Слайд 2

What is a Programming Language?
a tool for instructing machines
a means of
communicating between programmers
a vehicle for expressing high-level designs
a notation for algorithms
a way of expressing relationships between concepts
a tool for experimentation
a means for controlling computerized devices
Слайд 3

Language Designers
Balance
… making computing convenient for programmers (a fool with a
tool is still a fool)
and making efficient use of computing machines (... Why do I have to state this?)
Слайд 4

Levels
Gross distinction between programming language
based on readability
based on independence
based on purpose
(specific … general)
Слайд 5

Levels
Machine level language
Assembly level language
High-level language (3GL)
sometimes 4GL - fourth Generation
Language
Слайд 6
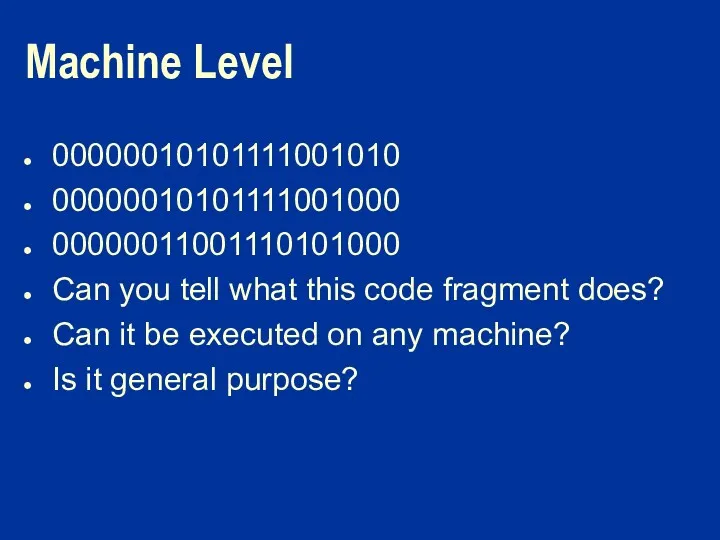
Machine Level
00000010101111001010
00000010101111001000
00000011001110101000
Can you tell what this code fragment does?
Can it be
executed on any machine?
Is it general purpose?
Слайд 7

Assembly Language
Look at figure 1.1
LD R1,”0”
LD R2, M
ST R2, R1
… real
assembly used mnemonics
Add A(M), …. Had to do your own indexing
What does this program do?
Слайд 8

Assembly Language
Look at page 63 in your text and figure 3.1
Can
you understand what it does now?
Слайд 9
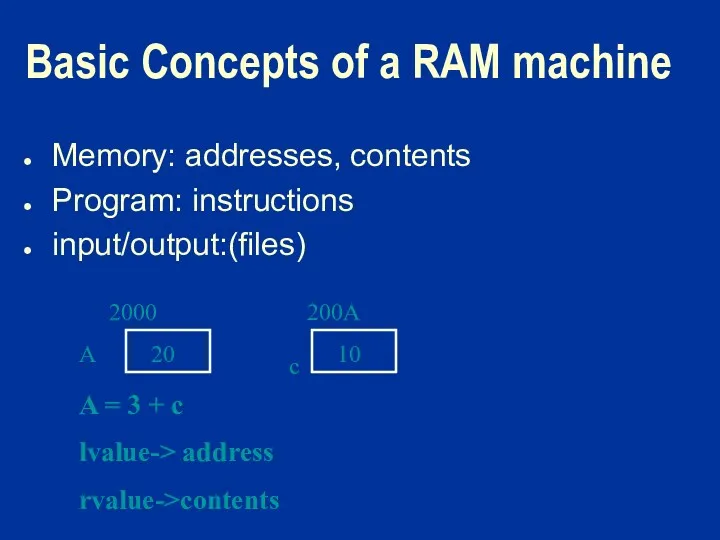
Basic Concepts of a RAM machine
Memory: addresses, contents
Program: instructions
input/output:(files)
20
2000
A
10
200A
c
A = 3
+ c
lvalue-> address
rvalue->contents
Слайд 10

