Содержание
- 2. Lecture Outline 1 – Introduction: Evolution of General Principles of Law as a Source of International
- 3. GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF LAW 1- INTRODUCTION: EVOLUTION OF GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF LAW AS A SOURCE OF
- 4. The “third” source of international law?
- 5. Origins of General Principles of Law Development of General Principles of Law Basic definition: Method of
- 6. I. Origins of General Principles of Law I.1. First arbitral awards I.2. World Court’s Statute and
- 7. I.1. First arbitral awards “All the private legislation of the States forming the European concert admits,
- 8. Committee of Jurists II.2. The International Court’s Statute and case-law
- 9. Elihu Root (USA) Baron Edouard Descamps (Belgium) “The following rules are to be applied by the
- 10. Lord Phillimore (United Kingdom) New draft: the Court should apply, as well as treaties and custom,
- 11. Permanent Court of International Justice PCIJ Statute International Court of Justice ICJ Statute
- 12. The International Court’s Case-Law ICJ, 1966, South West Africa (Ethiopia v. South Africa) (Liberia v. South
- 13. PCIJ, 1928, Chorzów Factory: “it is a principle of international law, and even a general conception
- 14. ICJ, 1949, Corfu Channel Non-foro domestico principles
- 15. II. Development of General Principles of Law as a Source of Law II.1. Generalisation of General
- 16. II.1. Generalisation of GPL as a source of law Inter-states disputes PCA Optional Rules for Arbitration
- 17. International Criminal Law
- 18. Investment arbitration ICSID, 1984, Amco v. Indonesia ‘the full compensation of prejudice, by awarding to the
- 19. Commercial Arbitration, Sport Arbitration CAS 98/2000, AEK Athens & Slavia Prague v. UEFA The Panel is
- 20. II.2. General Principles of Law under the scrutiny of ILC Marcelo Vázquez-Bermúdez, special rapporteur (Ecuador)
- 21. GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF LAW 2 DOCTRINE: DISPUTED NATURE OF GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF LAW 1 – Introduction:
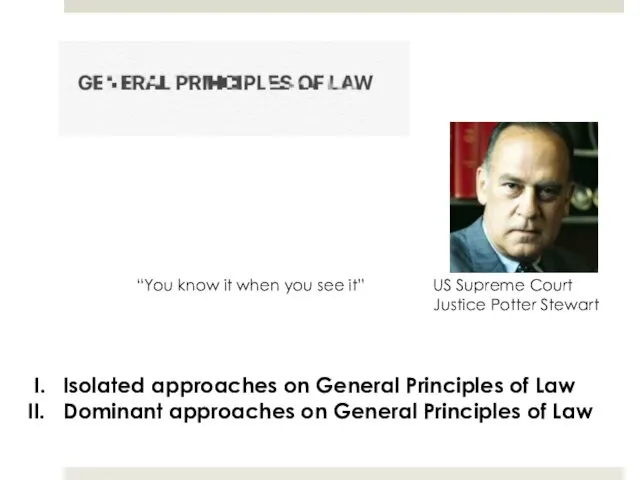
- 22. Isolated approaches on General Principles of Law Dominant approaches on General Principles of Law “You know
- 23. I. Isolated approaches on GPL I.1. GPL as a non-source of international law I.2. GPL as
- 24. I.1. General principles of law as a non-source of international law Grigori Tunkin (USSR) Article 38
- 25. I.2. General principles of law as natural law ICJ, 1951, Advisory Opinion on Reservations to the
- 26. ICJ, 1966, South West Africa (Ethiopia v. South Africa) (Liberia v. South Africa), Dissenting Opinion of
- 27. ICJ Statute
- 28. I.3. General principles of law as customary law ICJ, 1949, Corfu Channel
- 29. II. Dominant approaches on GPL II. 1. Principles in foro domestico II.2. Principles in foro domestico
- 30. II.1. Principles in foro domestico H. Lauterpacht A. Pellet GPL: “general principles of municipal jurisprudence, in
- 31. II.2. Principles in foro domestico and in international law ICSID, 2012 award, CIRDI, Occidental Petroleum Corporation
- 33. Скачать презентацию





























 Формирование и совершенствование имиджа менеджера организации ИП Гайсина Ю.Ф
Формирование и совершенствование имиджа менеджера организации ИП Гайсина Ю.Ф Презентация к уроку технология, изделие Торт
Презентация к уроку технология, изделие Торт Сталинградская битва
Сталинградская битва Пищеварение в ротовой полости
Пищеварение в ротовой полости Litania do Ducha Świętego
Litania do Ducha Świętego Деревья
Деревья Пять уроков творчества
Пять уроков творчества Я люблю свой город
Я люблю свой город Класс Земноводные, или амфибии
Класс Земноводные, или амфибии Формы работы с родителями учащихся начальных классов
Формы работы с родителями учащихся начальных классов Фитопатогенные грибы
Фитопатогенные грибы Интерактивный тренажёр. Буквы потерялись. Русский язык, 4 класс
Интерактивный тренажёр. Буквы потерялись. Русский язык, 4 класс Презентация Моя инициатива в образовании.
