Содержание
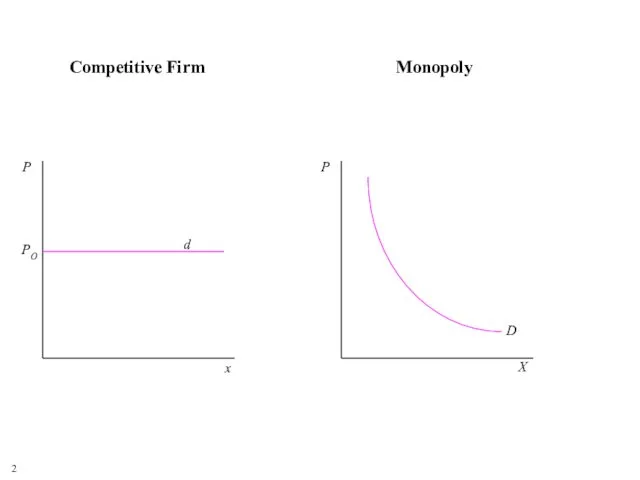
- 2. 2 Competitive Firm Monopoly
- 3. The Tradeoff The monopoly can either choose price or quantity, but not both. The monopolist faces
- 4. Revenue Profit = Revenue – Total Costs Revenue = TR = Unit price • Quantity =
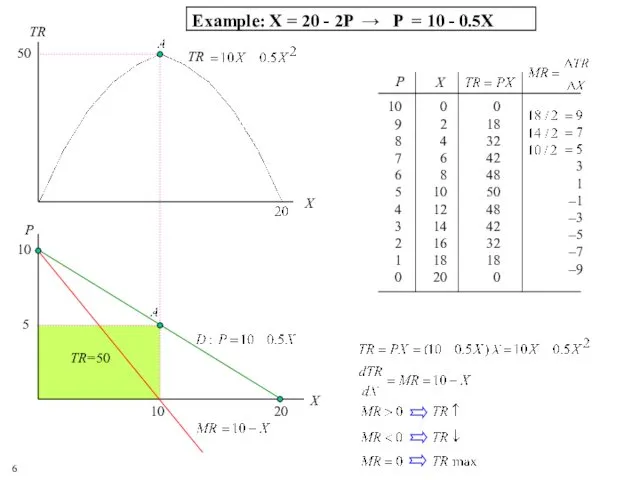
- 5. Marginal Revenue Marginal Revenue = MR= the change in total revenue from increasing output by a
- 6. 109 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 2 4 6 8 10
- 7. Profit Maximization ? = TR(X)- TC(X) ?’ = MR(X) – MC(X)=0 Monopoly chooses X so that
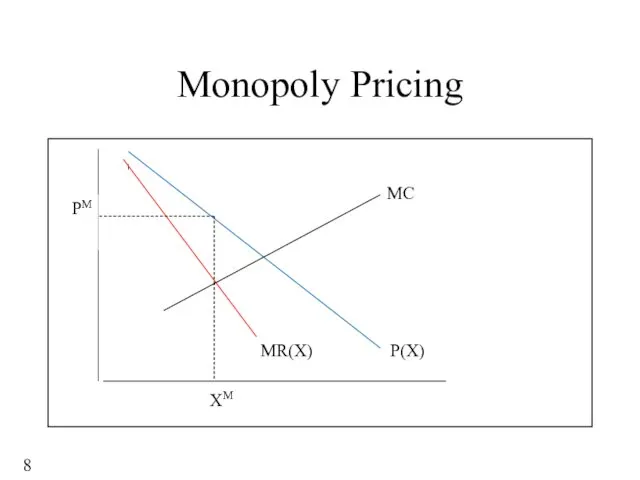
- 8. Monopoly Pricing MC P(X) MR(X) XM PM 8
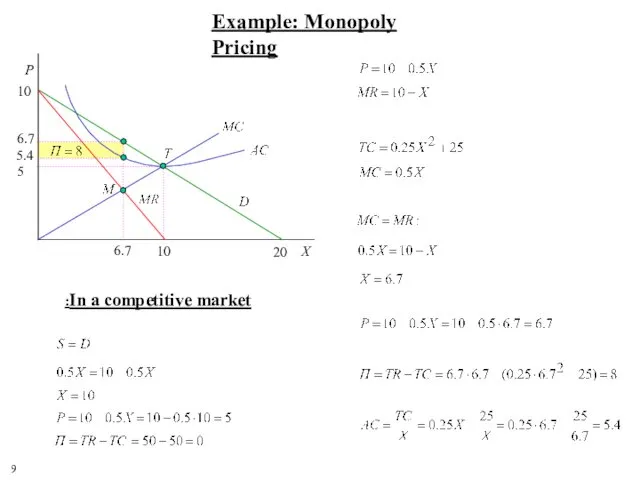
- 9. 9 10 20 In a competitive market: Example: Monopoly Pricing
- 10. Elasticity E=1: Changing price doesn’t change Revenue – PX unchanged. E>1: Decreasing price increases Revenue –
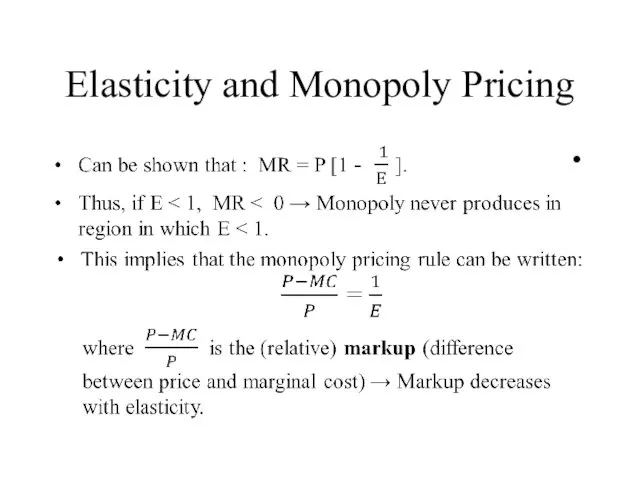
- 11. Elasticity and Monopoly Pricing
- 12. Example
- 14. Скачать презентацию






 Сигналы оповещения об опасностях, порядок их доведения до населения и действия по ним работников организаций
Сигналы оповещения об опасностях, порядок их доведения до населения и действия по ним работников организаций Геометрия недр
Геометрия недр Сайты сети Интернет по истории и культуре Красноярского края
Сайты сети Интернет по истории и культуре Красноярского края Деловые игры. Программа Импульс в действии
Деловые игры. Программа Импульс в действии педсовет в ДОУ Инновационная деятельность как условие формирования профессиональной компетентности педагогов ДОУ.
