Содержание
- 2. Myology is the study of the muscular system, including the study of the structure, function and
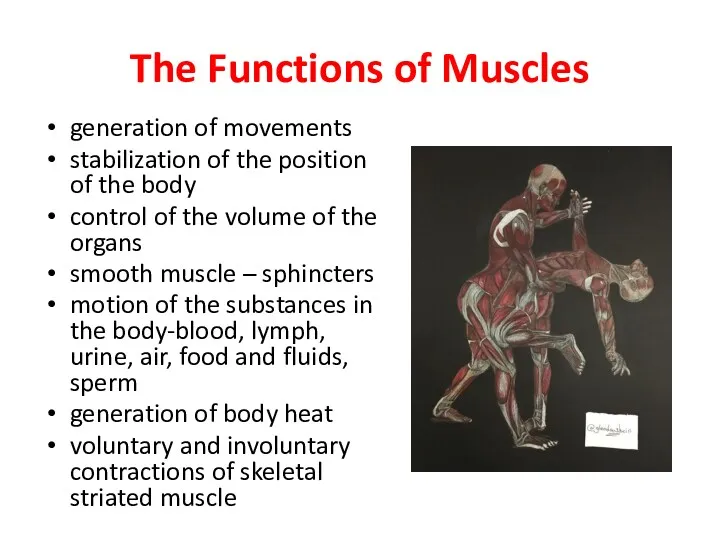
- 3. The Functions of Muscles generation of movements stabilization of the position of the body control of
- 4. 3 types of muscle tissue Smooth muscle tissue (textus muscularis levis) Striated muscle tissue (textus muscularis
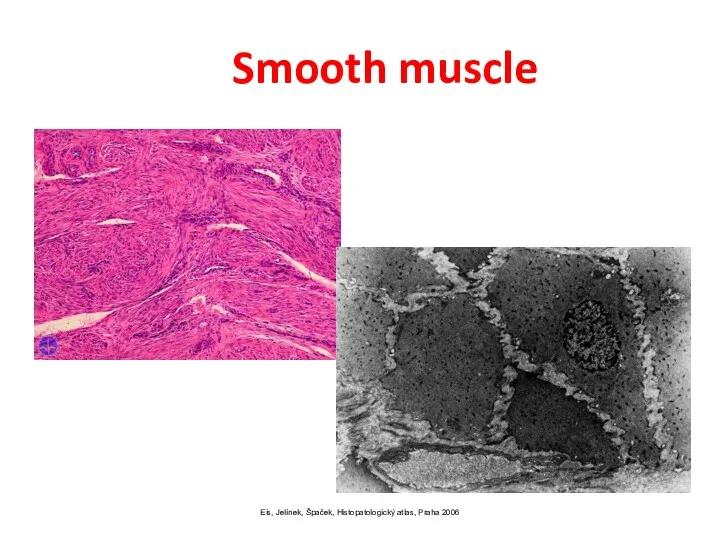
- 5. Eis, Jelínek, Špaček, Histopatologický atlas, Praha 2006 Smooth muscle
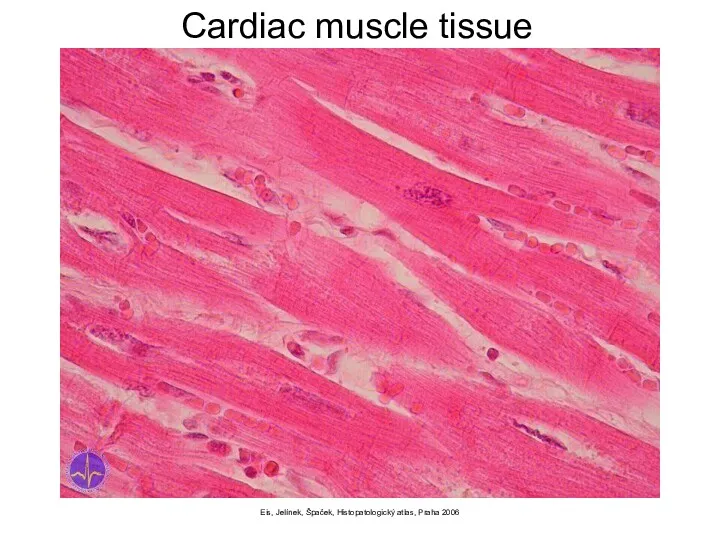
- 6. Eis, Jelínek, Špaček, Histopatologický atlas, Praha 2006 Cardiac muscle tissue
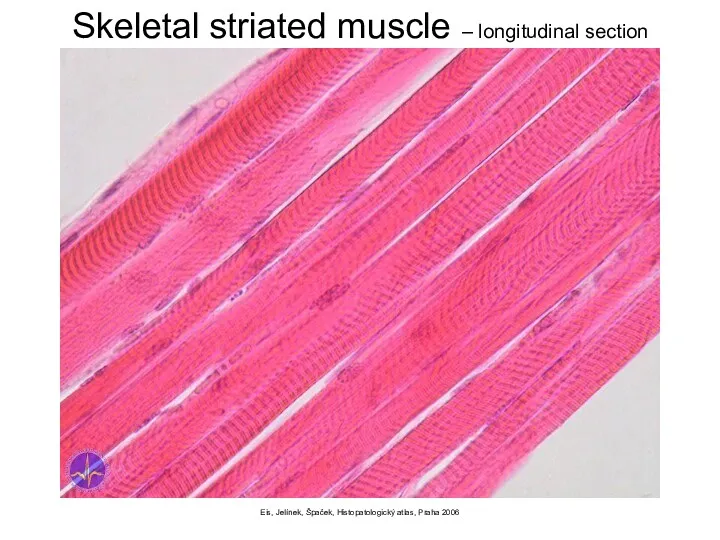
- 7. Eis, Jelínek, Špaček, Histopatologický atlas, Praha 2006 Skeletal striated muscle – longitudinal section
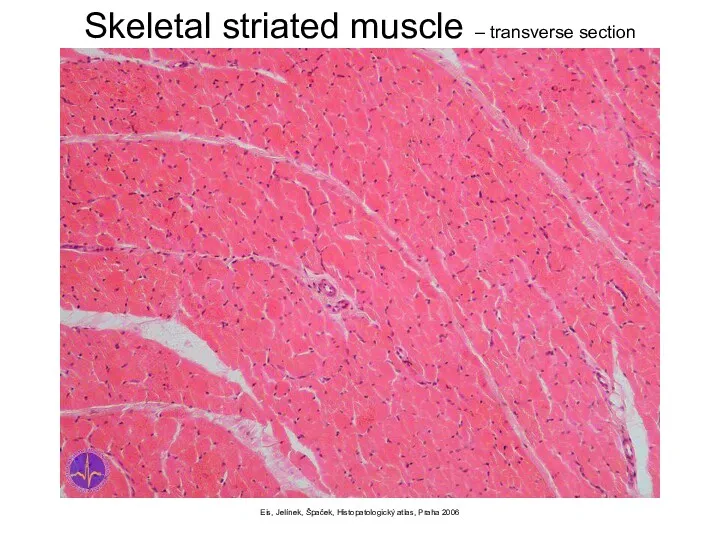
- 8. Eis, Jelínek, Špaček, Histopatologický atlas, Praha 2006 Skeletal striated muscle – transverse section