High Level
Readable familiar notations
machine independence
availability of program libraries
consistency check (check data
types)
Слайд 11

Problems of Scale
Changes are easy to make
isolated program fragments can be
understood
BUT… one small bug can lead to disaster
read the NOT story about Mariner rockets
Notice how the chairman does not understand that a “small” problem can lead to devastating result and why it was not caught
Слайд 12

Bugs
Programming testing can be used to show the presence of bugs,
but never their absence!
Dijkstra
Programming Languages can help
readable and understandable
organize such that parts can be understood
Слайд 13

Role of Programming Languages
Art (science) of programming is organizing complexity
Must organize
in such a way that our limited powers are sufficient to guarantee that the computation will establish the desired effect
(Dijkstra - structured programming, sometimes referred to as goto-less programming)
Слайд 14
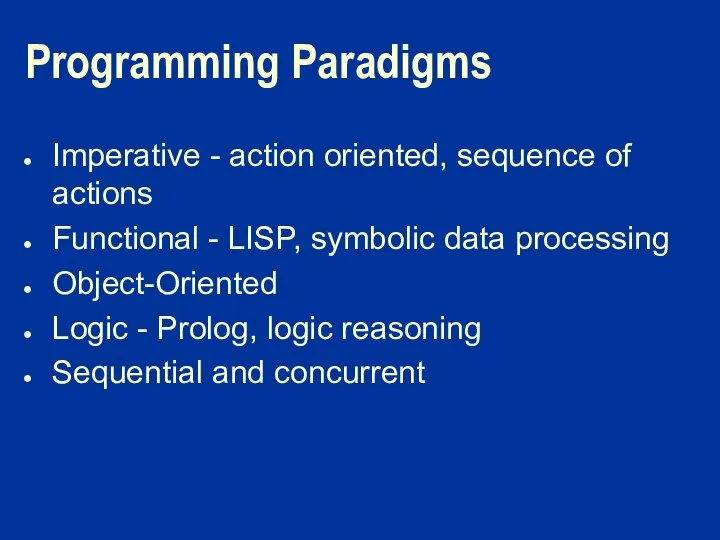
Programming Paradigms
Imperative - action oriented, sequence of actions
Functional - LISP, symbolic
data processing
Object-Oriented
Logic - Prolog, logic reasoning
Sequential and concurrent
Слайд 15
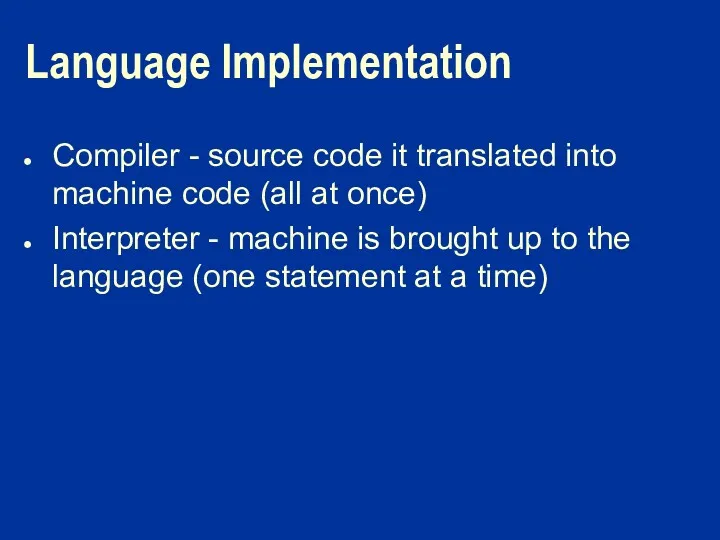
Language Implementation
Compiler - source code it translated into machine code (all
at once)
Interpreter - machine is brought up to the language (one statement at a time)
Слайд 16
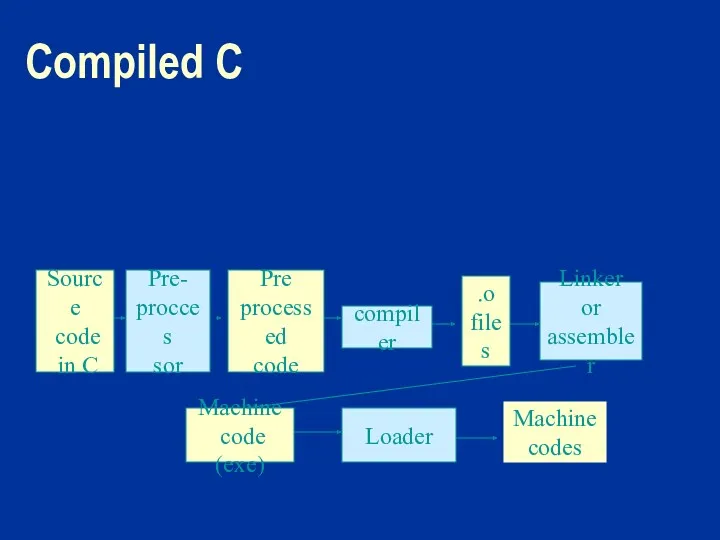
Compiled C
Source
code
in C
Pre-
procces
sor
compiler
Linker
or
assembler
Machine
code (exe)
Loader
Machine
codes
.o
files
Pre
processed
code
Слайд 17

