Содержание
- 2. Речь какого-нибудь лица, передаваемая буквально так, как она была произнесена, называется прямой речью (direct speech). Речь,
- 3. Direct Speech She says, "I phone my friends every day". (утвердительное предложение) Reported Speech She says
- 4. Direct Speech The grandfather says to Mary, “What mark did you get at school?” (вопросительное предложение)
- 5. Direct Speech The teacher said to the pupils, "Don't open your books.“ (просьба / приказ) Reported
- 6. При переводе предложения из прямой речи в косвенную соблюдаются следующие правила: 1. Запятая, отделяющая слова, вводящие
- 7. 2. Все личные и притяжательные местоимения изменяются по смыслу. Direct Speech Bob said, “I am learning
- 8. Direct Speech He said, "I don't like to watch cartoons.” Reported Speech He said (that) he
- 9. Direct Speech The manager says to Mike: “Does your father work at a factory?” Reported Speech
- 10. Direct Speech Kate said to her grandmother, "Help me to cook the soup, please!“ Reported Speech
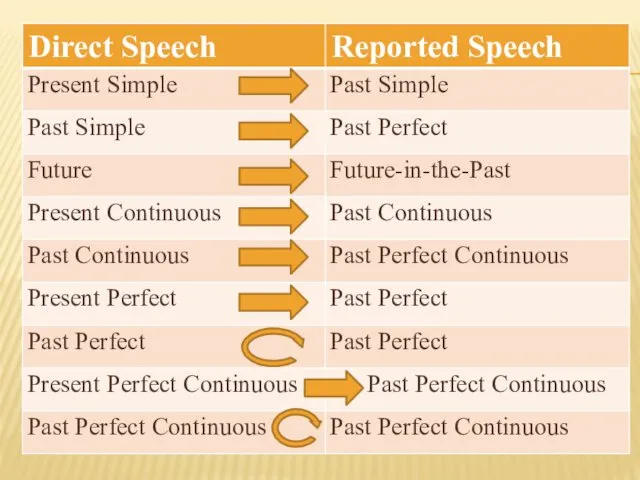
- 11. 3. При переводе из прямой речи в косвенную в первую очередь следует обращать внимание на грамматическое
- 12. а) Если глагол, вводящий косвенную речь, стоит в одном из настоящих или будущих времен, грамматическое время
- 13. Direct Speech Не says, "I can't remember where I've put the tickets. (Present Simple) Reported Speech
- 14. Direct Speech He has already said, "I can't remember where he's put the tickets. (Present Perfect)
- 15. Direct Speech If you ask him about the tickets, he'll say, "I can't remember where I've
- 16. b) Если глагол, вводящий косвенную речь, стоит в одном из прошедших времен, глагол в придаточном предложении
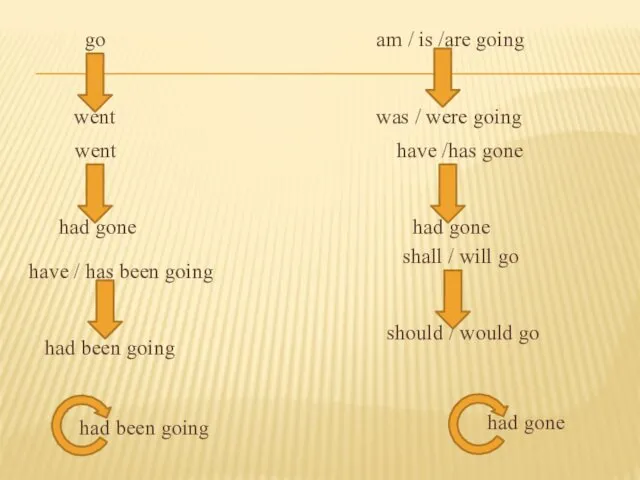
- 18. go went went had gone have / has been going had been going am / is
- 19. Direct Speech Tom said to the boys, “Who has tickets for “Hamlet”? (Present Simple) Reported Speech
- 20. Direct Speech Mary said, “I will do it after my arrival”. (Future Simple) Reported Speech Mary
- 21. Direct Speech Sam said, “He didn’t get on with his stepma”. (Past Simple) Reported Speech Sam
- 22. Правило согласования времен не действует в следующих случаях: 1) Если сказуемое в придаточном предложении выражает общеизвестное
- 23. Правило согласования времен не действует в следующих случаях: 2) Если в придаточном предложении указано время совершения
- 24. Правило согласования времен не действует в следующих случаях: 3) В предложениях, в придаточных которых употребляется сослагательное
- 25. 4. При переводе прямой речи в косвенную меняются также слова, обозначающие место и время действия.
