Содержание
- 2. Alternative Energy Sources Solar Wind Hydropower Tidal Power Biomass Geothermal
- 3. Solar Power
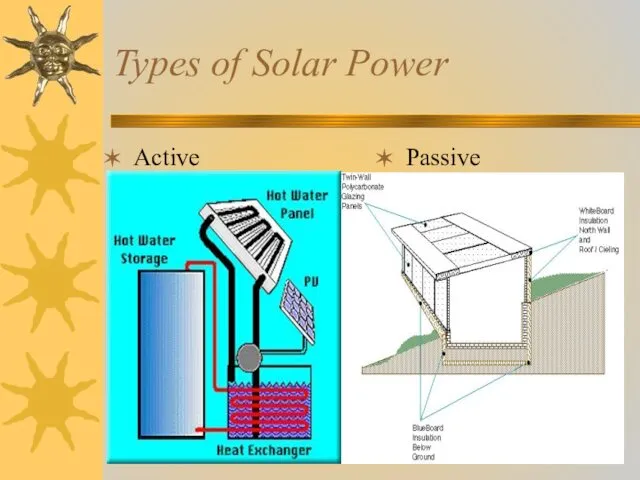
- 4. Types of Solar Power Active Passive
- 5. Active Solar Power Energy from sun is stored in a “thermal mass” When needed, heat from
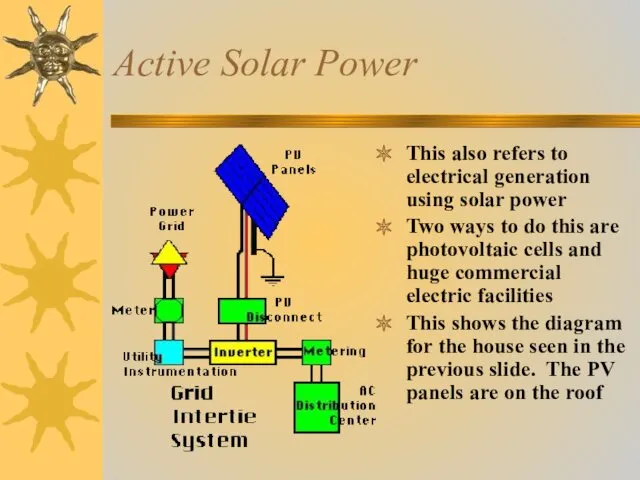
- 6. Active Solar Power This also refers to electrical generation using solar power Two ways to do
- 7. Large-scale Solar Electric Site
- 8. Large-scale Solar Electric Site These facilities use solar power to heat water to form steam. The
- 9. Passive Solar Power Works on the principle that hot air rises and cool air sinks (convection)
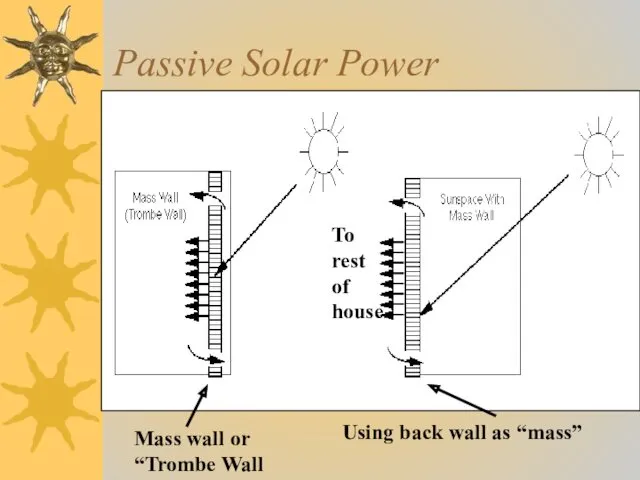
- 10. Passive Solar Power Mass wall or “Trombe Wall Using back wall as “mass” To rest of
