Содержание
- 2. Plan Alternative energy sources INTRODUCTION BASICS OF KAZAKHSTAN’S ECOLOGICAL ENERGY STRATEGY ECOLOGICAL ENERGY FUTURE: A STRATEGY
- 3. The world is currently undergoing a transformation the complexity of which has only become clear of
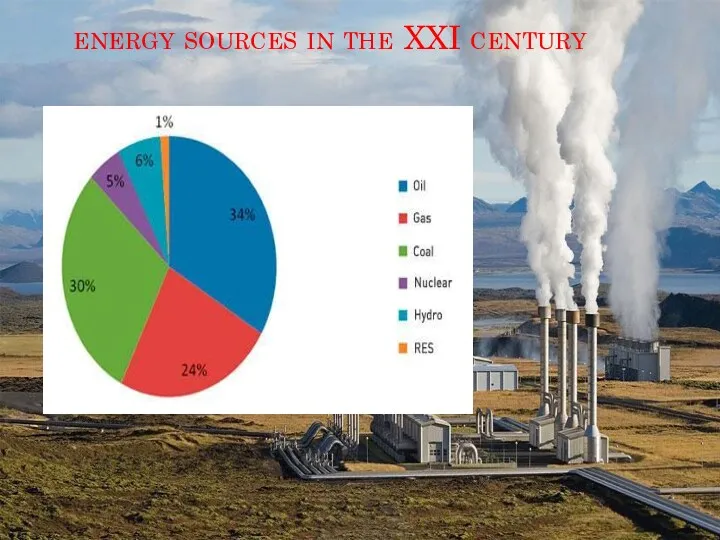
- 4. energy sources in the XXI century
- 5. Environmental impacts of power Environmental impact of electricity generation: The environmental impact of electricity generation is
- 6. Environmental impacts of power Environmental impacts of power The amount of water usage is often of
- 7. Most electricity today is generated by burning fossil fuels and producing steam which is then used
- 8. Nuclear power plants do not burn fossil fuels and so do not directly emit carbon dioxide;
- 9. Environmental power - replacement of conventional energy
- 10. alternative energy sources By 2050, one-third of the world's energy will need to come from solar,
- 11. Alternative energy is any energy source that is an alternative to fossil fuel. These alternatives are
- 12. Renewable energy is the energy source which, according to human scale, are inexhaustible The basic principle
- 13. Renewable Energy Sources Wind energy Water power The energy of the tides Wave energy The energy
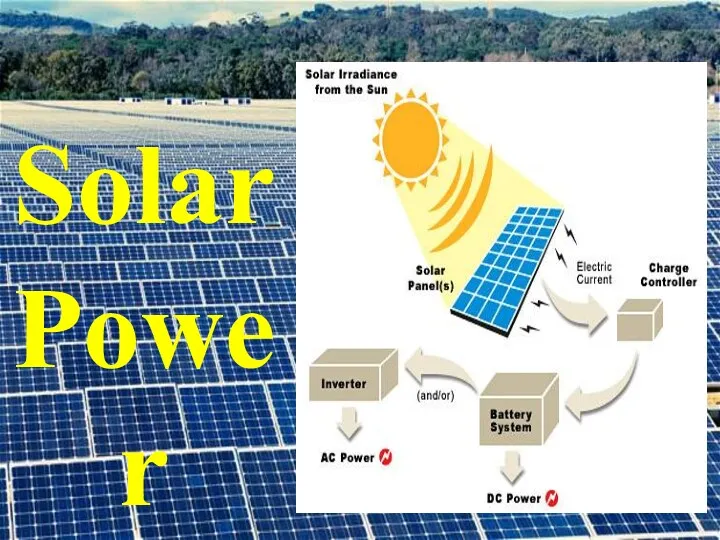
- 14. Solar Power
- 15. Wind Power
- 16. ALTERNATIVE ENERGY SOURCES:WIND POWER Wind power, as an alternative to burning fossil fuels, is plentiful, renewable,
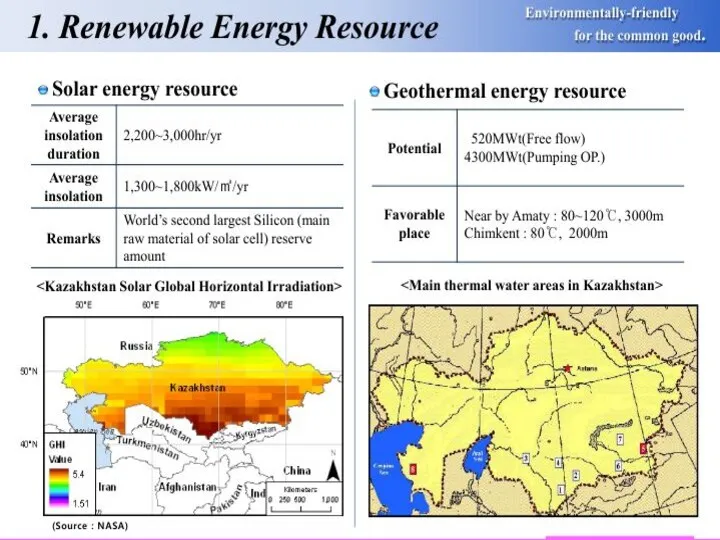
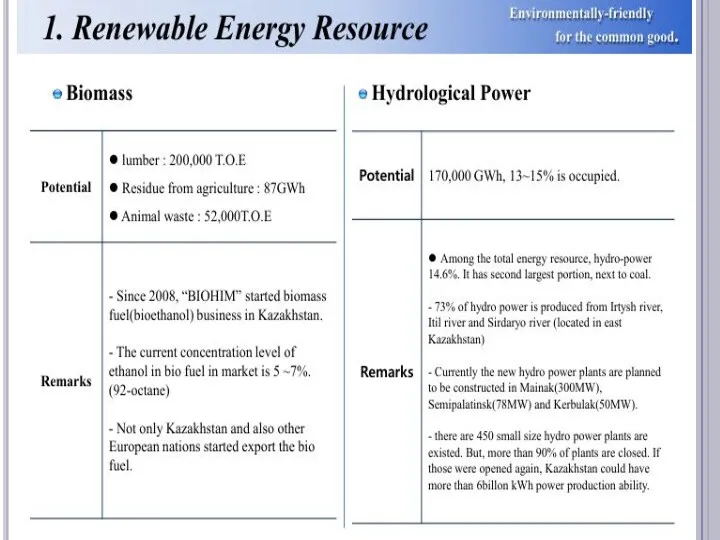
- 17. Basics of Kazakhstan’s ecological energy strategy In the President’s address to the nation concerning the national
