Содержание
- 2. Class – why? Classes split application code to parts (from sophisticated to simple) Very often class
- 3. Class Description class name { // field declarations // method declarations } * Infopulse Training Center
- 4. Class Fields Class fields should be declared inside class out of all class methods Fields can
- 5. Defining Methods return_type method_name (parameter_list){ // method body } Example: int getFinalData(int a, int r){ int
- 6. Return Type The return type describes the value that comes back from the method A method
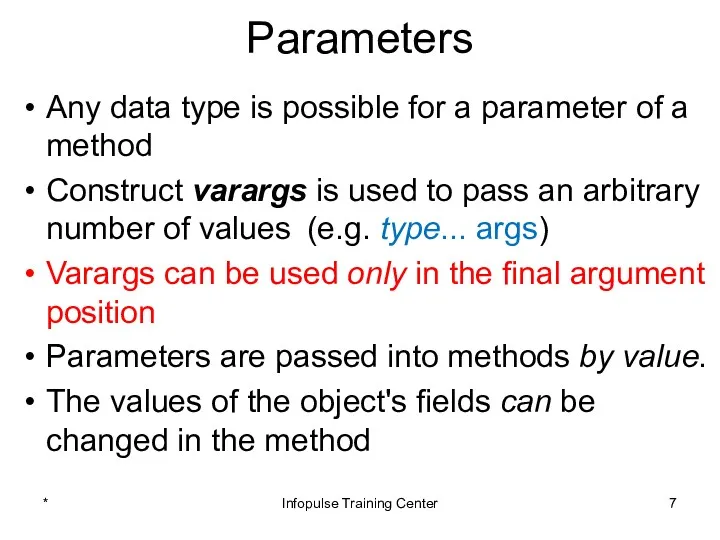
- 7. Parameters Any data type is possible for a parameter of a method Construct varargs is used
- 8. Constructors Constructor name should be the same as class name Constructor has no return type The
- 9. Objects Creating Object: class_name object_variable = new construtor_call; Declaring a Variable to Refer to an Object:
- 10. Using the this Keyword this is a reference to the current object The most common example:
- 11. Complex Numbers (1 of 4) Is it always possible to solve square equation within real numbers
- 12. Complex Numbers (2 of 4) Is it always possible to solve square equation within real numbers
- 13. Complex Numbers (3 of 4) Number of a + b * i type where a and
- 14. Complex Numbers (4 of 4) To add complex numbers use formula To multiply complex numbers use
- 15. Exercise 2.4.1. Create a class for saving and manipulating complex numbers. * Infopulse Training Center
- 16. Step by Step Solution Check problem definition. If it is clear go to step 2 Create
- 17. Step by Step Solution Check problem definition. If it is clear go to step 2 Create
- 18. Class for Complex Numbers /** * Represents complex numbers */ class Complex { } * Infopulse
- 19. Step by Step Solution Check problem definition. If it is clear go to step 2 Create
- 20. Class for Complex Numbers class Complex { /** * Real part of a complex number */
- 21. Step by Step Solution Check problem definition. If it is clear go to step 2 Create
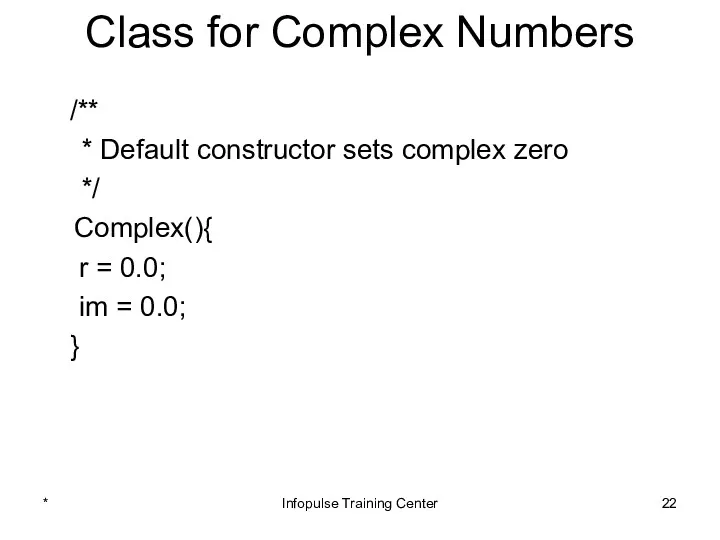
- 22. Class for Complex Numbers /** * Default constructor sets complex zero */ Complex(){ r = 0.0;
- 23. Class for Complex Numbers /** * Initializes a complex number * @param r - real part
- 24. Class for Complex Numbers double getR() { return r; } void setR(double value){ r = value;
- 25. Accessors in Eclipse Right click in text editor, and select Source > Generate Getters and Setters
- 26. Step by Step Solution Check problem definition. If it is clear go to step 2 Create
- 27. Class for Complex Numbers /** * Returns module of the complex number */ double getModule(){ }
- 28. Step by Step Solution Check problem definition. If it is clear go to step 2 Create
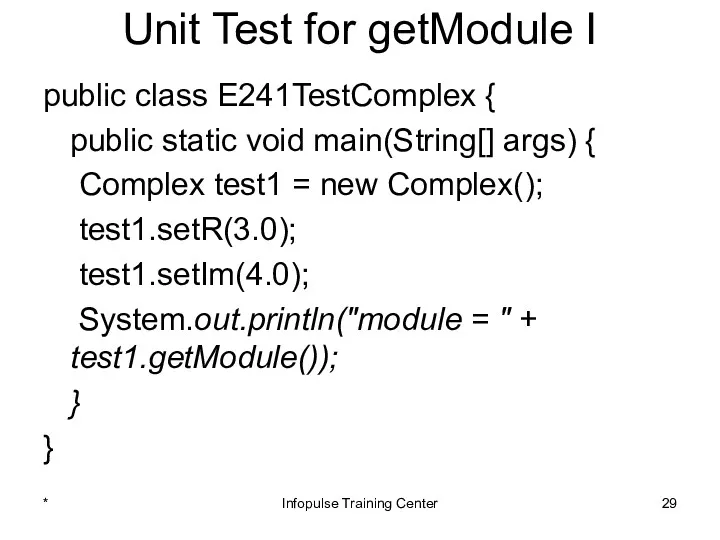
- 29. Unit Test for getModule I public class E241TestComplex { public static void main(String[] args) { Complex
- 30. Unit Test for getModule II public class E241TestComplex { public static void main(String[] args) { Complex
- 31. Step by Step Solution Check problem definition. If it is clear go to step 2 Create
- 32. Class for Complex Numbers /** * Returns module of the complex number */ double getModule(){ return
