Содержание
- 2. Historical reference 1981- СDC-center for Disease (USA) registered among homosexuals increase morbidity of pneumocytosis and Kaposi’s
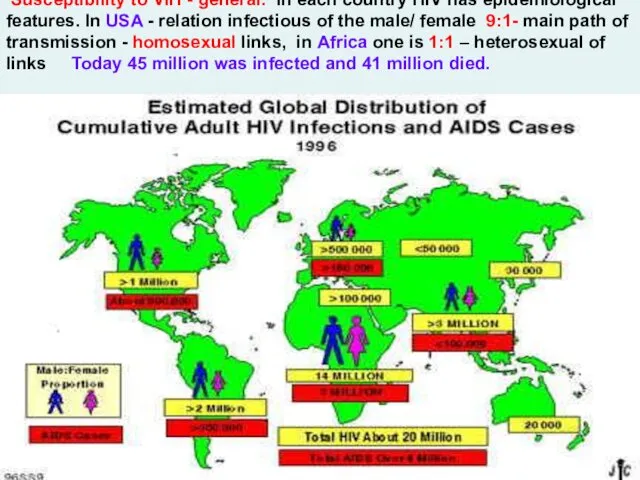
- 3. HIV- infection in world ( 2007) Quantity of people living with HIV Common — 33.2 million
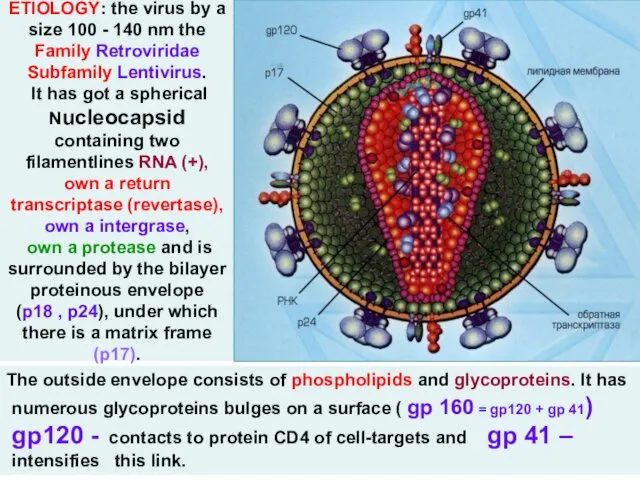
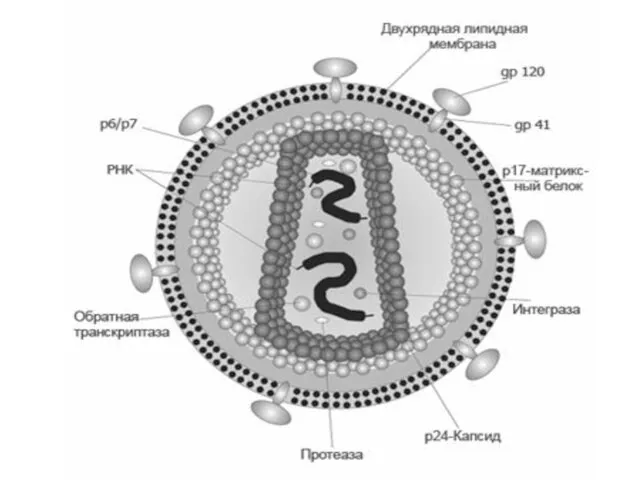
- 4. ETIOLOGY: the virus by a size 100 - 140 nm the Family Retroviridae Subfamily Lentivirus. It
- 6. Therefore virus is capable to penetrate only into those cells, on which surface there are the
- 7. Stability of the virus in the external environment is low: - at desiccation is perished through
- 8. EPIDEMIOLOGY Pandemic of a HIV- infection annually carries of millions human lives and for its not
- 9. Modes of TRANSMISSION: Main mode of transmission in world is sexual ( 80 %) - the
- 10. The parenteral mode of transmission: - any biological tissue past testing on HIV is not absolutely
- 11. The risk оf an infection at one contact with the source of a VIH infection: blood
