Содержание
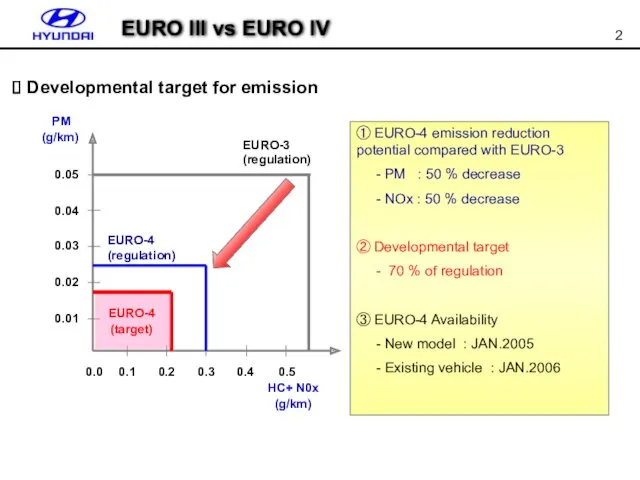
- 2. EURO III vs EURO IV Developmental target for emission ① EURO-4 emission reduction potential compared with
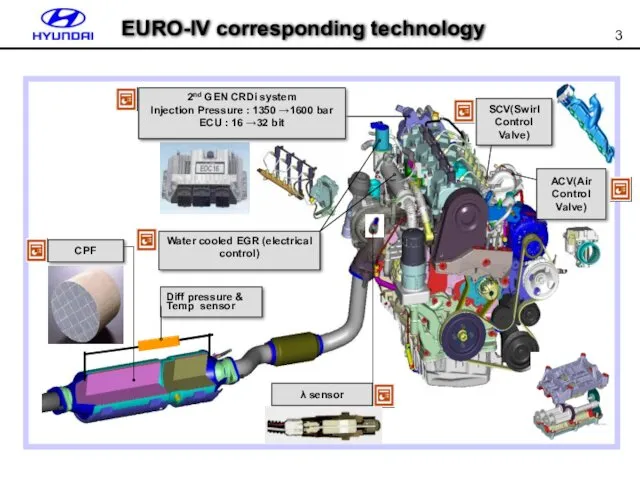
- 3. SCV(Swirl Control Valve) λ sensor CPF Diff pressure & Temp sensor ACV(Air Control Valve) 2nd GEN
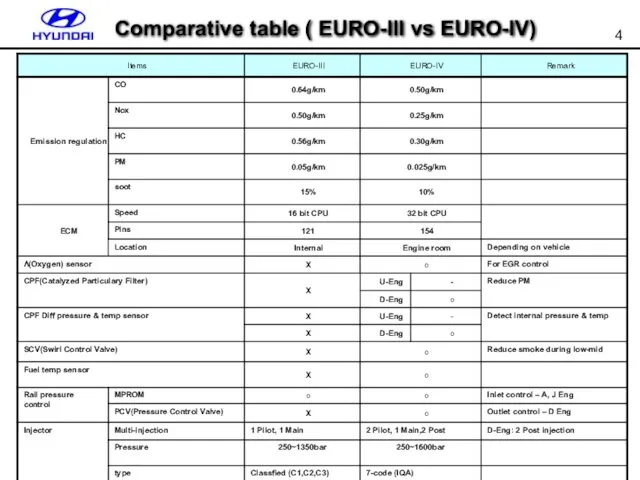
- 4. Comparative table ( EURO-III vs EURO-IV)
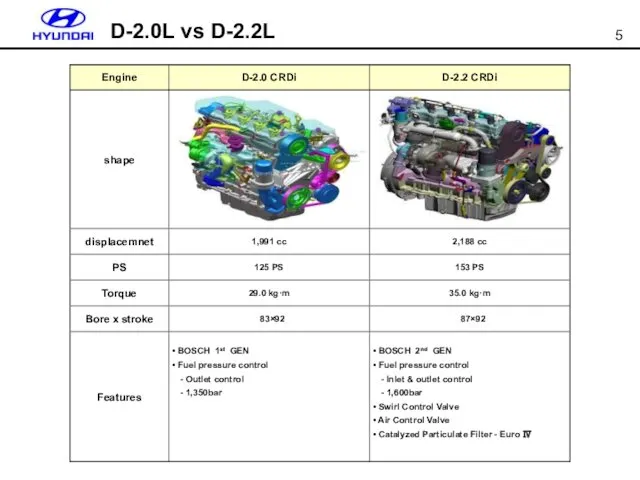
- 5. D-2.0L vs D-2.2L
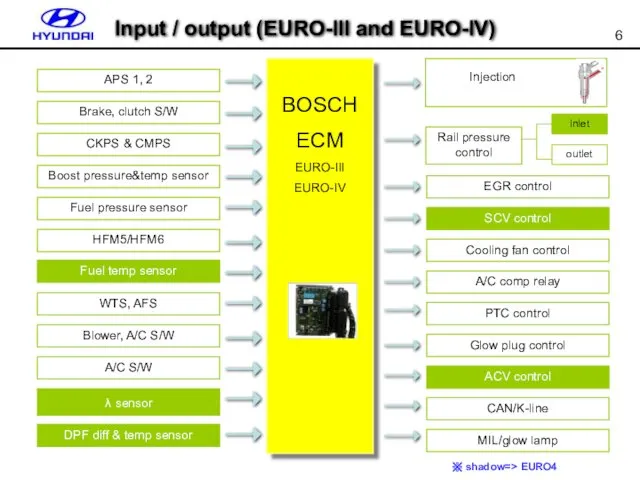
- 6. Input / output (EURO-III and EURO-IV) APS 1, 2 Brake, clutch S/W CKPS & CMPS Boost
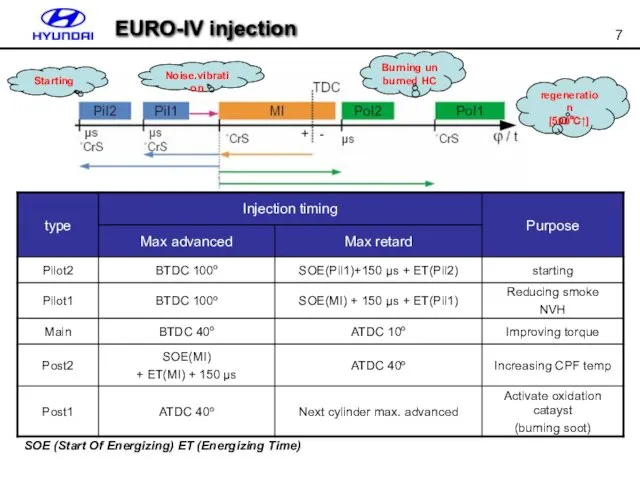
- 7. EURO-IV injection SOE (Start Of Energizing) ET (Energizing Time)
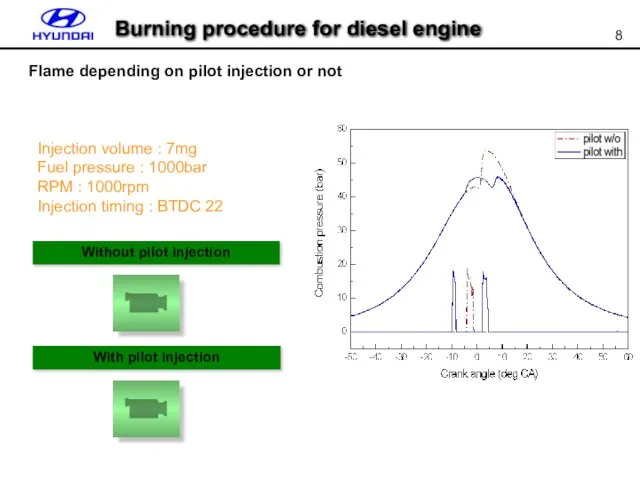
- 8. Burning procedure for diesel engine Flame depending on pilot injection or not Without pilot injection With
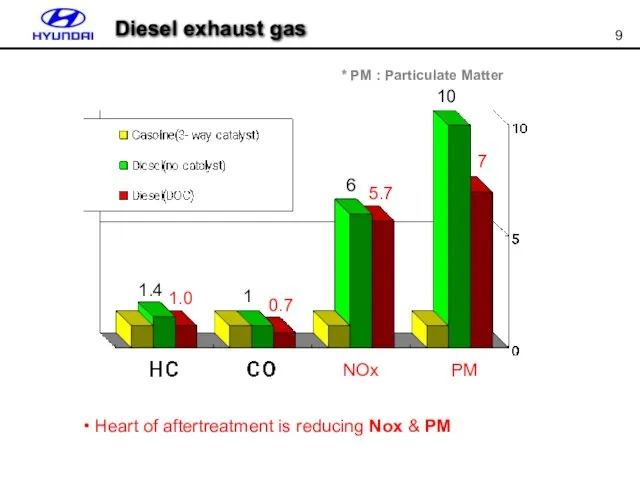
- 9. 1.4 1 6 10 7 5.7 0.7 1.0 NOx PM * PM : Particulate Matter Heart
- 10. CPF (Catalyzed Particulate Filter)
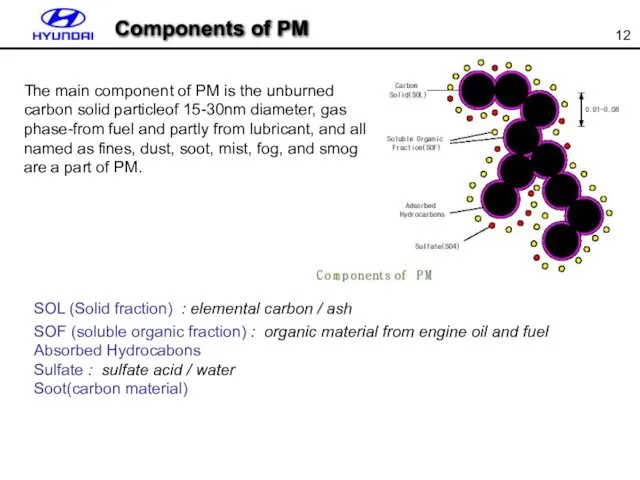
