EYE
STRUCTURE
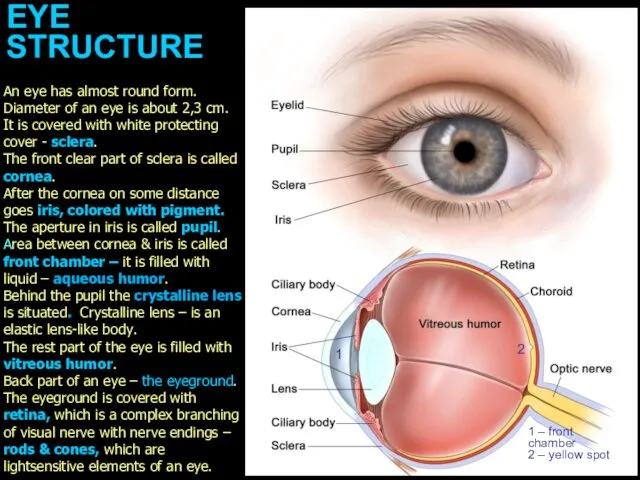
1
1 – front
chamber
2 – yellow spot
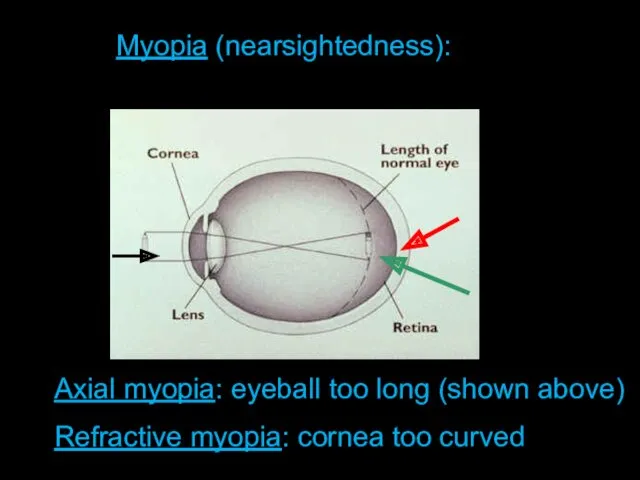
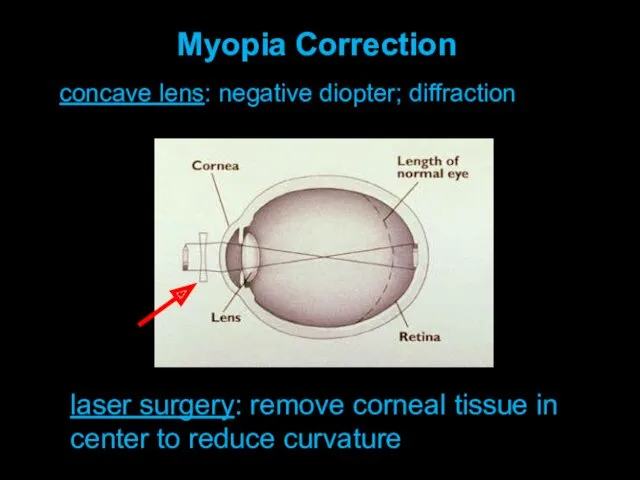
An eye has almost
round form. Diameter of an eye is about 2,3 cm. It is covered with white protecting cover - sclera.
The front clear part of sclera is called cornea.
After the cornea on some distance goes iris, colored with pigment. The aperture in iris is called pupil. Area between cornea & iris is called front chamber – it is filled with liquid – aqueous humor.
Behind the pupil the crystalline lens is situated. Crystalline lens – is an elastic lens-like body.
The rest part of the eye is filled with vitreous humor.
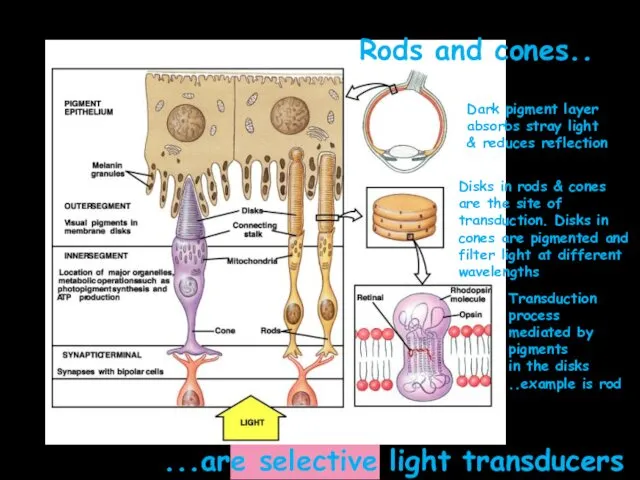
Back part of an eye – the eyeground. The eyeground is covered with retina, which is a complex branching of visual nerve with nerve endings – rods & cones, which are lightsensitive elements of an eye.
2



 Характеристика топливно-энергетической базы Крыма
Характеристика топливно-энергетической базы Крыма Вред курения
Вред курения Презентация. Летний оздоровительный лагерь.
Презентация. Летний оздоровительный лагерь. Анализ динамики экономических показателей России и США
Анализ динамики экономических показателей России и США Биосфера. Среды жизни
Биосфера. Среды жизни Аллергия. Аллергены
Аллергия. Аллергены Презентация Заповеди Блаженствпо предмету ОПК
Презентация Заповеди Блаженствпо предмету ОПК Облік, контроль і аналіз непрямих виробничих витрат
Облік, контроль і аналіз непрямих виробничих витрат Конспект внеклассного занятия на тему: Законы жизни класса.
Конспект внеклассного занятия на тему: Законы жизни класса. Внутренние воды РТ
Внутренние воды РТ Формирование культурной среды небольшого города/села
Формирование культурной среды небольшого города/села аналогічні-гомологічні органи
аналогічні-гомологічні органи Организаторская и воспитательная работа командира подразделения по укреплению воинской дисциплины. Тема № 5
Организаторская и воспитательная работа командира подразделения по укреплению воинской дисциплины. Тема № 5 О мерах по поддержки генерирующих объектов на основе ВИЭ. Законодательная база поддержки генерации ВИЭ
О мерах по поддержки генерирующих объектов на основе ВИЭ. Законодательная база поддержки генерации ВИЭ Интернет в жизни старшеклассника: за или против
Интернет в жизни старшеклассника: за или против Тольятти. История любимого города
Тольятти. История любимого города Пейзаж — поэтичная и музыкальная живопись
Пейзаж — поэтичная и музыкальная живопись Особенности рельефа территории России
Особенности рельефа территории России Направления реализации Национальной стратегии по обращению с ТКО и ВМР
Направления реализации Национальной стратегии по обращению с ТКО и ВМР ФЭМП 14.04.2020
ФЭМП 14.04.2020 Логические операторы
Логические операторы Обрезка яблони и груши
Обрезка яблони и груши Проектирование современного урока биологии, географии в соответствии с требованиями ФГОС
Проектирование современного урока биологии, географии в соответствии с требованиями ФГОС Правовое регулирование предпринимательской деятельности
Правовое регулирование предпринимательской деятельности Презентация для детей
Презентация для детей Миотоническая дистрофия Россолимо-Штейнерта-Куршманна-Баттена
Миотоническая дистрофия Россолимо-Штейнерта-Куршманна-Баттена Плотность
Плотность Праздники и календари. Основы мировых религиозных наук (4 класс)
Праздники и календари. Основы мировых религиозных наук (4 класс)