- 12. VIH - is not transmitted by : - at touches, embraces, hand shakes, kisses ( if
- 13. Susceptibility to VIH - general. In each country HIV has epidemiological features. In USA - relation
- 14. PATHOGENY Infectious the dose can makes only 10 viruses!! 1.Infiltration into an organism through a injury
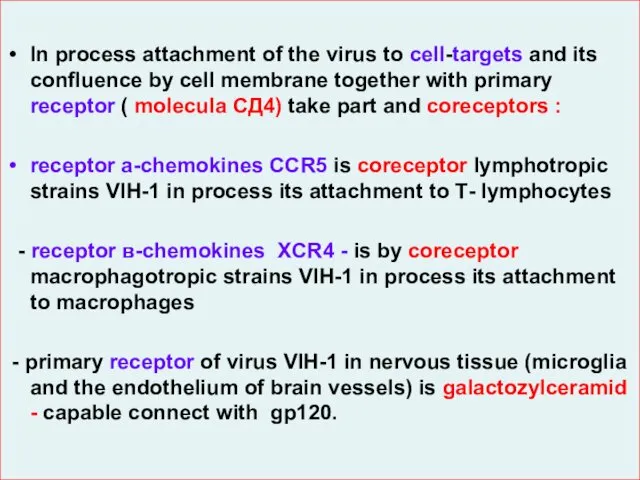
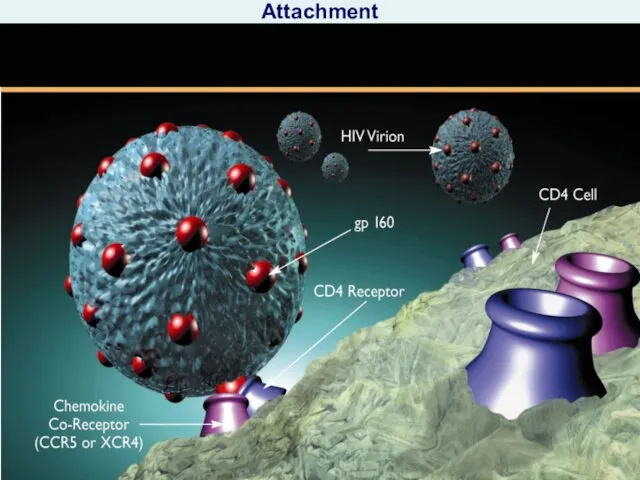
- 15. In process attachment of the virus to cell-targets and its confluence by cell membrane together with
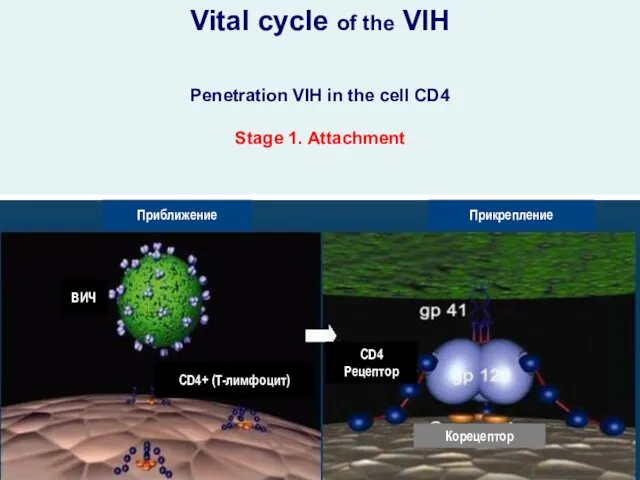
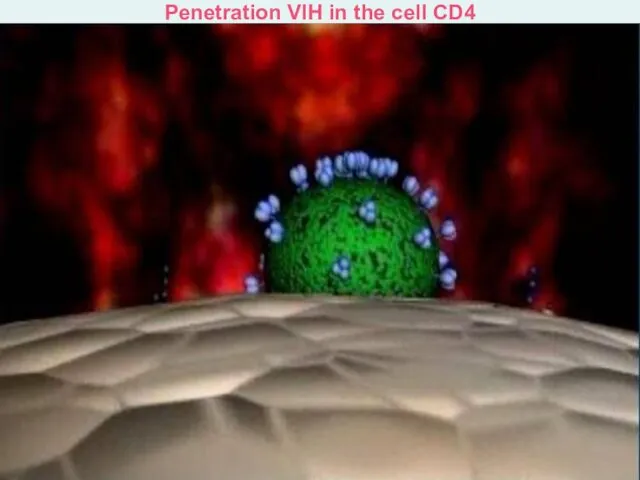
- 16. Penetration VIH in the cell CD4 Stage 1. Attachment Vital cycle of the VIH
- 17. The HIV Life Cycle; Merck & Co 2006 Attachment
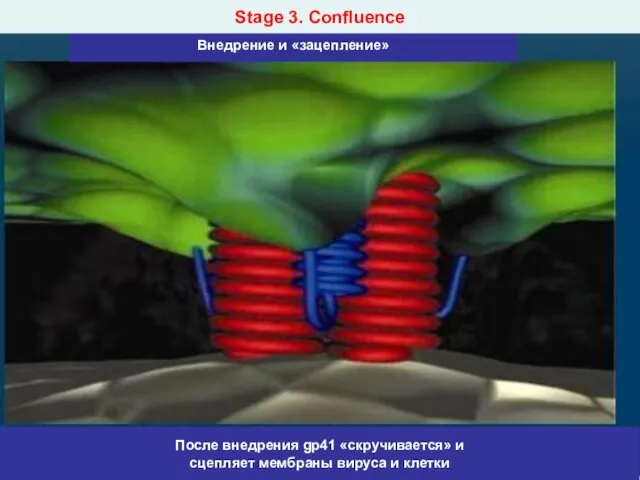
- 18. Stage 3. Сonfluence
- 19. Penetration VIH in the cell CD4
- 20. 4. Destroy by enzymes of a cell of the envelope of a virus and Infiltration of
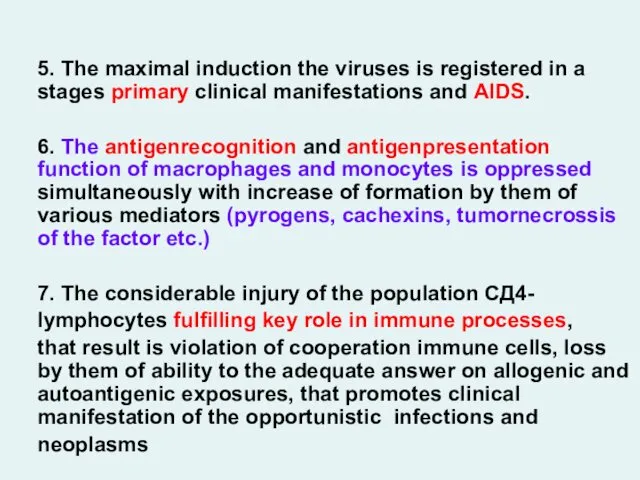
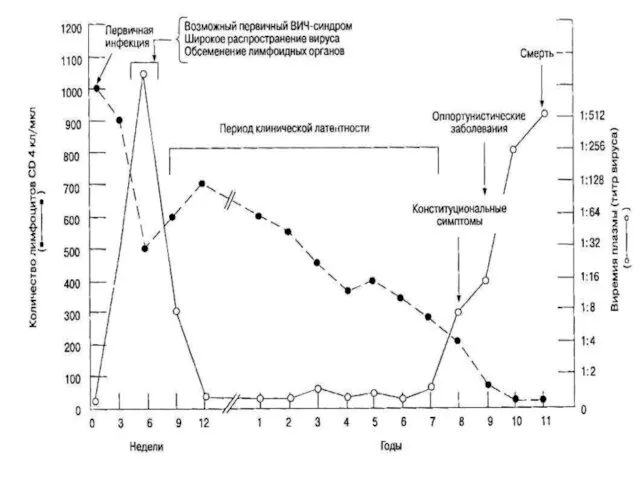
- 21. 5. The maximal induction the viruses is registered in a stages primary clinical manifestations and AIDS.
