Содержание
- 2. G 3. Construction Contracts Types of contracts Recognition methods : Presentation :
- 3. IAS 11 (International Accounting Standards) Construction Contracts provides requirements on the allocation of contract revenue and
- 4. History of IAS 11 — Construction Contracts
- 5. TYPES OF CONSTRUCTION CONTRACTS Two broad categories: Price Given in Advance Contracts (Priced-based Contracts) Cost Reimbursement
- 6. TYPES OF CONSTRUCTION CONTRACTS 1. Lump Sum Contact 2. Contract based on a Bill of Quantities
- 7. 1. Lump Sum Contact Main Aspects 1. Payment may be staged at intervals of time. 2.
- 8. 1. Lump Sum Contact Advantages The final price is known The contractor has more incentive to
- 9. 2. Contract based on a Bill of Quantities Sometimes called Unit Price Contract Main Aspects Items
- 10. 2. Contract based on a Bill of Quantities Sometimes called Unit Price Contract Advantages 1. Saving
- 11. 3. Schedule of Rates Contract Main Aspects 1. A Schedule of the work items without quantities.
- 12. 3. Schedule of Rates Contract Advantages 1. Work can be commenced earlier than if a full
- 13. 4. Cost plus Percentage of Cost Main Aspects 1. The contractor is reimbursed for all his
- 14. 4. Cost plus Percentage of Cost Advantages 1. Construction can start before design is completed. 2.
- 15. 5. Cost plus Fixed Fee Main Aspects 1. The owner pays all costs of construction with
- 16. 6. Target Cost with Variable Fees Contract Main Aspects 1. The contractor and owner agree to
- 17. 6. Target Cost with Variable Fees Contract Advantages 1. There is an incentive to carry out
- 18. 7. Guaranteed Maximum Price Contract (GMP) 1. The contractor guarantees that he will construct the project
- 19. Recognition methods Stage of Completion (Percentage of Completion) Value Based Methods Cost Based Method - See
- 21. Скачать презентацию


















 Про присудження ступеня доктора філософії
Про присудження ступеня доктора філософії Информационно-справочные документы
Информационно-справочные документы Жилищное право
Жилищное право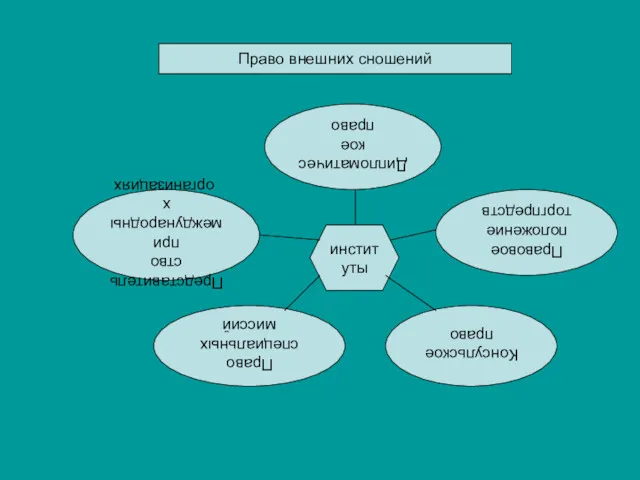 Право внешних сношений
Право внешних сношений Gene Doping
Gene Doping Сучасні вимоги до оформлення службових документів
Сучасні вимоги до оформлення службових документів Обязательства – 2 (начало и продолжение в способах обеспечения)
Обязательства – 2 (начало и продолжение в способах обеспечения) Порядок и особенности дознания в рамках ст. 219 УК РФ
Порядок и особенности дознания в рамках ст. 219 УК РФ Трудовой кодекс Российской Федерации. Трудовые отношения
Трудовой кодекс Российской Федерации. Трудовые отношения Земельно-имущественные отношения
Земельно-имущественные отношения Экспертиза временной нетрудоспособности
Экспертиза временной нетрудоспособности Что такое закон. Почему важно соблюдать законы?
Что такое закон. Почему важно соблюдать законы? Оформление организационных документов
Оформление организационных документов Защита прав лиц с ограниченными возможностями
Защита прав лиц с ограниченными возможностями Тактика предъявления для опознания
Тактика предъявления для опознания Юридические границы подросткового возраста
Юридические границы подросткового возраста Оставление искового заявления без рассмотрения
Оставление искового заявления без рассмотрения Конституционно-правовые отношения и конституционные нормы. Ответственность
Конституционно-правовые отношения и конституционные нормы. Ответственность Преступления в сфере высоких технологий
Преступления в сфере высоких технологий Техническое регулирование и стандартизация
Техническое регулирование и стандартизация Исполнение обязательств. Способы обеспечения и исполнения обязательств
Исполнение обязательств. Способы обеспечения и исполнения обязательств Правовой режим информации
Правовой режим информации Субъективная сторона преступления. Тема 6.3
Субъективная сторона преступления. Тема 6.3 История развития типологии теоретического правопонимания
История развития типологии теоретического правопонимания Прекращение уголовного дела и уголовного преследования
Прекращение уголовного дела и уголовного преследования Privacy on the edge of technology
Privacy on the edge of technology Преступления в сфере экономики
Преступления в сфере экономики Республиканың мемлекеттік тәуелсіздікке ие болуы, оның Қазақстан халқы үшін тарихи маңызы
Республиканың мемлекеттік тәуелсіздікке ие болуы, оның Қазақстан халқы үшін тарихи маңызы