Содержание
- 2. Introduction What problems you have had with fuels: - during bunkering? with the quality of bunkers?
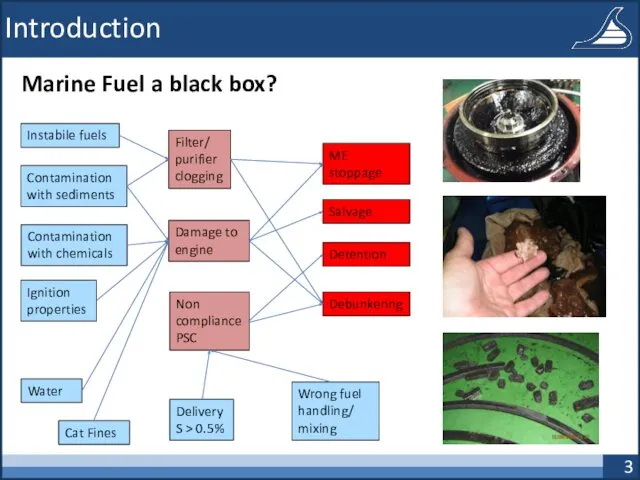
- 3. Introduction Marine Fuel a black box? Instabile fuels Contamination with sediments Filter/ purifier clogging Damage to
- 4. IMO 2020 General From the 01.01.2020 the global sulphur limit will be 0.5% inlet engines! No
- 5. IMO 2020/ Definition of fuels ISO 8217 Specification RM = Residual Fuels (HFO) DM = Distillate
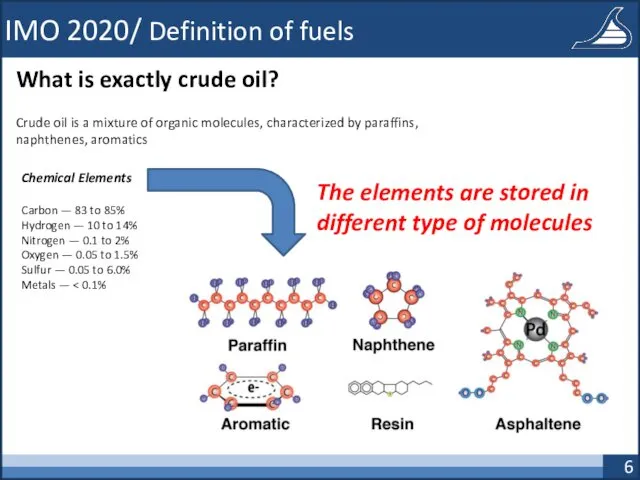
- 6. IMO 2020/ Definition of fuels What is exactly crude oil? Chemical Elements Carbon — 83 to
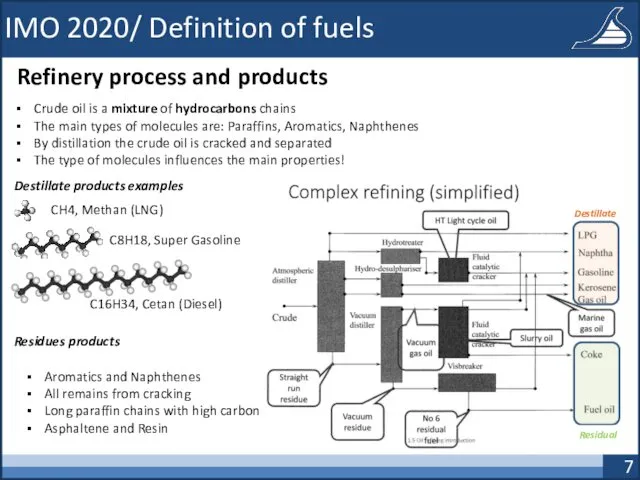
- 7. IMO 2020/ Definition of fuels Refinery process and products Crude oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons
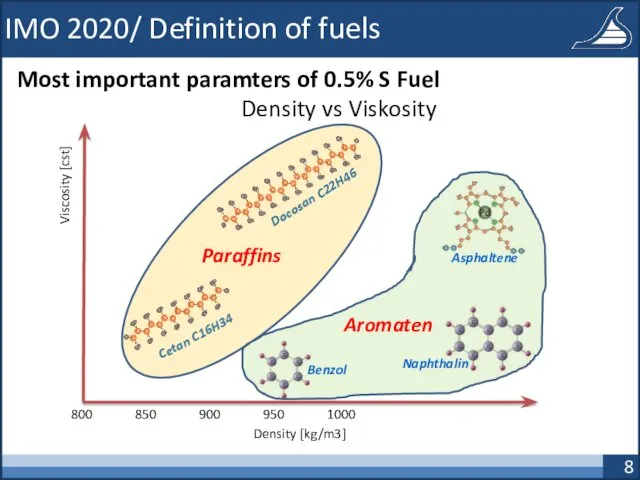
- 8. IMO 2020/ Definition of fuels Most important paramters of 0.5% S Fuel Density vs Viskosity Density