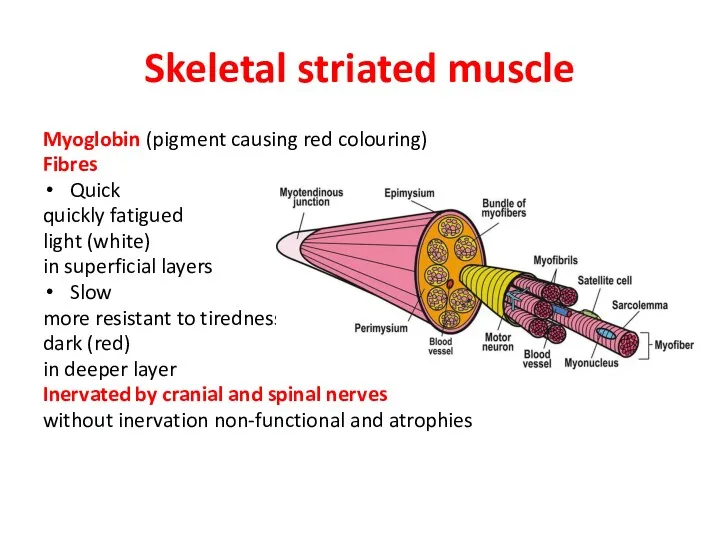
- 9. Skeletal striated muscle Myoglobin (pigment causing red colouring) Fibres Quick quickly fatigued light (white) in superficial
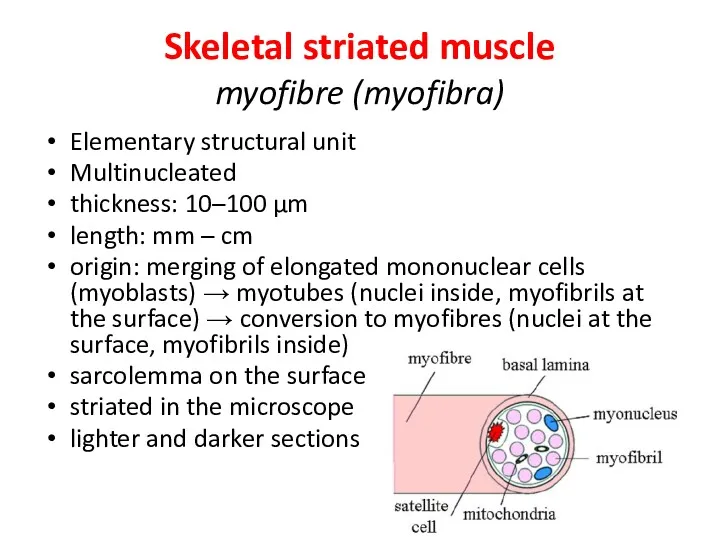
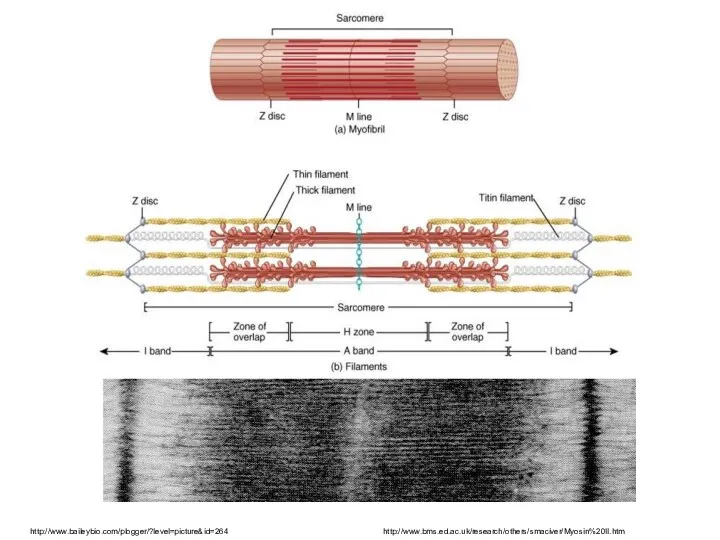
- 10. Skeletal striated muscle myofibre (myofibra) Elementary structural unit Multinucleated thickness: 10–100 µm length: mm – cm
- 11. http://www.baileybio.com/plogger/?level=picture&id=264 http://www.bms.ed.ac.uk/research/others/smaciver/Myosin%20II.htm
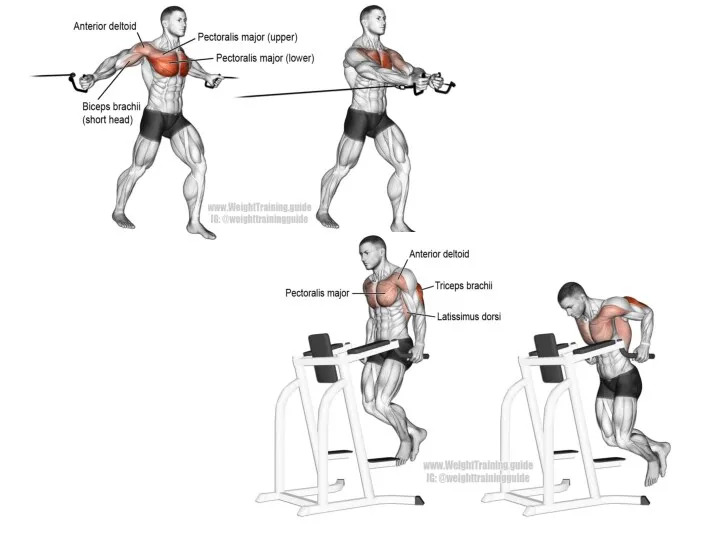
- 12. Functions of skeletal muscle Movement of animal body 2. Control of body openings and passages "maintain
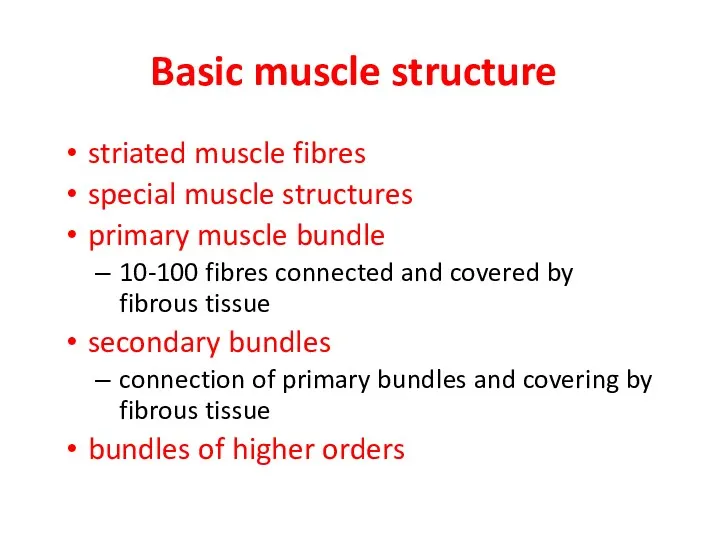
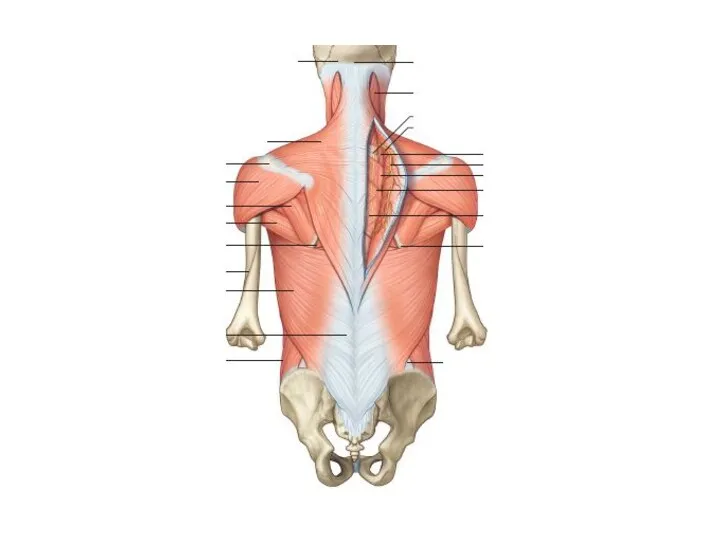
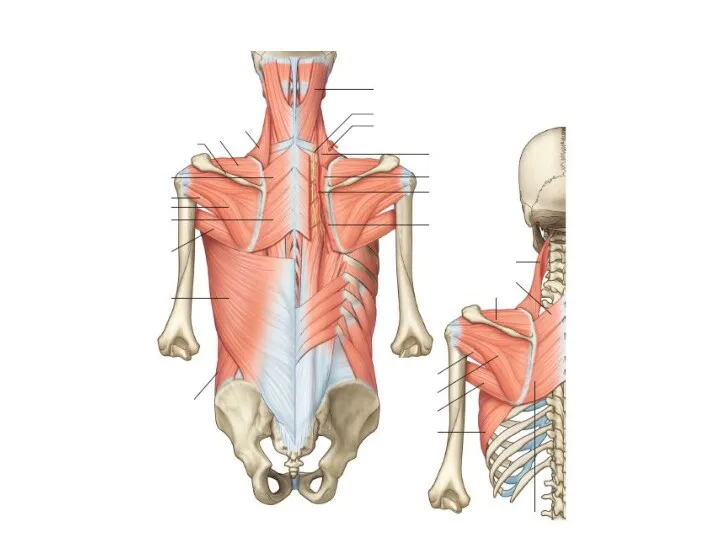
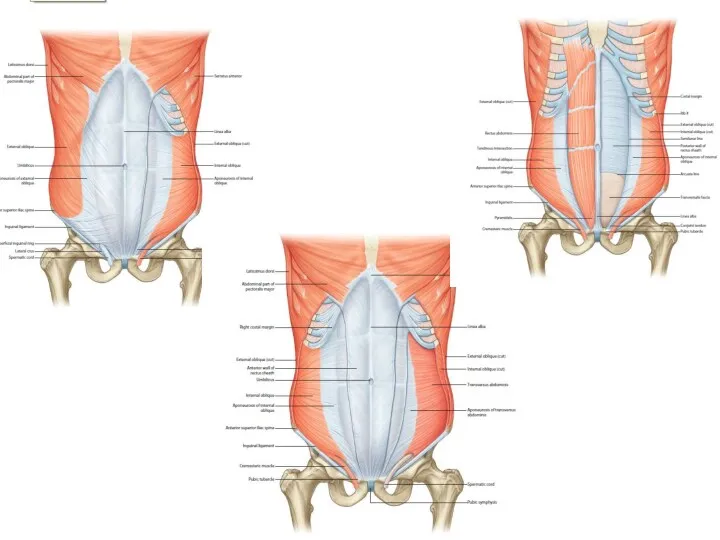
