Содержание
- 2. * Nerve tissue is a system of nerve cells and neuroglia that provide specific functions of
- 3. Nerve cells - neurons - the main component of nerve tissue. Neuroglia - provides the existence
- 4. * NT develops from ectoderm For 18 day the neural plate (thickening of the dorsal ectoderm)
- 5. *
- 6. * In the cranial part of the embryo, thickening of the ectoderm is formed - placodes
- 7. The ventricular zone consists of ependymocyte progenitor cells The intermediate zone consists of neuroblasts and glioblasts.
- 8. The marginal zone is formed from the axons of neuroblasts and macroglia and gives rise to
- 9. These are specialized cells, responsible for the reception, conduction, processing of the impulse and its transmission
- 10. * Structure of neuron Neurons are composed of the body (pericarion) and processes (1 axon and
- 11. *
- 12. * Нейроны
- 13. *
- 14. *
- 15. Plasmolemma has the ability to generate and conduct impulse The nucleus is usually one Among other
- 16. Chromatophilic substance (tigroid or Nissl's body) - detected in the cytoplasm in the form of basophilic
- 17. NISSLE BODIES *
- 18. The cytoskeleton is represented by neurofibrils (12 nm) and neurotubules (24-27 nm). In the body of
- 19. * CYTOSKELETON
- 20. Unipolar (with one process - axon) - a person has only embryogenesis Bipolar (with two processes
- 21. *
- 22. Functional classification of neurons Sensitive (afferent, receptor) - located in the spinal node. They generate n.
- 23. In the cytoplasm and axons are large granules of neurosecrete, which are excreted into the blood
- 24. CNS PNS * GLIAL CELLS
- 25. CNS glial cells are divided into: 1) macroglia (originates from the glioblast of the neural tube)
- 26. * Ependymocytes - form lining of the ventricles of the brain and central canal of spinal
- 27. * Astrocytes: - protoplasmic (present in the gray central nervous system, have short branching processes) -
- 28. * отростки А тя-нутся к капилля-рам, телам и ден-дритам нейронов, к мягкой мозговой оболочке. Эти клетки
- 29. * Oligodendrocytes Have few processus Present in gray matter near perikarions of neurons In white, they
- 30. Come from blood monocyte! Function - protecting brain tissue from infection Microglia cells are motile, capable
- 31. Neurolemmocytes (Schwann cells) form the sheaths of the processes of nerve cells in the nerve fibers
- 32. are processes of nerve cells which are covered with sheath. Process is almost always AXON (axial
- 33. Non-myelinated nerve fibers Are part of vegetative NS. The axial cylinders of several neurons take part
- 34. They are found both in the central nervous system and in peripheral NS. They consist of
- 35. *
- 36. In myelin fiber of nodesRanvier (after 1-2 mm) and myelin incisions are distinguished * during myelinisation
- 37. * MYELINISATION The speed of impulse transmission along myelin fibers (5-120 m / s), along bezmyelinovyh
- 38. *
- 39. They are divided into 3 groups according to functions: - motor (effector) - sensitive (receptor) -
- 40. Structurally: - axodendritic - axosomatic - axoaxial muscle or motor plaques By transmission method: - chemical
- 41. * Chemical Transmit impulse using mediators The axon terminal is the presynaptic part . It contains
- 42. *
- 43. Low molecular weight mediators: - Acetylcholin, norepinephrine, serotonin, histamine, glutamate, glycine, GABA, dopamine, Neuropeptides: - endorphins,
- 44. The processes in the synapse are developed as follows: Depolarization wave reaches presynaptic membrane Ca channels
- 45. They are terminal apparatuses of axons of motor cells of somatic or vegetative With their participation
- 46. * Neuromuscular nerve ending Myelin ed nerve fiber loses the myelin layer and is submerged in
- 47. In the smooth muscle tissue nerve endings are clearly distinct thickenings occurring among smooth myocytes. Secretory
- 48. 1) By localization: extero- and interoreceptors 2) By the specificity of perception: chemoreceptors, mechanoreceptors, baroreceptors, thermoreceptors,
- 49. * FREE N.E. PRESENT in the epithelium Myelin fibers approach the epithelial layer, lose myelin, axial
- 50. * A variety of receptors is found in connective tissue. Lamellar bodies of Fater-Pacini (0.5-2 mm)
- 51. They are located at the apex of the connective tissue papillae of the skin. They consist
- 52. Meissner's tactile bodies *
- 54. Скачать презентацию
 Презентация к классному часу: Наш северный город Урай.