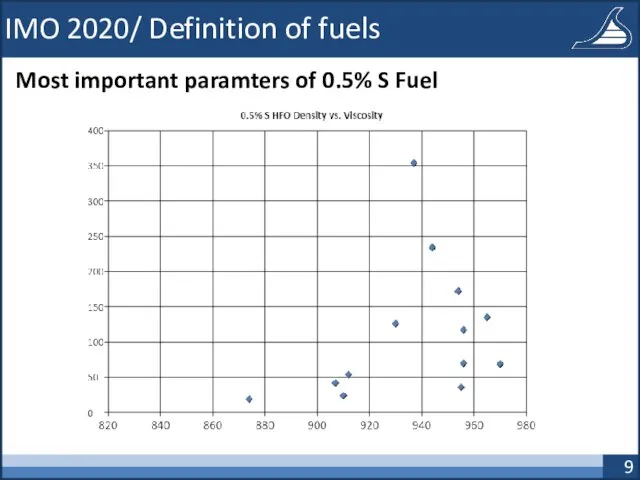
- 9. IMO 2020/ Definition of fuels Most important paramters of 0.5% S Fuel
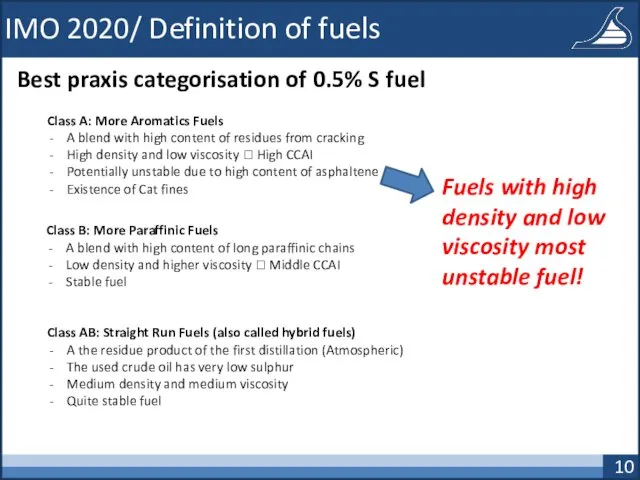
- 10. IMO 2020/ Definition of fuels Best praxis categorisation of 0.5% S fuel Class A: More Aromatics
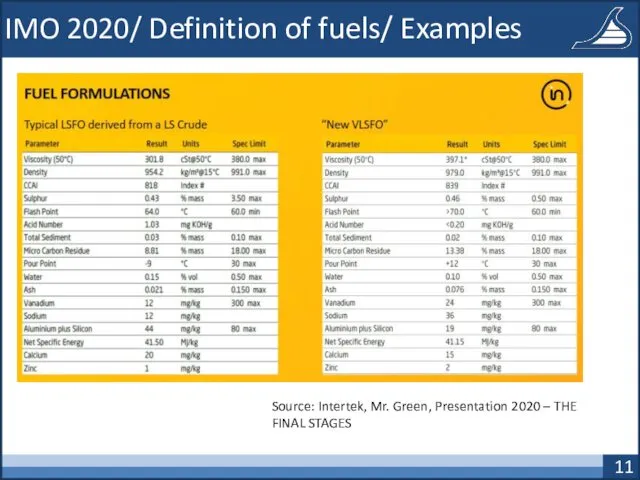
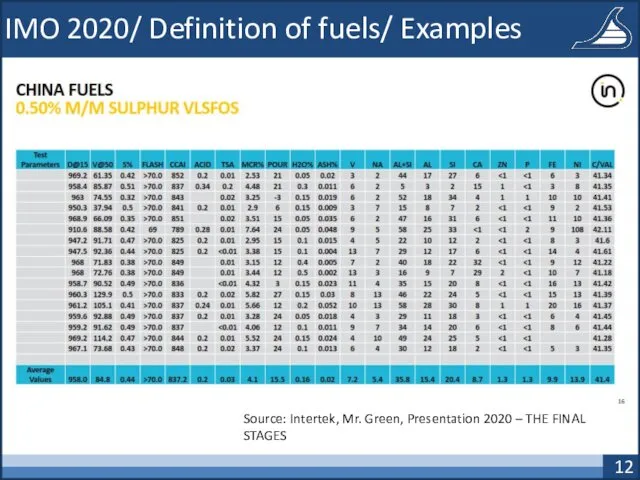
- 11. IMO 2020/ Definition of fuels/ Examples Source: Intertek, Mr. Green, Presentation 2020 – THE FINAL STAGES
- 12. IMO 2020/ Definition of fuels/ Examples Source: Intertek, Mr. Green, Presentation 2020 – THE FINAL STAGES
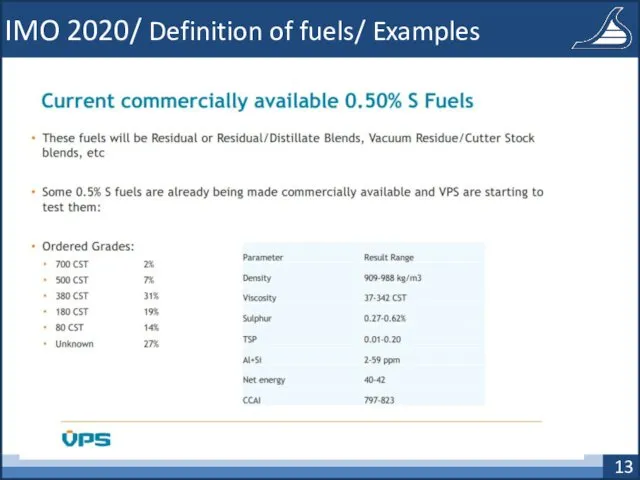
- 13. IMO 2020/ Definition of fuels/ Examples
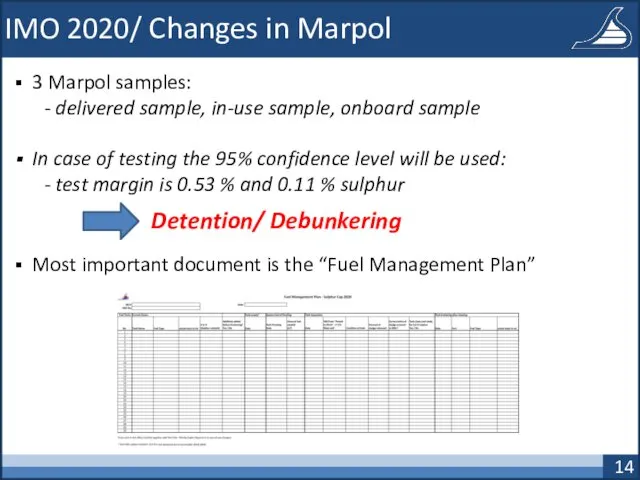
- 14. IMO 2020/ Changes in Marpol 3 Marpol samples: - delivered sample, in-use sample, onboard sample In
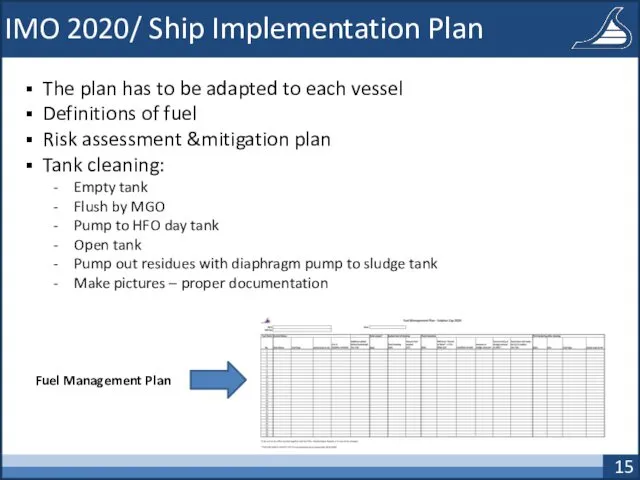
- 15. IMO 2020/ Ship Implementation Plan The plan has to be adapted to each vessel Definitions of
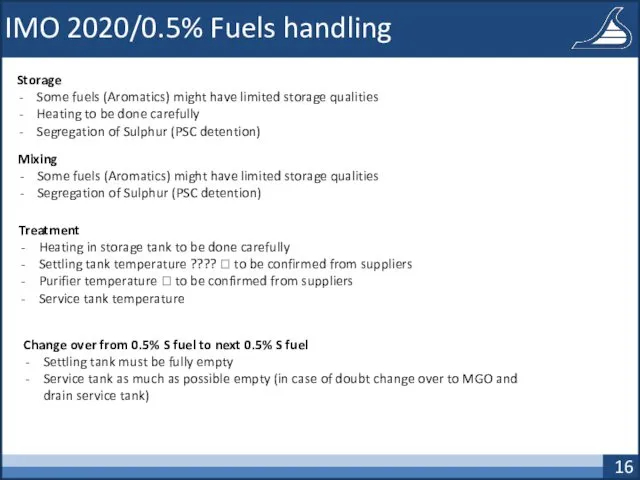