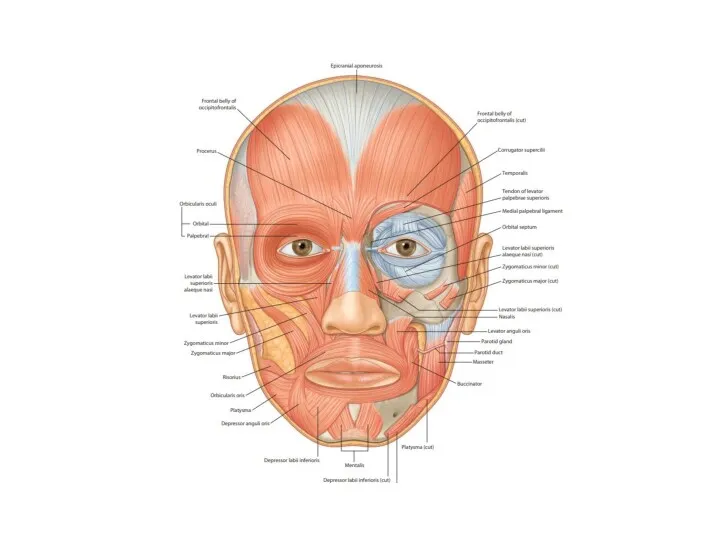
- 13. Basic muscle structure striated muscle fibres special muscle structures primary muscle bundle 10-100 fibres connected and
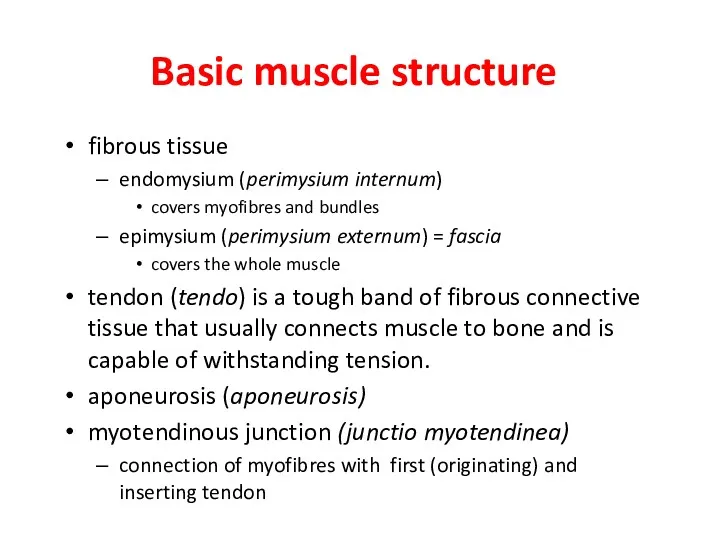
- 14. Basic muscle structure fibrous tissue endomysium (perimysium internum) covers myofibres and bundles epimysium (perimysium externum) =
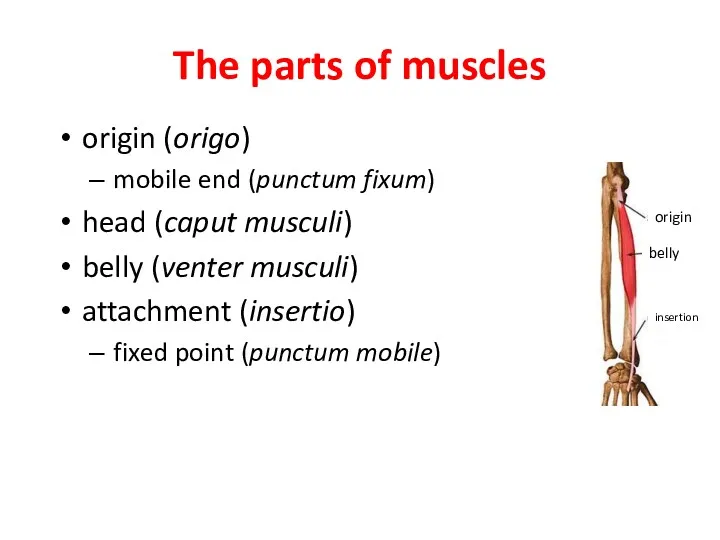
- 15. The parts of muscles origin (origo) mobile end (punctum fixum) head (caput musculi) belly (venter musculi)
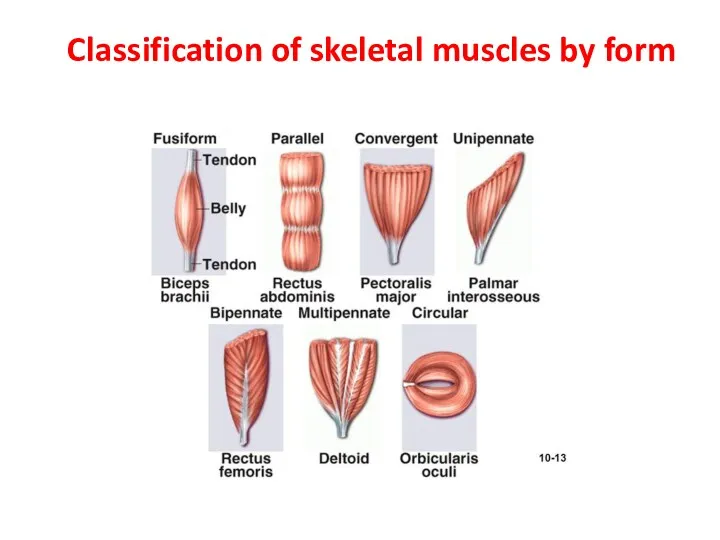
- 16. Classification of skeletal muscles by form
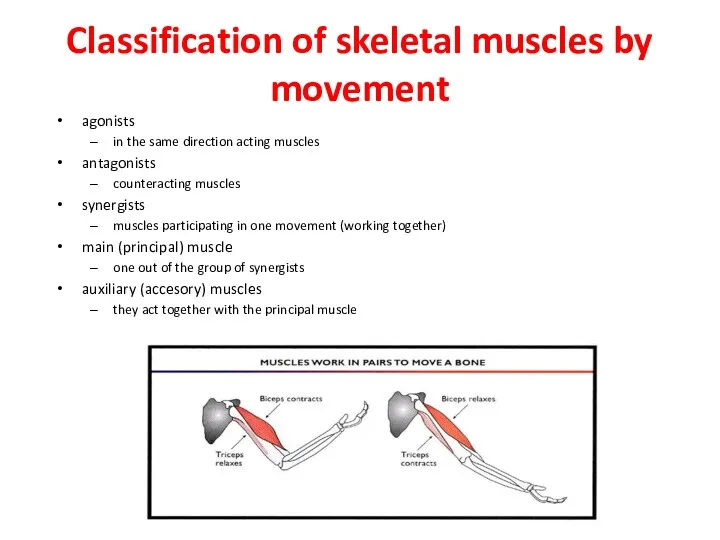
- 17. Classification of skeletal muscles by movement agonists in the same direction acting muscles antagonists counteracting muscles
- 18. Classification of skeletal muscles by number of joints one-jointed muscles they´re causing the movement only in
