях реализации ФГОС НОО и ООО Образование формирование образов. Современные модели образования
Образование формирование образов. Современные модели образования Оценивание и ФГОС
Оценивание и ФГОС Первый раз в первый класс по новым стандартам!
Первый раз в первый класс по новым стандартам! Презентация
Презентация Реализация деятельностного подхода к обучению с использованием ИКТ
Реализация деятельностного подхода к обучению с использованием ИКТ Индивидуальный образовательный маршрут
Индивидуальный образовательный маршрут Case study
Case study О создании рабочей группы школ по подготовке/корректировке проекта программы развития школы
О создании рабочей группы школ по подготовке/корректировке проекта программы развития школы День учителя в России
День учителя в России Как студенту написать научную статью
Как студенту написать научную статью Презентация Духовно-нравственное здоровье школьника
Презентация Духовно-нравственное здоровье школьника Зовнішнє незалежне оцінювання з української мови і літератури: досвід і перспективи
Зовнішнє незалежне оцінювання з української мови і літератури: досвід і перспективи Тренинг: Основы публичного выступления
Тренинг: Основы публичного выступления Who wants to be the best
Who wants to be the best Опыт Челябинской области в организации профессионального образования и профессионального обучения лиц с ОВЗ и инвалидов
Опыт Челябинской области в организации профессионального образования и профессионального обучения лиц с ОВЗ и инвалидов Влияние основных тенденций развития современного образования на формирование личности учащихся
Влияние основных тенденций развития современного образования на формирование личности учащихся Дессиминатор образовательной сферы
Дессиминатор образовательной сферы