- 11. What is PM (Particulate Material or Matter) Specialty Definition: PARTICULATE MATTER Energy Unburned fuel particles that
- 12. Components of PM SOL (Solid fraction) : elemental carbon / ash SOF (soluble organic fraction) :
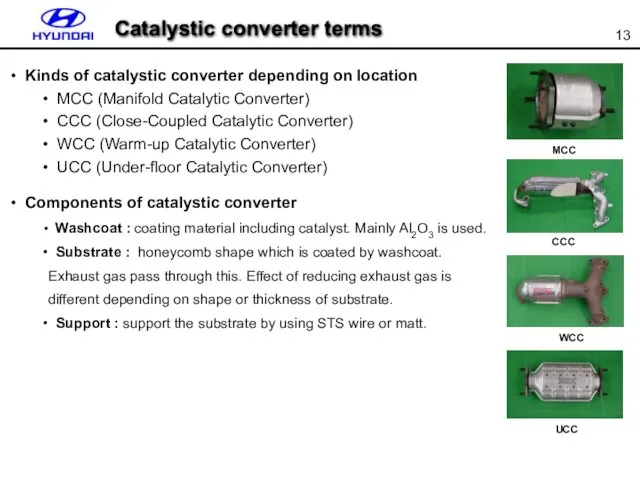
- 13. Kinds of catalystic converter depending on location MCC (Manifold Catalytic Converter) CCC (Close-Coupled Catalytic Converter) WCC
- 14. Washcoat Substrate Catalystic converter terms
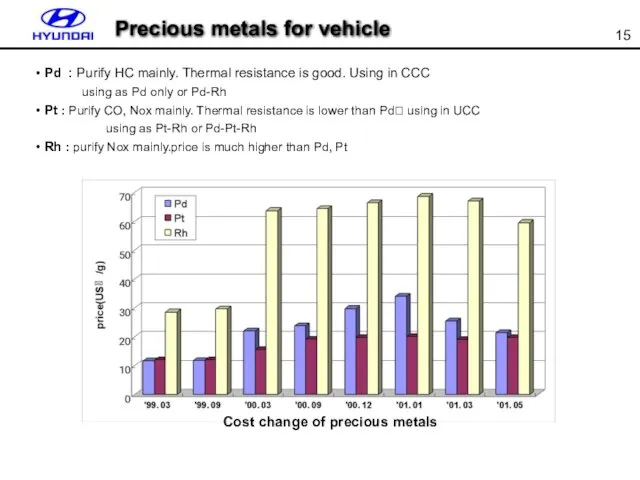
- 15. Pd : Purify HC mainly. Thermal resistance is good. Using in CCC using as Pd only
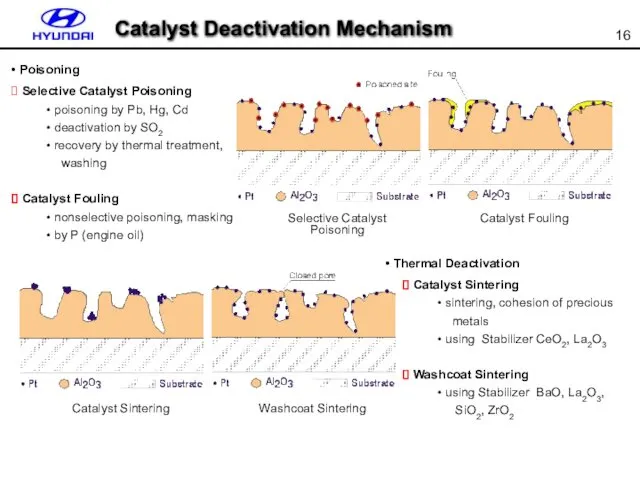
- 16. Selective Catalyst Poisoning Catalyst Fouling Catalyst Sintering Washcoat Sintering Selective Catalyst Poisoning poisoning by Pb, Hg,
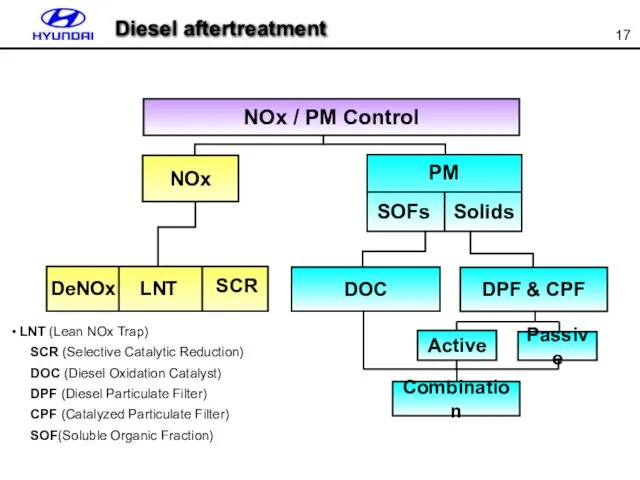
- 17. LNT (Lean NOx Trap) SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) DOC (Diesel Oxidation Catalyst) DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter)
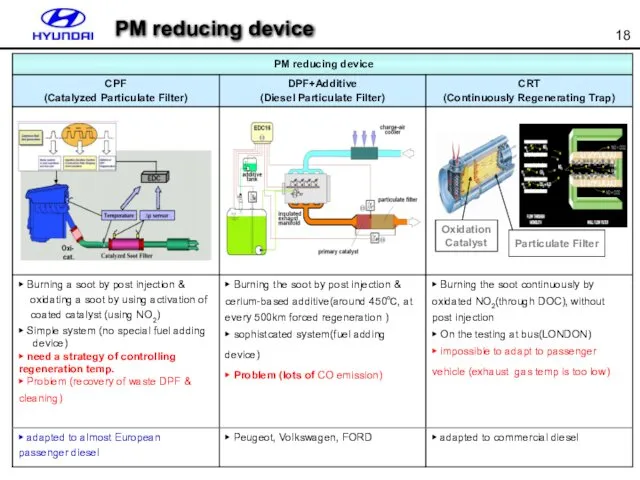
- 18. PM reducing device
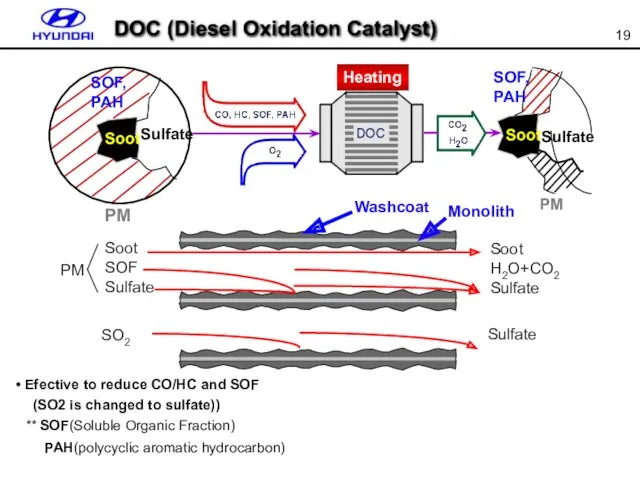
- 19. Efective to reduce CO/HC and SOF (SO2 is changed to sulfate)) ** SOF(Soluble Organic Fraction) PAH(polycyclic