- 21. G-global project and energy-saving strategies
- 22. The Global Energy and Economical Strategy, which was initiated by N. Nazarbayev offered to the world
- 23. FROM THE SPEECH OF THE PRESIDENT OF KAZAKHSTAN IN CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY ON 26.07.2012 STATEMENTS OF THE
- 24. G-global project and energy-saving strategies G-Global - a feature-rich platform to create the conditions for the
- 25. GOALS AND OBJECTIVES: Consolidate the efforts of the world community in understanding the global challenges of
- 26. G-GLOBAL is five principles: 1 evolution and rejection of revolutionary change in policy 2 justice, equality,
- 27. Simple Strategies to Maximize Energy Savings 1) Use programmable thermostats (properly) 2) Implement lighting changes 3)
- 28. Efficient energy use, sometimes simply called energy efficiency, is the goal to reduce the amount of
- 30. Water Resources
- 31. Water is a strategic resources in 21th . Water resources are sources of water that are
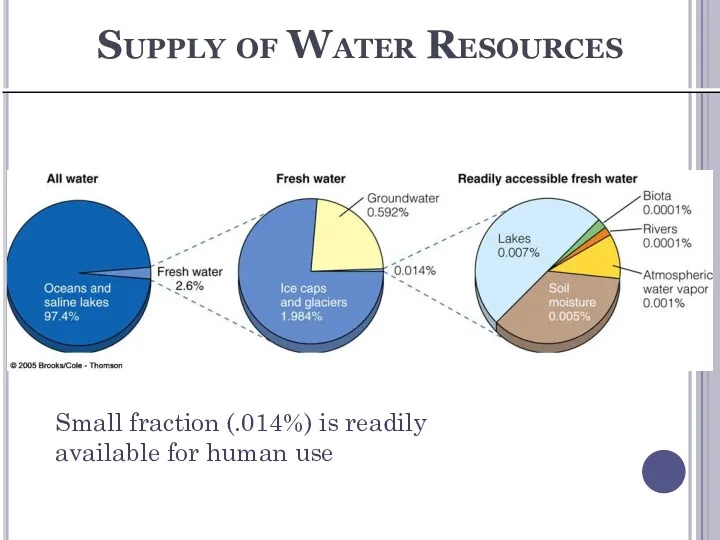
- 32. Supply of Water Resources Small fraction (.014%) is readily available for human use
- 34. Use of Water Resources Humans directly or indirectly use about 54% of reliable runoff Withdraw 34%
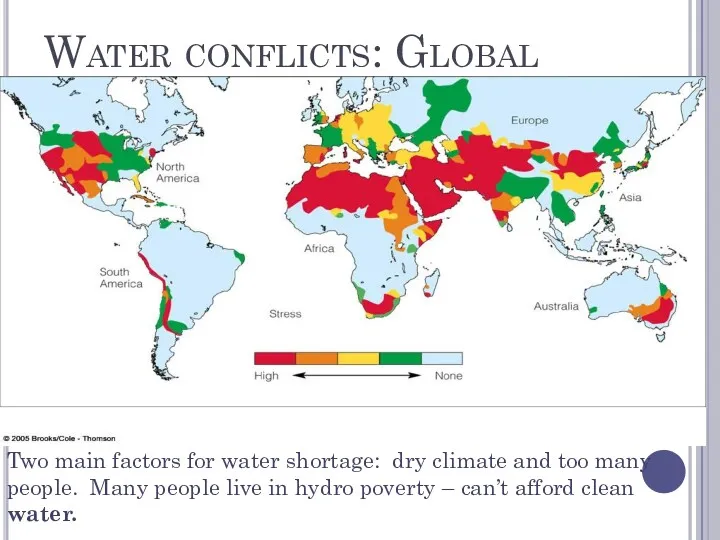
- 35. Water conflicts: Global Two main factors for water shortage: dry climate and too many people. Many
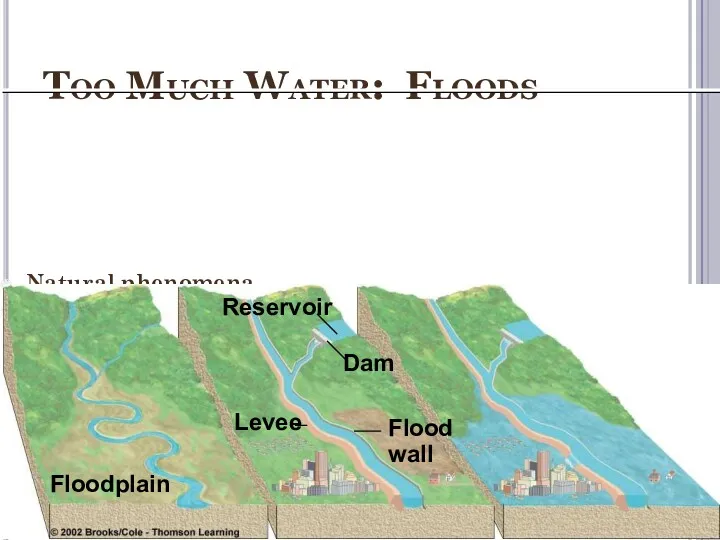
- 36. Too Much Water: Floods Natural phenomena Aggravated by human activities Rain on snow Living on floodplains
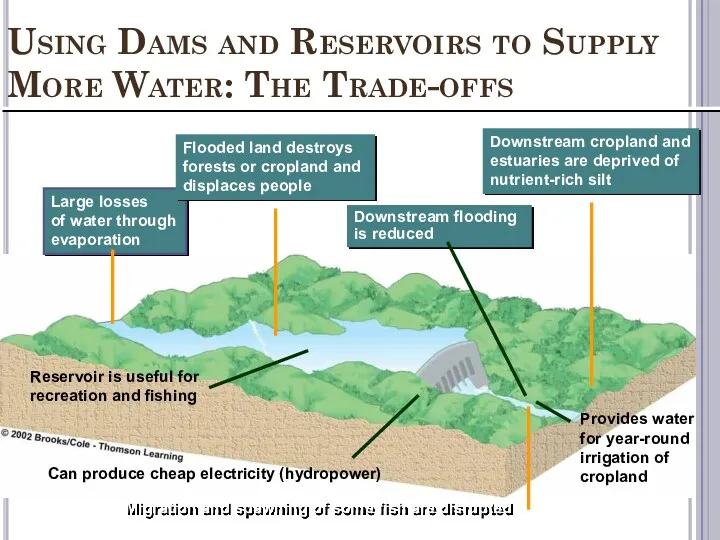
