- Главная
- Без категории
- Introduction to private equity

Содержание
- 2. Economics and chrematistics Economics (from Greek word οἰκονομία) – "household management". Chrematistics (from Greek: χρηματιστική) according
- 4. Henry Ford "Nothing can be made except by makers, nothing can be managed except by managers.
- 5. WIKI: What is private equity Private equity is an asset class consisting of equity securities and
- 6. WIKI: What is private equity Bloomberg Businessweek has called private equity a rebranding of leveraged buyout
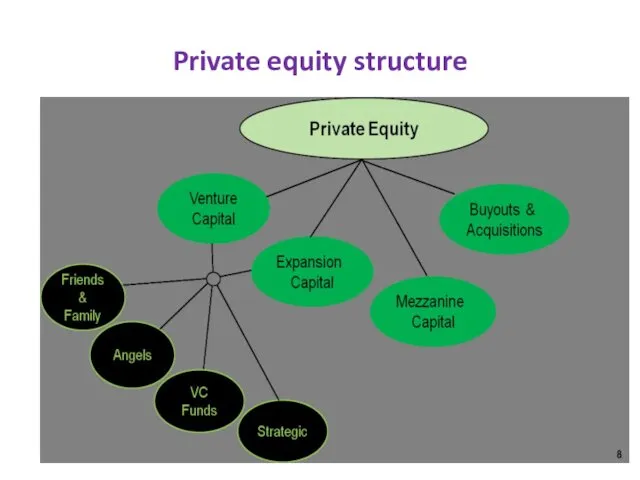
- 7. Private equity structure
- 8. WIKI: What is venture capital Venture capital (VC) is financial capital provided to early-stage, high-potential, high
- 9. WIKI: What is expansion capital Growth capital (also called expansion capital and growth equity) is a
- 10. WIKI: What is mezzanine capital Mezzanine capital, in finance, refers to a subordinated debt or preferred
- 11. WIKI: What is mezzanine capital . The higher cost of capital associated with mezzanine financings is
- 12. WIKI: What is buyout and acquisition A takeover is the purchase of one company (the target)
- 13. Warren Buffet: Discipline, Patience and Value "The essence of Warren's thinking is that the business world
- 15. Скачать презентацию
Economics and chrematistics
Economics (from Greek word οἰκονομία) – "household management".
Chrematistics (from Greek: χρηματιστική) according to Thales of
Economics and chrematistics
Economics (from Greek word οἰκονομία) – "household management".
Chrematistics (from Greek: χρηματιστική) according to Thales of
Aristotle contradistinguished economics and chrematistics
Henry Ford
"Nothing can be made except by makers, nothing can be managed except
Henry Ford
"Nothing can be made except by makers, nothing can be managed except
"Two classes of people lose money; those who are too weak to guard what they have; those who win money by trick. They both lose in the end.“
"When people are 'stung' in false investment schemes there are three causes; greed of something for nothing; sheer inability to know their mind; or infantile trustfulness.“
"What right have you, save service to the world, to think that other men's labor should contribute to your gains?"
Assorted quotations from Ford News, 1922
WIKI: What is private equity
Private equity is an asset class consisting of equity securities and debt in operating companies
WIKI: What is private equity
Private equity is an asset class consisting of equity securities and debt in operating companies
A private equity investment will generally be made by a private equity firm, a venture capital firm or an angel investor. Each of these categories of investor has its own set of goals, preferences and investment strategies; however, all provide working capital to a target company to nurture expansion, new-product development, or restructuring of the company’s operations, management, or ownership.