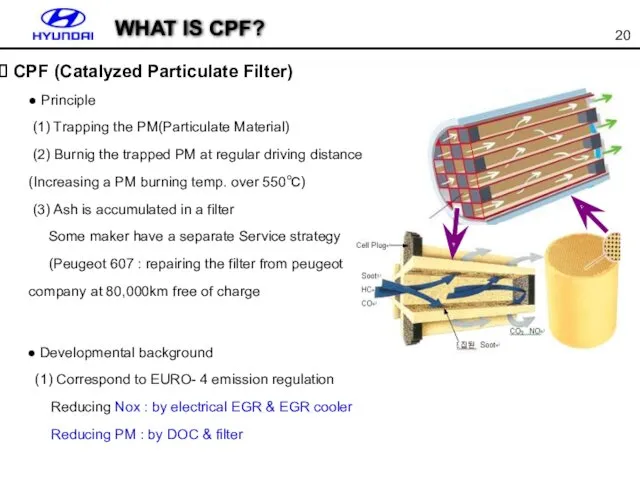
- 20. ● Principle (1) Trapping the PM(Particulate Material) (2) Burnig the trapped PM at regular driving distance
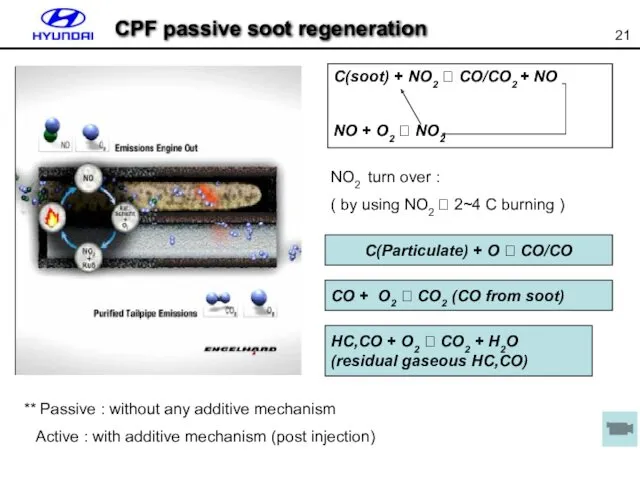
- 21. CPF passive soot regeneration ** Passive : without any additive mechanism Active : with additive mechanism
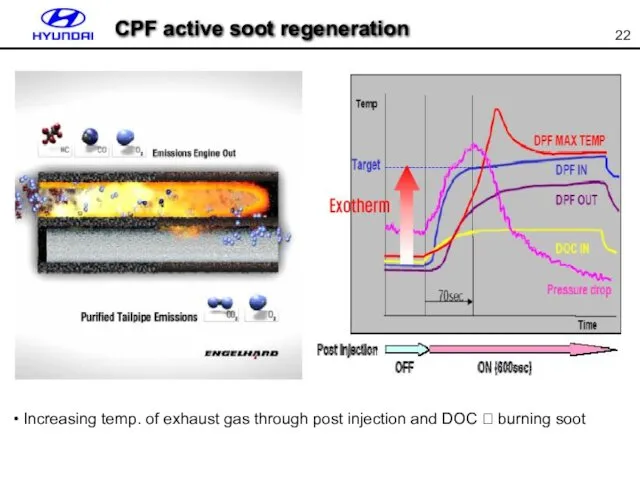
- 22. CPF active soot regeneration Increasing temp. of exhaust gas through post injection and DOC ? burning
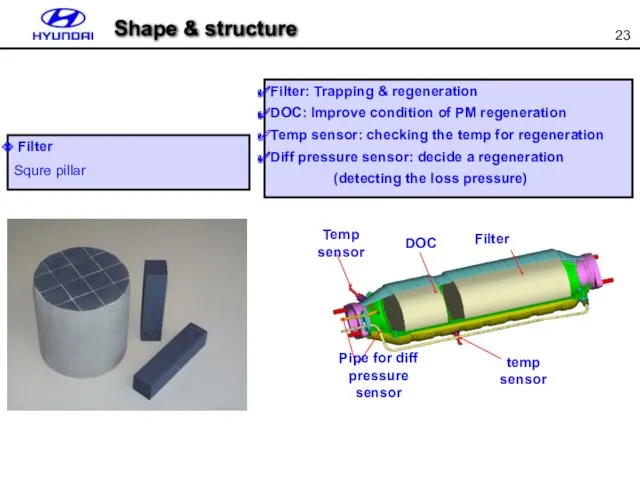
- 23. Filter Squre pillar Filter: Trapping & regeneration DOC: Improve condition of PM regeneration Temp sensor: checking
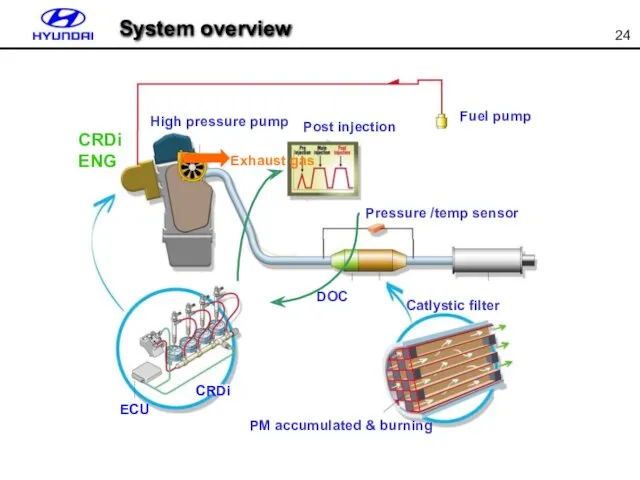
- 24. CRDi ECU DOC 머플러 Pressure /temp sensor Post injection Fuel pump High pressure pump CRDi ENG
- 25. 1. Accumulating ash Regeneration procedure
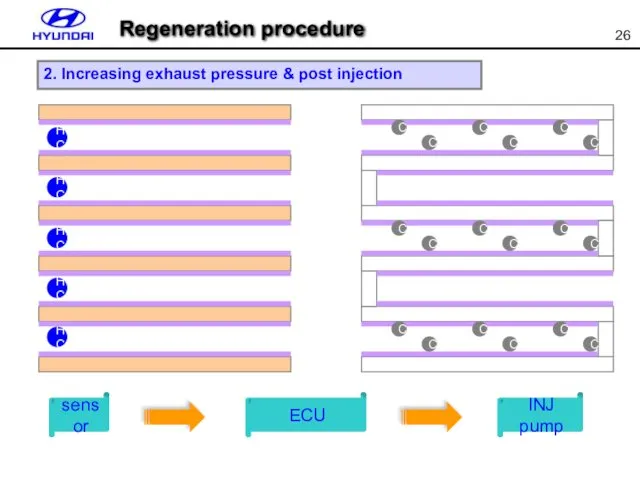
- 26. sensor ECU INJ pump 2. Increasing exhaust pressure & post injection Regeneration procedure
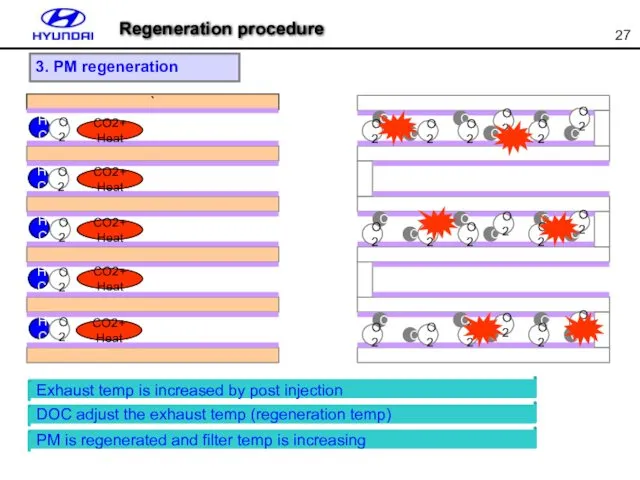
- 27. ` CO2+Heat CO2+Heat CO2+Heat CO2+Heat CO2+Heat 3. PM regeneration Exhaust temp is increased by post injection