- 37. Using Dams and Reservoirs to Supply More Water: The Trade-offs
- 38. Solutions Sustainable Water Use Not depleting aquifers Preserving ecological health of aquatic systems Preserving water quality
- 39. It is estimated that 22% of worldwide water is used in industry. Major industrial users include
- 40. Water resource management Water resource management is the activity of planning, developing, distributing and managing the
- 41. Water is an essential resource for all life on the planet. Of the water resources on
- 42. Water in the Future: One of the biggest concerns for our water-based resources in the future
- 43. CONCLUSIONS Basic conditions for an ecological energy policy to be successful in the course of the
- 44. The present XXI century is an epoch of strengthening integration of civilizations, their dialogue and partnership
- 45. References http://epswa.com.au/ http://climatepolicyinitiative.org/ http://e-lib.kazntu.kz/ http://www.noblepower.com/ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Environmental_impact_of_electricity_generation "Executive Summary: Assessment of Parabolic Trough and Power Tower Solar
- 47. Скачать презентацию




































 Революція на граніті
Революція на граніті Rice Cooker HD3033 df Technical Info. Product Features
Rice Cooker HD3033 df Technical Info. Product Features Выбор и подготовка материалов для резки
Выбор и подготовка материалов для резки Троянская война и поэмы Гомера
Троянская война и поэмы Гомера Stalingradskaya_bitva_02_02_22
Stalingradskaya_bitva_02_02_22 Новые лица
Новые лица Химия и живопись.
