Слайд 2

The mechanism of passive transport
Слайд 3

Learning objective
to explain the mechanism of passive transport
Слайд 4

Success criteria
Describe types of passive transport in an oral or
written form.
Explain passive transport mechanism.
In order to achieve learning objectives fulfill correctly at least 80% of work.
Слайд 5

Terminology
Passive transport
Diffusion
Facilitate diffusion
Osmosis
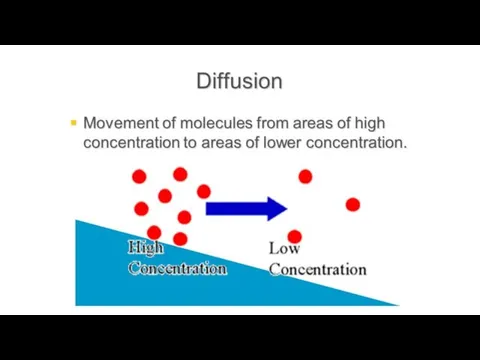
Concentration gradient
Channel proteins
Gate
Carrier proteins
Plasma membrane/permeable membrane
Randomly
Passive movement
Lower/high
solute concentration
Isotonic/hypertonic/hypotonic
Слайд 6
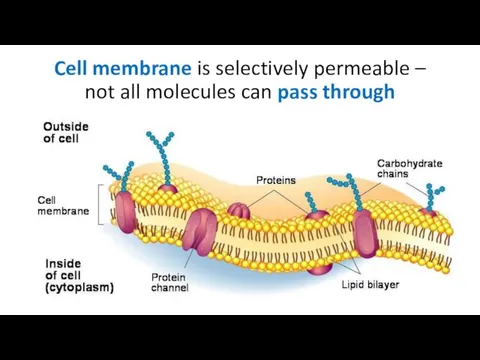
Cell membrane is selectively permeable – not all molecules can pass
through
Слайд 7
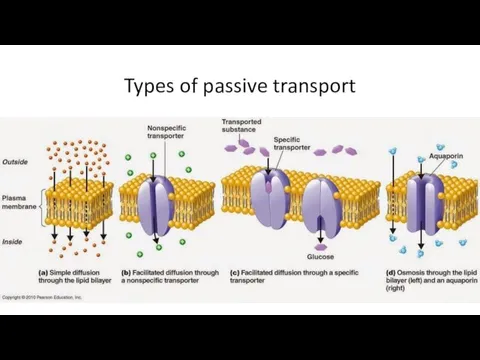
Types of passive transport
Слайд 8

Passive transport
The movement of substances down a concentration gradient from an
area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration without the need for energy to be used.
3 types are passive transport:
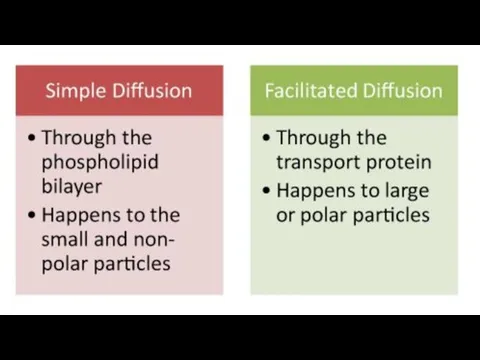
Simple diffusion
Facilitate diffusion
Osmosis
Слайд 9

Слайд 10
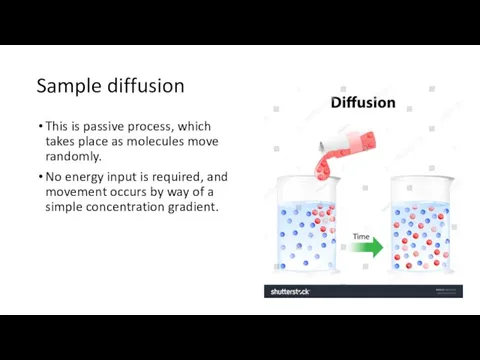
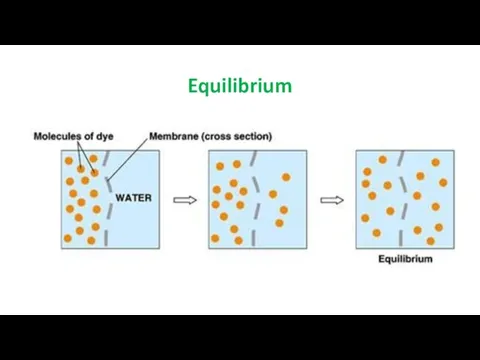
Sample diffusion
This is passive process, which takes place as molecules
move randomly.
No energy input is required, and movement occurs by way of a simple concentration gradient.
Слайд 11
Слайд 12
Слайд 13
Слайд 14

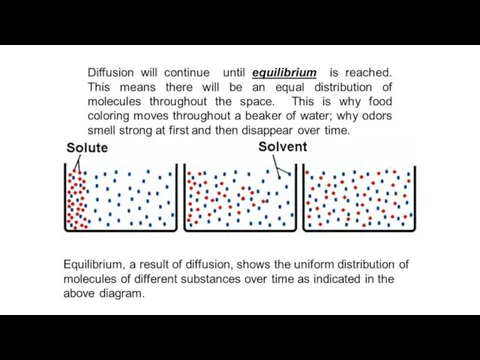
Sample diffusion
Many molecules pass into and out of cells by
diffusion, for example:
Oxygen
CO2
Water
Слайд 15
Слайд 16
Слайд 17