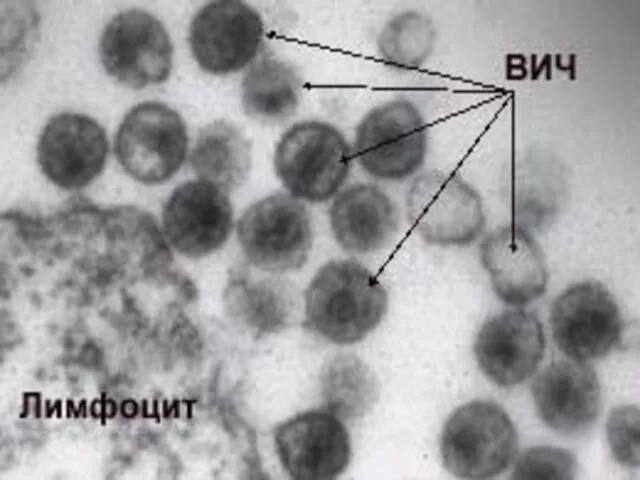
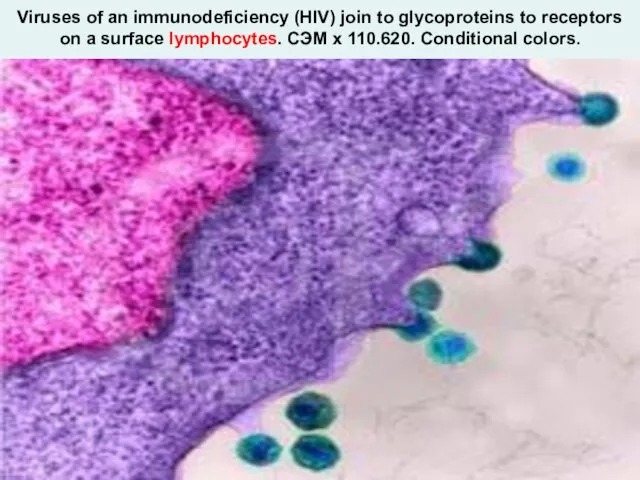
- 23. Viruses of an immunodeficiency (HIV) join to glycoproteins to receptors on a surface lymphocytes. СЭМ х
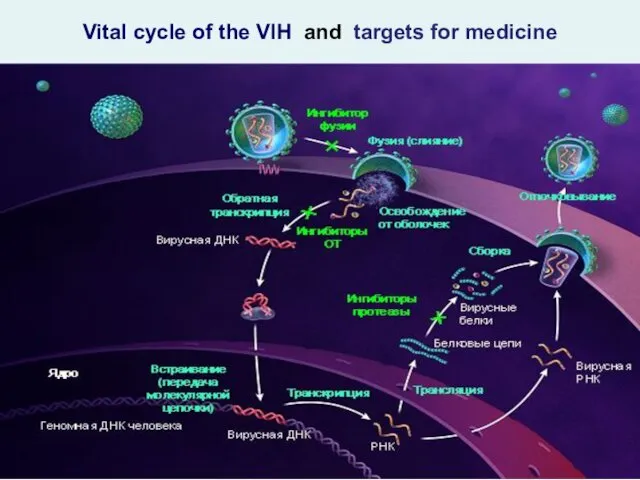
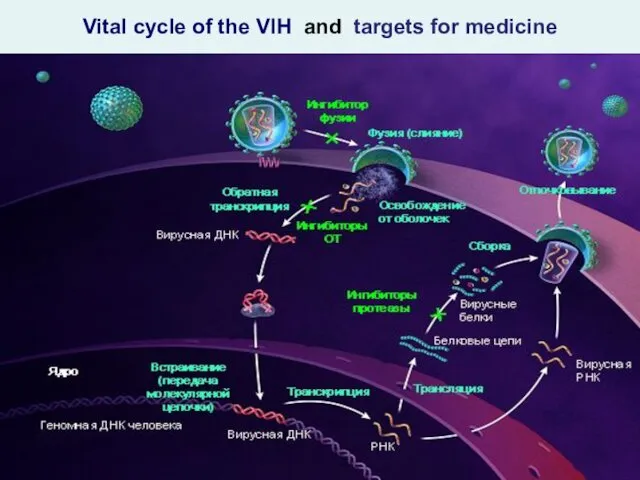
- 24. Vital cycle of the VIH and targets for medicine
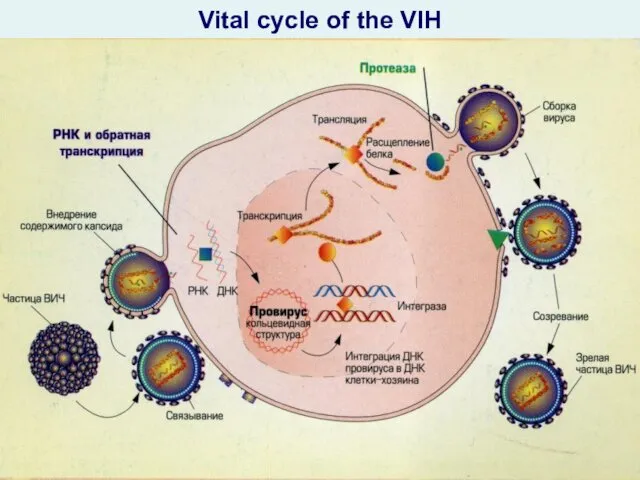
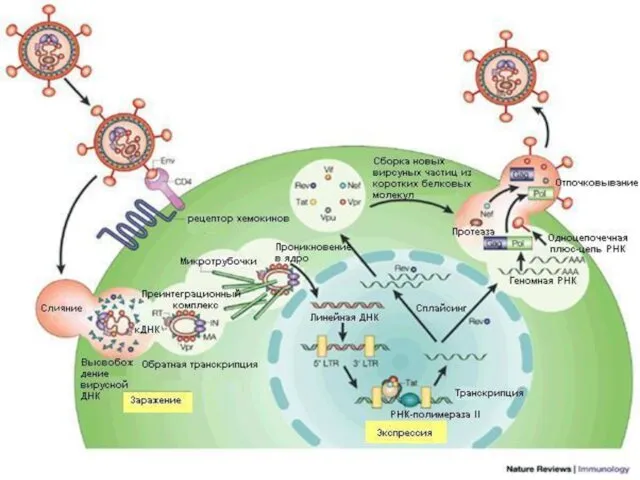
- 25. Vital cycle of the VIH
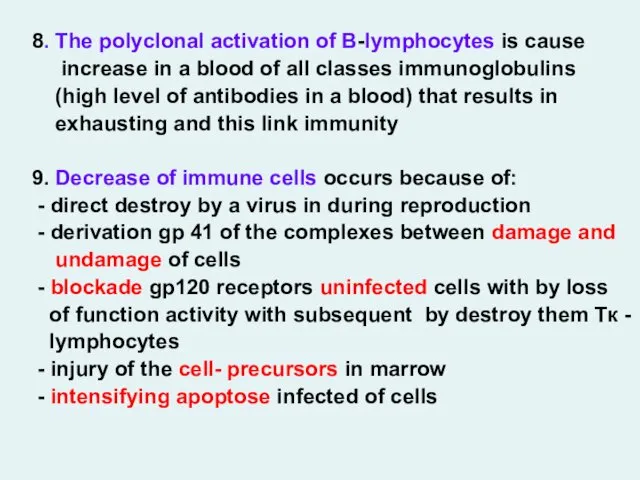
- 26. 8. The polyclonal activation of B-lymphocytes is cause increase in a blood of all classes immunoglobulins
- 27. 10. Occurs anergy of a skin and mucous, are depressed inflammatory responses. 11. Under influence of
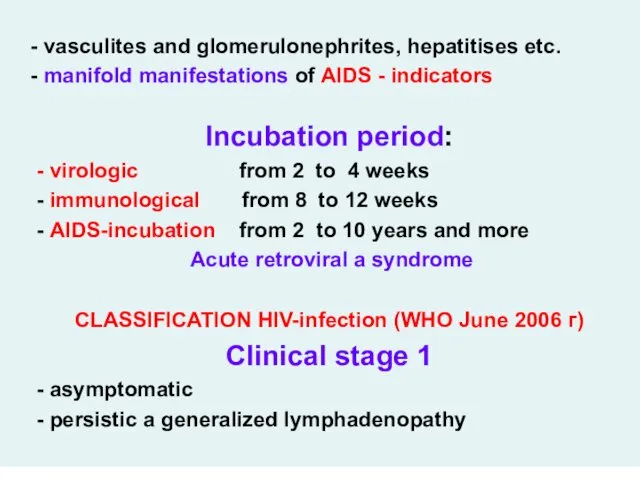
- 28. - vasculites and glomerulonephrites, hepatitises etc. - manifold manifestations of AIDS - indicators Incubation period: -
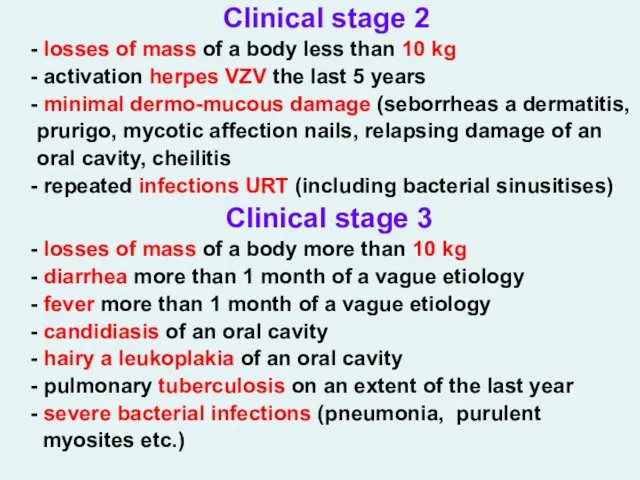
- 29. Clinical stage 2 - losses of mass of a body less than 10 kg - activation
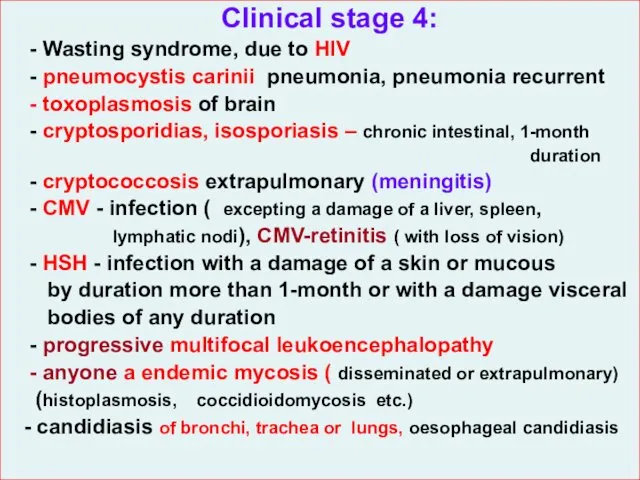
- 30. Clinical stage 4: - Wasting syndrome, due to HIV - pneumocystis carinii pneumonia, pneumonia recurrent -