- 26. Direct Speech She said, "I left Natalie a message an hour ago”. Reported Speech She said
- 27. Direct Speech The teacher said, "Did you read an English book last year?“ Reported Speech The
- 28. The boyfriend said, “Take this book, please”. Reported Speech The boyfriend asked her girl to take
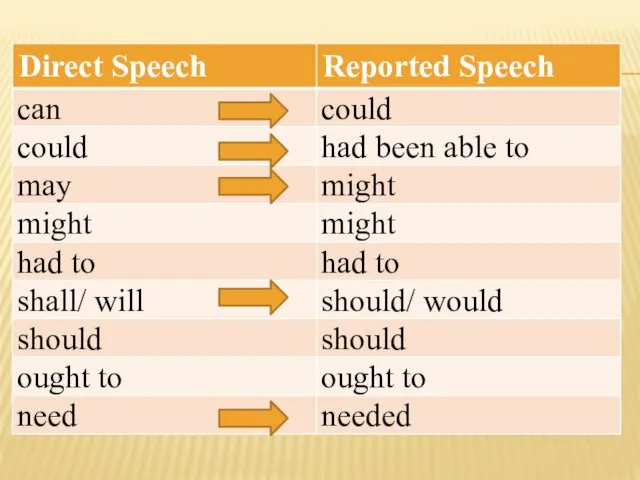
- 29. 5. Если в предложении содержатся модальные глаголы, то они подвергаются изменениям при переводе прямой речи в
- 31. Direct Speech Ann: "I can't skate." Reported Speech Ann says (that) she can't skate. Ann said
- 32. Direct Speech The teacher said, “You ought to be very serious about your homework. Reported Speech
- 33. Запомни! Глагол must заменяется в косвенной речи глаголом had, только когда must выражает необходимость совершения действия
- 34. 1. Direct Speech My mother said, “You must consult a doctor”. Reported Speech My mother said
- 36. Скачать презентацию






























 Новогодний сбор продуктов для бабушек и дедушек
Новогодний сбор продуктов для бабушек и дедушек Презентация Развитие зрительно-пространственной и зрительно-моторной координации
Презентация Развитие зрительно-пространственной и зрительно-моторной координации Простые вещества. Металлы
Простые вещества. Металлы Обработка скважин на основе грязевой кислоты в условиях Сорочинско-Никольского месторождения с обеспечением обучения
Обработка скважин на основе грязевой кислоты в условиях Сорочинско-Никольского месторождения с обеспечением обучения Аурулардың доминантты,рецессивті және кодоминатты тұқым қуалау түрлерінің сипаттамасы
Аурулардың доминантты,рецессивті және кодоминатты тұқым қуалау түрлерінің сипаттамасы Методы оптимальных решений в условиях риска, неопределенности, конфликта
Методы оптимальных решений в условиях риска, неопределенности, конфликта ПТЭ в электроустановках
ПТЭ в электроустановках Презентация-викторина по ПДД Юный знаток автомобилей
Презентация-викторина по ПДД Юный знаток автомобилей Транспортное средство штабелёр
Транспортное средство штабелёр Первый этап Великой Отечественной войны 1941 – 1945 г.г
Первый этап Великой Отечественной войны 1941 – 1945 г.г Межклеточные сигнальные молекулы (первичные посредники)
Межклеточные сигнальные молекулы (первичные посредники) Виды предпринимательской деятельности
Виды предпринимательской деятельности Les_01_Introduction
Les_01_Introduction Особенности взаимодействия педагогического коллектива ДОУ с семьями воспитанников
Особенности взаимодействия педагогического коллектива ДОУ с семьями воспитанников Театр Дель Арте
Театр Дель Арте Материя как философская категория. Понятия материя и дух
Материя как философская категория. Понятия материя и дух Проектирование системы РСПД Аст-Петрол
Проектирование системы РСПД Аст-Петрол Intercultural communication competence in everyday life
Intercultural communication competence in everyday life Онкология. Отличия доброкачественных опухолей от злокачественных
Онкология. Отличия доброкачественных опухолей от злокачественных Қазақстан экологиясының өткір де өзекті мәселелерін шешуге бағытталған қандай әдістер бар
Қазақстан экологиясының өткір де өзекті мәселелерін шешуге бағытталған қандай әдістер бар Использование Лего-технологий в работе учителя- логопеда.
Использование Лего-технологий в работе учителя- логопеда. Внутренняя энергия. Теплопередача. Работа в термодинамике
Внутренняя энергия. Теплопередача. Работа в термодинамике Лучевая терапия. Брахитерапия. Сочетанно-лучевая терапия
Лучевая терапия. Брахитерапия. Сочетанно-лучевая терапия Технологии растениеводства. Технологии обработки почвы
Технологии растениеводства. Технологии обработки почвы Кабинет географии
Кабинет географии Тема урока Углерод. 9 класс.
Тема урока Углерод. 9 класс. Особенности остеопатического сопровождения детей с головной болью в препубертатном периоде
Особенности остеопатического сопровождения детей с головной болью в препубертатном периоде Will You Be My Valentine Song
Will You Be My Valentine Song