- 16. IMO 2020/0.5% Fuels handling Storage Some fuels (Aromatics) might have limited storage qualities Heating to be
- 17. Bunker Sampling, Official Sample, BDN 1. Number of samples (Supplier and Vessels Sample) 2. Official Samples/
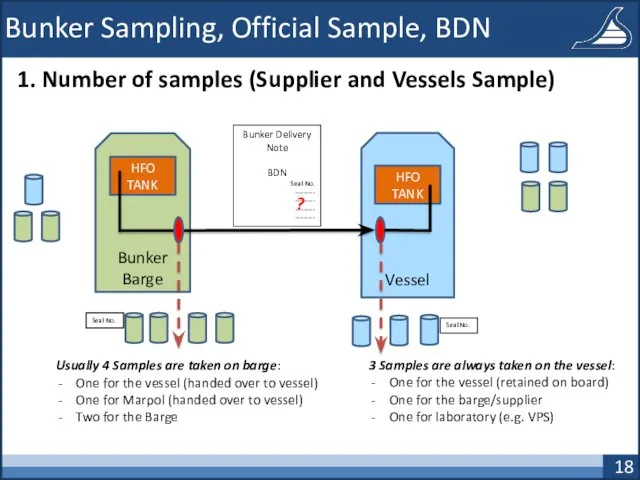
- 18. Bunker Sampling, Official Sample, BDN 1. Number of samples (Supplier and Vessels Sample) Vessel Bunker Barge
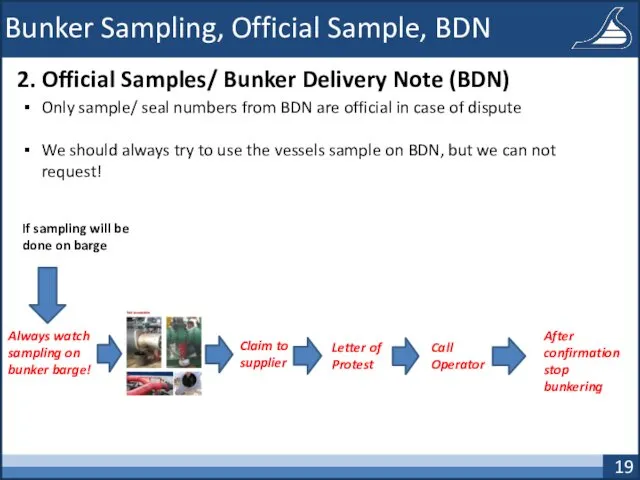
- 19. Bunker Sampling, Official Sample, BDN 2. Official Samples/ Bunker Delivery Note (BDN) Only sample/ seal numbers
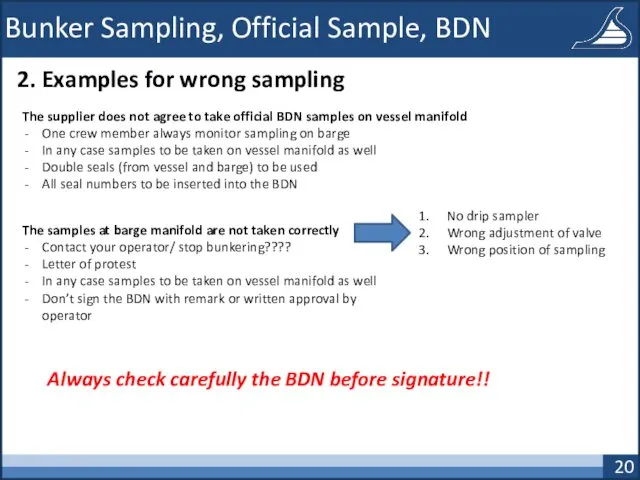
- 20. Bunker Sampling, Official Sample, BDN 2. Examples for wrong sampling The supplier does not agree to
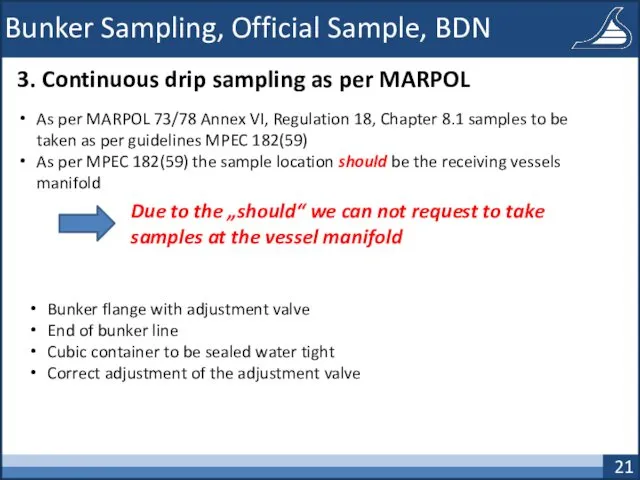
- 21. Bunker Sampling, Official Sample, BDN 3. Continuous drip sampling as per MARPOL As per MARPOL 73/78
- 22. Bunker Sampling, Official Sample, BDN 3. Continuous drip sampling as per MARPOL