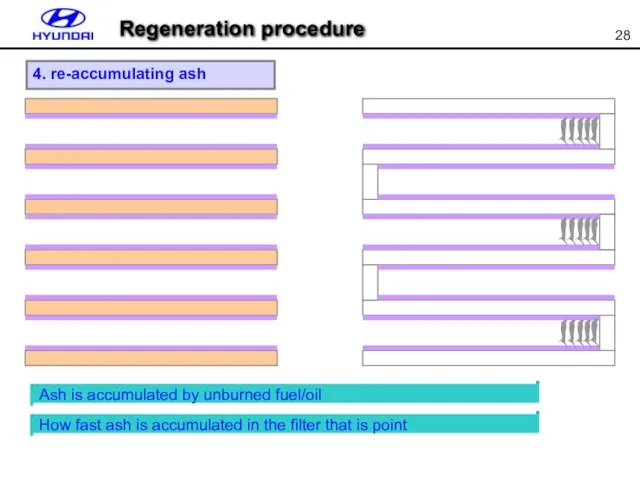
- 28. 4. re-accumulating ash Ash is accumulated by unburned fuel/oil How fast ash is accumulated in the
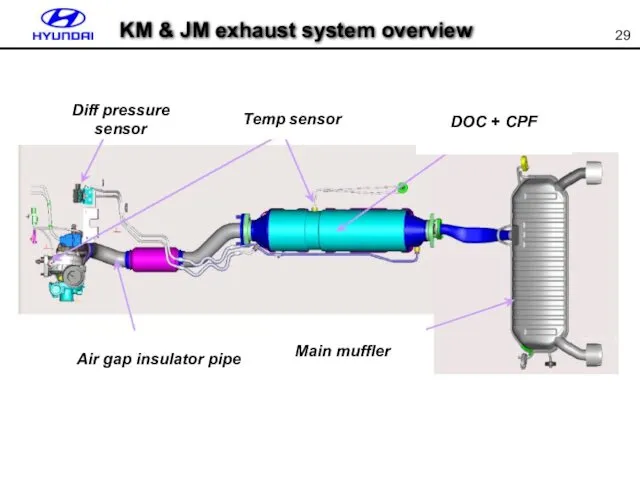
- 29. KM & JM exhaust system overview Diff pressure sensor Temp sensor Air gap insulator pipe Main
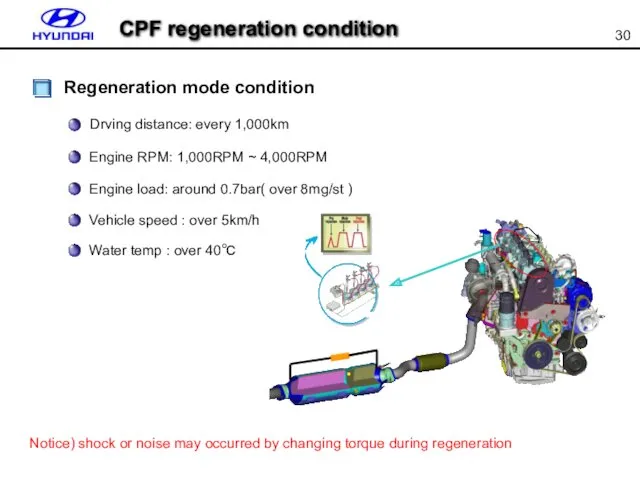
- 30. Regeneration mode condition Drving distance: every 1,000km Engine RPM: 1,000RPM ~ 4,000RPM Engine load: around 0.7bar(
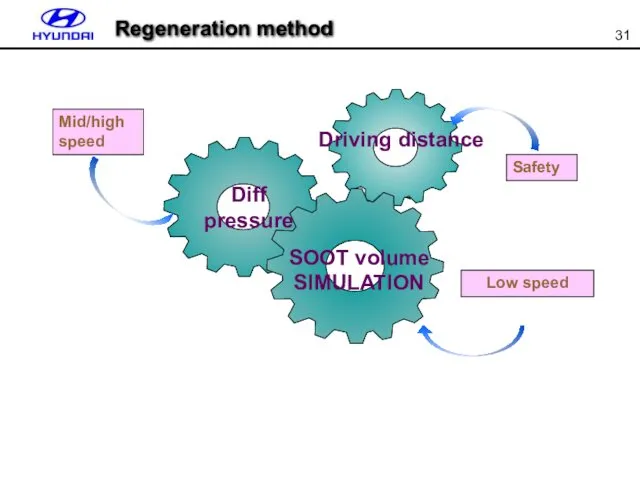
- 31. Low speed Mid/high speed Safety Diff pressure SOOT volume SIMULATION Driving distance Regeneration method
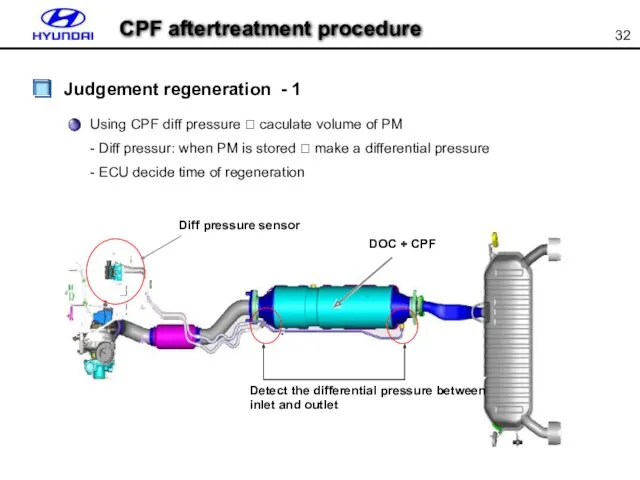
- 32. Judgement regeneration - 1 Using CPF diff pressure ? caculate volume of PM - Diff pressur:
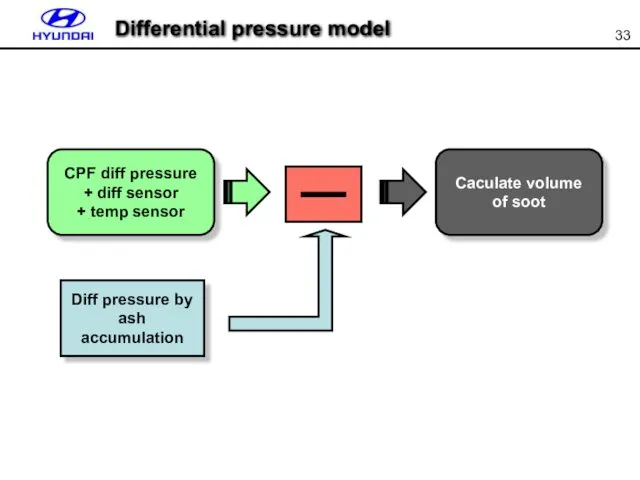
- 33. Differential pressure model
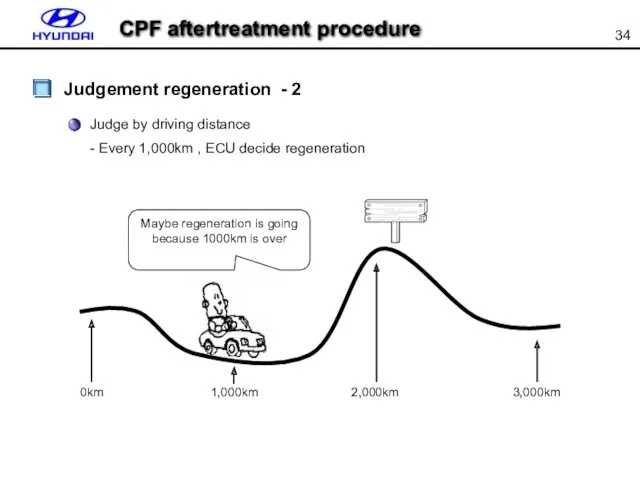
- 34. Judge by driving distance - Every 1,000km , ECU decide regeneration Maybe regeneration is going because
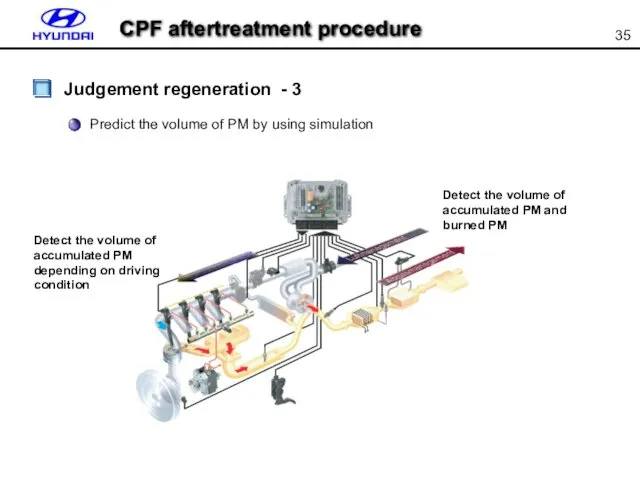
