Содержание
- 2. 3 How managers can make a decision in certainty environment? Search for options with the maximum
- 3. 4 How managers can make a decision in risk – and uncertainty environment?
- 4. Unlike short-term decisions, long-term decisions are made under risk and uncertainty I don't know what events
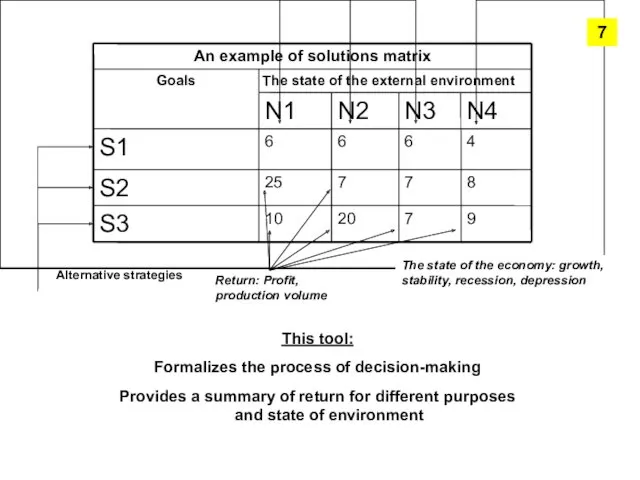
- 5. Solutions matrix I wonder, what is it? Payment matrix In conditions of risk and uncertainty typical
- 6. This tool: Formalizes the process of decision-making Provides a summary of return for different purposes and
- 7. Decision-making in terms of risk
- 8. Methods of risk evaluation: (Risk – probability of undesired occurense) 9
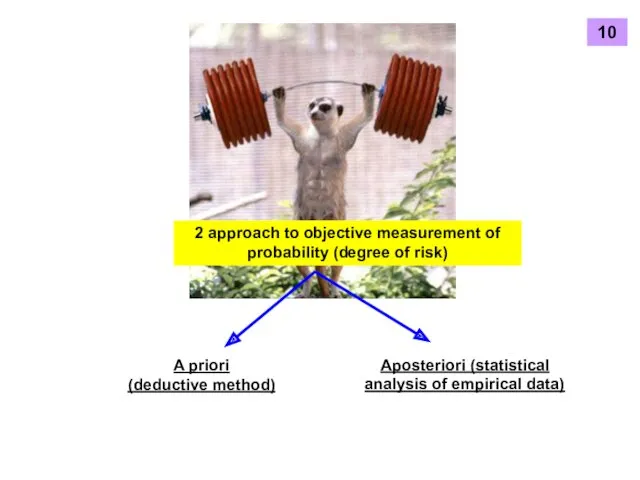
- 9. 2 approach to objective measurement of probability (degree of risk) A priori (deductive method) Aposteriori (statistical
- 10. A priori (deductive method) No experiment and analysis of past experience characteristics of possible cases are
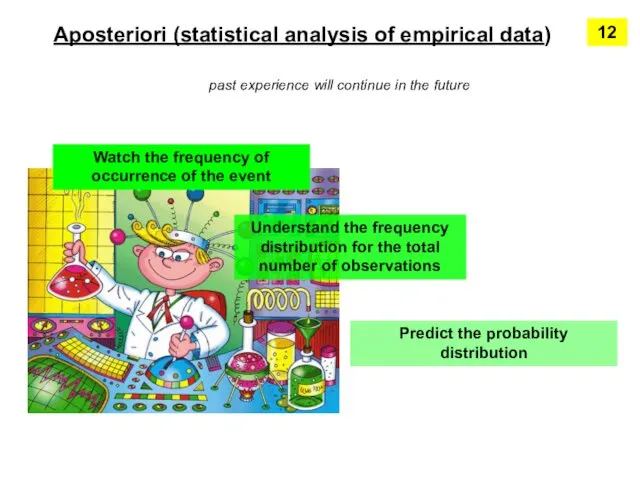
- 11. Aposteriori (statistical analysis of empirical data) past experience will continue in the future Watch the frequency
- 12. Frequency distribution can be converted into a probability distribution 13 If a certain load factor appeared
- 13. Determine and minimize the risks inherent to a particular project One of the methods: the calculation
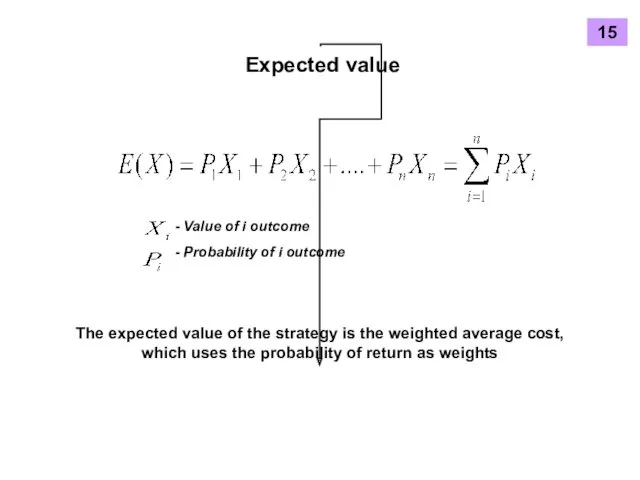
- 14. Expected value - Value of i outcome - Probability of i outcome The expected value of
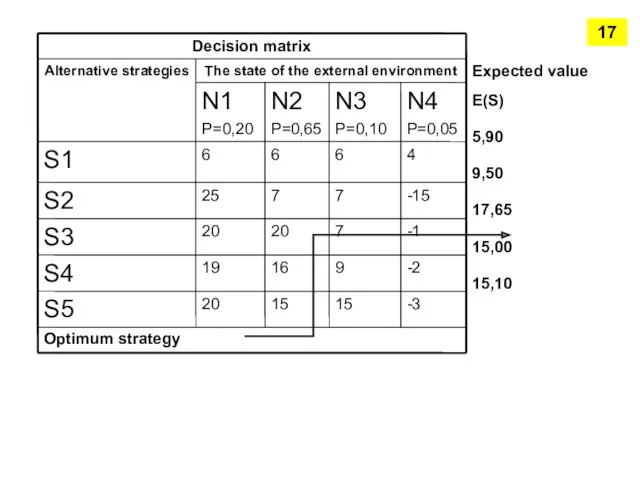
- 15. Manager choose strategy with the highest expected value 16