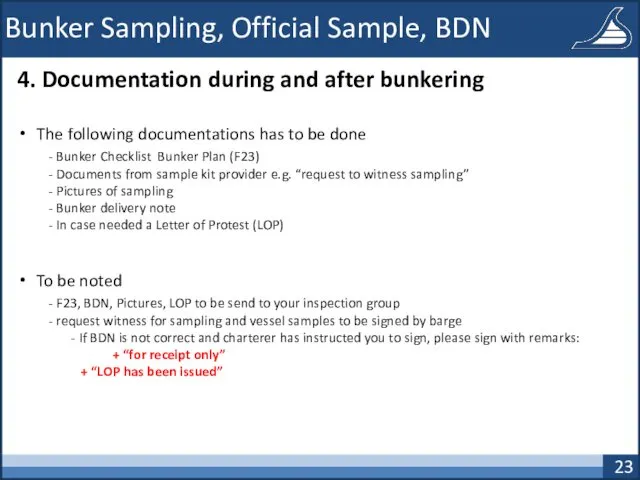
- 23. Bunker Sampling, Official Sample, BDN 4. Documentation during and after bunkering The following documentations has to
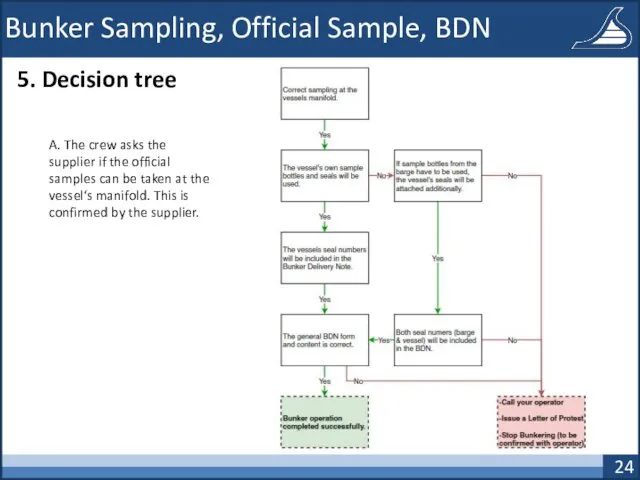
- 24. Bunker Sampling, Official Sample, BDN 5. Decision tree A. The crew asks the supplier if the
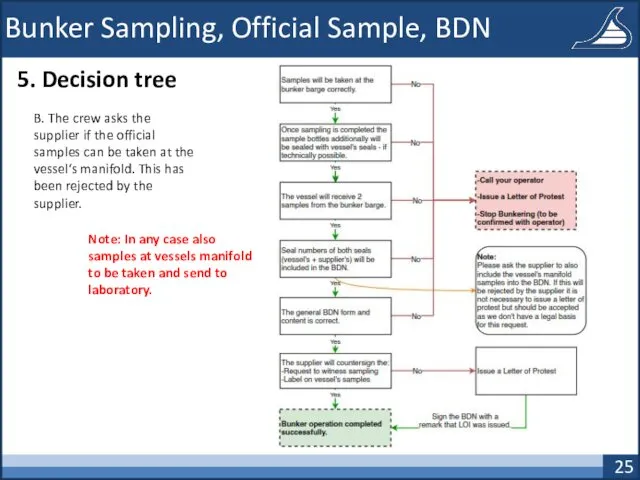
- 25. Bunker Sampling, Official Sample, BDN 5. Decision tree B. The crew asks the supplier if the
- 26. Bunker Sampling, Official Sample, BDN 6. Letter of protest “LOP” Examples can be found in circular
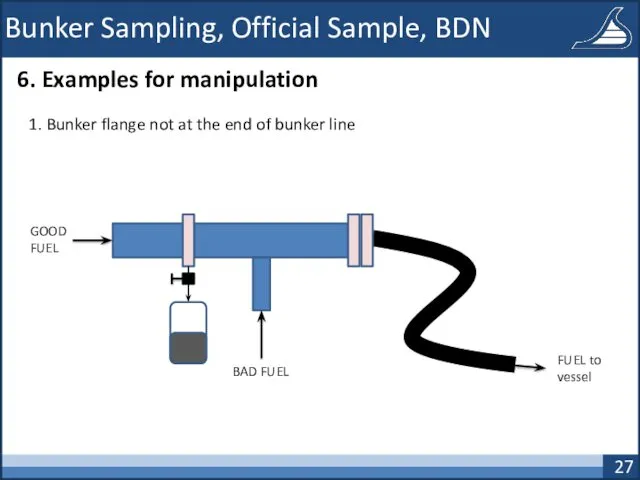
- 27. Bunker Sampling, Official Sample, BDN 6. Examples for manipulation 1. Bunker flange not at the end
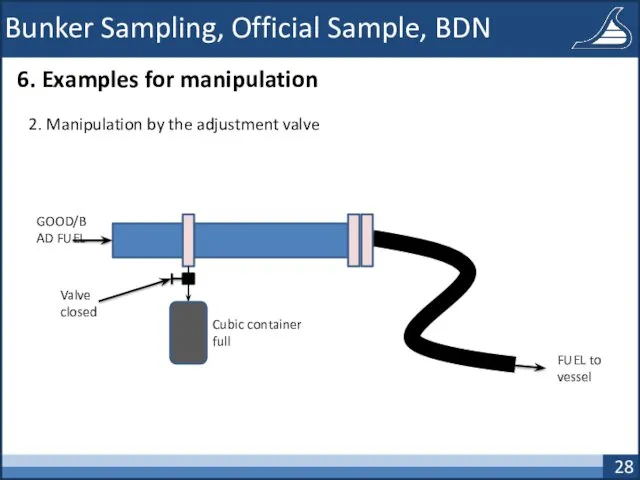
- 28. Bunker Sampling, Official Sample, BDN 6. Examples for manipulation 2. Manipulation by the adjustment valve GOOD/BAD
- 29. Bunker Sampling, Official Sample, BDN 6. Examples for manipulation 3. Manipulation of the samples Sample bottles