- 35. Predict the volume of PM by using simulation Detect the volume of accumulated PM depending on
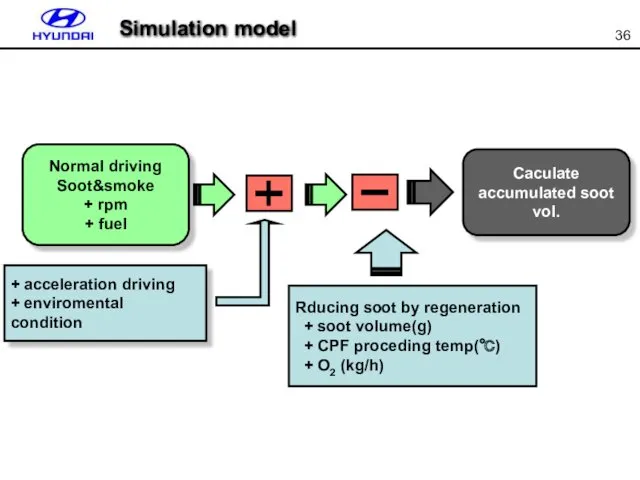
- 36. Simulation model
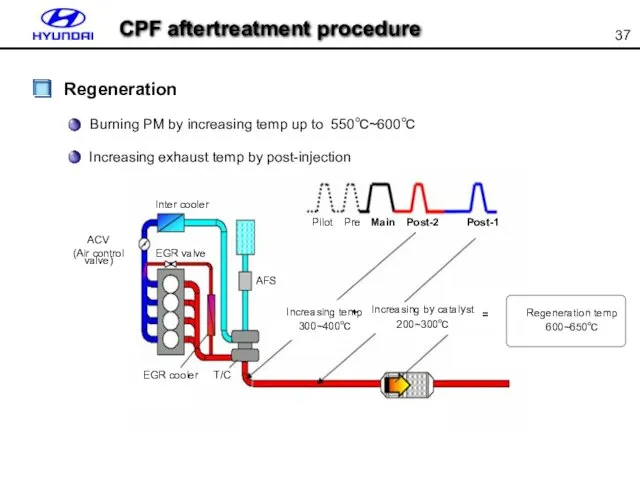
- 37. Burning PM by increasing temp up to 550℃~600℃ Regeneration Inter cooler ACV (Air control valve) EGR
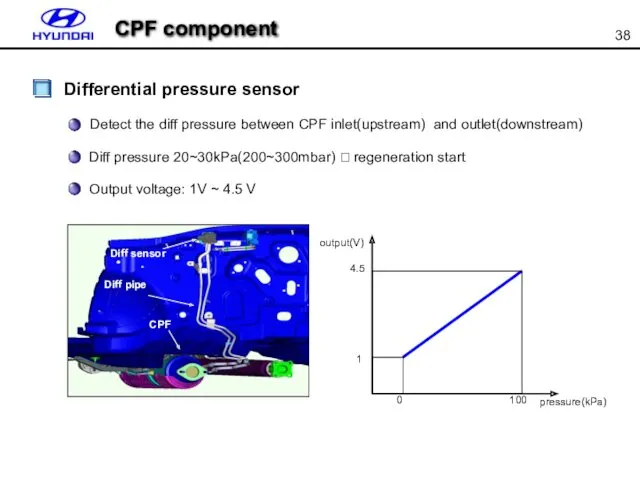
- 38. CPF component Differential pressure sensor Diff sensor Diff pipe CPF output(V) 4.5 1 0 100 pressure(kPa)
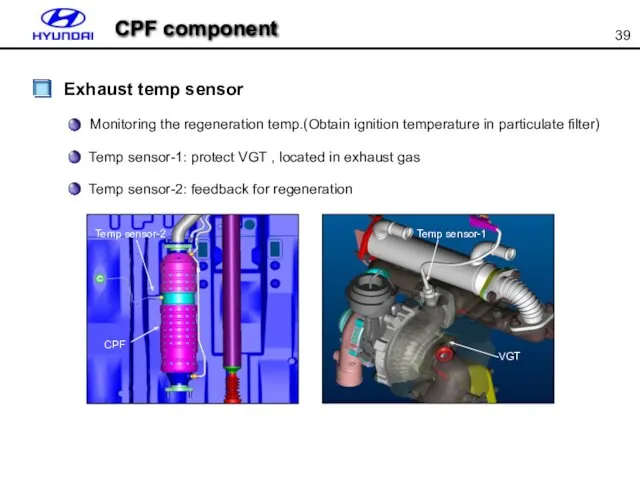
- 39. CPF component Exhaust temp sensor Monitoring the regeneration temp.(Obtain ignition temperature in particulate filter) Temp sensor-1:
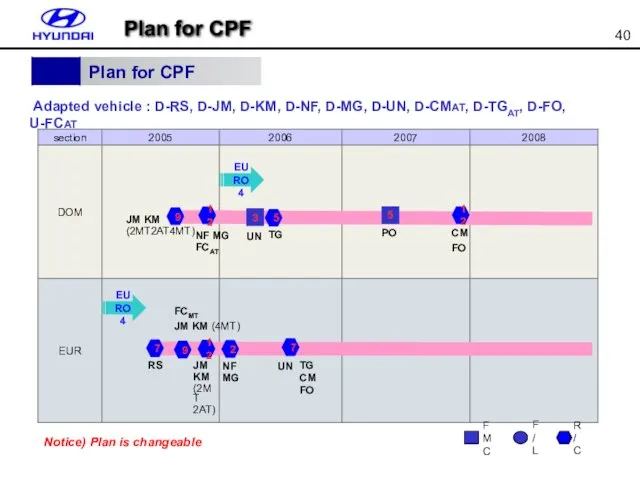
- 40. Adapted vehicle : D-RS, D-JM, D-KM, D-NF, D-MG, D-UN, D-CMAT, D-TGAT, D-FO, U-FCAT 2007 EUR DOM
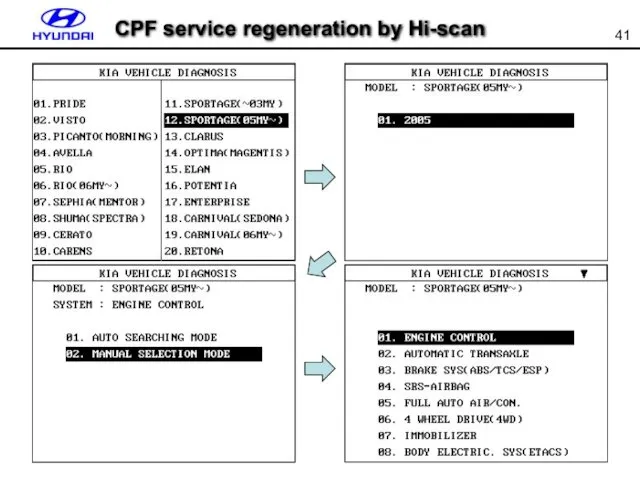
- 41. CPF service regeneration by Hi-scan
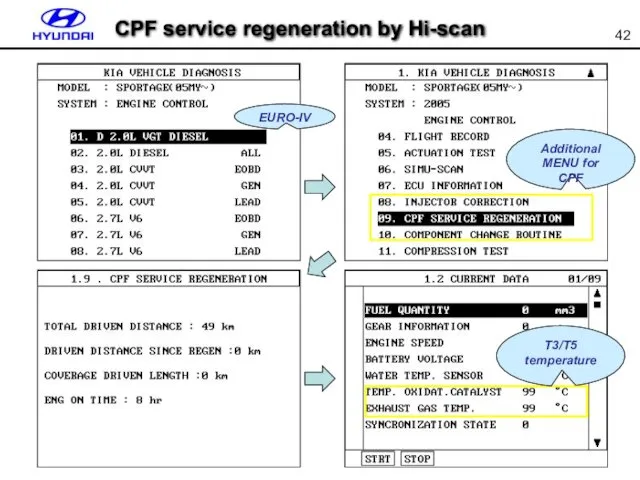
- 42. EURO-IV Additional MENU for CPF T3/T5 temperature CPF service regeneration by Hi-scan
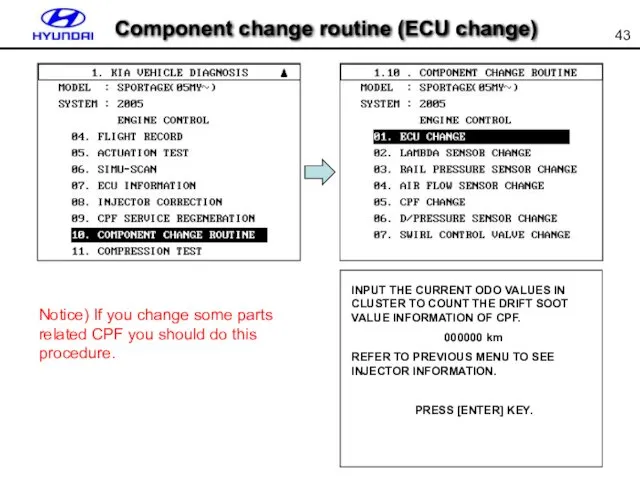
- 43. Component change routine (ECU change) Notice) If you change some parts related CPF you should do