- 16. Expected value E(S) 5,90 9,50 17,65 15,00 15,10 Optimum strategy 17
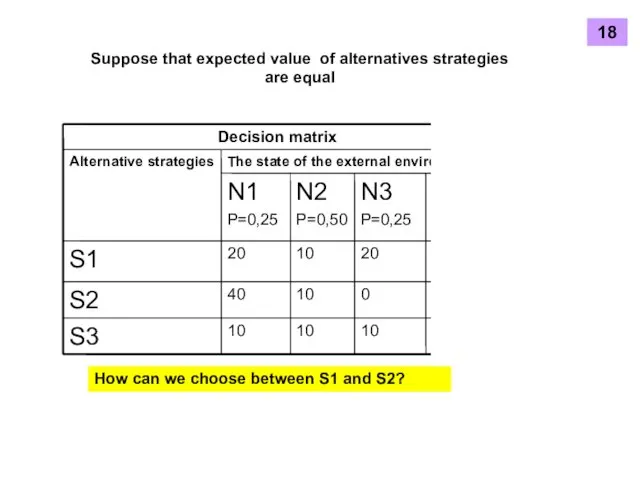
- 17. Suppose that expected value of alternatives strategies are equal How can we choose between S1 and
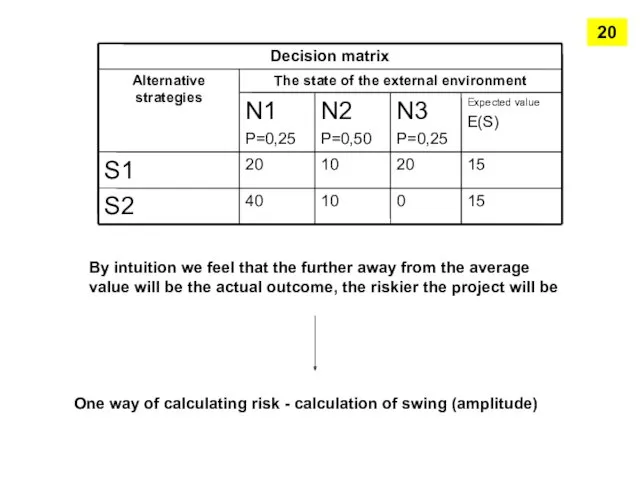
- 18. New criteria – degree of risk May be determined as deviation scope of probable outcome from
- 19. By intuition we feel that the further away from the average value will be the actual
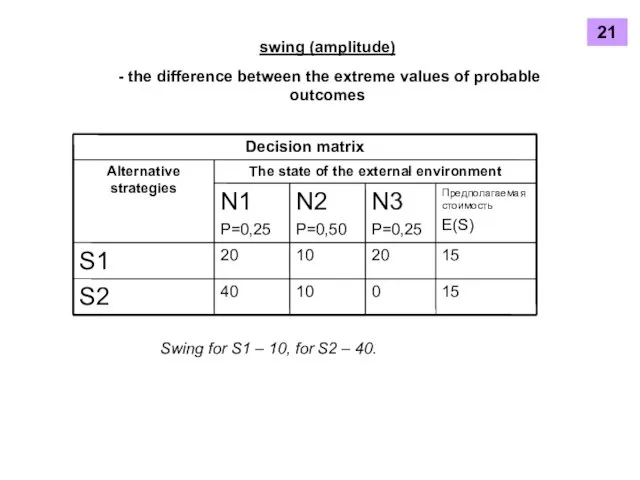
- 20. swing (amplitude) - the difference between the extreme values of probable outcomes Swing for S1 –
- 21. root-mean-square deviation The higher root-mean-square deviation - the higher risk 22
- 22. Calculation of the root-mean-square deviation: 23
- 24. Скачать презентацию












 Готовность ребёнка к школе
Готовность ребёнка к школе презентация к семинару для педагогов
презентация к семинару для педагогов Пути выхода из конфликтных ситуаций
Пути выхода из конфликтных ситуаций Психолого-педагогическое сопровождение адаптации учащихся 10-х классов к новой ситуации обучения
Психолого-педагогическое сопровождение адаптации учащихся 10-х классов к новой ситуации обучения Психічне старіння
Психічне старіння Психологічні особливості педагогічного спілкування. (Лекція 7)
Психологічні особливості педагогічного спілкування. (Лекція 7) Технология развития критического мышления
Технология развития критического мышления Индивидуально-психологические особенности руководителя
Индивидуально-психологические особенности руководителя Взаимодействие группы Почемучки с семьями воспитанников. Современные подходы и формы взаимодействия с семьёй