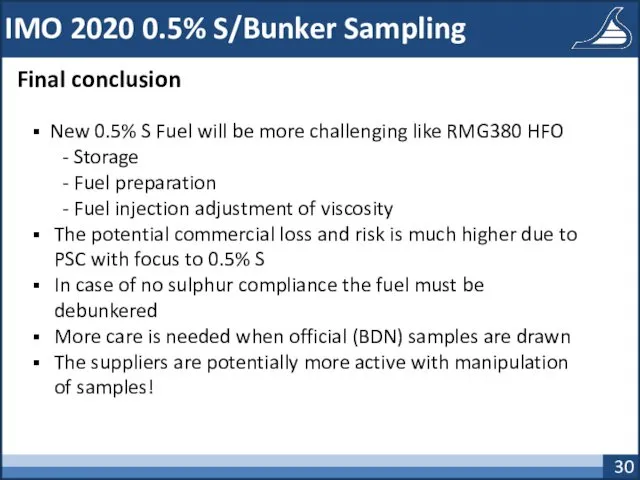
- 30. IMO 2020 0.5% S/Bunker Sampling Final conclusion New 0.5% S Fuel will be more challenging like
- 32. Скачать презентацию





 Лечение эпилепсии. Фармакотерапия
Лечение эпилепсии. Фармакотерапия Владимир Красное Солнышко
Владимир Красное Солнышко Обследование пассажиропотоков в городах .Неравномерность перевозок
Обследование пассажиропотоков в городах .Неравномерность перевозок Управление транспортными системами. Грузовые перевозки
Управление транспортными системами. Грузовые перевозки Подбор контрацептивного препарата
Подбор контрацептивного препарата В гостях у сказки
В гостях у сказки Жанры изобразительного искусства
Жанры изобразительного искусства Факоматозы. Наследственные нейрокожные заболевания
Факоматозы. Наследственные нейрокожные заболевания Модель психологической службы в организациях образования РК
Модель психологической службы в организациях образования РК Культурные ландшафты России