Презентация Моя инициатива в образовании. Источники противопожарного водоснабжения
Источники противопожарного водоснабжения Интерактивные валюты
Интерактивные валюты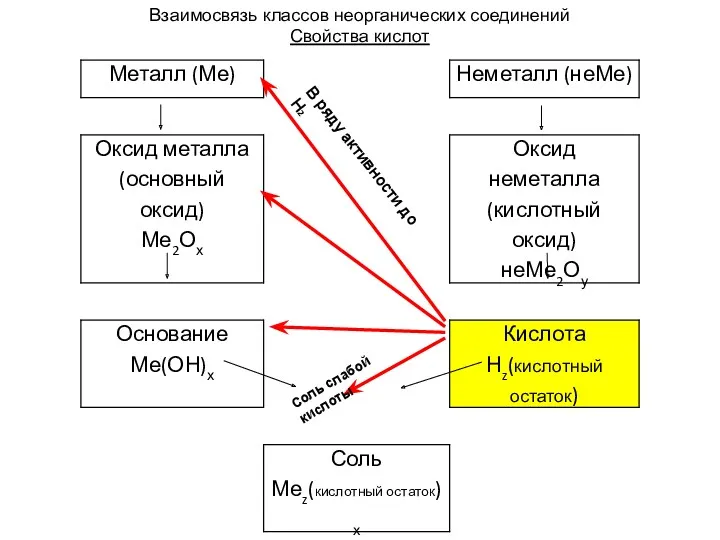 8 класс тема 6 Электролитическая диссоциация
8 класс тема 6 Электролитическая диссоциация Низкопотенциальная геотермальная энергия (тепловые насосы) в энергоэффективном проектировании
Низкопотенциальная геотермальная энергия (тепловые насосы) в энергоэффективном проектировании Мониторинг и прогнозирование чрезвычайных ситуаций
Мониторинг и прогнозирование чрезвычайных ситуаций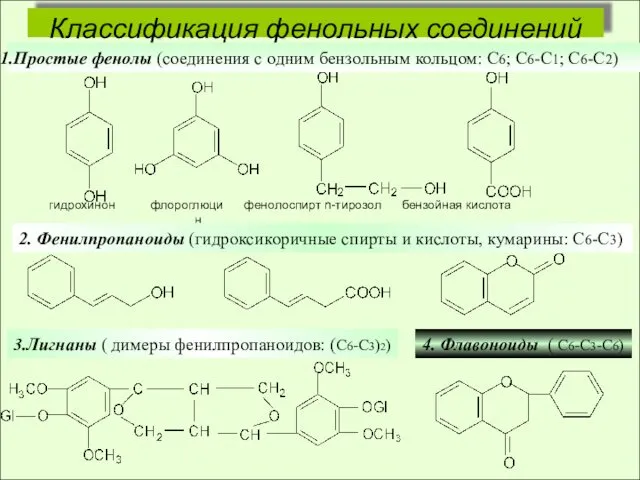 Классификация фенольных соединений
Классификация фенольных соединений Меры безопасности при пользовании предметами бытовой химии
Меры безопасности при пользовании предметами бытовой химии Снятие мерок для построения чертежа фартука
Снятие мерок для построения чертежа фартука Моя Югра
Моя Югра ТВОРЧЕСКАЯ ДЕЯТЕЛЬНОСТЬ ОБЪЕДИНЕНИЯ ДЕКОРАТИВНО-ПРИКЛАДНОЕ ТВОРЧЕСТВО
ТВОРЧЕСКАЯ ДЕЯТЕЛЬНОСТЬ ОБЪЕДИНЕНИЯ ДЕКОРАТИВНО-ПРИКЛАДНОЕ ТВОРЧЕСТВО Занятие по экологии в группе продленного дня
Занятие по экологии в группе продленного дня Жүре пайда болған кемақылдық деменция
Жүре пайда болған кемақылдық деменция Водоросли. Многообразие водорослей
Водоросли. Многообразие водорослей ЭОСВ
ЭОСВ Автоматизация звука Ш
Автоматизация звука Ш