- 31. - visceral leishmaniasis - extrapulmonary a tuberculosis - atypical mycobacteriosis disseminated or extrapulmonary) B - cellular
- 32. - headache - 32 % - nausea and vomiting - 27 % - hepatospleenmegaly - 14
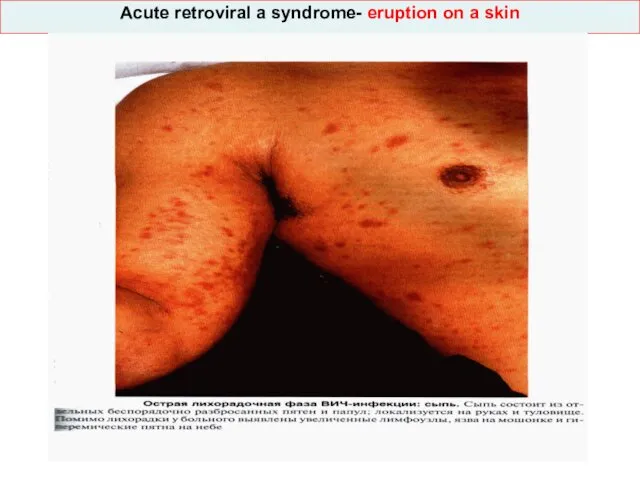
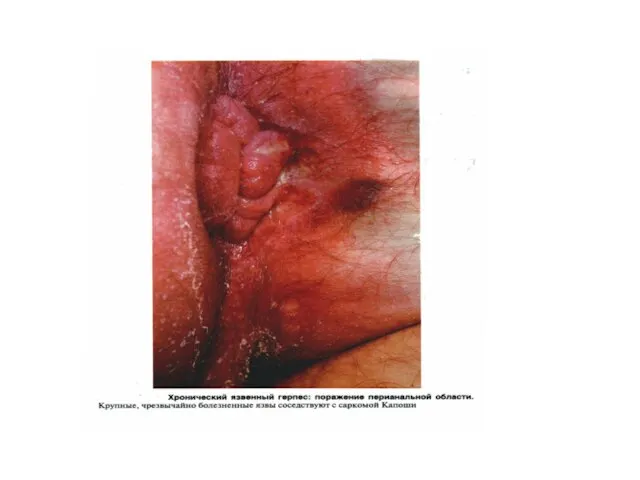
- 33. Acute retroviral a syndrome- eruption on a skin
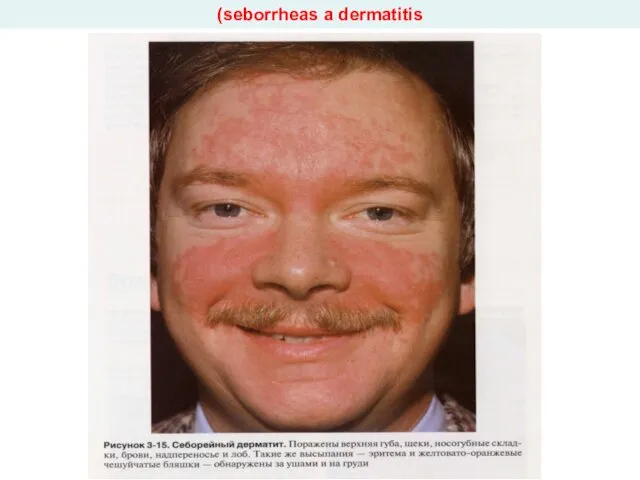
- 34. (seborrheas a dermatitis
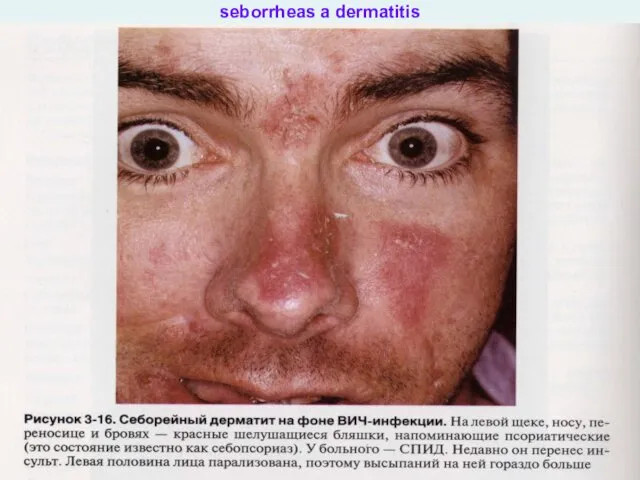
- 35. seborrheas a dermatitis
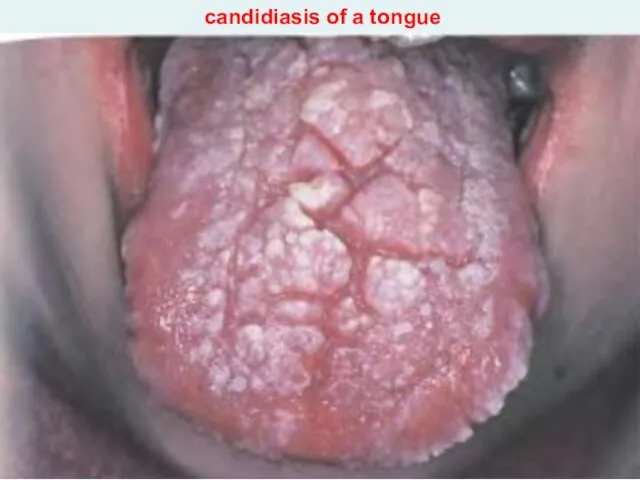
- 36. candidiasis of a tongue
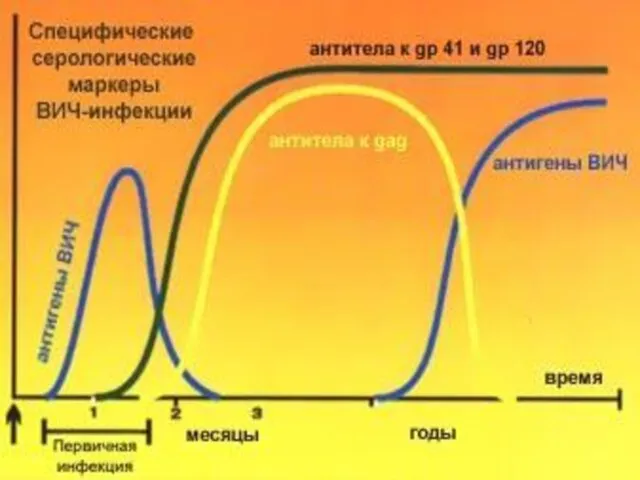
- 37. LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS HIV: The data epidanamnesis , parenteral anamnesis and sexual behaviour, presence HIV for the
- 40. ANTIRETROVIRAL TREATMENT ( ART) АRТ is a reception of specific drugs, which operating on various components
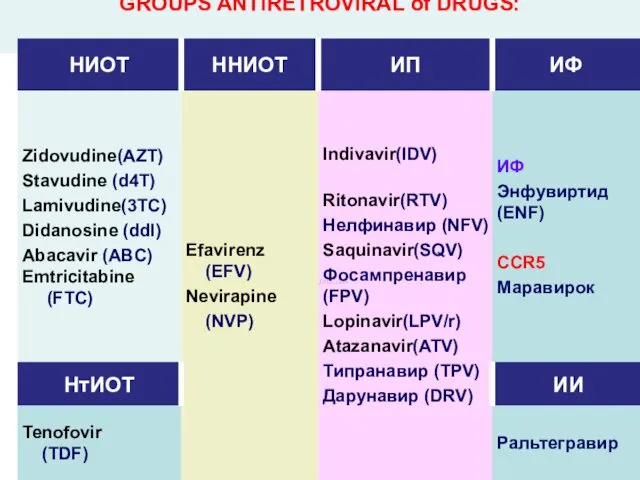
- 41. GROUPS ANTIRETROVIRAL of DRUGS: 1.Nucleozid`s inhibitors return transcriptasa- (d4T, AZT, ddl, 3TC …) 2. Unnucleozid`s inhibitors