WIKI: What is private equity
Bloomberg Businessweek has called private equity a rebranding of leveraged
WIKI: What is private equity
Bloomberg Businessweek has called private equity a rebranding of leveraged
Private equity structure
Private equity structure
WIKI: What is venture capital
Venture capital (VC) is financial capital provided to early-stage, high-potential, high risk, growth startup
WIKI: What is venture capital
Venture capital (VC) is financial capital provided to early-stage, high-potential, high risk, growth startup
WIKI: What is expansion capital
Growth capital (also called expansion capital and growth equity) is a type of private
WIKI: What is expansion capital
Growth capital (also called expansion capital and growth equity) is a type of private
Companies that seek growth capital will often do so in order to finance a transformational event in their lifecycle. These companies are likely to be more mature than venture capital funded companies, able to generate revenue and operating profits but unable to generate sufficient cash to fund major expansions, acquisitions or other investments
WIKI: What is mezzanine capital
Mezzanine capital, in finance, refers to a subordinated debt or preferred equity instrument that
WIKI: What is mezzanine capital
Mezzanine capital, in finance, refers to a subordinated debt or preferred equity instrument that
Mezzanine capital is often a more expensive financing source for a company than secured debt or senior debt.
WIKI: What is mezzanine capital
. The higher cost of capital associated with mezzanine financings is
WIKI: What is mezzanine capital
. The higher cost of capital associated with mezzanine financings is
WIKI: What is buyout and acquisition
A takeover is the purchase of one company (the target) by another (the acquirer,
WIKI: What is buyout and acquisition
A takeover is the purchase of one company (the target) by another (the acquirer,
Buyout is an investment transaction by which the ownership equity of a company, or a majority share of the stock of the company is acquired. The acquiror thereby "buys out" the present equity holders of the target company. A buyout will often include the purchasing of the target company's outstanding debt, which is referred to as "assumed debt" by the purchaser.
Warren Buffet: Discipline, Patience and Value
"The essence of Warren's thinking is that the business
Warren Buffet: Discipline, Patience and Value
"The essence of Warren's thinking is that the business
They are understandable.
They see their profits in cash flow.
They have strong franchises and, therefore, freedom to price.
They don't take a genius to run.
Their earnings are predictable.
The management is owner-oriented.











 Викторина Зелёное море тайги
Викторина Зелёное море тайги презентация ученицы 3 класса о себе
презентация ученицы 3 класса о себе День космонавтики. Игра-викторина для учащихся 7-9 классов
День космонавтики. Игра-викторина для учащихся 7-9 классов Александр I. Загадка Старца
Александр I. Загадка Старца Серия мин ТМ-62
Серия мин ТМ-62 Желудок и поджелудочная железа. Очищение
Желудок и поджелудочная железа. Очищение Математическая разминка: НОД и НОК чисел.
Математическая разминка: НОД и НОК чисел. Методическая разработка урока производственного обучения
Методическая разработка урока производственного обучения Мои любимые друзья. Открытки и стихи
Мои любимые друзья. Открытки и стихи Тренажер для глаз
Тренажер для глаз Phrase of the day. Lesson 1. Block 2
Phrase of the day. Lesson 1. Block 2 Автоматизация блока выделения изопентановой фракции. Топливное производство
Автоматизация блока выделения изопентановой фракции. Топливное производство Вооруженные силы России
Вооруженные силы России В гостях у С.Я.Маршака
В гостях у С.Я.Маршака Окислительно-восстановительные реакции в органической и неорганической химии
Окислительно-восстановительные реакции в органической и неорганической химии Подбор игроков для команды Динамо (Санкт-Петербург)
Подбор игроков для команды Динамо (Санкт-Петербург) Управление промышленными мехатронными системами
Управление промышленными мехатронными системами Презентация Железнодорожный транспорт
Презентация Железнодорожный транспорт Вопросы преемственности ФГТ и ФГОС
Вопросы преемственности ФГТ и ФГОС Концертная симфония для арфы с оркестром Фрески Софии Киевской, В. Кикты
Концертная симфония для арфы с оркестром Фрески Софии Киевской, В. Кикты Как разрешить проблемы компании
Как разрешить проблемы компании Окислительно-восстановительные реакции в органической химии
Окислительно-восстановительные реакции в органической химии Тері өңдеу
Тері өңдеу 20231204_uxvxqttrqwmziabkxemjea
20231204_uxvxqttrqwmziabkxemjea Основы исламской культуры
Основы исламской культуры Глаз человека
Глаз человека Программирование Lego-роботов
Программирование Lego-роботов Филимоновская игрушка
Филимоновская игрушка