Культурные ландшафты России Постпозитивизм К. Поппера. И. Лакатос
Постпозитивизм К. Поппера. И. Лакатос Благодарность, смысл жизни. Сочинение на ОГЭ-2017. (Задание 15.3)
Благодарность, смысл жизни. Сочинение на ОГЭ-2017. (Задание 15.3) Двенадцатипульсовые схемы управляемых выпрямителей
Двенадцатипульсовые схемы управляемых выпрямителей Устройство и ремонт асинхронного электродвигателя с короткозамкнутым ротором
Устройство и ремонт асинхронного электродвигателя с короткозамкнутым ротором Учебный мини-проект на уроке технологии Магнит в подарок бабушке и дедушке
Учебный мини-проект на уроке технологии Магнит в подарок бабушке и дедушке Экологический урок Свобода от отходов
Экологический урок Свобода от отходов Презентация о российский поэте, драматурге, педагоге РУБИНСКОМ КОНСТАНТИНЕ СЕРГЕЕВИЧЕ
Презентация о российский поэте, драматурге, педагоге РУБИНСКОМ КОНСТАНТИНЕ СЕРГЕЕВИЧЕ Работа системы управления Turbotronic 4
Работа системы управления Turbotronic 4 Жидкие вещества
Жидкие вещества Учись разгадывать ребусы. Приёмы разгадывания.
Учись разгадывать ребусы. Приёмы разгадывания. Революция в россии - революция в живописи. Красный: философия цвета
Революция в россии - революция в живописи. Красный: философия цвета Физминутка для глаз.
Физминутка для глаз. Применение дальтон технологии в решении проектных задач Саблина С А
Применение дальтон технологии в решении проектных задач Саблина С А Топливно-энергетический комплекс России
Топливно-энергетический комплекс России Оптимизация добычи скважинной продукции путем подбора рациональной технологии и борьбы с осложнениями
Оптимизация добычи скважинной продукции путем подбора рациональной технологии и борьбы с осложнениями Материаловедение. Теория сплавов. (Тема 6)
Материаловедение. Теория сплавов. (Тема 6) Скажем НЕТ наркотикам!
Скажем НЕТ наркотикам! Скрипты продаж для мебели
Скрипты продаж для мебели