- 33. Class for Complex Numbers Complex add(Complex value){ } Complex multiply(Complex value){ } * Infopulse Training Center
- 34. Unit Test for getModule public class E241TestComplex { public static void main(String[] args) { Complex conjugate1
- 35. Class for Complex Numbers Complex add(Complex value){ return new Complex(this.r + value.getR(), this.im + value.getIm()); }
- 36. Exercise 2.4.1. See 241Complex project for the full text * Infopulse Training Center
- 37. Exercise 2.4.2 (1 of 2) 3D Vector is ordered sequence of 3 numbers (vector’s coordinates): Sum
- 39. Скачать презентацию

































 Фотосъёмка. Виды и методы
Фотосъёмка. Виды и методы Социологический метод исследование рынка и потребительского поведения
Социологический метод исследование рынка и потребительского поведения Транспортное строительство. Защита от шума жилой застройки
Транспортное строительство. Защита от шума жилой застройки Беседа с элементами инсценировки о вреде курения Курить – здоровью вредить
Беседа с элементами инсценировки о вреде курения Курить – здоровью вредить Мотивы плохого поведения ребёнка
Мотивы плохого поведения ребёнка Детский творческо-исследовательский проект В кругу моей семьи
Детский творческо-исследовательский проект В кругу моей семьи Система маркетинговой информации и маркетинговые исследования
Система маркетинговой информации и маркетинговые исследования Система автоматического освещения рабочего пространства
Система автоматического освещения рабочего пространства Этапы решения задач с помощью ЭВМ
Этапы решения задач с помощью ЭВМ Дедуктивные выводы из сложных суждений. Логика
Дедуктивные выводы из сложных суждений. Логика Программа Основы производственного менеджмента
Программа Основы производственного менеджмента Смешанные дистрофии. Нарушение обмена хромо- и нуклеопротеидов
Смешанные дистрофии. Нарушение обмена хромо- и нуклеопротеидов Самые необычные флаги в мире
Самые необычные флаги в мире Именные реакции в органической химии
Именные реакции в органической химии Самый умный. Финал
Самый умный. Финал Повторение Сложение и вычитание, Свойства сложения
Повторение Сложение и вычитание, Свойства сложения К уроку технологии 1 класс
К уроку технологии 1 класс Рельеф Евразии
Рельеф Евразии Система работи з обдарованими дітьми
Система работи з обдарованими дітьми Моя профессия – Помощник машиниста локомотива
Моя профессия – Помощник машиниста локомотива Мұнайды мазутқа дейін өңдеу. Процестің материалдық балансы
Мұнайды мазутқа дейін өңдеу. Процестің материалдық балансы Методическое объединение преподавателей математики. О работе объединения в 2017-2018 учебном году
Методическое объединение преподавателей математики. О работе объединения в 2017-2018 учебном году Arany nagykőrösi ballada korszaka
Arany nagykőrösi ballada korszaka Модель учебного центра компании Ростех
Модель учебного центра компании Ростех Локальные очистные сооружения
Локальные очистные сооружения Oil_and_gas_transportation_Kholomeeva_T
Oil_and_gas_transportation_Kholomeeva_T Электроника России. История и современность
Электроника России. История и современность Professions (начальная школа)
Professions (начальная школа)