- 42. Vital cycle of the VIH and targets for medicine
- 43. GROUPS ANTIRETROVIRAL of DRUGS:
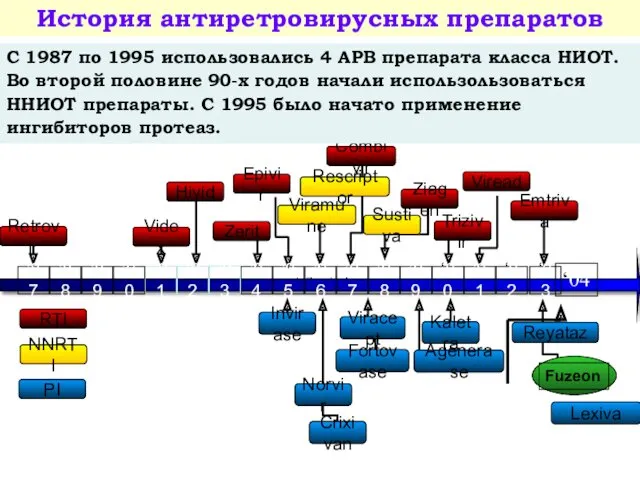
- 44. NNRTI ’87 ’91 ’92 ’94 ’95 ’96 ’97 ’98 ’99 ‘00 ’88 ’89 ’90 RTI PI
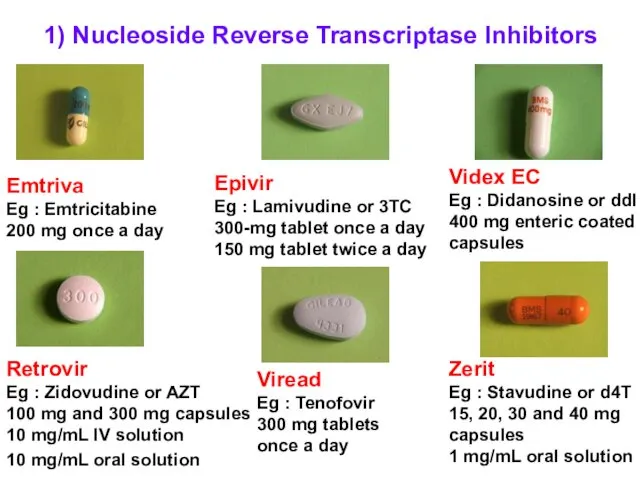
- 45. 1) Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors Epivir Eg : Lamivudine or 3TC 300-mg tablet once a day
- 46. 2) Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors Sustiva Eg : Efavirenz 50, 100 and 200 mg capsules Viramune
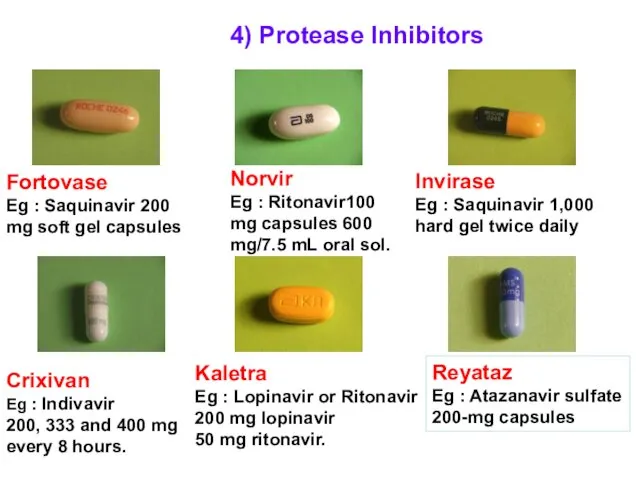
- 47. 4) Protease Inhibitors Kaletra Eg : Lopinavir or Ritonavir 200 mg lopinavir 50 mg ritonavir. Reyataz
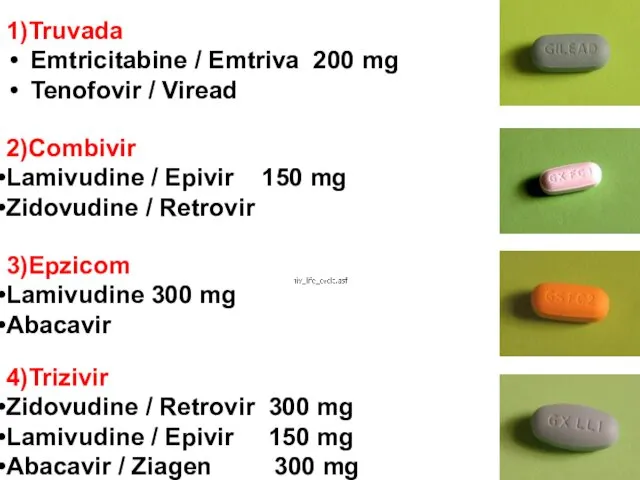
- 48. 1)Truvada Emtricitabine / Emtriva 200 mg Tenofovir / Viread 300 mg 2)Combivir Lamivudine / Epivir 150
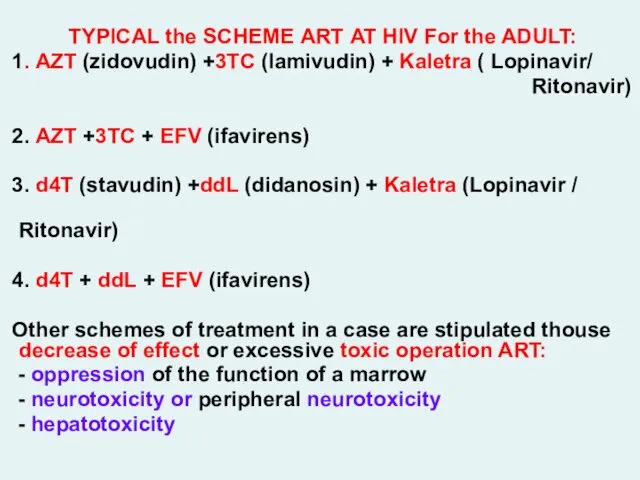
- 49. TYPICAL the SCHEME АRТ AT HIV For the ADULT: 1. АZT (zidovudin) +3ТС (lamivudin) + Kaletra
- 50. - appearance of an exanthema or enanthema - syndrome of the diarrhea - pancreatitis - lowering
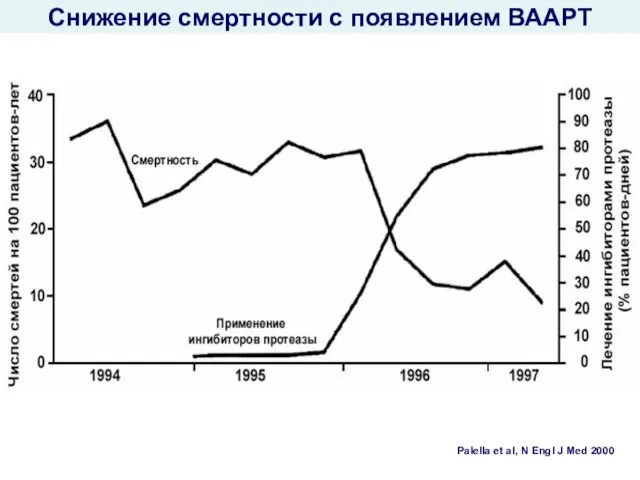