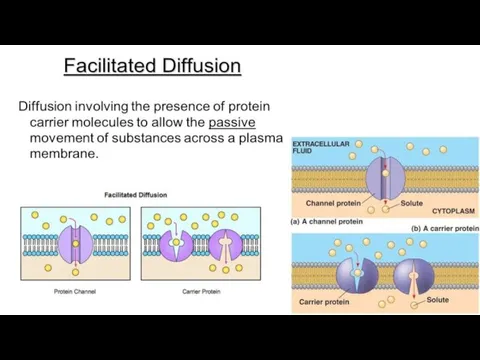
Facilitated diffusion
Many polar molecules movement through channel proteins.
Polar molecules cannot
diffuse through the lipid bilayer of the membrane.
Carrier protein first combines with the diffusing molecules on one side of the membrane, carries them through the channel protein and releases them on the other side.
Faster then sample diffusion.
No ATP energy input.
Слайд 18
Слайд 19

Facilitated diffusion
The movement of substances down a concentration gradient from
an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration without the need for energy to be used.
Слайд 20

Слайд 21
Слайд 22
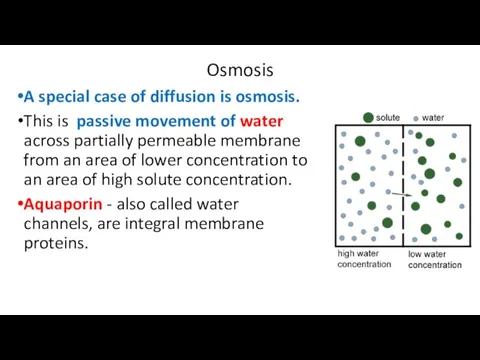
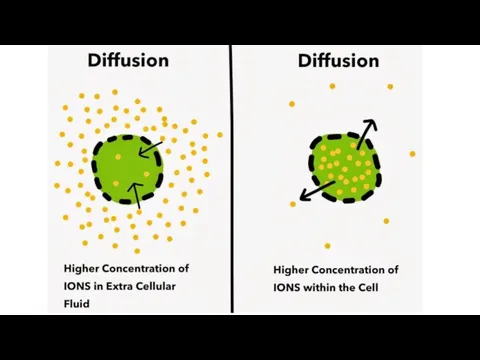
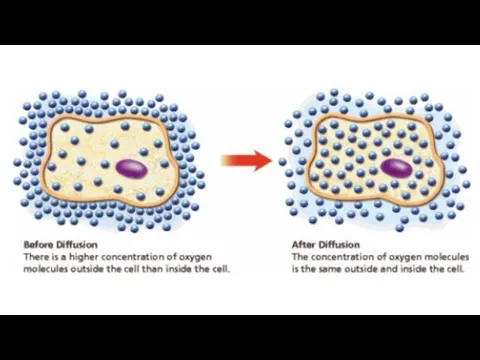
Osmosis
A special case of diffusion is osmosis.
This is passive movement
of water across partially permeable membrane from an area of lower concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
Aquaporin - also called water channels, are integral membrane proteins.
Слайд 23

Слайд 24

Success criteria
Describe types of passive transport in an oral or
written form.
Explain passive transport mechanism.
In order to achieve learning objectives fulfill correctly at least 80% of work.























 Лейтенантская проза
Лейтенантская проза классный час для 1 класса День космонавтики
классный час для 1 класса День космонавтики Анализ ассортимента и потребительских свойств макаронных изделий быстрого приготовления
Анализ ассортимента и потребительских свойств макаронных изделий быстрого приготовления Chocolate
Chocolate Система локализации аварий РБМК-1000
Система локализации аварий РБМК-1000 Бағдарламалық жасақтама
Бағдарламалық жасақтама Мудры. Презентация.
Мудры. Презентация. Ядролық отын және онын қорлары
Ядролық отын және онын қорлары Проект энергоэффективных мероприятий по газификации и техническому перевооружению теплового хозяйства в/городка № 1
Проект энергоэффективных мероприятий по газификации и техническому перевооружению теплового хозяйства в/городка № 1 Решение размерных цепей, методом, обеспечивающим полную взаимозаменяемость
Решение размерных цепей, методом, обеспечивающим полную взаимозаменяемость Устройство компьютера
Устройство компьютера Электрические явления. Повторение. 8 класс
Электрические явления. Повторение. 8 класс Найди своего героя
Найди своего героя Основы религиозных культур и светской этики. Наша родина Россия
Основы религиозных культур и светской этики. Наша родина Россия Клиентоориентированность
Клиентоориентированность Интерьер. Культура дома
Интерьер. Культура дома Наш город Киров. Команда №19. Задание 3. ВятГУ Челлендж
Наш город Киров. Команда №19. Задание 3. ВятГУ Челлендж Республика Карелия
Республика Карелия Напряженность электростатического поля. Линии напряженности электростатического поля
Напряженность электростатического поля. Линии напряженности электростатического поля Гидравлический разрыв пласта
Гидравлический разрыв пласта Проблема выбора программы и учебно-методического комплекса в школьном географическом образовании
Проблема выбора программы и учебно-методического комплекса в школьном географическом образовании Игровые технологии в работе с дошкольниками
Игровые технологии в работе с дошкольниками Осциллограф. Виды осциллографов, функциональная схема
Осциллограф. Виды осциллографов, функциональная схема История, которая вас удивит: что изучает историческая наука и как писать историю
История, которая вас удивит: что изучает историческая наука и как писать историю Строение зуба человека
Строение зуба человека Южная Осетия. Лекция 7.1
Южная Осетия. Лекция 7.1 Разработка урока Измерение скорости
Разработка урока Измерение скорости Sampling
Sampling