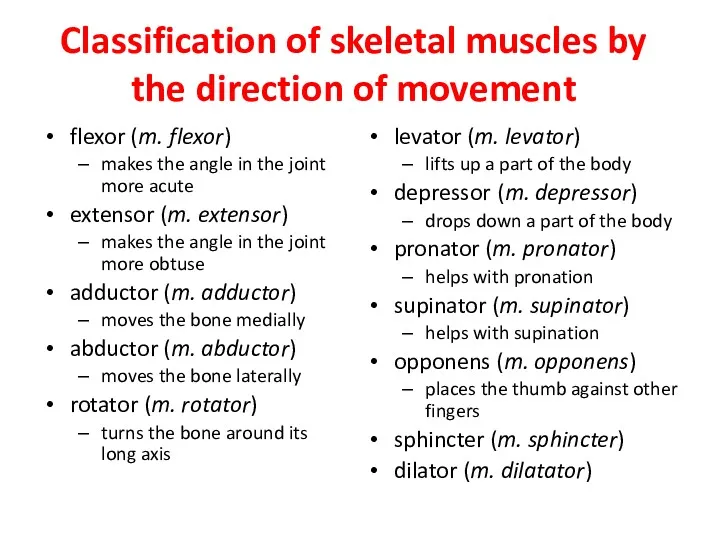
- 19. Classification of skeletal muscles by the direction of movement flexor (m. flexor) makes the angle in
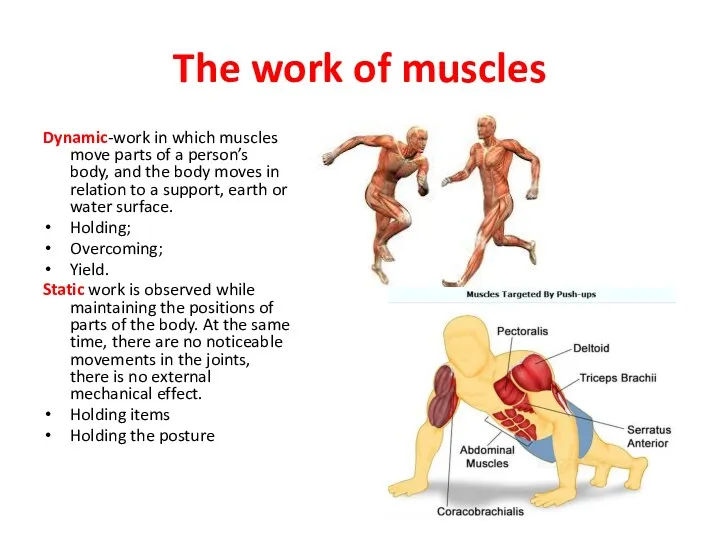
- 20. The work of muscles Dynamic-work in which muscles move parts of a person’s body, and the
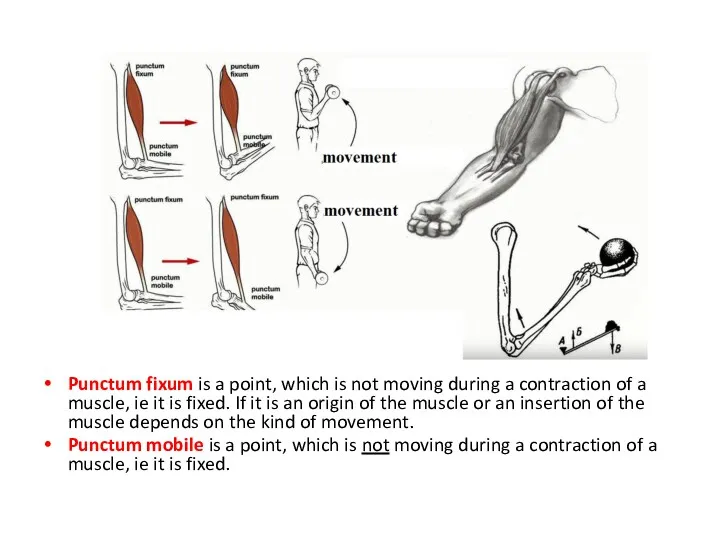
- 21. Punctum fixum is a point, which is not moving during a contraction of a muscle, ie
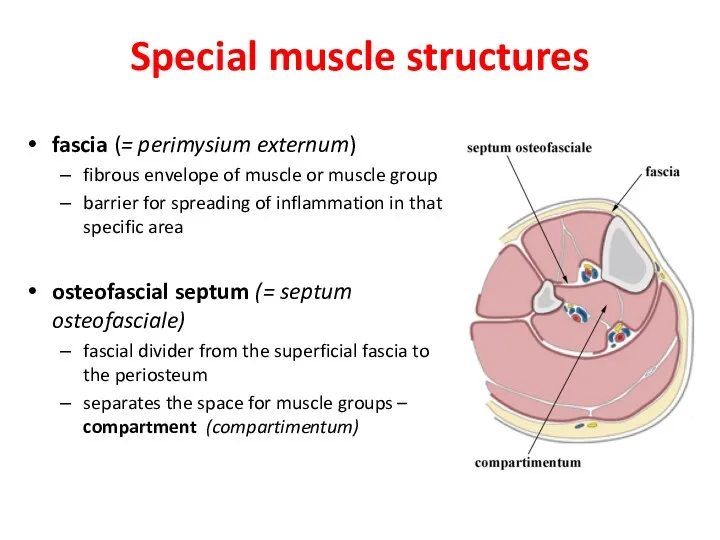
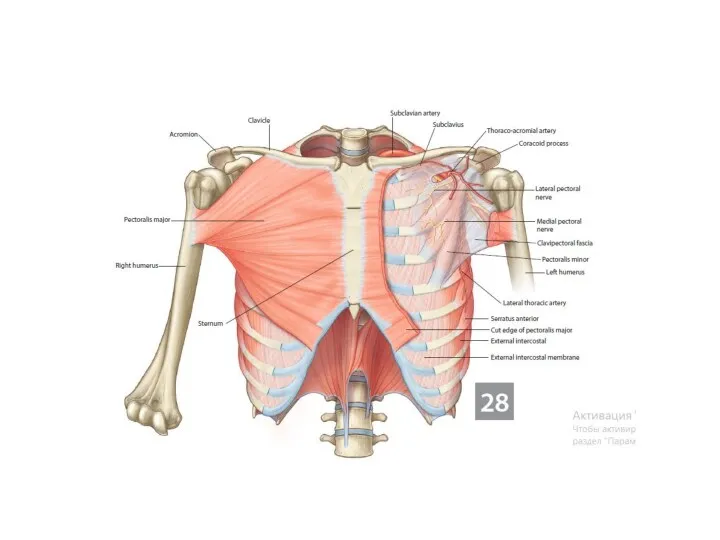
- 22. Special muscle structures fascia (= perimysium externum) fibrous envelope of muscle or muscle group barrier for
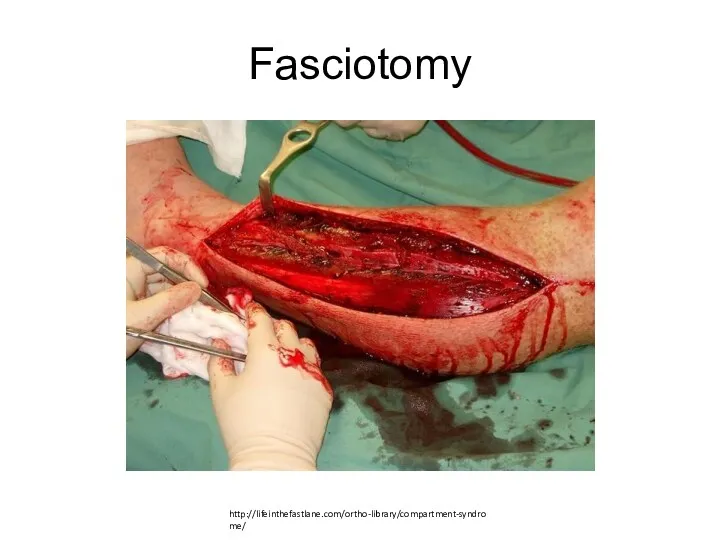
- 23. Fasciotomy http://lifeinthefastlane.com/ortho-library/compartment-syndrome/
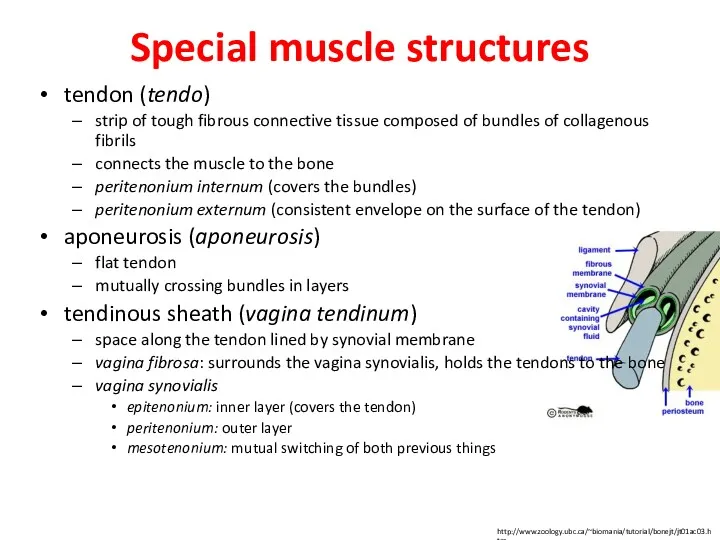
- 24. Special muscle structures tendon (tendo) strip of tough fibrous connective tissue composed of bundles of collagenous