- 51. Снижение смертности с появлением ВААРТ Palella et al, N Engl J Med 2000
- 52. PROPHYLAXIS (there is no specific prophylaxis!!!) - revealing groups of hazard and their testing ( with
- 53. usage of special containers at a transportation of test tubes with anyone biological by materials obtained
- 54. ENDING OF THE LECTURE
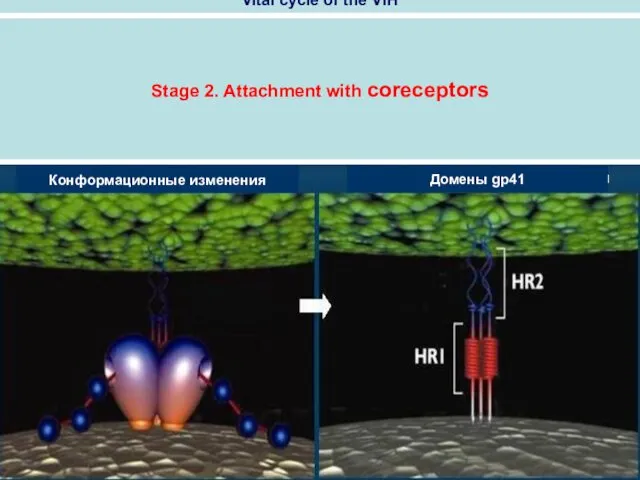
- 55. Stage 2. Attachment with coreceptors Vital cycle of the VIH
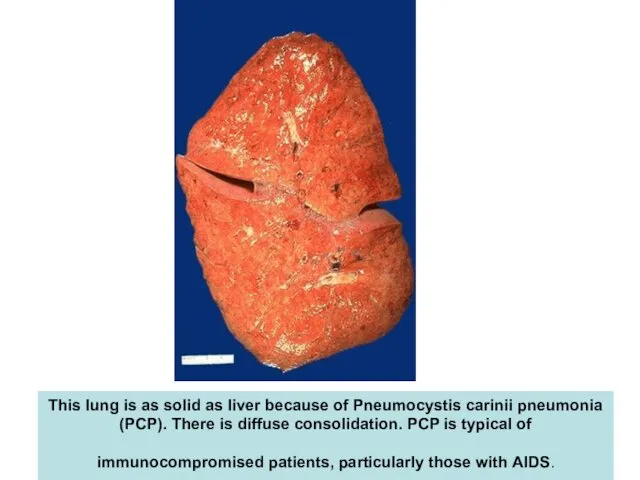
- 58. This lung is as solid as liver because of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP). There is diffuse
- 60. Скачать презентацию




















 Слово в лексической системе языка
Слово в лексической системе языка Сочинение по картине А.В. Сайкиной Детская спортивная школа
Сочинение по картине А.В. Сайкиной Детская спортивная школа Профилактика алкоголизма
Профилактика алкоголизма Конечность и бесконечность Вселенной. Расширяющаяся Вселенная
Конечность и бесконечность Вселенной. Расширяющаяся Вселенная День Защитника Отечества
День Защитника Отечества Презентация Способы получения металлов