- 11. Solar Power Benefits Abundant No greenhouse gases, few other pollutants Simple, minimal repair needed Cheap over
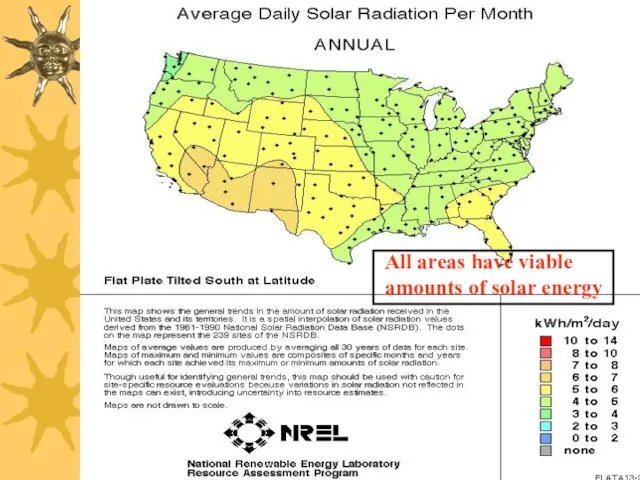
- 12. All areas have viable amounts of solar energy
- 13. Some solar power history Solar power furnace was used by Lavoisier to discover elements, particularly nitrogen
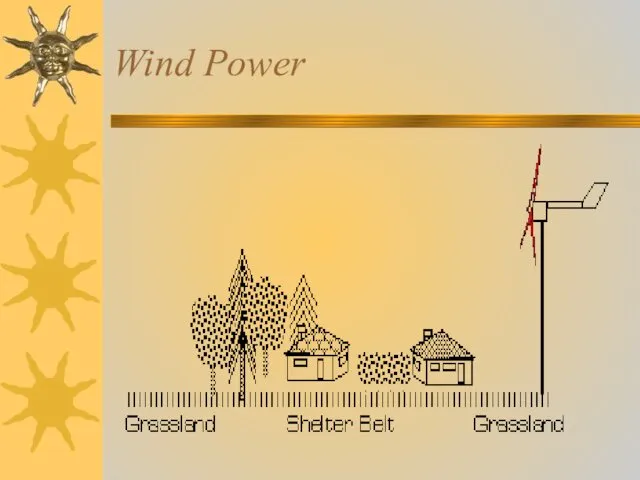
- 14. Wind Power
- 15. Wind power Can be used for mechanical tasks, e.g. pumping water Can be used for generation
- 16. Mechanical Power Windmills High torque, low-speed to pump water, grind grain, saw wood
- 17. Electrical Power Windmills High speed, low torque machines Will turn themselves off if wind speed exceeds
- 18. Effects of windpower No greenhouse gases Few other pollutants Cheap Abundant Simple Some noise pollution Metal
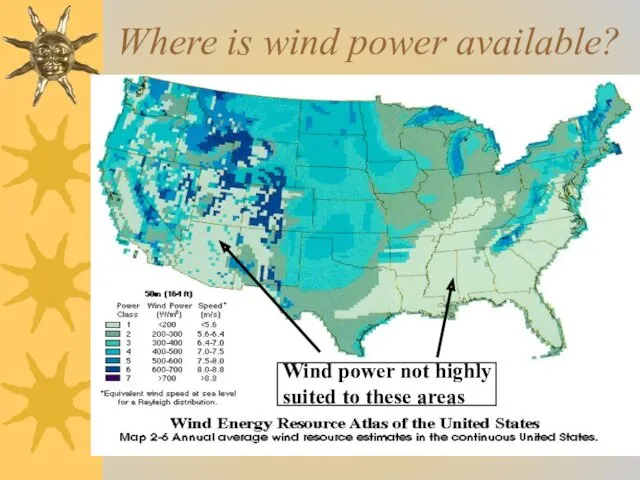
- 19. Where is wind power available? Wind power not highly suited to these areas