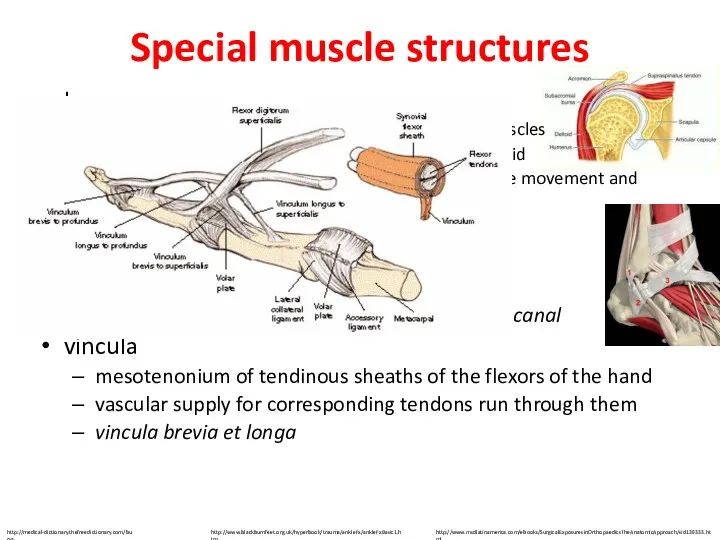
- 25. Special muscle structures bursae mucosae pouches in the vincinity of the joints, tendons and muscles lined
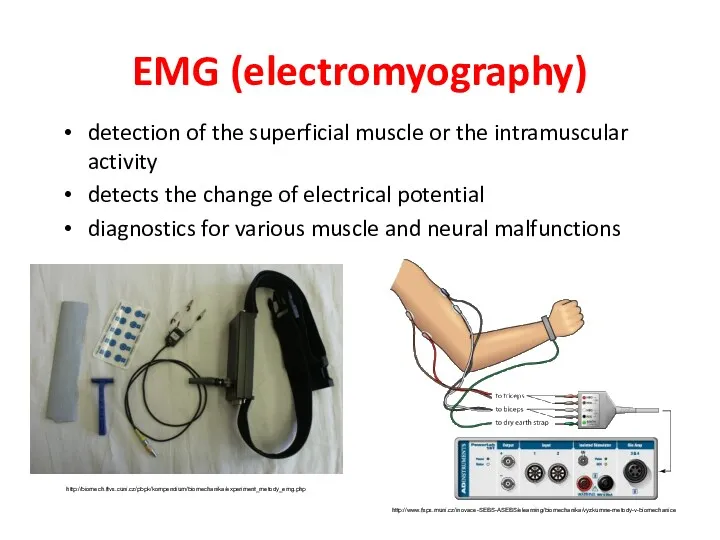
- 35. EMG (electromyography) detection of the superficial muscle or the intramuscular activity detects the change of electrical
- 36. Functional muscle test informs us about the muscle strength helps to assess the extent and location
- 37. spasm – involuntary contraction of one muscle cramp – painful spasm tetanus – multiple spasms of
- 39. Скачать презентацию







 Когда появилась одежда. (1 класс)
Когда появилась одежда. (1 класс) Регистры. Счетчики
Регистры. Счетчики Polymer Flooding for Enhanced Oil Recovery
Polymer Flooding for Enhanced Oil Recovery Автоматизация и механизация процессов листовой штамповки