Interpreted Code
Each instruction is interpreted by machine interpreter
does not produce object
code
Слайд 18

Comparisons
Compilation more efficient
interpreted more flexible
Слайд 19

Testing your skill
Do 1.4 (a,b,c) in PL book
Do 1.5
For each file,
include a file header:
what this file accomplishes - description
what “entities” are in this file
dependencies
structure
Слайд 20

Testing your skill
For each module, include a module header:
what this module
accomplishes - description
dependencies ( parameters(in, out, inout), global data (accessed or modified), called by (fanin), calls (fanout) )
restrictions
programmer
date created
modifications



















 Свариваемость сталей и сплавов
Свариваемость сталей и сплавов Структура физических знаний
Структура физических знаний Дерматополимиозит. Этиологиясы
Дерматополимиозит. Этиологиясы Стадии развития групп презентация
Стадии развития групп презентация Наполненные полимеры. Структура и физико-химические свойства. Введение
Наполненные полимеры. Структура и физико-химические свойства. Введение Презентация к конкурсной семейной программе Как домовёнок Кузя семью искал
Презентация к конкурсной семейной программе Как домовёнок Кузя семью искал Колебательные процессы
Колебательные процессы Дети войны
Дети войны Блаженная Ксения Петербургская
Блаженная Ксения Петербургская 20240104_kursy_po_vyboru
20240104_kursy_po_vyboru 20230919_domashniy_ochag
20230919_domashniy_ochag Презентация-семинар Методика Никитиных
Презентация-семинар Методика Никитиных Проектирование системы РСПД Аст-Петрол
Проектирование системы РСПД Аст-Петрол Тайны озёр смерти
Тайны озёр смерти Какие службы защищают население?
Какие службы защищают население? Эффективное общение
Эффективное общение С чего начинаются шахматы
С чего начинаются шахматы Абайдың педагогикалық ой -тағылымдары
Абайдың педагогикалық ой -тағылымдары Актуальные аспекты управления качеством таможенных услуг
Актуальные аспекты управления качеством таможенных услуг Народный художественный промысел России
Народный художественный промысел России Работы по шумоизоляции, вентиляции
Работы по шумоизоляции, вентиляции Өзіміз туралы айтайық
Өзіміз туралы айтайық презентация Правила движения - достойны уважения.
презентация Правила движения - достойны уважения. Об ответственности родителей...
Об ответственности родителей... Оформление витрин и контроль их состояния
Оформление витрин и контроль их состояния Презентация по технологии _Как это устроено
Презентация по технологии _Как это устроено Обряды на Егорьев день. Образ Георгия Победоносца
Обряды на Егорьев день. Образ Георгия Победоносца Презентация Успешный учитель-успешный ученик
Презентация Успешный учитель-успешный ученик