Презентация к классному часу: Наш северный город Урай. Разработка технологического процесса сборки и сварки изделия. Стойка поворотного устройства кантователя
Разработка технологического процесса сборки и сварки изделия. Стойка поворотного устройства кантователя Инновационные технологии и технические средства для высокоскоростного железнодорожного движения в Российской Федерации
Инновационные технологии и технические средства для высокоскоростного железнодорожного движения в Российской Федерации Нефтегазоносность и угленосность бассейнов
Нефтегазоносность и угленосность бассейнов Гимнастика для глаз
Гимнастика для глаз Консультация по подготовке к экзамену. (Задания 8,9,15,16. ЕГЭ)
Консультация по подготовке к экзамену. (Задания 8,9,15,16. ЕГЭ) Путешествие по стране Литература
Путешествие по стране Литература История мыловарения.
История мыловарения. 20231203_zadachi_na_dvizhenie_2_1
20231203_zadachi_na_dvizhenie_2_1 Выездная школа ЭМШ
Выездная школа ЭМШ Жидкие лекарственные формы
Жидкие лекарственные формы Параметры разгона процессора
Параметры разгона процессора Уроки математики в 5 классе
Уроки математики в 5 классе Занятие по обучению грамоте Лесная школа
Занятие по обучению грамоте Лесная школа Презентация деятельности школьного музея в рамках районного проекта Школьный музей
Презентация деятельности школьного музея в рамках районного проекта Школьный музей Особенности оценивания экспериментальных заданий в ОГЭ – 9 кл по физике
Особенности оценивания экспериментальных заданий в ОГЭ – 9 кл по физике Ультразвуковая диагностика
Ультразвуковая диагностика Презентация -Редкие породы кошек
Презентация -Редкие породы кошек Utilization of seismic and infrasound signals for characterizing mining explosions
Utilization of seismic and infrasound signals for characterizing mining explosions Электротехническая часть осветительных и облучательных установок
Электротехническая часть осветительных и облучательных установок Получение электрической энергии в промышленных масштабах
Получение электрической энергии в промышленных масштабах Образ Базарова в романе И.С. Тургенева Отцы и дети
Образ Базарова в романе И.С. Тургенева Отцы и дети Российское движение школьников. Красноярский край
Российское движение школьников. Красноярский край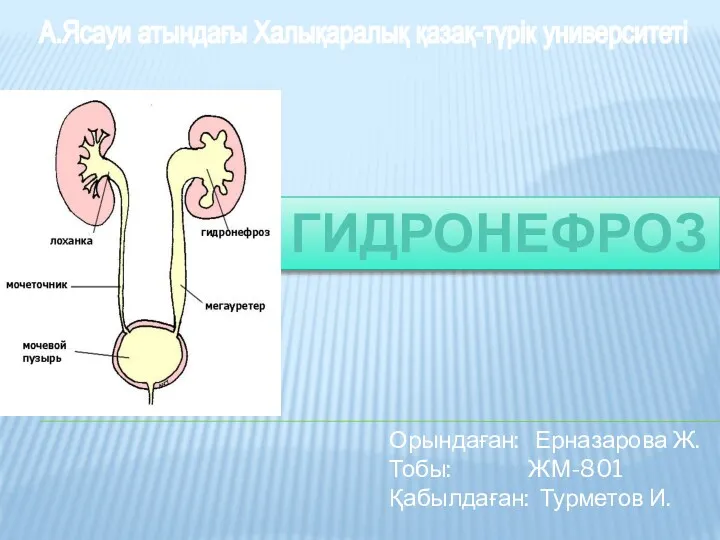 Гидронефроз
Гидронефроз Какие СМИ я читаю и почему
Какие СМИ я читаю и почему Работоспособность и активность дошкольников с задержкой психического развития на разных этапах занятия
Работоспособность и активность дошкольников с задержкой психического развития на разных этапах занятия Бүйрек туберкулезінің салыстырмалы диагностикасы
Бүйрек туберкулезінің салыстырмалы диагностикасы Хирургия және травматологияда қолданатын заманауи синтетикалық материалдар
Хирургия және травматологияда қолданатын заманауи синтетикалық материалдар