Взаимодействие группы Почемучки с семьями воспитанников. Современные подходы и формы взаимодействия с семьёй Девиантное поведение подростков
Девиантное поведение подростков Вчимося жити разом
Вчимося жити разом Психология саморегуляции: структура курса
Психология саморегуляции: структура курса Понятие об уровнях коммуникации
Понятие об уровнях коммуникации Потреби людей
Потреби людей Проведение экспертизы медийных продуктов
Проведение экспертизы медийных продуктов Как научиться понимать других людей
Как научиться понимать других людей Психологические закономерности общения
Психологические закономерности общения Психологические основы профессиональной деятельности
Психологические основы профессиональной деятельности Физиологические и психологические особенности подросткового возраста
Физиологические и психологические особенности подросткового возраста Сущность и содержание деловых коммуникаций
Сущность и содержание деловых коммуникаций Устранение причин стресса путем совершенствования поведенческих навыков
Устранение причин стресса путем совершенствования поведенческих навыков Научное исследование как особая форма познавательной деятельности в области психологии и педагогики
Научное исследование как особая форма познавательной деятельности в области психологии и педагогики Дискурсивное поведение мужчин и женщин
Дискурсивное поведение мужчин и женщин The Reasoned Action Approach
The Reasoned Action Approach Қазіргі этнопсихология
Қазіргі этнопсихология Всесвітній день запобігання самогубствам
Всесвітній день запобігання самогубствам Обучение
Обучение Как работать с желаниями
Как работать с желаниями