Содержание
- 2. The relationship between genetic variation and evolution
- 3. Learning objective explain the relationship between genetic variation and evolution
- 4. Success criteria Name at least three ways due to which the initial population can change and
- 5. Terminology Natural selection, genetic variation, gene/allele variability, genetype, phenotype, mutation, formation of new allele, rapid reproduction,
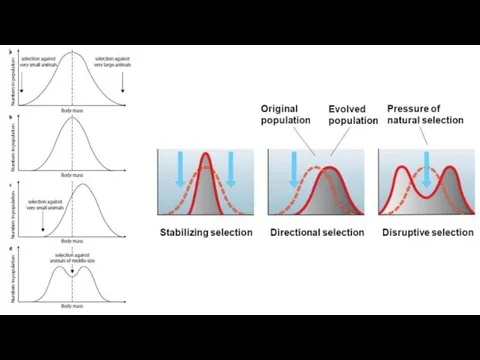
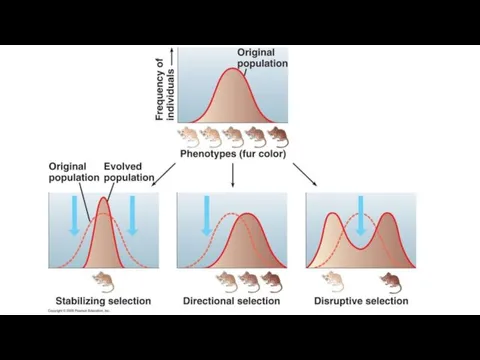
- 6. Common Forms of Natural Selection 1. Stabilizing Selection 2. Directional Selection 3. Disruptive Selection 4. Sexual
- 7. Darwin’s theory of natural selection depends on: Overproduction A struggle for existence Variation within a species
- 8. Lamarck has an alternative proposal! Darwin believed: environment Variation Adaptation selects Lamarck: Environmental causes variation This
- 9. Natural selection Natural selection operates on individuals, or rather on their phenotypes. The concept of natural
- 10. Natural selection Natural selection causes the frequency of certain alleles to increase or decrease in a
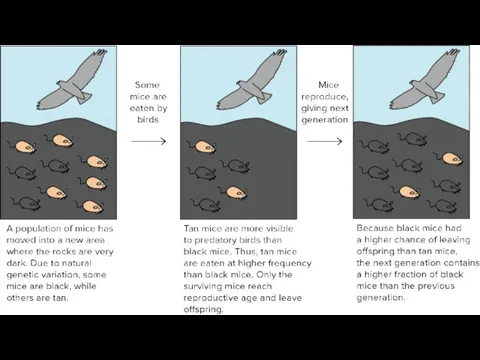
- 11. Selection pressure Predation by foxes is an example of a selection pressure. Selection pressures increase the
- 14. Evolution causes: Genetic variation Mutation Sexual reproduction
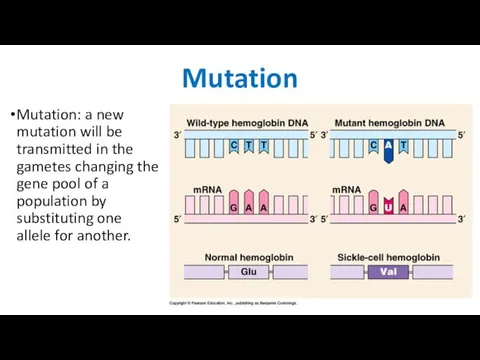
- 15. Mutation Mutation: a new mutation will be transmitted in the gametes changing the gene pool of
- 16. Sexual reproduction Random fusion Crossing over Free assortment
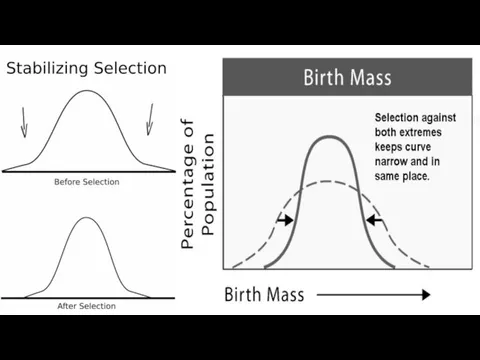
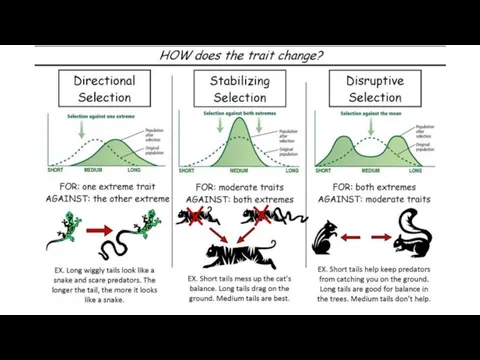
- 18. Stabilizing Selection Occurs when environmental conductions are largely unchanging. Eliminates variants and abnormalities that are useless
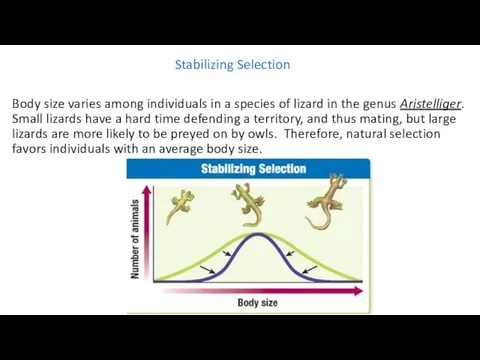
- 20. Stabilizing Selection Body size varies among individuals in a species of lizard in the genus Aristelliger.
