Содержание
- 2. Today you will learn more about: Changes to IDEA and the new IEP form Strategies for
- 3. The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act – IDEA 2004 1975 – Education of All Handicapped Children
- 4. The law tells us that parents are expected to be equal partners in planning and implementing
- 5. IDEA ’04 Requirement New monitoring priority in 2004 – in State Performance Plan Increase the percent
- 6. Preparing for the Planning and Placement Team Meeting - PPT The PPT meets to: Initiate and
- 7. The PPT consists of: The child’s parent or parents; At least one regular education teacher if
- 8. The PPT consists of: An individual who can interpret evaluation results; Others at the discretion of
- 9. Attendance at PPTs – IDEA 2004 A PPT member may be excused when: The parent and
- 10. Building Blocks Knowledge of the child – who is this child? How does this disability affect
- 11. Communication Strategies Acknowledge your own communication style and feelings – be willing to move forward Encourage
- 12. Preparing for the PPT Meeting Gather important and relevant information – create a home file Think
- 13. The IEP The Individualized Education Program (IEP) is a written plan that details each child’s special
- 14. Components of the IEP: The IEP must include: Present levels of academic achievement and functional performance
- 15. Components of the IEP Prior Written Notice – page 3 Provides written notice of the action(s)
- 16. Reporting on Progress: IEP must include: A description of how progress toward meeting annual goals will
- 17. IEP Includes Service and Supports that Allow the Child to: Advance towards meeting annual goals; Progress
- 18. Related Services on the IEP Related services are developmental, corrective, or supportive services required to assist
- 19. Examples of Related Services Assistive Technology Audiology Services Counseling Physical Therapy Parent Training School Nurse Services
- 20. IEP Services Must be based on peer-reviewed research to the extent practicable; Must refer to the
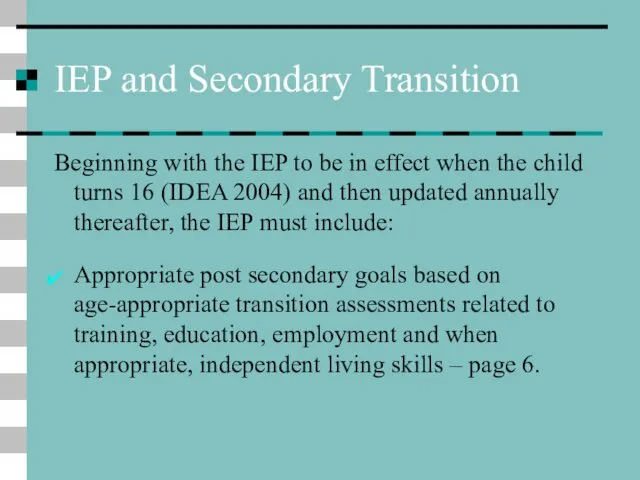
- 21. IEP and Secondary Transition Beginning with the IEP to be in effect when the child turns
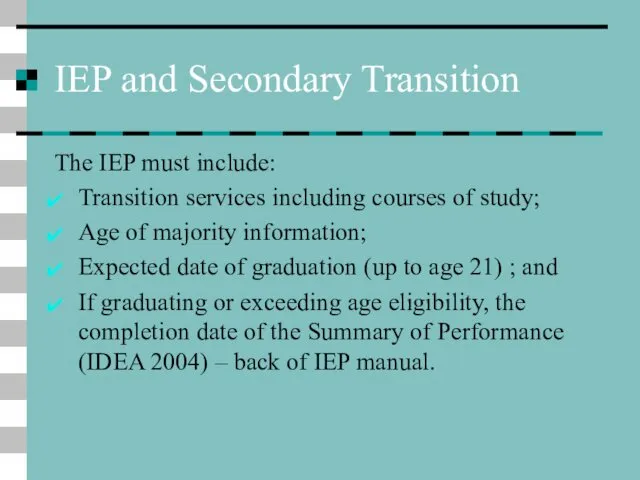
- 22. IEP and Secondary Transition The IEP must include: Transition services including courses of study; Age of
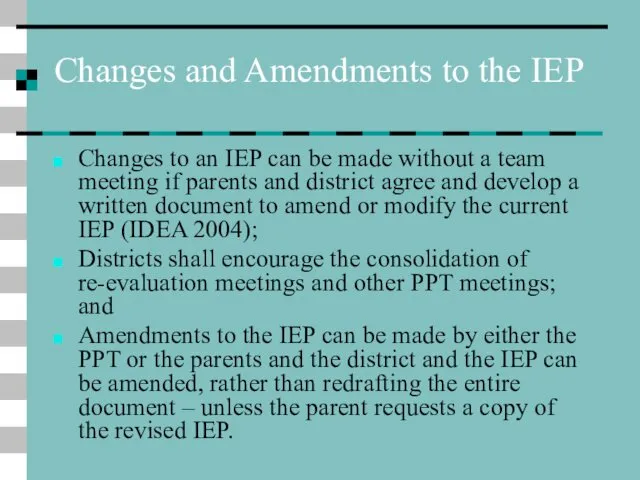
- 23. Changes and Amendments to the IEP Changes to an IEP can be made without a team
- 24. What to do when you disagree: Share your vision and priorities for the child. Try not
- 25. Conflict Resolution Options Compromise Informal mediation or facilitated IEP – identify an ally in the school
- 26. Resolution Options Mediation Due Process Hearing Advisory Opinion Resolution Session (IDEA 2004) File a complaint
- 27. Mediation Mediation is an informal process that is voluntary and confidential. Both sides must agree to
- 28. Mediation The mediator does not make decisions for the parties. A successful mediation will result in
- 29. Due Process Hearing Due Process Hearing is a formal legal proceeding. The parties, their attorneys or
- 30. Resolution Session Within 15 days of the Due Process Hearing request by a parent, the district
- 31. Advisory Opinion The Advisory Opinion is an optional process in CT, available to parties of a
- 32. Advisory Opinion Each party has 45 minutes to explain their cases and then an additional 15
- 33. Filing a Complaint A complaint is filed with the CT State Department of Education (SDE) if
- 34. What Happens When It’s Over? Win or lose, you still have to work together for the
- 36. Скачать презентацию






























 System administracji publicznej w Hondurasie
System administracji publicznej w Hondurasie Презентация ЗОЖ
Презентация ЗОЖ Носилов К.Д.