педсовет в ДОУ Инновационная деятельность как условие формирования профессиональной компетентности педагогов ДОУ. Цукерки. Технологія виготовлення
Цукерки. Технологія виготовлення Типы арифметических задач
Типы арифметических задач Закон электромагнитной индукции
Закон электромагнитной индукции Травмы живота
Травмы живота Первые люди на земле
Первые люди на земле Выборг - святой город средневековья
Выборг - святой город средневековья Особливості роботи машинних сільськогосподарських агрегатів (лекция № 1)
Особливості роботи машинних сільськогосподарських агрегатів (лекция № 1) Фотоальбом
Фотоальбом Ремонтно - оперативная радиосвязь (РОРС)
Ремонтно - оперативная радиосвязь (РОРС) Printers. Type of printer
Printers. Type of printer Развитие мелкой моторики у девочек дошкольного возраста (гендерное направление)
Развитие мелкой моторики у девочек дошкольного возраста (гендерное направление) Відстані в просторі
Відстані в просторі Психология памяти
Психология памяти Делимость чисел. Правила
Делимость чисел. Правила 20230923_protsessy_odnokletochnyh
20230923_protsessy_odnokletochnyh Загадки по лексической теме - Мебель
Загадки по лексической теме - Мебель Презентация День знаний.
Презентация День знаний. Мінерал класу карбонатів доломіт
Мінерал класу карбонатів доломіт Коренной перелом в Великой Отечественной войне
Коренной перелом в Великой Отечественной войне ЭКГ при ИБС
ЭКГ при ИБС Психологическая готовность к школе.
Психологическая готовность к школе. Семь чудес света. Импрессионизм
Семь чудес света. Импрессионизм Библейские сказания
Библейские сказания