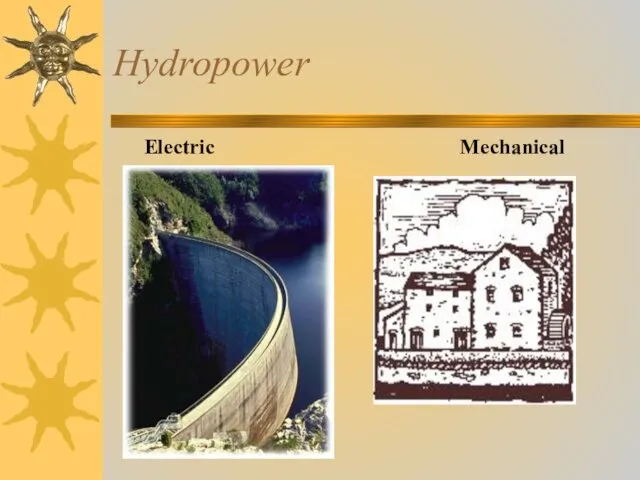
- 20. Hydropower Electric Mechanical
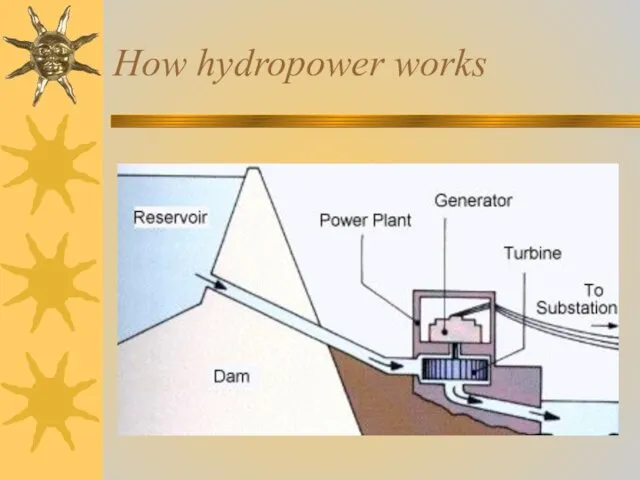
- 21. How hydropower works
- 22. Negative effects of Hydropower Flooding the land Displacement of local inhabitants Local climatic changes Tectonic activities
- 23. Positive Effects of Hydropower Can generate electricity Can do mechanical work, e.g. grind grain No greenhouse
- 24. Tidal Power
- 25. Tidal Power Essentially entails placing a dam across an ocean inlet and harnessing the energy as
- 26. Biomass Energy
- 27. Biomass Pros & Cons Burning biomass gets rid of solid waste Creates energy Creates new markets
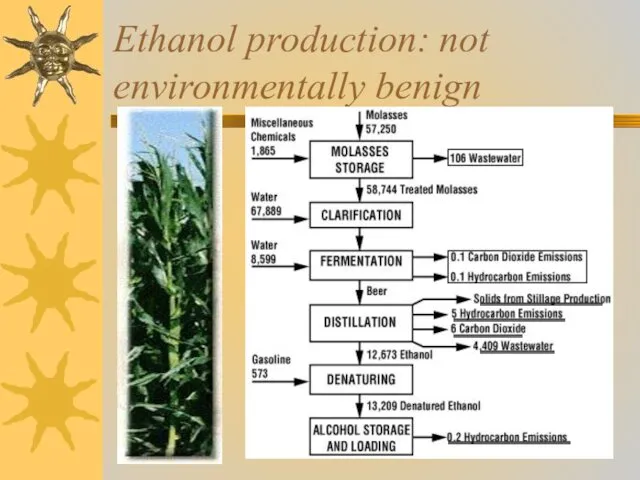
- 28. Ethanol production: not environmentally benign
- 29. Geothermal Energy
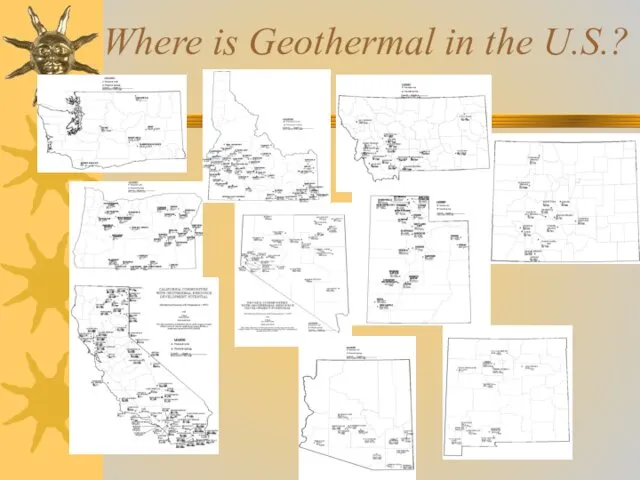
- 30. Where is Geothermal in the U.S.?