Химия и живопись. Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence Эффективность применения программы Преобразование обучения для XXI века в работе педагога в адаптационный период обучающихся первых классов к школьному обучению
Эффективность применения программы Преобразование обучения для XXI века в работе педагога в адаптационный период обучающихся первых классов к школьному обучению Палех - город мастеров
Палех - город мастеров Технология ручной дуговой сварки
Технология ручной дуговой сварки Крупнейшие экологические катастрофы - презентация к конференции по географии Глобальные проблемы человечества
Крупнейшие экологические катастрофы - презентация к конференции по географии Глобальные проблемы человечества Виды ислама
Виды ислама Страны Востока в XVI – XVIII веках
Страны Востока в XVI – XVIII веках Приглашаем студентов на практику и трудоустройство. Акционерное общество Ижевский радиозавод
Приглашаем студентов на практику и трудоустройство. Акционерное общество Ижевский радиозавод Health is above wealth
Health is above wealth музыка в кино
музыка в кино Подготовка к сочинению по картине И.Э.Грабаря Февральская лазурь
Подготовка к сочинению по картине И.Э.Грабаря Февральская лазурь Физические основы механики молекулярная физика. Основы термодинамики
Физические основы механики молекулярная физика. Основы термодинамики Презентация Воспоминания о Великой Отечественной Войне ветерана ВОВ Киселева Степана Павловича( в стихах его собственного сочинения).
Презентация Воспоминания о Великой Отечественной Войне ветерана ВОВ Киселева Степана Павловича( в стихах его собственного сочинения). Массивы в языке Pascal. (Урок 42)
Массивы в языке Pascal. (Урок 42) Қазақстан Республикасында тілдердің қызметі мен дамуын қамтамасыздандырудағы әрекеттері
Қазақстан Республикасында тілдердің қызметі мен дамуын қамтамасыздандырудағы әрекеттері Виды фундаментов. (Лекция 16)
Виды фундаментов. (Лекция 16)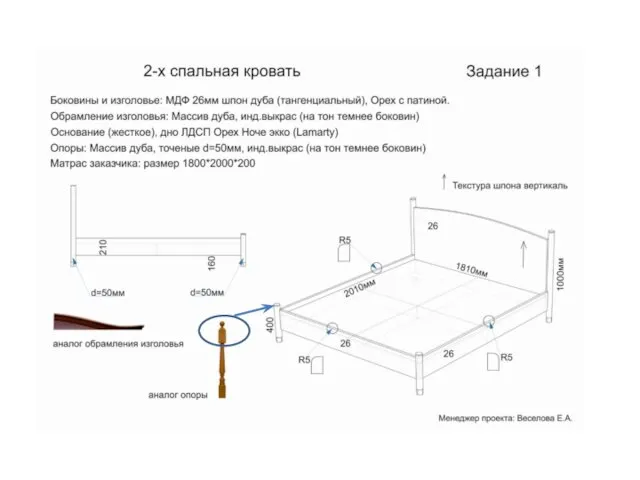 2-х спальная кровать
2-х спальная кровать Кариес зубов у детей. Лечение
Кариес зубов у детей. Лечение Türk EÄitim Tarihi 3
Türk EÄitim Tarihi 3 Волонтёры Победы. Курск
Волонтёры Победы. Курск ФК Русичи-2008 г. Орёл
ФК Русичи-2008 г. Орёл