Презентация Способы получения металлов Памятки, правила, алгоритмы, таблицы
Памятки, правила, алгоритмы, таблицы Бухгалтерский учет операций по выдаче (размещению) денежных средств по договорам займа и банковского вклада. Глава 4
Бухгалтерский учет операций по выдаче (размещению) денежных средств по договорам займа и банковского вклада. Глава 4 Первая мировая война
Первая мировая война Создание социально-развивающей среды
Создание социально-развивающей среды Энергия приливов и отливов. Энергия волн океана. Малые ГЭС
Энергия приливов и отливов. Энергия волн океана. Малые ГЭС Кома кезіндегі визуальды диагностикасы
Кома кезіндегі визуальды диагностикасы Источники права в РБ. Нормативный правовой акт
Источники права в РБ. Нормативный правовой акт Моя семья
Моя семья Реклама: цели, задачи, функции и основные характеристики
Реклама: цели, задачи, функции и основные характеристики Кейс-метод при обучении химии в условиях перехода на ФГОС ООО
Кейс-метод при обучении химии в условиях перехода на ФГОС ООО Учебно-методический материал - Семья
Учебно-методический материал - Семья Совершенства (атрибуты) Бога
Совершенства (атрибуты) Бога Буквы Ч, ч, обозначающие звук [ч,]( второй урок) УМК Школа России
Буквы Ч, ч, обозначающие звук [ч,]( второй урок) УМК Школа России Презентация для педагогов Аппликация во второй младшей группе
Презентация для педагогов Аппликация во второй младшей группе В ночь перед Рождеством
В ночь перед Рождеством Способы эксплуатации нефтяных, газовых и газоконденсатных скважин
Способы эксплуатации нефтяных, газовых и газоконденсатных скважин Краткая клиническая характеристика ВИЧ-инфекции
Краткая клиническая характеристика ВИЧ-инфекции Формирование коммуникативных способностей у старших дошкольников
Формирование коммуникативных способностей у старших дошкольников Коррекционно-восстановительная работа при сенсорной афазии
Коррекционно-восстановительная работа при сенсорной афазии XXI век - эпоха женщины
XXI век - эпоха женщины Насекомые леса. Окружающий мир. 2 класс
Насекомые леса. Окружающий мир. 2 класс Современные образовательные технологии для формирования ключевых компетенций
Современные образовательные технологии для формирования ключевых компетенций