- 31. Primarily in western U.S. Pros – Can be used for electricity generation, space heating, cooking &
- 32. How does it work? Drill to deep, hot rock Either wet system where heated water belowground
- 34. Скачать презентацию





















 Биполярные транзисторы
Биполярные транзисторы Групповое занятие по коррекции устной и письменной речи у младших школьников.
Групповое занятие по коррекции устной и письменной речи у младших школьников. Кем я вижу себя через 7 лет. Ващев Евгений
Кем я вижу себя через 7 лет. Ващев Евгений Презентация 11. Бытовой жанр в живописи 70-80-х годов
Презентация 11. Бытовой жанр в живописи 70-80-х годов Договорные отношения в туристической деятельности. Тема 4
Договорные отношения в туристической деятельности. Тема 4 Самоуправление- важнейший компонент воспитательной системы школы
Самоуправление- важнейший компонент воспитательной системы школы Розвиток мовлення 4 клас ІІ семестр
Розвиток мовлення 4 клас ІІ семестр Основные производственные процессы в тепловодном карповом прудовом хозяйстве
Основные производственные процессы в тепловодном карповом прудовом хозяйстве Walk, crawl, stagger
Walk, crawl, stagger Современные информационно-управляющие системы в управлении движением на железнодорожном транспорте
Современные информационно-управляющие системы в управлении движением на железнодорожном транспорте Природоведение. Урок знакомства.
Природоведение. Урок знакомства. Емдік тамақтандыру. Анемия. Қызба. Оттегі терапия
Емдік тамақтандыру. Анемия. Қызба. Оттегі терапия Специфика исследований в бизнесе и менеджменте
Специфика исследований в бизнесе и менеджменте Опухоли, опухолеподобные поражения и кисты слюнных желез. Клиника, диагностика, лечение. (Лекция 7)
Опухоли, опухолеподобные поражения и кисты слюнных желез. Клиника, диагностика, лечение. (Лекция 7) Резные кружева. Русская домовая резьба
Резные кружева. Русская домовая резьба Красный основной соус и его производные
Красный основной соус и его производные Поздравление мамам
Поздравление мамам Pour rire sans reflechir
Pour rire sans reflechir Канальное кодирование. Основы помехоустойчивого кодирования
Канальное кодирование. Основы помехоустойчивого кодирования Склейка Ландыши
Склейка Ландыши Физминутка для глаз Звездочет
Физминутка для глаз Звездочет Использование игровых методов при принятии решений в условиях риска и неопределенности понятие об игровых методах. Тема 8
Использование игровых методов при принятии решений в условиях риска и неопределенности понятие об игровых методах. Тема 8 Вопросы репродуктивного здоровья, современные методы обследования и лечения бесплодия
Вопросы репродуктивного здоровья, современные методы обследования и лечения бесплодия Универсальные семейные ценности
Универсальные семейные ценности Интерактивная игра-викторина по русским народным сказкам для детей старшего дошкольного возраста с ОИН
Интерактивная игра-викторина по русским народным сказкам для детей старшего дошкольного возраста с ОИН Оборудование и технология для гибридной лазерно-дуговой сварки сталей и алюминиевых сплавов
Оборудование и технология для гибридной лазерно-дуговой сварки сталей и алюминиевых сплавов Готовимся к ЕГЭ по биологии. Презентация – практикум по подготовке к успешному выполнению задания С5
Готовимся к ЕГЭ по биологии. Презентация – практикум по подготовке к успешному выполнению задания С5 Псков. Мастеровой. Гости праздника
Псков. Мастеровой. Гости праздника