- 44. IN THIS MODE, CAN RESET THE DISTANCE OF LAST CHANGED CPF AND OTHERS RELATED PARAMETERS. PRESS
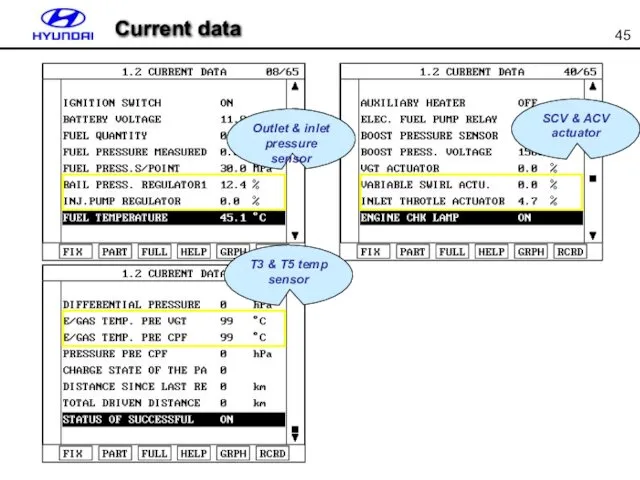
- 45. Current data SCV & ACV actuator Outlet & inlet pressure sensor T3 & T5 temp sensor
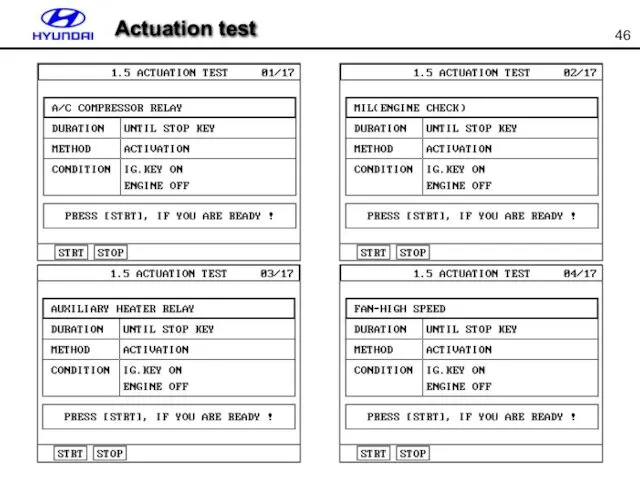
- 46. Actuation test
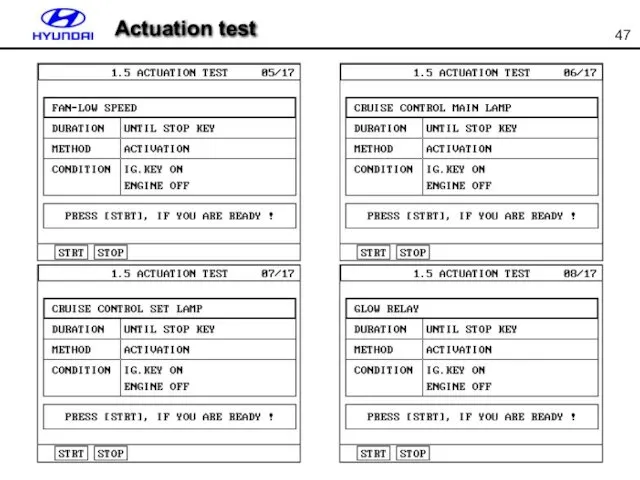
- 47. Actuation test
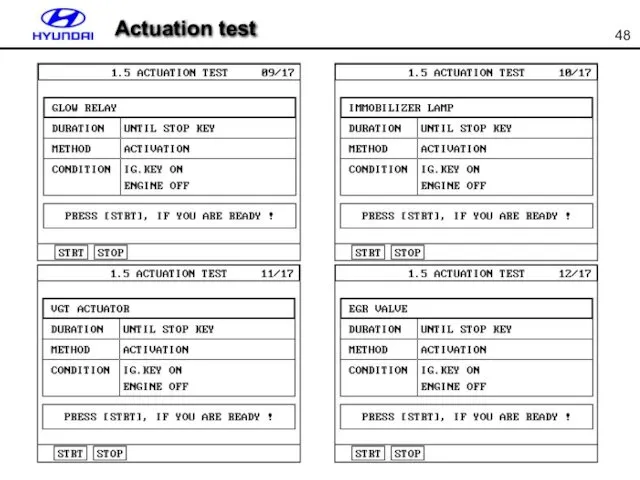
- 48. Actuation test
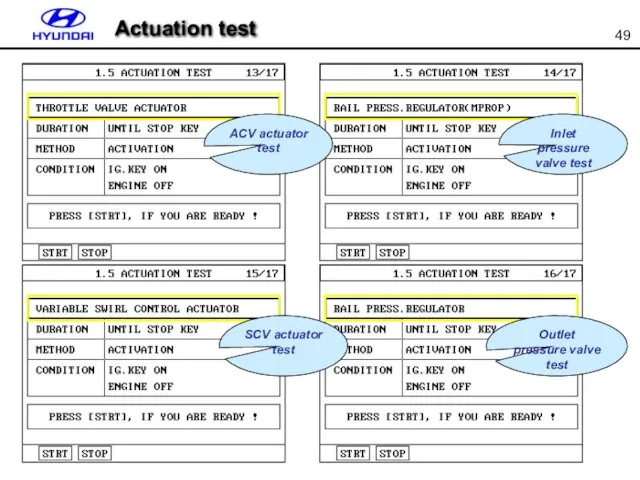
- 49. Actuation test Inlet pressure valve test ACV actuator test Outlet pressure valve test SCV actuator test
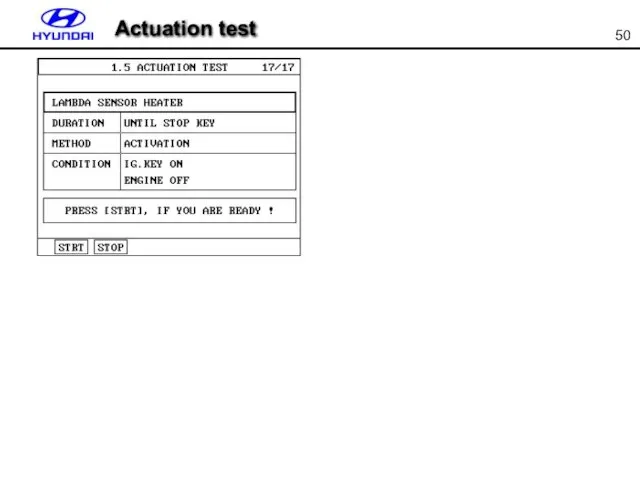
- 50. Actuation test
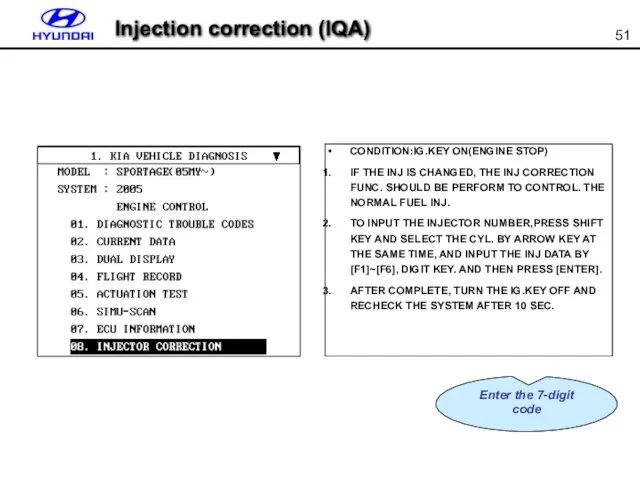
- 51. Injection correction (IQA) Enter the 7-digit code
- 53. Скачать презентацию




 Классификация строительных машин
Классификация строительных машин Метод расчета конструкций по предельным состояниям
Метод расчета конструкций по предельным состояниям Презентация
Презентация Технология обогащения медно-цинковых руд
Технология обогащения медно-цинковых руд HeidelbergCement Kazakhstan. Инструкция для поставщиков. Регистрация на портале EasySupply