Автоматизация и механизация процессов листовой штамповки Творческий проект по теме: Жанр романтической поэмы в творчестве М.Ю. Лермонтова
Творческий проект по теме: Жанр романтической поэмы в творчестве М.Ю. Лермонтова Аллергия. Аллергены
Аллергия. Аллергены Соединения на гвоздях
Соединения на гвоздях Зима в картинах русских художников
Зима в картинах русских художников Автоматизация производства. ИП Акулов Николай Николаевич
Автоматизация производства. ИП Акулов Николай Николаевич Атмосферные явления
Атмосферные явления Религиозные праздники России в XVI веке
Религиозные праздники России в XVI веке Комплаентность пациента с артериальной гипертензией. Роль фельдшера
Комплаентность пациента с артериальной гипертензией. Роль фельдшера Автоматизированные системы для мониторинга газовых выбросов из фиксированных источников
Автоматизированные системы для мониторинга газовых выбросов из фиксированных источников Біблійна антропологія. Вчення про людину – розділ систематичної теології
Біблійна антропологія. Вчення про людину – розділ систематичної теології Залізничний транспорт
Залізничний транспорт Приоритеты в организации и содержании управления на основе выявленных проблем системы образования города Новосибирска
Приоритеты в организации и содержании управления на основе выявленных проблем системы образования города Новосибирска Повторение: подготовка к ГИА по математике: алгебра, геометрия, теория вероятностей (8, 9 класс) Диск Диск Диск Диск
Повторение: подготовка к ГИА по математике: алгебра, геометрия, теория вероятностей (8, 9 класс) Диск Диск Диск Диск Принцесса Грёз или Женщина - Гражданка О чем писали женские журналы в 1917 году
Принцесса Грёз или Женщина - Гражданка О чем писали женские журналы в 1917 году урок с презентацией химия 9класс Предмет органической химии
урок с презентацией химия 9класс Предмет органической химии Презентация Игрушки из скрученных полосок
Презентация Игрушки из скрученных полосок Возбуждение и рассмотрение дела об административном правонарушении
Возбуждение и рассмотрение дела об административном правонарушении Коммутация и программирование щитов
Коммутация и программирование щитов Понятие о методах обучения и их классификация
Понятие о методах обучения и их классификация Сети. Интернет. Протоколы
Сети. Интернет. Протоколы Шоколадное печенье в виде футбольного мяча
Шоколадное печенье в виде футбольного мяча Итоги обучения в 3 классе!
Итоги обучения в 3 классе! Ішекті өңдеу. Ішек компектісі туралы түсінік. (Дәріс 11-12)
Ішекті өңдеу. Ішек компектісі туралы түсінік. (Дәріс 11-12) Умножение многочленов. Формулы сокращенного умножения
Умножение многочленов. Формулы сокращенного умножения