Different approaches to the NTB
Four major propositions:
belongingness need is innate
in humans and thus universal
two distinct orientations exist as to how the need for belongingness guides one’s interaction with the social world (growth orientation and deficit-reduction orientation)
prior social experiences will dictate how the need for belongingness will develop into one of the two belongingness need orientations
people’s belongingness orientations not only lead to different social experiences but also influence how they are actually perceived and treated by others
Belongingness Orientation Model








 Классификация профессий Климов
Классификация профессий Климов Арт-терапия. Музыкотерапия
Арт-терапия. Музыкотерапия Особенности развития личности в подростковом возрасте
Особенности развития личности в подростковом возрасте Педагогический совет Психология крика
Педагогический совет Психология крика Методы оценки уровня стресса
Методы оценки уровня стресса Сын тұрғысынан ойлау технологиясы арқылы оқушылардың ой-өрісін дамыту
Сын тұрғысынан ойлау технологиясы арқылы оқушылардың ой-өрісін дамыту Преодоление стресса
Преодоление стресса Мифы о нисхождении в подземный мир в психотерапии кризисных состояний
Мифы о нисхождении в подземный мир в психотерапии кризисных состояний Психология как наука. Лекция № 1
Психология как наука. Лекция № 1 Личностное развитие. План индивидуального развития
Личностное развитие. План индивидуального развития 5 шагов к настоящему Доверию
5 шагов к настоящему Доверию Особенности деловых коммуникаций
Особенности деловых коммуникаций Одаренность.Иллюзия и реальность.
Одаренность.Иллюзия и реальность. Будь смелым. 6 класс
Будь смелым. 6 класс Психология общения
Психология общения Жестокое обращение с детьми в семье родительское собрание
Жестокое обращение с детьми в семье родительское собрание Диагностика эмоциональной сферы ребенка. Методика Метаморфозы
Диагностика эмоциональной сферы ребенка. Методика Метаморфозы Физиологические процессы внимания
Физиологические процессы внимания Социальная установка
Социальная установка Особенности когнитивного стиля личности юношей с преступным поведением
Особенности когнитивного стиля личности юношей с преступным поведением ПСИХОЛОГИЧЕСКОЕ ЗДОРОВЬЕ
ПСИХОЛОГИЧЕСКОЕ ЗДОРОВЬЕ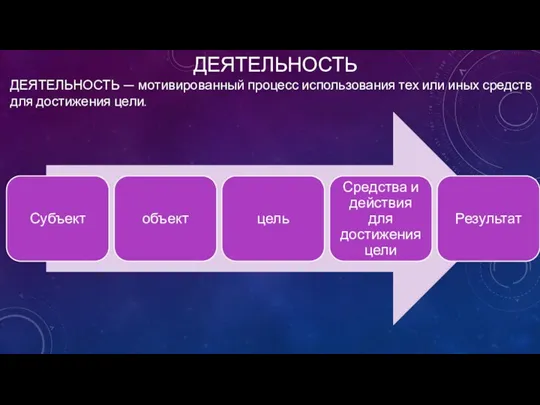 Деятельность человека. 4 урок
Деятельность человека. 4 урок Консультирование трудных клиентов
Консультирование трудных клиентов Как бороться со стрессом
Как бороться со стрессом Способы аргументации
Способы аргументации Психотипы. Практическое занятие
Психотипы. Практическое занятие Проблема буллинга в российских школах: анализ, последствия и предложения
Проблема буллинга в российских школах: анализ, последствия и предложения