HeidelbergCement Kazakhstan. Инструкция для поставщиков. Регистрация на портале EasySupply Электроника негіздері. Аналогты және сандық электроника. Аналогты электрониканың элементтері
Электроника негіздері. Аналогты және сандық электроника. Аналогты электрониканың элементтері Изменения в нормативной базе для НФО (4937-У, 5075-У, 5084-У, 32-ФЗ)
Изменения в нормативной базе для НФО (4937-У, 5075-У, 5084-У, 32-ФЗ) Шаблон 9 мая. Зима
Шаблон 9 мая. Зима презентация Путешествие в страну Светофория
презентация Путешествие в страну Светофория Скорость прямолинейного равноускоренного движения. График скорости. Перемещение тела при прямолинейном равноускоренном движении
Скорость прямолинейного равноускоренного движения. График скорости. Перемещение тела при прямолинейном равноускоренном движении Я гражданин страны великой
Я гражданин страны великой Оформление библиографического списка к научной работе
Оформление библиографического списка к научной работе ир звезд
ир звезд Презентация: Сказочный мир продленки
Презентация: Сказочный мир продленки Project work. My favorite and unusual building
Project work. My favorite and unusual building Презентация к уроку технологии Поделка в подарок папе к 23 февраля 3 класс
Презентация к уроку технологии Поделка в подарок папе к 23 февраля 3 класс Источники права
Источники права Презентация к уроку по теме Кремний
Презентация к уроку по теме Кремний Боги и люди в Синтоизме
Боги и люди в Синтоизме Prepositions of place
Prepositions of place Принципиальные электрические схемы систем автоматизации
Принципиальные электрические схемы систем автоматизации Презентация по теме Алканы
Презентация по теме Алканы Методическая разработка проекта Безопасная дорога детства.
Методическая разработка проекта Безопасная дорога детства. Диапазоны частот
Диапазоны частот Презентация Мама - самый родной и любимый человек
Презентация Мама - самый родной и любимый человек Характеристика нервової системи тварин та людини
Характеристика нервової системи тварин та людини If You Love Me and You Know It Song
If You Love Me and You Know It Song Чрезвычайные ситуации экологического характера
Чрезвычайные ситуации экологического характера