Содержание
- 2. Queen Anne (1665 / 1702 – 1714), the last of the Stuarts In 1707, during the
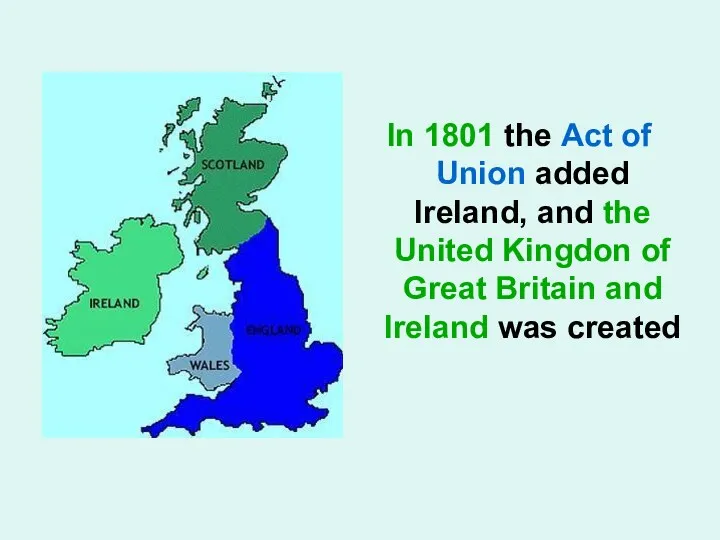
- 3. In 1801 the Act of Union added Ireland, and the United Kingdon of Great Britain and
- 4. House of Hanover (1714 – 1901) In 1714 the royal House of Hanover succeeded to the
- 5. Robert Walpole – the first British Prime Minister
- 6. In the XVIII century England became the leading military power in Europe. British victories in the
- 7. The British Empire Britain became the largest empire in history. It gained large territories in North
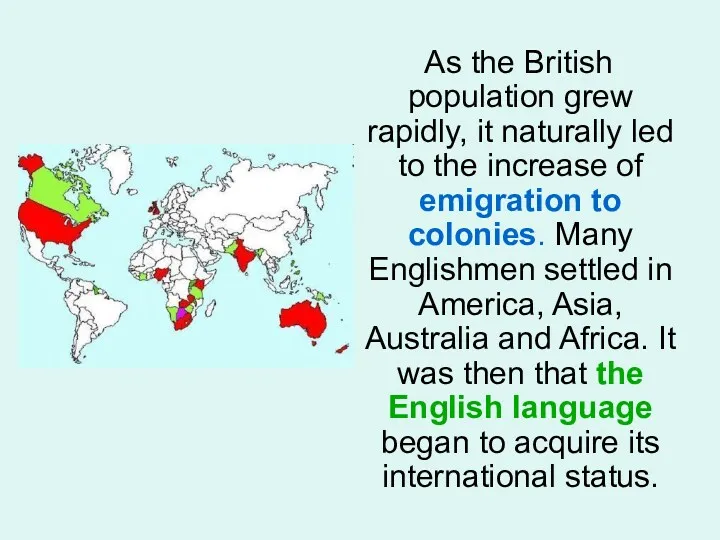
- 8. As the British population grew rapidly, it naturally led to the increase of emigration to colonies.
- 9. Britain in the Napoleonic Wars In 1805 one of the greatest sea victories in English history
- 10. Britain in the Napoleonic Wars Duke of Wellington became the leading British general after he defeated
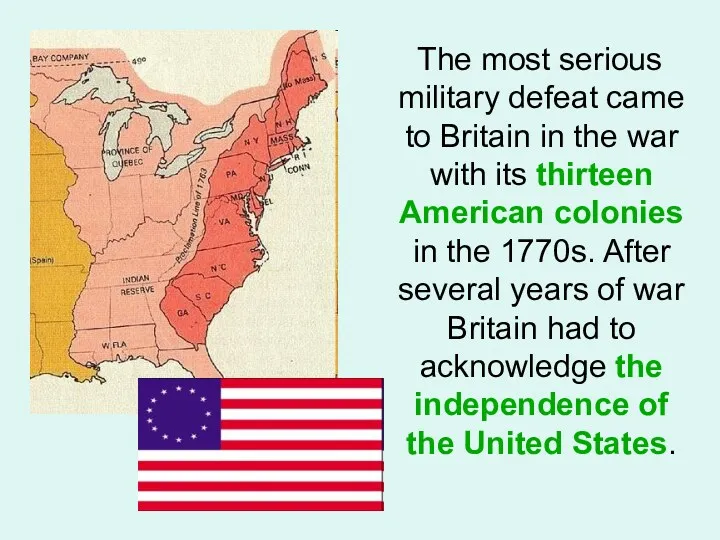
- 11. The most serious military defeat came to Britain in the war with its thirteen American colonies
- 12. The Industrial Revolution Great Britain rapidly grew into a leading capitalist country. It went through the
- 13. Coal mining and iron manufacturing were the most important branches of industry in the XIX century
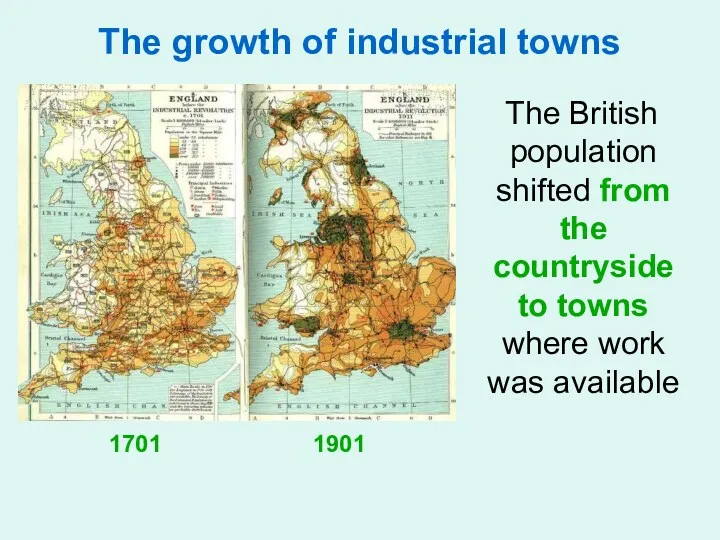
- 14. The growth of industrial towns The British population shifted from the countryside to towns where work
- 15. The life of the poor Great wealth and power was in the hands of the financial
- 16. Luddites – destroyers of the looms Some workers blamed their poor life on the introduction of
- 17. The Enlightenment Era The XVIII century is known in European history as the Enlightenment epoch. The
- 18. British literature of the Enlightenment Age The Enlighteners spread their ideas through literature. The leading genre
- 19. The age of science and technology In 1765 James Watt produced the steam engine
- 20. The First British Railway The first railway locomotive, constructed by George Stephenson (1814) The opening of
- 21. The British science of the XIX century Michael Faraday, the founder of the electromag-netism theory James
- 22. The Age of Romanticism in revolt against the “common sense” George Gordon Byron Percy Bysshe Shelley
- 23. The age of classical realism in literature Charles Dickens William Makepeace Thackeray The Bronte Sisters
- 24. Robert Adam and his neoclassical architecture Old College, Edinburgh Charlotte Square, Edinburgh
- 25. John Nash and his architecture Royal Pavilion, Brighton All Souls, London Terrace in Regent’s Park, London
- 26. Westminster Palace in neo-Gothic style
- 27. The British Painting In the XVIII century a distinctive British style of painting began to appear.
- 28. William Hogarth. Self-Portrait
- 29. William Hogarth. A Distressed Poet
- 30. W.Hogarth. Falstaff Examining His Recruits
- 31. William Hogarth. The Bench
- 32. Joshua Reynolds. Self-Portrait
- 33. J.Reynolds. Portrait of Mrs. Stanhope
- 34. J.Reynolds. Portrait of Mrs. Beresford
- 35. J.Reynolds. Lady Sunderlin
- 36. Thomas Gainsborough. Self-Portrait