- 21. Directional Selection May result from changing environmental conditions. In these situations the majority of an existing
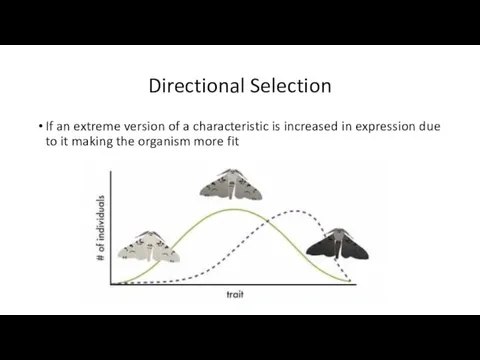
- 23. Directional Selection If an extreme version of a characteristic is increased in expression due to it
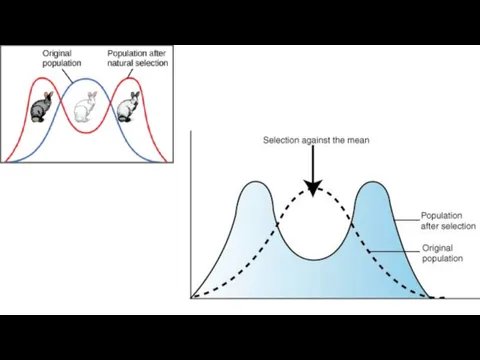
- 24. Disruptive Selection Occurs when particular environmental conditions favour the extremes of a phenotypic range over intermediate
- 26. Disruptive Selection A population of insects, newly introduced to a forest, is adapting to different breeding
- 30. Sexual selection A form of natural selection in which individuals with certain inherited characteristics are more
- 31. Speciation A species is a population whose members have the potential to interbreed in nature and
- 32. Speciation causes: isolation Geographic Polyploidy Habitat Behavioral Temporal Reproductive
- 33. Reproductive isolation Closely related species may be unable to mate because of anatomical incompatibility. The inability
- 35. Geographic isolation Occurs when species are separated: river, mountain range and etc. Two population that are
- 37. Habitat isolation Occurs when two organisms live in the same area but encounter each other rarely.
- 38. Behavioral isolation Occurs when two animals become isolated from each other because of some change in
- 39. Temporal isolation Temporal refers to times. Two species cannot breed if their species breeding patterns are
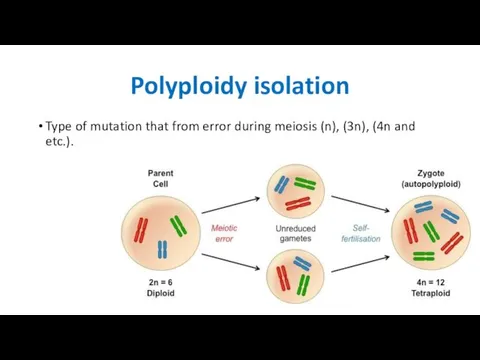
- 40. Polyploidy isolation Type of mutation that from error during meiosis (n), (3n), (4n and etc.).
- 42. Скачать презентацию





























 Основы микроэлектроники
Основы микроэлектроники Первая помощь при черепно-мозговой травме, травме груди, травме живота, при травме в области таза, при повреждениях позвоночника
Первая помощь при черепно-мозговой травме, травме груди, травме живота, при травме в области таза, при повреждениях позвоночника Презентация к внеклассному мероприятию Мисс математика
Презентация к внеклассному мероприятию Мисс математика Фирма в теории организации рынков
Фирма в теории организации рынков Поражение нервной системы при ВИЧ инфекции
Поражение нервной системы при ВИЧ инфекции Онкогенные вирусы
Онкогенные вирусы Трудовое воспитание детей
Трудовое воспитание детей Обработка конических поверхностей
Обработка конических поверхностей презентация урока-практикума по темеБелки в 10 классе
презентация урока-практикума по темеБелки в 10 классе Image comparison
Image comparison Cтрессовые расстройства в стоматологии (Дентофобия)
Cтрессовые расстройства в стоматологии (Дентофобия) Law of person
Law of person Проект Дорожная азбука Диск
Проект Дорожная азбука Диск Let’s play ball with the future play
Let’s play ball with the future play Финансовое управление администрации МОГО Ухта
Финансовое управление администрации МОГО Ухта Соединение проводов и жил кабелей
Соединение проводов и жил кабелей ЭКГ при аритмиях
ЭКГ при аритмиях Презентация Мой друг ВЕЛОСИПЕД
Презентация Мой друг ВЕЛОСИПЕД Среды обитания организмов
Среды обитания организмов Общие сведения по холодному и горячему водоснабжению. Системы и схемы водопроводов (Тема 1)
Общие сведения по холодному и горячему водоснабжению. Системы и схемы водопроводов (Тема 1) Санкт-Петербургская городская Масленица
Санкт-Петербургская городская Масленица Математический анализ
Математический анализ Отрезок. Длина отрезка. Прямая. Луч. 5 класс
Отрезок. Длина отрезка. Прямая. Луч. 5 класс Ученый и врач Владимир Михайлович Бехтерев
Ученый и врач Владимир Михайлович Бехтерев Изготовление домашнего халата
Изготовление домашнего халата Урок по природоведению на тему Почва
Урок по природоведению на тему Почва Кемеровская область
Кемеровская область Приемы фантазирования в коммуникативной деятельности и ознакомлении с художественной литературой старших дошкольников.
Приемы фантазирования в коммуникативной деятельности и ознакомлении с художественной литературой старших дошкольников.