Носилов К.Д. Краснянский В.Н
Краснянский В.Н Проект Чтение с увлечением
Проект Чтение с увлечением Архітектура модерну
Архітектура модерну Эволюция управленческой мысли
Эволюция управленческой мысли Праздник Пасха
Праздник Пасха Казакстандагы дини жагдай
Казакстандагы дини жагдай Винтовые забойные двигатели
Винтовые забойные двигатели Построение процесса обучения на основе инновационных технологий. Экспериментирование при использовании нетрадиционных материалов в художественной деятельности детей
Построение процесса обучения на основе инновационных технологий. Экспериментирование при использовании нетрадиционных материалов в художественной деятельности детей Воздействие сигнала и шума на ЧД (продолжение). Занятие №11
Воздействие сигнала и шума на ЧД (продолжение). Занятие №11 Өскемендегі өнеркәсіб орындары
Өскемендегі өнеркәсіб орындары Формирование метапредметных результатов в УМК Школа России презентация
Формирование метапредметных результатов в УМК Школа России презентация Строительство индивидуального жилого дома с террасой
Строительство индивидуального жилого дома с террасой Родительское собрание Проектная деятельность во 2 классе
Родительское собрание Проектная деятельность во 2 классе Основные принципы международного права как регулятора МО
Основные принципы международного права как регулятора МО История пожарной охраны
История пожарной охраны Ожоги. Виды ожогов. Солнечные ожоги. Тепловой удар
Ожоги. Виды ожогов. Солнечные ожоги. Тепловой удар Презентация по теме Кислоты
Презентация по теме Кислоты Влияние городского транспорта на окружающую среду
Влияние городского транспорта на окружающую среду Внеклассные мероприятия
Внеклассные мероприятия Государство на берегу Нила
Государство на берегу Нила О практике работы с молодежью Красноярской краевой организации Профсоюза строителей России
О практике работы с молодежью Красноярской краевой организации Профсоюза строителей России Творческий отчет Молодые рабочие – витамины роста предприятия! Слесарь механосборочных работ
Творческий отчет Молодые рабочие – витамины роста предприятия! Слесарь механосборочных работ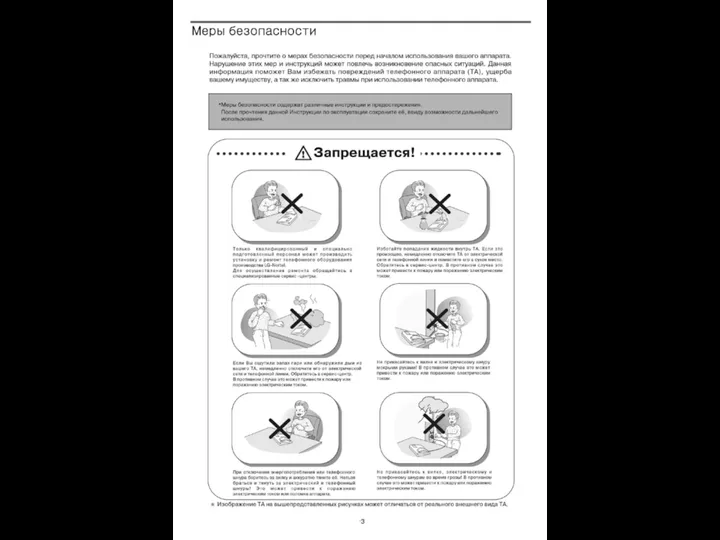 Инструкция к терминалу LDP-7224D
Инструкция к терминалу LDP-7224D Финансовая математика. Задание 17
Финансовая математика. Задание 17 Конспект родительского собрания Телевизор и книги в жизни первоклассника
Конспект родительского собрания Телевизор и книги в жизни первоклассника