- 37. T.Gainsborough. Portrait of a Lady in Blue
- 38. T.Gainsborough. Conversation in a Park
- 39. T.Gainsborough. Cottage Girl with Dog and Pitcher
- 40. Portrait of Sarah Siddons by Joshua Reynolds by Thomas Gainsborough
- 41. Joseph Turner. Self-Portrait
- 42. J.Turner. Fishing boats entering Calais harbour
- 43. J.Turner. The burning of the Houses of Parliament
- 44. J. Turner. Wreckers. Coast of Nothumberland
- 45. John Constable. Self-Portrait
- 46. J.Constable. The Hay Wain
- 47. J.Constable. Stratford Mill
- 49. Скачать презентацию










































 Характеристика топливно-энергетической базы Крыма
Характеристика топливно-энергетической базы Крыма Вред курения
Вред курения Презентация. Летний оздоровительный лагерь.
Презентация. Летний оздоровительный лагерь. Анализ динамики экономических показателей России и США
Анализ динамики экономических показателей России и США Биосфера. Среды жизни
Биосфера. Среды жизни Аллергия. Аллергены
Аллергия. Аллергены Презентация Заповеди Блаженствпо предмету ОПК
Презентация Заповеди Блаженствпо предмету ОПК Облік, контроль і аналіз непрямих виробничих витрат
Облік, контроль і аналіз непрямих виробничих витрат Конспект внеклассного занятия на тему: Законы жизни класса.
Конспект внеклассного занятия на тему: Законы жизни класса. Внутренние воды РТ
Внутренние воды РТ Формирование культурной среды небольшого города/села
Формирование культурной среды небольшого города/села аналогічні-гомологічні органи
аналогічні-гомологічні органи Организаторская и воспитательная работа командира подразделения по укреплению воинской дисциплины. Тема № 5
Организаторская и воспитательная работа командира подразделения по укреплению воинской дисциплины. Тема № 5 О мерах по поддержки генерирующих объектов на основе ВИЭ. Законодательная база поддержки генерации ВИЭ
О мерах по поддержки генерирующих объектов на основе ВИЭ. Законодательная база поддержки генерации ВИЭ Интернет в жизни старшеклассника: за или против
Интернет в жизни старшеклассника: за или против Тольятти. История любимого города
Тольятти. История любимого города Пейзаж — поэтичная и музыкальная живопись
Пейзаж — поэтичная и музыкальная живопись Особенности рельефа территории России
Особенности рельефа территории России Направления реализации Национальной стратегии по обращению с ТКО и ВМР
Направления реализации Национальной стратегии по обращению с ТКО и ВМР ФЭМП 14.04.2020
ФЭМП 14.04.2020 Логические операторы
Логические операторы Обрезка яблони и груши
Обрезка яблони и груши Проектирование современного урока биологии, географии в соответствии с требованиями ФГОС
Проектирование современного урока биологии, географии в соответствии с требованиями ФГОС Правовое регулирование предпринимательской деятельности
Правовое регулирование предпринимательской деятельности Презентация для детей
Презентация для детей Миотоническая дистрофия Россолимо-Штейнерта-Куршманна-Баттена
Миотоническая дистрофия Россолимо-Штейнерта-Куршманна-Баттена Плотность
Плотность Праздники и календари. Основы мировых религиозных наук (4 класс)
Праздники и календари. Основы мировых религиозных наук (4 класс)